ENWC McCarthy Midterm
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Wildlife
Includes all non domesticated plants, animals, and other organisms and how they live together
Conservation
primary focus is to maintain the health of the natural world
Ethics of resource use, allocation, and protection
Saving
Ecology:
study of interactions among organism and between organisms and their environment
Scientist who created study of ecology: Ernest Haeckel
Mammals
have hair, mammary glands, and 3 ear bones (unlike birds, reptiles, and amphibians)
Mammal species in the world:
5,500
other species
8,200 species in the world: reptiles
6,500 species in the world: amphibians
In most danger
Ecosystem:
A biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area as well as all the non living physical components of the environment
Carbon Cycle
Respirated into the atmosphere by animals and fossil fuels
Energy:
comes from the sun and is turned into chemical energy
birds
Have feathers
Class - aves
Species: 9,900
Biomes
communities varying in space
Plants:
Critical link between the sun and all other life on earth
Community
living part of ecosystem
biotic community
plant and animal community
succession
the process of change in the species that make up an ecological community over time.
Monotremes:
Egg laying mammals
Carnivora
Have prominent canines and sharp claws
Based on the definitions given in class: the term "Wildlife" can include ALL living things, whether domesticated or non-domesticated
FALSE
Ecology is the scientific study of the distributions, abundance and relations of organisms and their interactions with the environment. Choose ALL of the correct root terms used by Ernst Haeckel in creating the word "Ecology".
Oikos "home" Logos "study of"
"Conservation" includes the concept of using our natural resources, e.g. via timber harvest, fishing, and hunting, but doing so in a manner that is sustainable
True
Choose all answers that are defining characteristics of the class Mammalia, i.e., traits that you will only find in mammals and no other animals.
Mammary glands, Vertebrae, Claws, Teeth
Choose all answers that are defining characteristics of the class Mammalia, i.e., traits that you will only find in mammals and no other animals
Three inner ear bones, hair, mammary glands
Choose all answers that are defining characteristics of the class Aves (Birds), i.e., traits that you will only find in birds and no other animals
feathers
How communities (the living part of an ecosystem) vary across time after a disturbance (e.g., a forest fire) is described by the term "Biome"
False
One way to identify if a snake may be venomous is from the shape of its head, even if you do not know which species it is
True
Pioneer communities in the rainforest of Costa Rica create habitat for what are called early successional wildlife species
True
What is the difference between primary and secondary succession?
In primary succession, seeds must blow in from outside the area, and soil needs to be created, whereas in secondary succession, soil already exists and the plants that grow tend to be from the seedbank already in the soil.
When one animal kills and eats another animal this is known as Predation , however, other interactions between animals are also present. One such as interaction is when one species benefits from the actions of another, but the other species is not affected either way. This is called [ Select ] and is seen in species like cattle egret that benefit from feeding on insects stirred up by cattle, but the cattle themselves are not affected either way. Another interaction is when two different species compete for the same resource, which is called [ Select ] . An example would be when brown bears and mountain lions compete over a deer kill. A fourth interaction is seen when two different species have a symbiotic relationship in which both animals benefit. This interaction, , is exemplified by the gobi fish and pistol shrimp, who share a burrow in the ocean and "help" each other.
Predation
Commensalism:
Mutualism?
Habitat can be separated into four broad, but important categories. Fill in the appropriate category to the following scenario (IMPORTANT, use a single word answer for each, i.e., either shelter or cover is appropriate and equivalent, do not type shelter/cover or the system will not recognize it): The bald eagle occurs during its breeding season in virtually any kind of American wetland habitat such as seacoasts, rivers, large lakes or marshes or other large bodies of open water with an abundance of fish, these fish are the —— component of habitat.
Studies have shown a preference for bodies of water with a circumference greater than 11 km (7 mi), and lakes with an area greater than 10 km2 (4 sq mi) are optimal for breeding bald eagles, this is the ___component
The bald eagle typically requires old-growth and mature stands of coniferous or hardwood trees for perching, roosting, and nesting, this is the ___ component of habitat. Tree species reportedly is less important to the eagle pair than the tree's height, composition and location. Perhaps of paramount importance for this species is an abundance of comparatively large trees surrounding the body of water.
Bald eagles and eaglets (baby eagles) derive the ___ component of habitat from their food. However, adults will sometimes drink while bathing, if fresh water is available.
food
Space
Shelter
Water
The term habitat, as defined in class, refers to (select all that apply):
The behaviors exhibited by a species of a long time period (e.g. millions of years).
The area that an animal protects from all other individuals or species
The physical and biological resources needed by an animal to survive
The role that an animal plays in its environement (it's job).
The physical and biological resources needed by an animal in order to reproduce
The physical and biological resources needed by an animal to survive, The physical and biological resources needed by an animal in order to reproduce
Choose all correct answers: As you move up in trophic level, e.g., from producer "up" to primary consumer, or primary consumer "up" to secondary consumer
There is a decrease in numbers of organisms; there is a loss of approximately 90% of the energy available
A niche is considered an animals habitat, i.e., the physical and biological resources required by an organism for its survival and reproduction
False
Which of the following steps are part of the process of Natural Selection?
Some individuals are able to outcompete others for limited resources and pass on their genes,
There must be genetic variation within a species
An overabundance of individuals leads to a shortage in resources
Climate change is one of the biggest threats to Monteverde Cloud Forest, because it is causing the forest to become warmer and drier, harming the many species in this forest that depend on the moisture.
True
Approximately 40% of the nation's migratory waterfowl use the Mississippi Flyway during their migration, more than any other flyway in the US.
True
A female cougar (also known as a mountain lion, catamount, or puma), reaches reproductive age at ~2 years old and produces a litter every two to three years. Female cougars are very protective of their cubs, which stay with their mother for up to 2 1/2 years. This reproductive system is best described as:
K strategist
In a monogamous species, having a sex ratio skewed towards females (i.e., more females than males) will provide the highest level of production/natality.
False
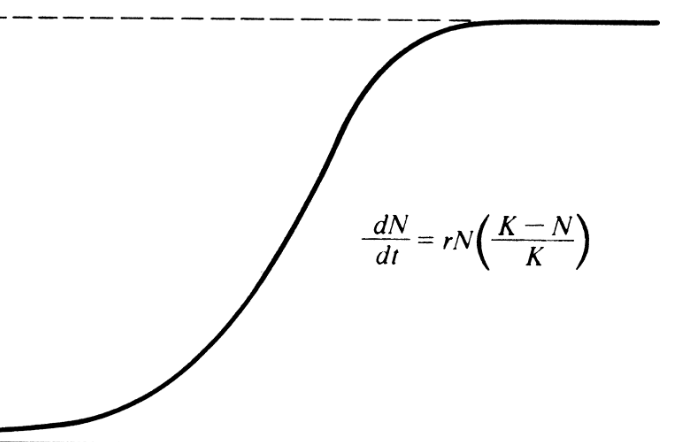
The following graph shows ___ growth Which exhibits a population that faces ___which results in the number of animals leveling off at K, also known as it's _____
logistic growth?
imiting factors?
Carrying Capacity
Which of these species has been credited with doing extensive damage within Yellowstone National Park due to over-population, primarily because of the removal of wolves?
Brown Bear
Elk
None of the above
Bison
Moose
Elk
Caribou are primarily active across the entire day, which suggest the are a ___ species
however their feeding activity occurs primarily around the dawn and dusk hours, which, if we were defining activity patterns based solely on feeding would suggest that they are a ___ species
Regardless, both of these classifications are general descriptions of their ___
Caribou are also migratory, moving from summer calving grounds to wintering grounds every year, this is part of their____
diurnal
Crepuscular
crepuscular
Circa annual cycle
what BEST describes the behavior of an animal that is more likely to emit a warning call to alert its group members that a predator is near whecludes close relatives, and less likely to emit a warning call when the group is not closely related. This warning call increases the emitters likelihood of being noticed by the predator, and thus endangers the individual.
Territoriality
Kin Selection
Many eyes hypothesis
Courtship
Atruism
Kin selection
One day you are walking to the grocery store (way to be ecologically conscious!) and enjoying the fresh, clean air and the gentle cool breeze from the nearby forest, this is a ____ ecosystem
When you get to the grocery store you wander in and purchase wild caught Alaskan salmon for a special dinner, you are benefiting from a ___ ecosystem
As you leave the store you take a detour through the local park and stumble across a cave with ancient paintings on the wall depicting wild animals. This suggests that a previous group of humans had a ____ benefit from their ecosystem.
Regulating
Provisioning
Cultural
The Monteverde Cloud Forest is known for having the highest orchid diversity in the world.
True
Leaf cutter ants cut leaves to take back to their underground colony where the leaves then grow a fungus that the ants eat, effectively making them farmers of their own food resource.
True
An early effort to develop a new whooping crane migratory population failed, because when whooping crane chicks imprinted upon sandhill crane mothers they not only learned to migrate and eat like sandhill cranes, but also tried to court/mate with sandhill cranes
True
The Pleistocene Overkill refers to the extinction of elephants, giraffes, giant bison, and many more species of megafauna (large animals) that was caused by humans after they crossed into North America
True
"Father of Wildlife Management"
Aldo Leopold
First Professor of Game Management, wrote first wildlife textbook
Aldo Leopold
An avid hunter and outdoorsman who's presidency in part led to the "Golden Age in Conservation"
Teddy Roosevelt
Tripled our National Forests and created first National Wildlife Refuge
Teddy Roosevelt
Fought to conserve Yosemite and founded the Sierra Club
John Muir
All wildlife in the United States has adequate regulation of their harvest (hunting) to prevent overexploitation.
False
This has led to increased __________ animals within the forest, which are then being sold both at local markets but more importantly at larger cities where there is a high demand
Harvest of
This _______ has shifted what used to be sustainable local consumption into an unsustainable use of wildlife in our tropical forests.
Bushmeat trade
The continued extraction of _____ from tropical forests is leading to an increase in access to within the forest, and also an increase in the connectivity (bigger roads) of small villages to larger population centers
Timber
The end result is ___________ , meaning that even before the forest is cut down there are few animals left within it.
Defaunation
Wetlands are more productive than many other land types and provide important habitat for many wildlife species. In the Chesapeake Bay watershed we have lost over 60% of this land type.
Wetlands
Panther underpasses have been completely successful in stopping Florida panther deaths due to car collisions, i.e., no panthers are killed on roads now and the main limit to their expansion is disease.
False
Because the burrowing owl is a species of special concern in Florida, burrows may not be destroyed without a permit, even if no owls are seen using the burrow.
True
Habitat destruction and fragmentation, often for housing developments or agriculture, is the greatest threat to gopher tortoises.
True
Eutrophication is caused by pesticides that we use on our crops. These pesticides make their way into water after rainfall and cause plants within our rivers, lakes, and oceans to die. This creates what is called a "Dead Zone".
False
______ is a _______ that is created when sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide enter the atmosphere and interact with clouds.
Acid rain; secondary air pollutant
This can cause various problems, including the removal of important _________, which reverberates up the food chain, causing snails to be unable to form shells and birds to produce fewer eggs.
Nutrients like calcium
Lake Erie has been plagued with massive algal blooms that lead to "dead zones" in the lake.
True
This river, which flows into Lake Erie, was known as one of the most polluted rivers in the country, catching fire a record 13 times.
Cuyahoga River
Hbaitat
The physical and biological resources required by an organism for its survival and reproduction
Basic components for habitat
food, shelter, water, space
Habitat selection
choice of setting that favor survival and reproduction
Two most important features of habitat selection
shelter and food
cover
provides protection from elements and predators
food
the energy in food provides metabolic fuel for all processes
Wood duck
north America; water with cover; nest inside trees
wood duck foods
water primrose, acorns, insects
Adaptations to limits long term
hibernation, estivation, migration
Adaptations to limits short term
fasting, reduces activity (torpor), rummaging
Adaptation to limits psychological
storing or using body fat stores
Excessive food shortages can result in
-starvation
-decreased reproduction
-increased death
CWD (Chronic wasting disease)
Caused by an infectious misfolded protein, or prion, that creates vacuoles in a deers brain and alters their behavior to the point that they slowly die from starvation
Zoonosis
An animal disease that can transfer to humans, but we are not a necessary part of the cycle
Epizootic
a disease that appears at an unexpected rate, synonymous with epidemic in humans
Resevoir
Any living or nonliving substance that may perpetuate a pathogen in nature
Vector
An organism that carries a pathogen from one host to another, or from a resevoir to a host
Starvation is not considered a disease, as it is not infectious and thus can not be "transmitted" from one animal to another
False
Brown tree snakes in Guam are an example of:
An introduced predator that is affecting populations of birds directly through predation
Starlings were introduced to the United States by Shakespeare enthusiasts. The birds have since spread across the United States and are out-competing native birds (like the blue bird).
True
Although greenhouse gasses are important for maintaining our earths climate, as we increase the amount of them in our atmosphere we are causing more long-wave radiation to be captured/reflected back to the earth, thus causing warming. Similar to how a greenhouse works for plants.
True
Increasing levels of acidity in our oceans (lower pH) is leading to an increase in the availability of free calcium, we will thus see an increase in the number of small organisms such as diatoms and dinoflagellates that are at the bottom of the food web.
False
If spring leaf out date in our eastern forests continue to be earlier and earlier, but migratory song birds return at the same time as always from central and South America, we may see what is called a _____________ mismatch. Breeding birds may suffer because they will miss critical food supplies tied to the leaf out date of trees.
Phenological
This disease is carried by bison, and is of great concern to ranchers bordering Yellowstone.
Brucellosis
The IUCN Red List is used to track whether species from across the world are threatened with extinction
True
When the extinction of a species is followed by extinctions of several other species due to the disruption of losing the first species, we call it a "waterfall effect".
False
Mississippi River
High sediment content, backwater important habitat
Mississippi River Birds
326 species, Mississippi Flyway, US/Canada to Gulf of Mexico/South America; 60% of North American birds
Mississippi River Species
260 species of fish; 25% of all fish species in N America
Monte Verde
Cloud forest climate
Cloud forest
forest in constant cloud cover
Natality
birth rate
r-strategist
reproductive strategy in which organisms reproduce early, bear many small, unprotected offspring (ex. insects, mice).
K strategist
reproductive strategy in which organisms reproduce late, bear few, cared for offspring (ex. humans, elephants).
compensatory mortality
the affect of one kind of mortality influences the affect of another source of mortality
additive mortality
the affect of one kind of mortality is independent of other sources of mortality