3.3 CS: Heart Auscultation
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
HEART AUSCULTATION
Listening to the heart sounds with the aid of the use of stethoscope
Heart sounds are caused by closing of the different heart valves
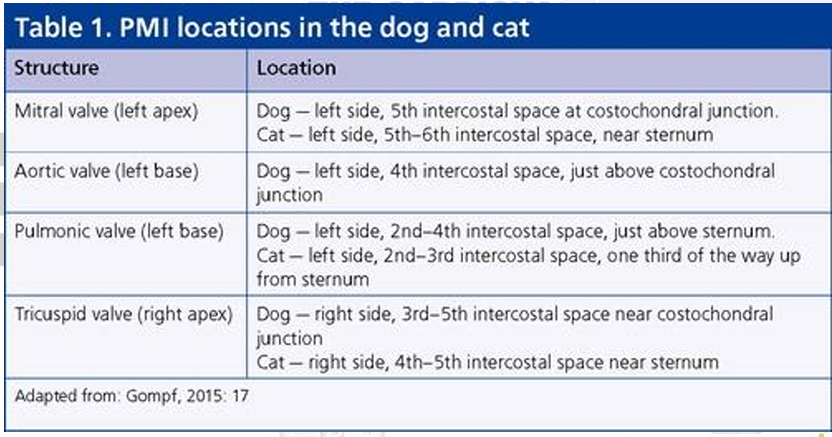
POINT OF MAXIMUM INTENSITY (PMI) /PUNCTA MAXIMA
It is a spot on the thoracic wall where a valve sound is the loudest
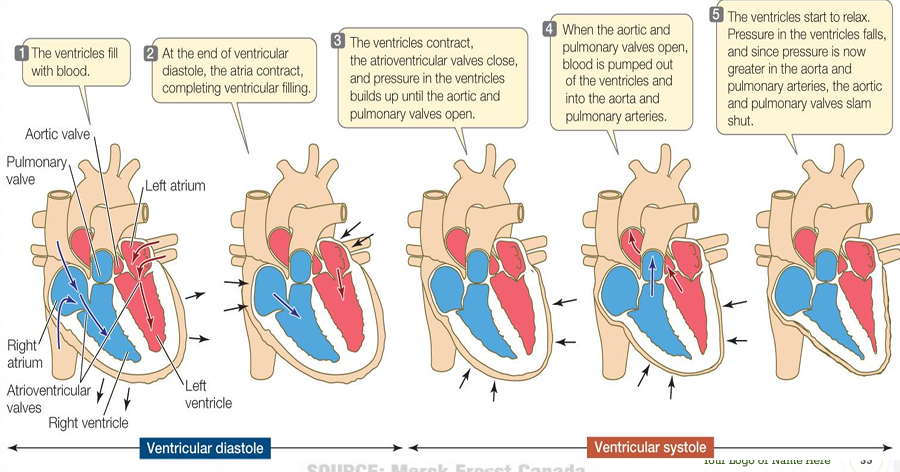
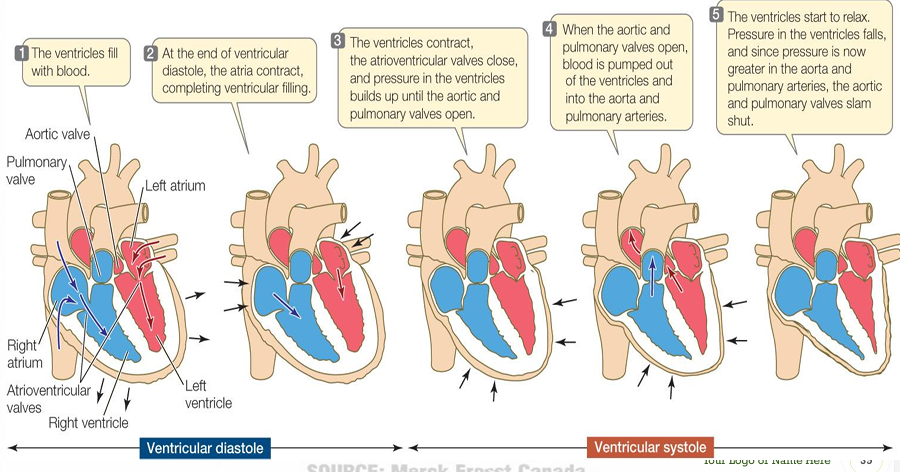
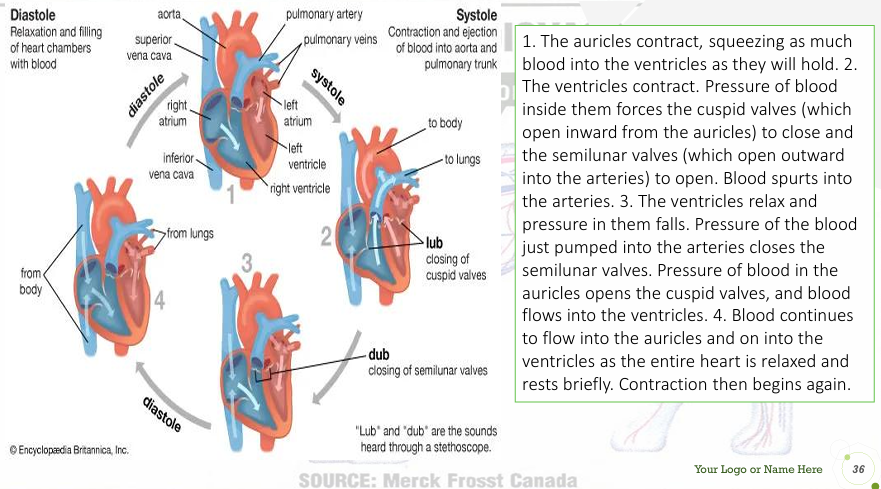
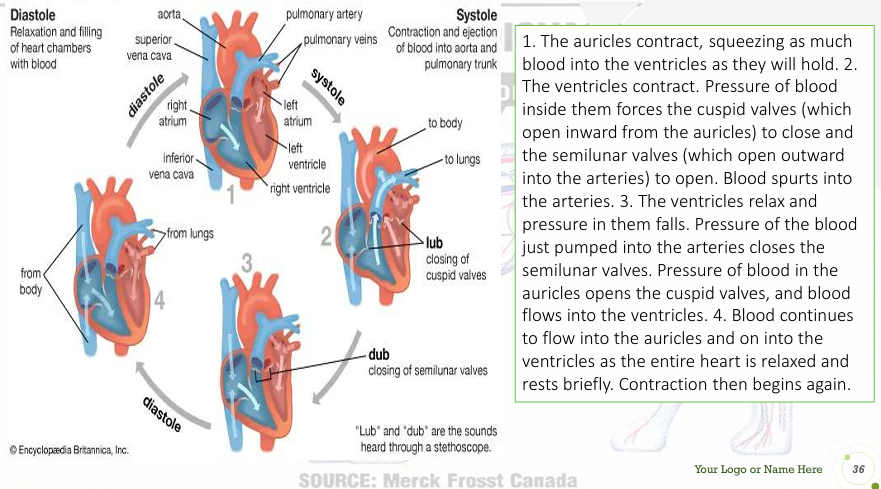
Ventricular contraction (systole)
an increase in ventricular pressure and close of the atrioventricular valves (1st heart sound) and opening of the semilunar valve (aortic and pulmonic valves)
Ventricular relaxation (diastole)
atrioventricular valves opens and the semilunar valves closes (2nd heart sound)due to back pressure in the aorta and pulmonary trunk
Systole
contraction of ventricles; occurs between the 1st and 2nd heart sounds
Diastole
relaxation of ventricles; occurs between the 2nd and 1st sounds
1st heart sound (“lub”)
caused by closure of AV valves at onset of systole
2ndheart sound (“dub”)
caused by closure of semilunar valves at the end of systole
Heart Murmurs
abnormal sounds caused by blood flow turbulence; it can either be due to valvular or non-valvular problems
Systolic murmur
occurs between the 1st and 2nd heart sounds; when the AV valves should be fully closed and the semilunar valves opens
Diastolic murmur
occurs between the 2nd and 1st heart sound when the semilunar valves is fully closed and the AV valves opens
Aortic stenosis
narrowing of the aortic valve; it impedes the normal left ventricular emptying.
Subaortic stenosis
most common form
Breed predisposed is Boxers, Golden Retrievers, Rotweillers, and German Shepherd
Pulmonic stenosis
refers to narrowing of the valve between the right ventricle (a chamber of the heart) and the pulmonic artery (the major blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the lungs).
Valvular form
most common; breed predilections such as English bulldogs, boxers, beagles, and Boykin Spaniels
Supravalvular form
uncommon and most often seen in Giant Schnauzers
Mitral valve stenosis
narrowing of the mitral valve opening caused by the abnormalities of the mitral valve
Rare in dogs and cats and it can occur together with other congenital defects such as subaortic stenosis, mitral valve dysplasia, and pulmonic stenosis
Mitral valve dysplasia
leads into a mitral insufficiency and systolic regurgitation of the blood into the left atrium; Canine breeds predisposed includes Bull terriers, German Shepherds, and Great Danes
Tricuspid valve dysplasia
leads into the tricuspid insufficiency and systolic regurgitation of blood into the right atrium; Breeds predisposed are Labrador Retrievers and German Shepherds
Atrial septal defect
It results when the foramen ovale and second foramen ovale overlaps; allowing blood to flow from left to right, leading into a poor oxygenation of the blood which can leads to cyanosis
Interventricular septal defect
Failure of the interventricular septum to close, involving the membranous part of the septum
The most common cardiac anomaly in large animals, it causes systolic murmur
Tetralogy of Fallot
most common defect that produces cyanosis
Pulmonic stenosis
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular septal defect
Overriding (dextropositioning) of aorta
what comprises the defect tetralogy of fallot (4)