APES Unit 4 : Earth Systems and Resources
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
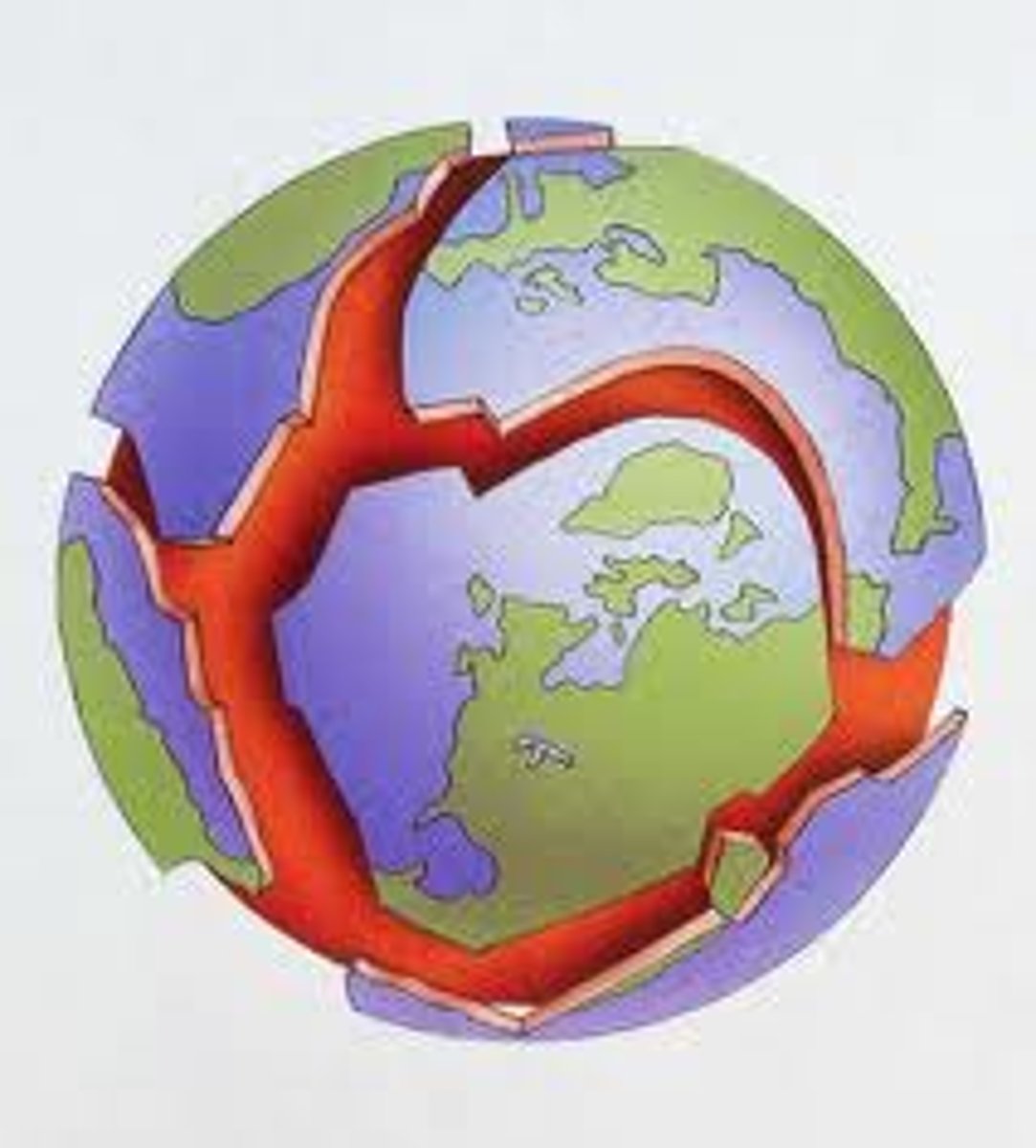
Plate Tectonic Theory
theory that Earth's lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates
-these tectonic plates move slowly on top of the asthenosphere
tectonic plates
a block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle

Lithosphere
A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust.
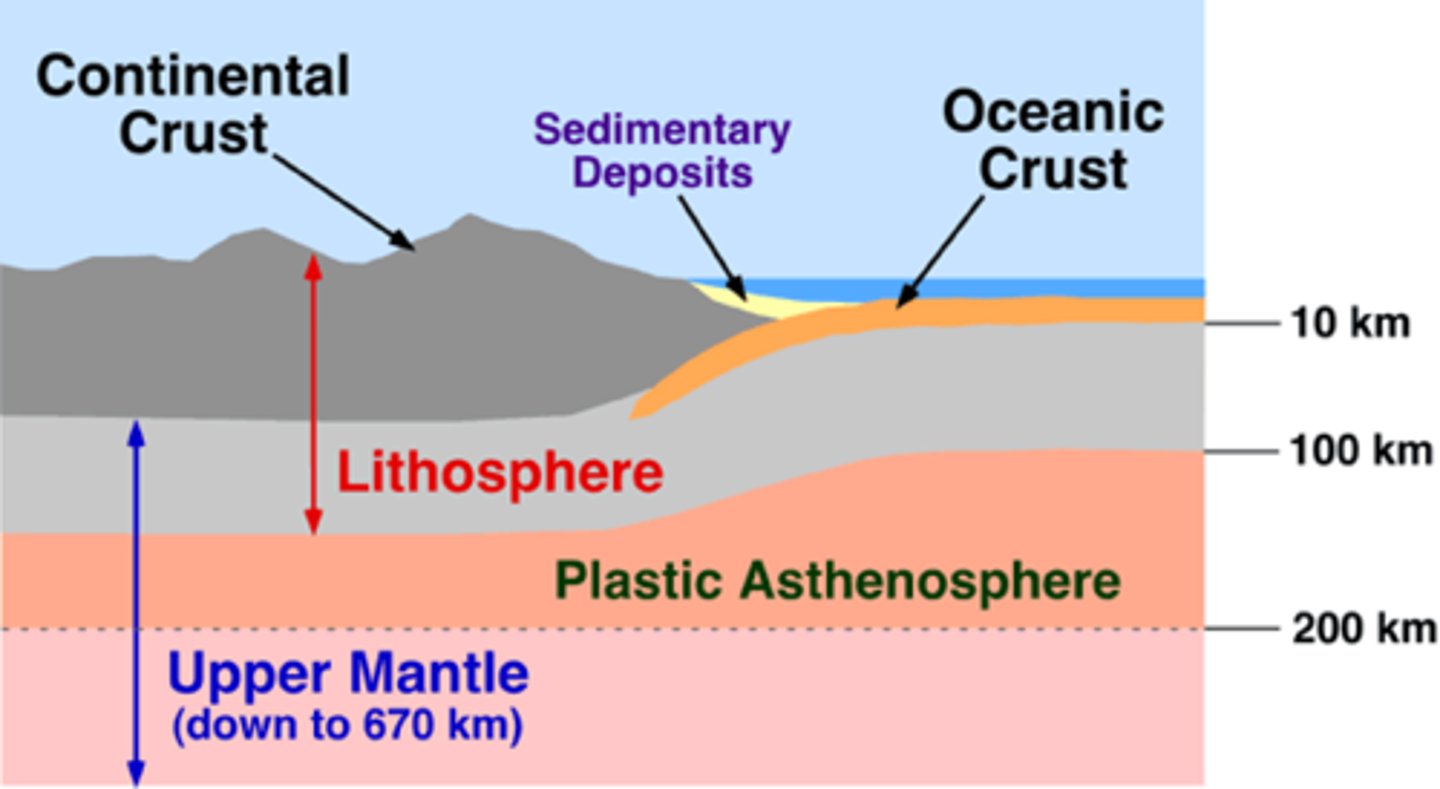
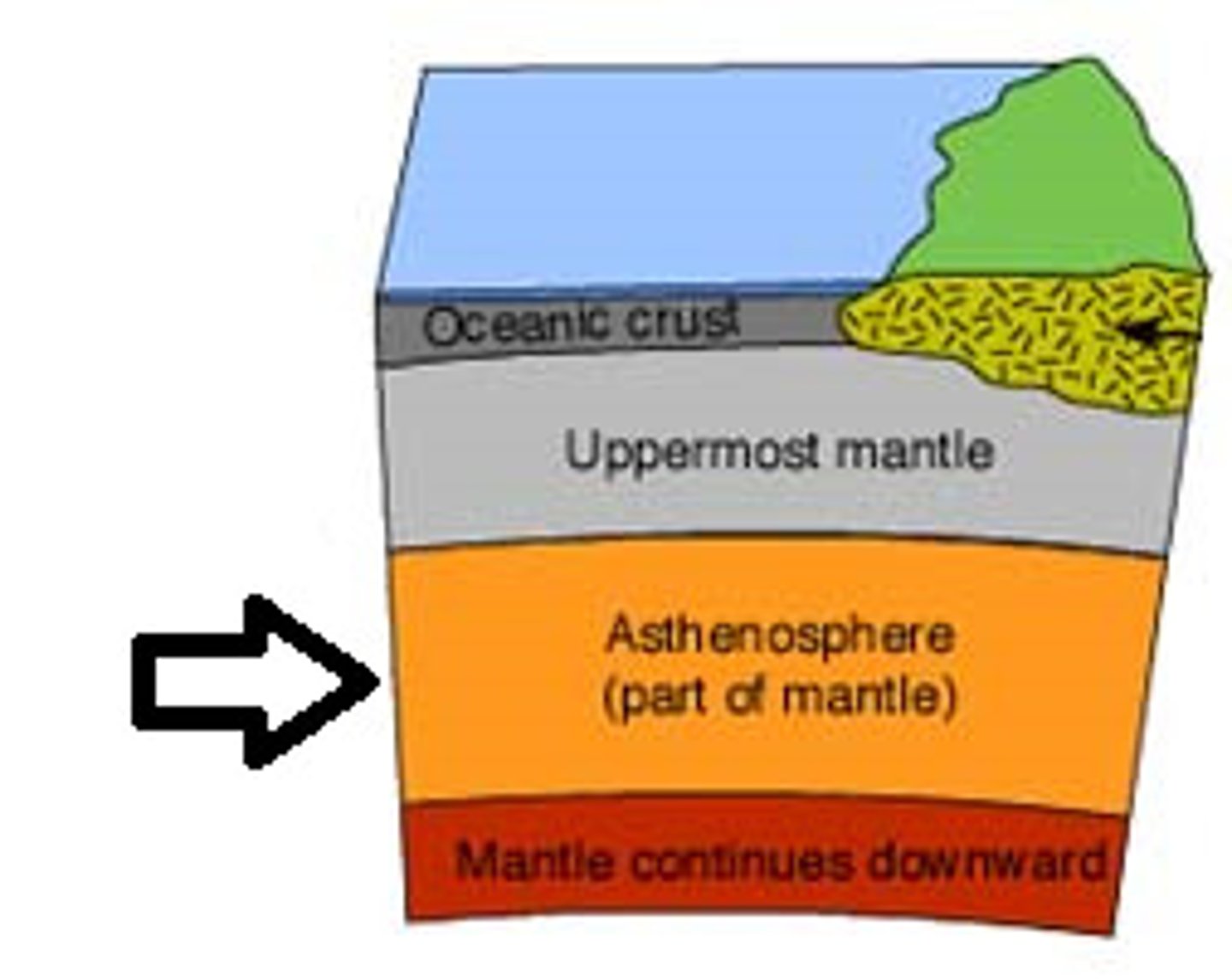
Asthenosphere
The soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move
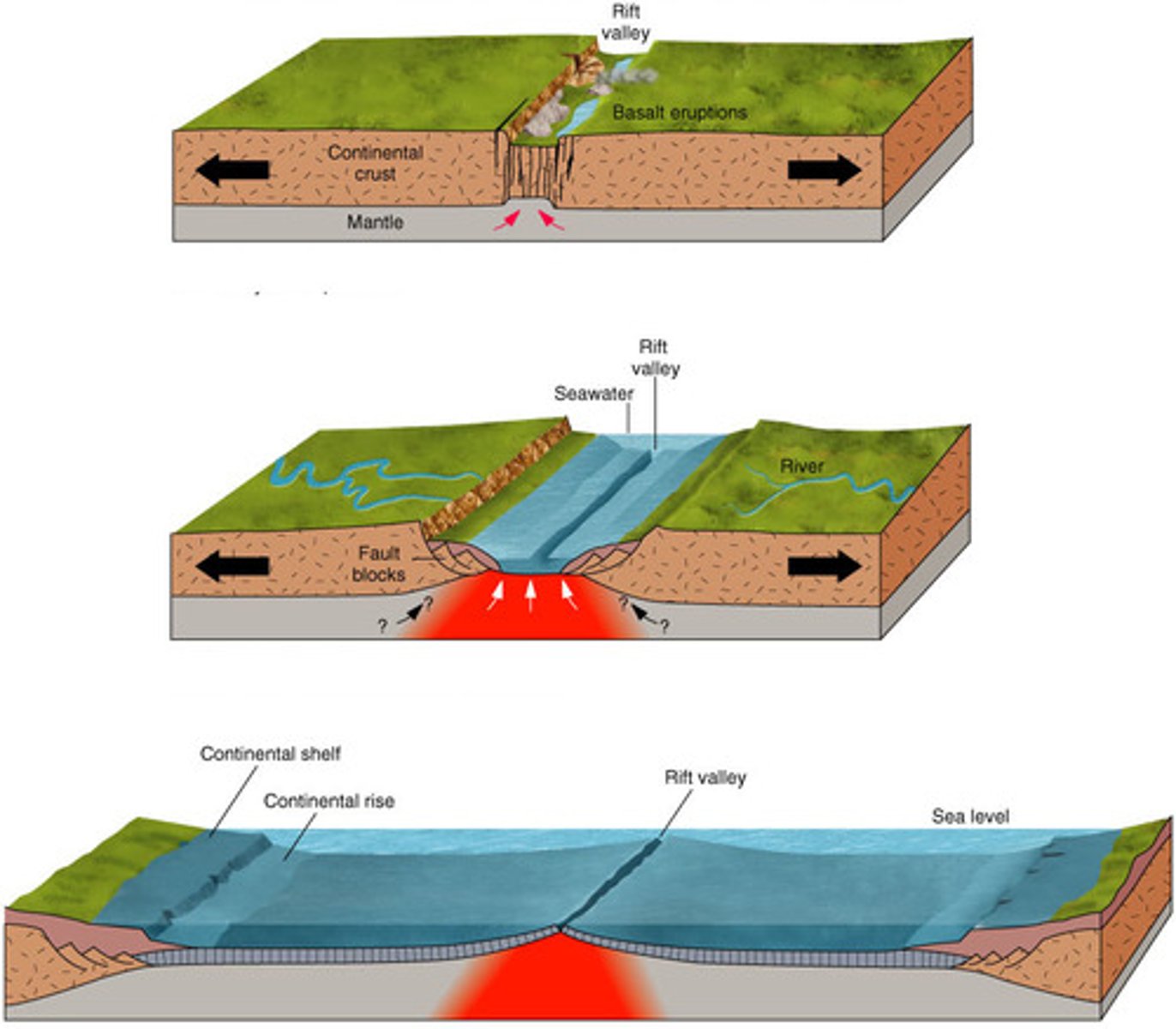
divergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other.
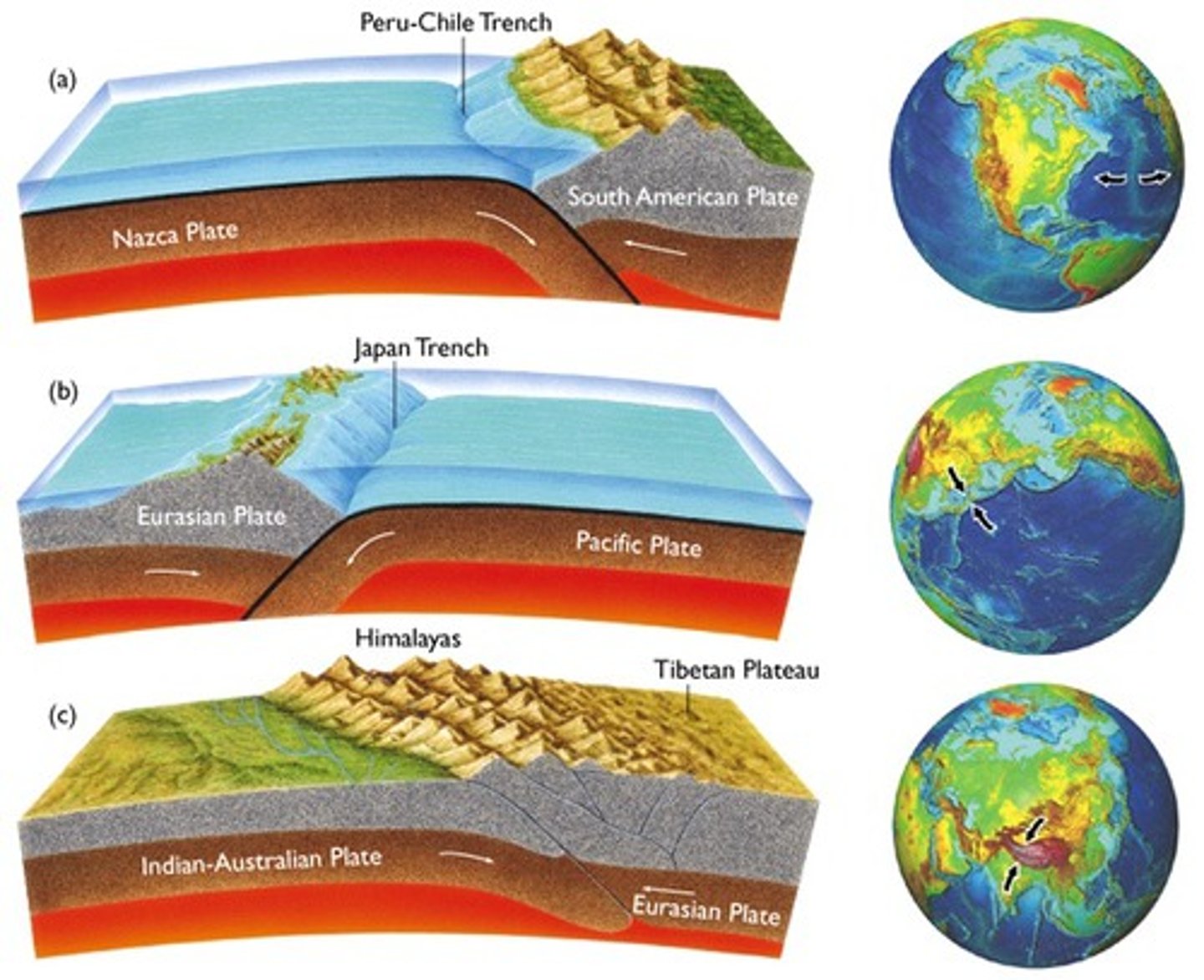
convergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other.
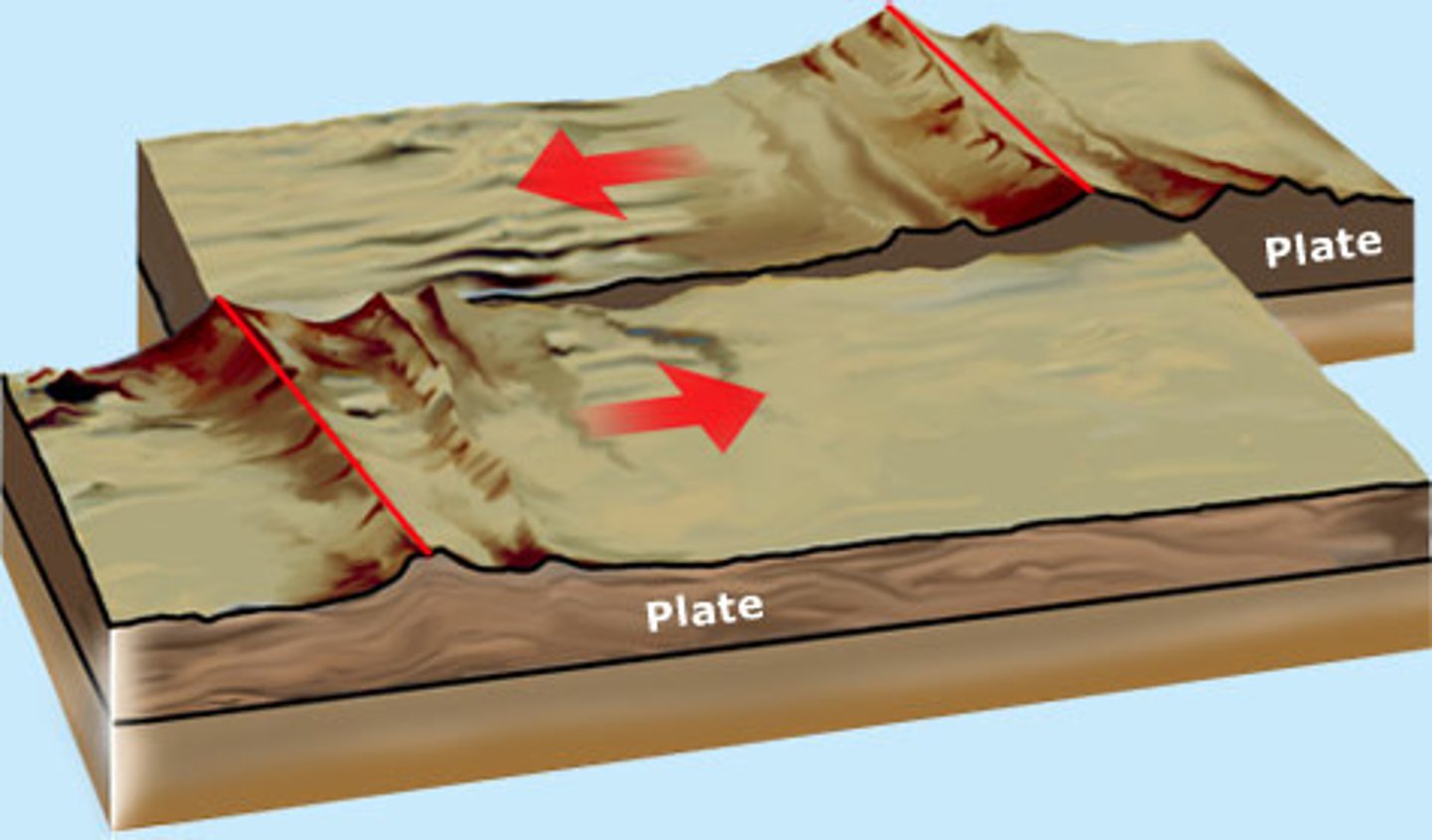
transform boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions
Weathering
The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.
Sediments
small pieces of rock, soil, and other materials
Erosion
Processes by which rock, sand, and soil are carried away
Deposition
Process in which sediment is laid down in new locations.
transportation
the moving of sediments from one place to another
soil profile
All the vertical layers or horizons that make up a soil in a particular place
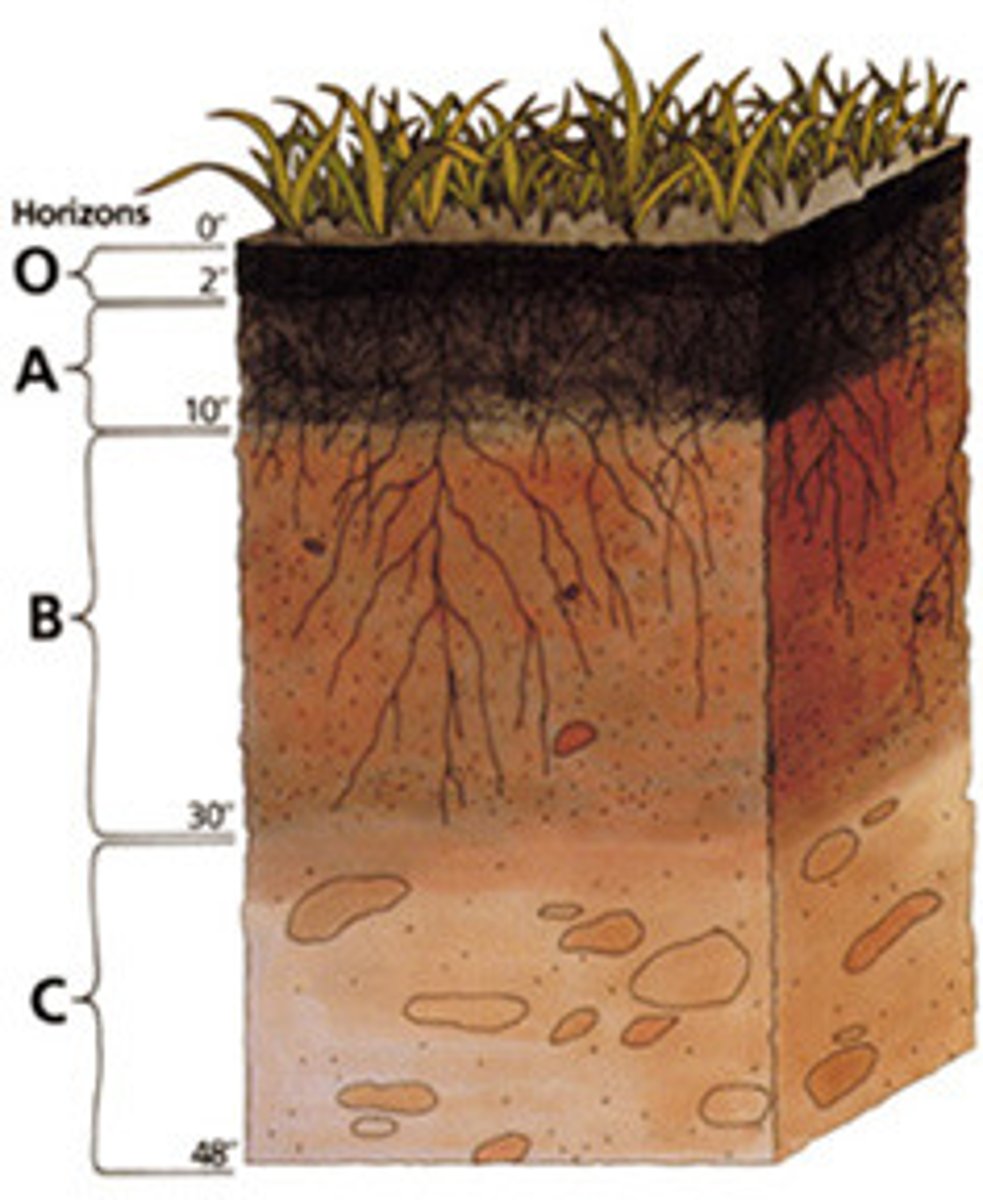
soil horizon
a distinct layer within a soil profile
soil erosion
wearing away of surface soi, especially topsoil, by water and wind
topsoil
Mixture of humus, clay, and other minerals that forms the crumbly, topmost layer of soil.
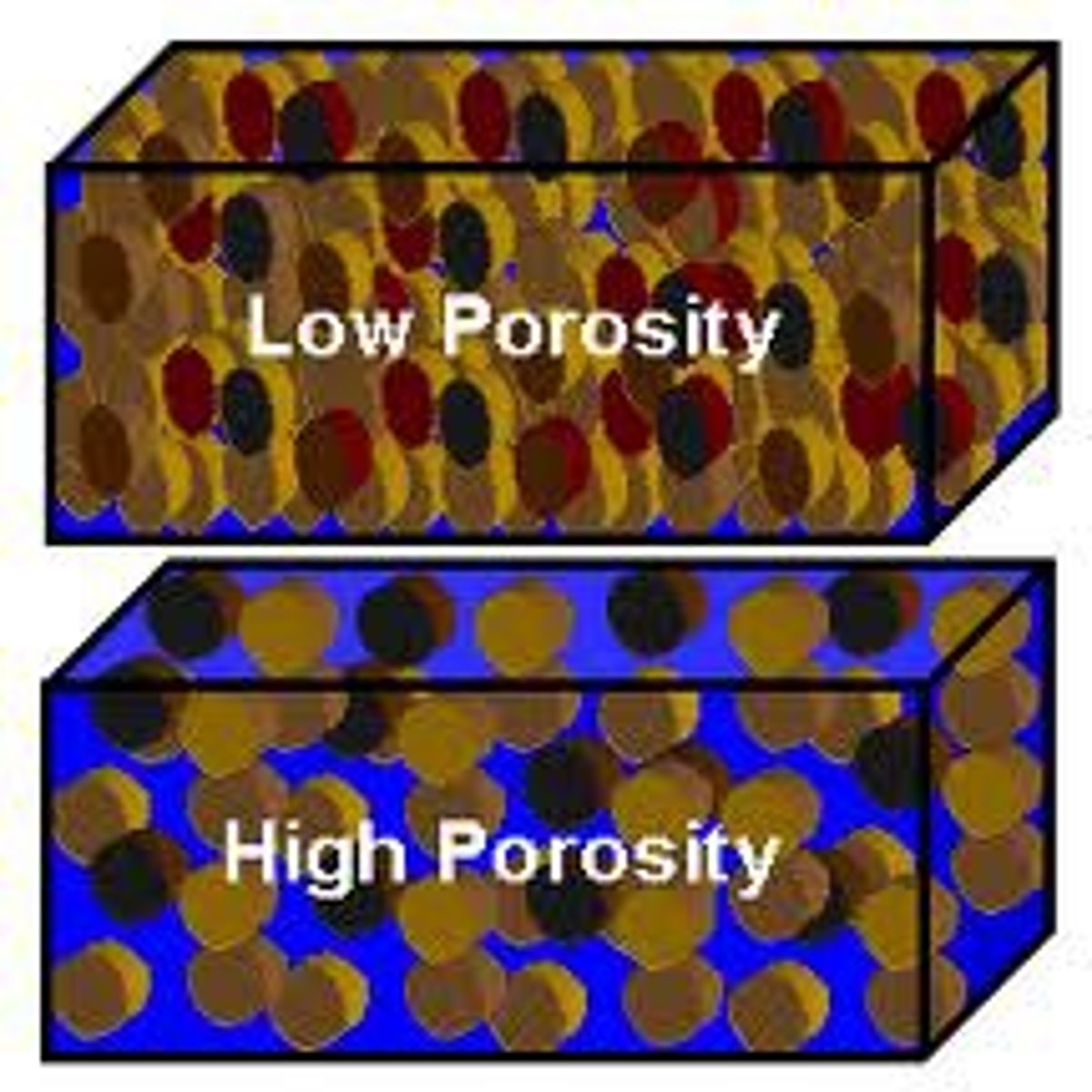
Porosity
The percentage of the total volume of a rock or sediment that consists of open spaces.
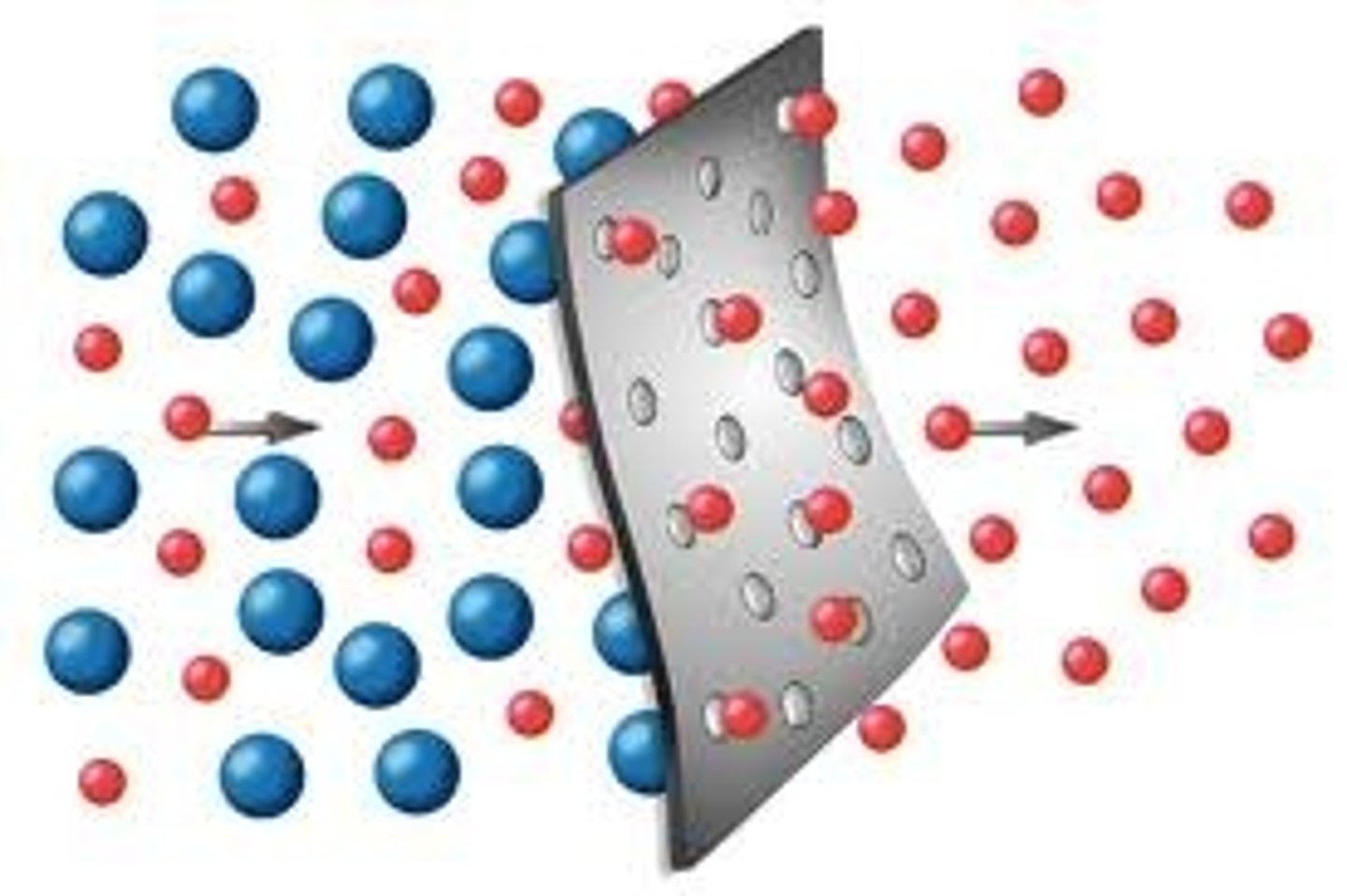
Permeability
Ability of rock or soil to allow water to flow through it
atmosphere
the layer of gases surrounding Earth
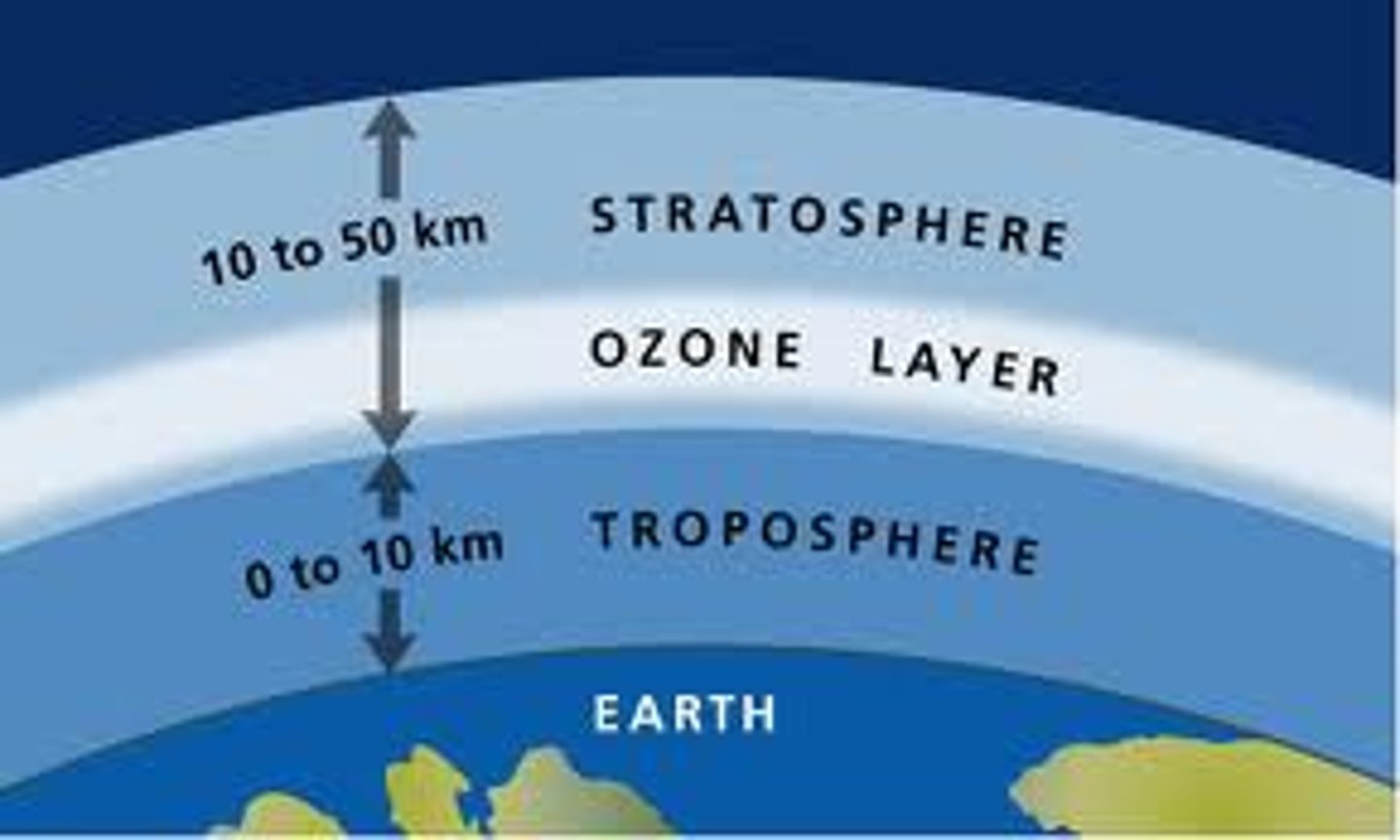
Troposphere
0-17 km above Earth's surface, site of weather, organisms, contains most atmospheric water vapor
Stratosphere
17 to 50 km, Ozone held here, absorbs UV radiation
Radiation
The transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves
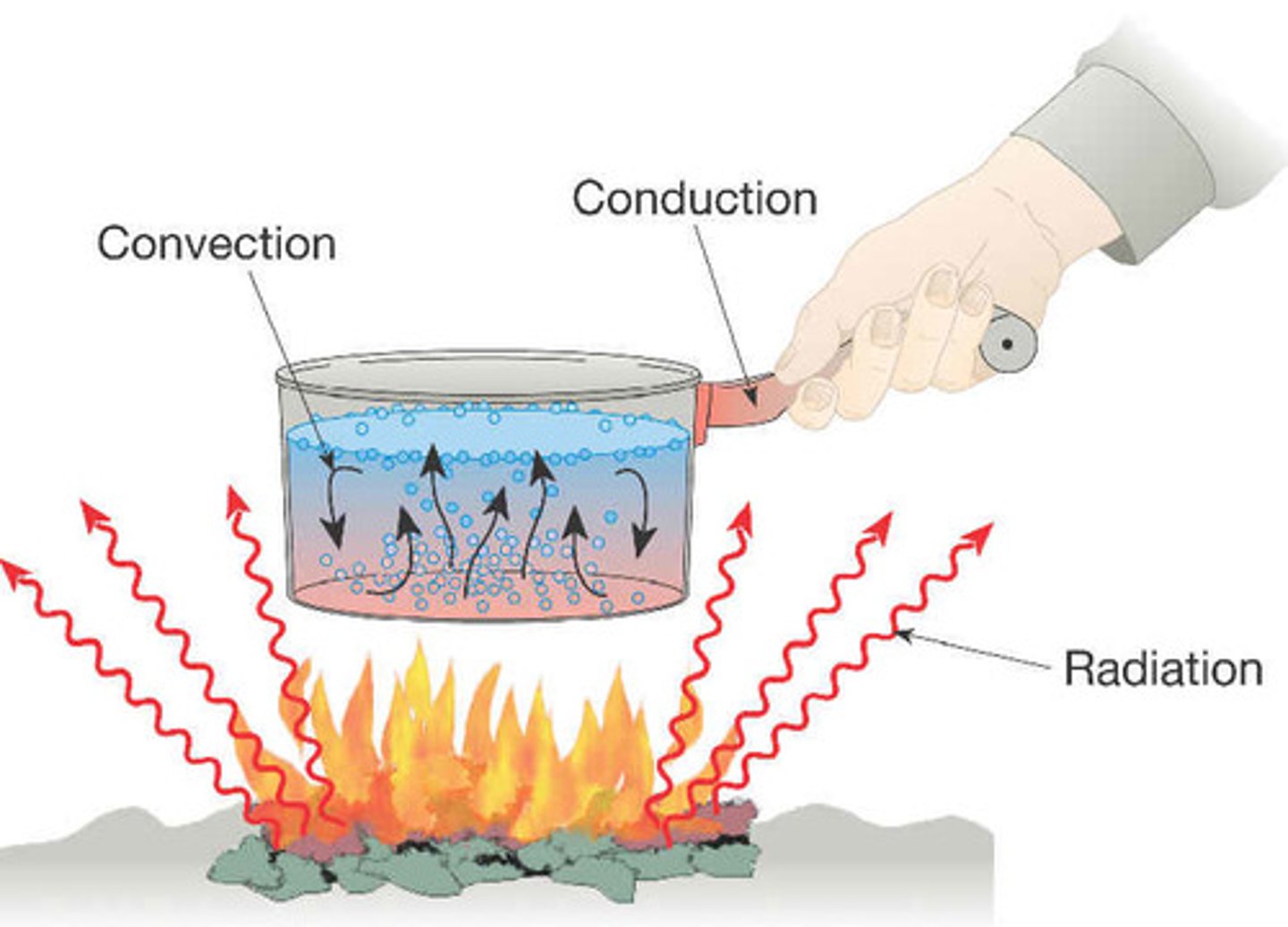
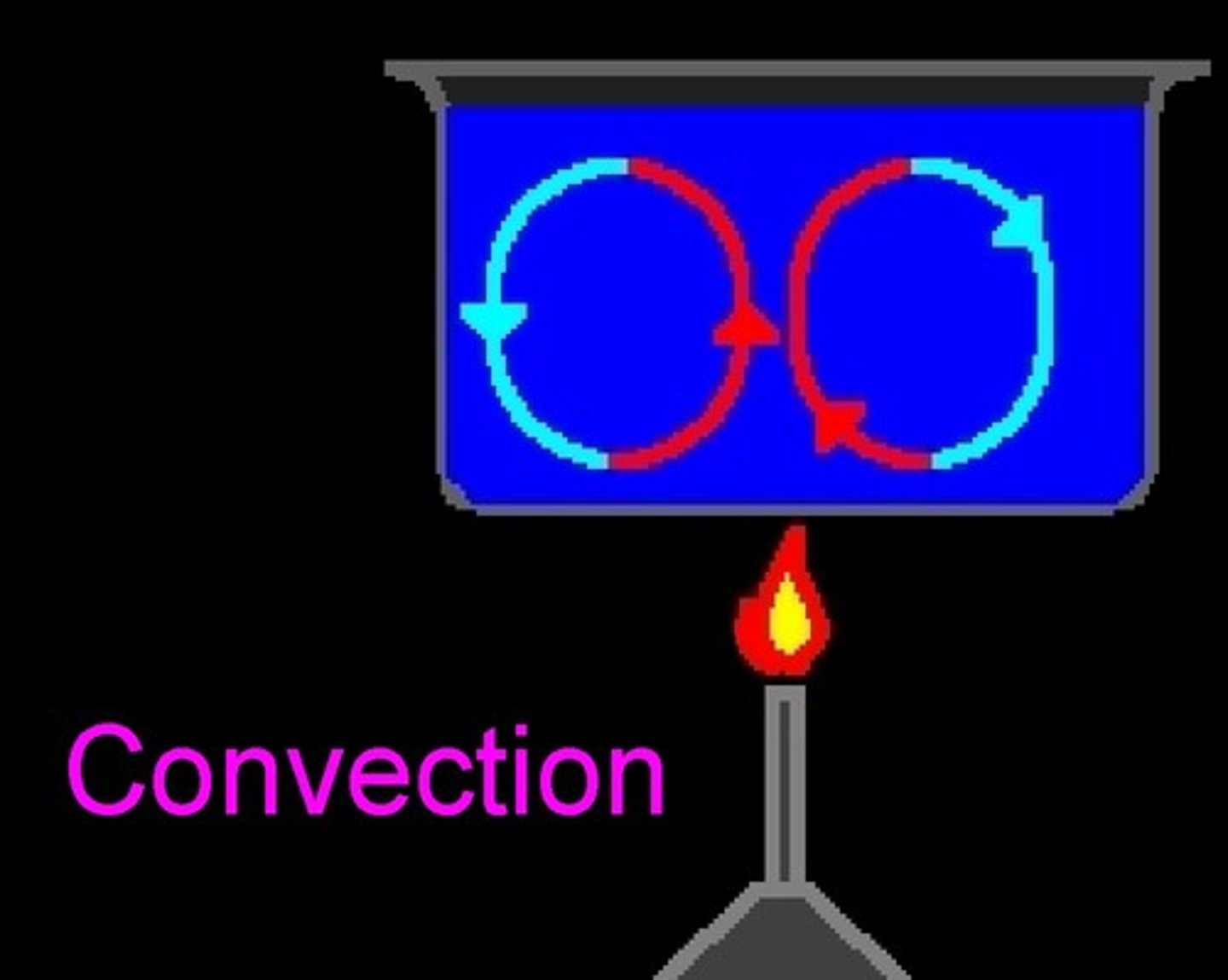
convection current
the movement of a fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of the fluid to another
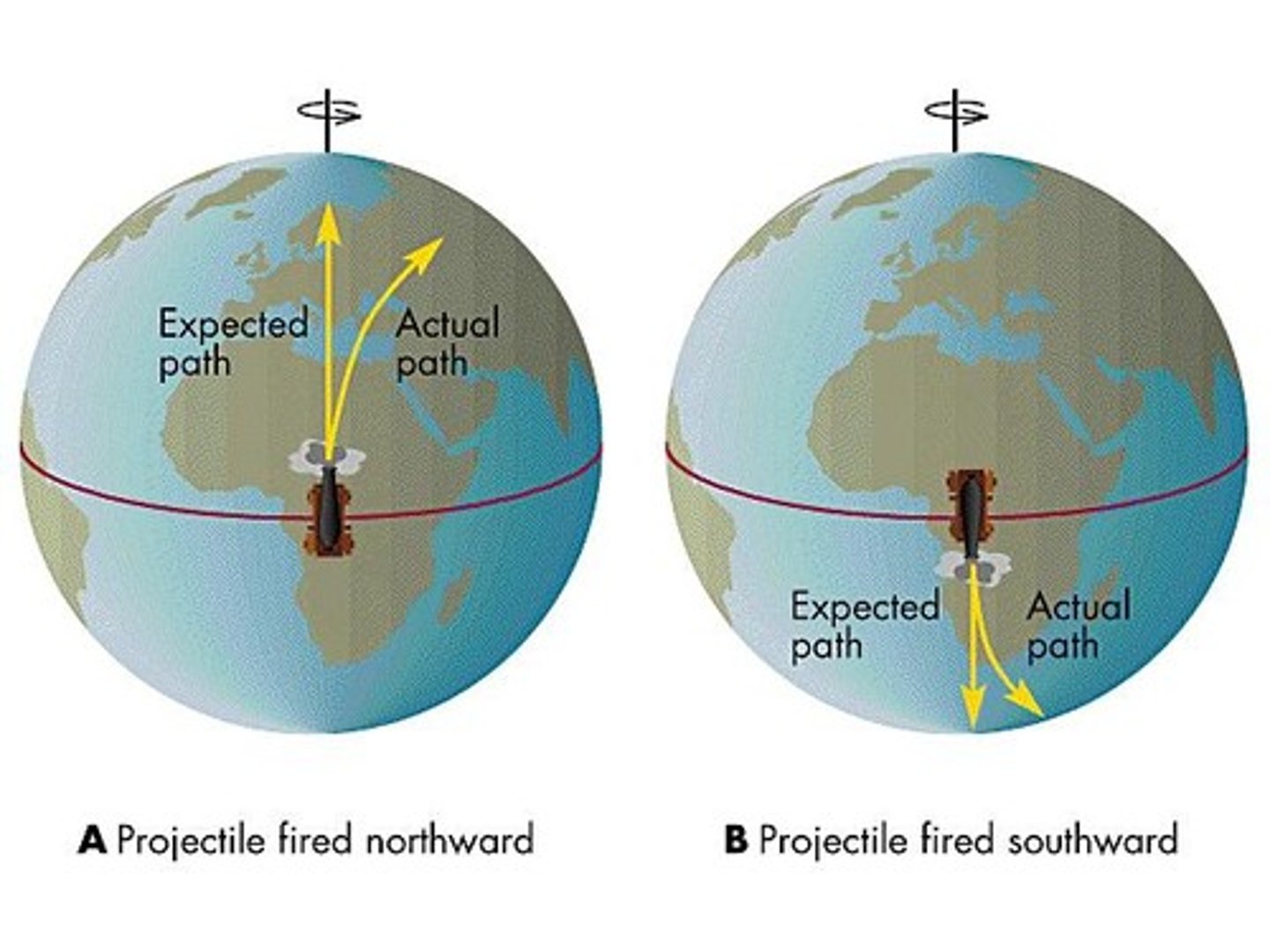
Coriolis effect
The effect of Earth's rotation on the direction of winds and currents.
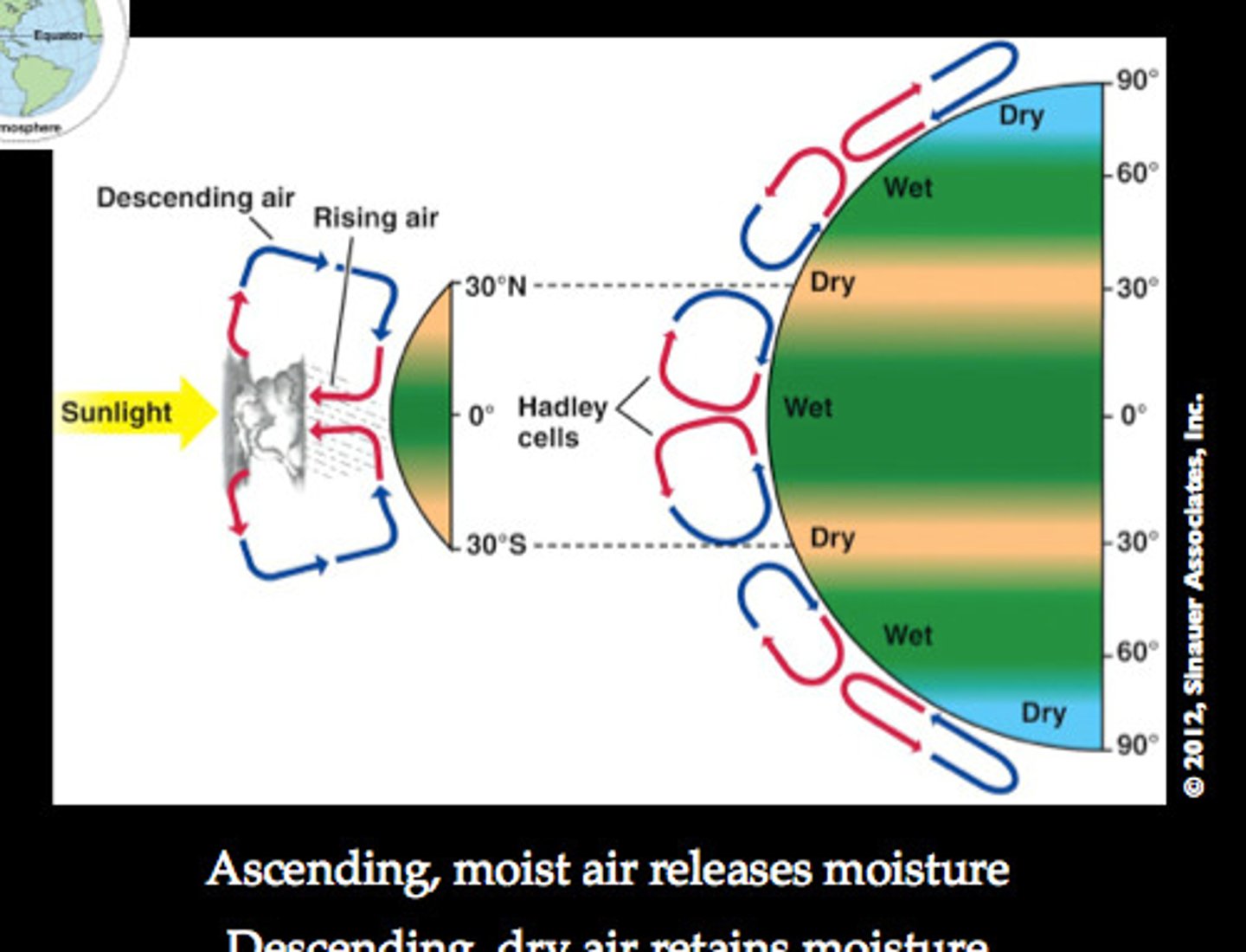
Hadley Cell
Convection currents that cycle between the equator, 30 degrees North and South.
Ferrell Cell
The middle atmospheric circulation in each hemisphere. Air in these cells rises at 60 degrees latitude and falls 30 degrees latitude.
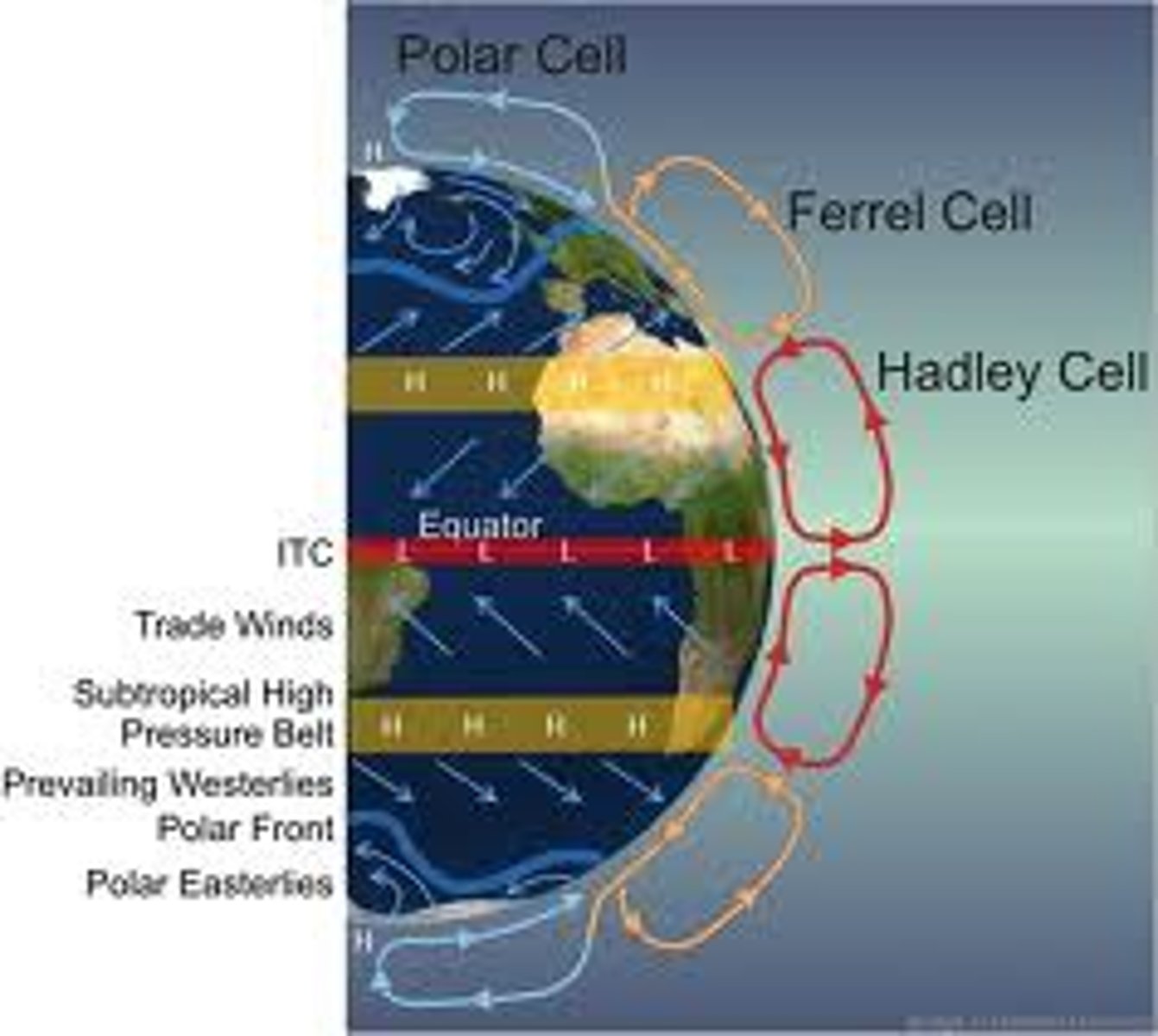
Polar Cell
Weak circulation cell that occurs between 60 and 90 degrees latitude. It results from upper air masses moving northward and descending at the poles, while at the same time surface air flows south.
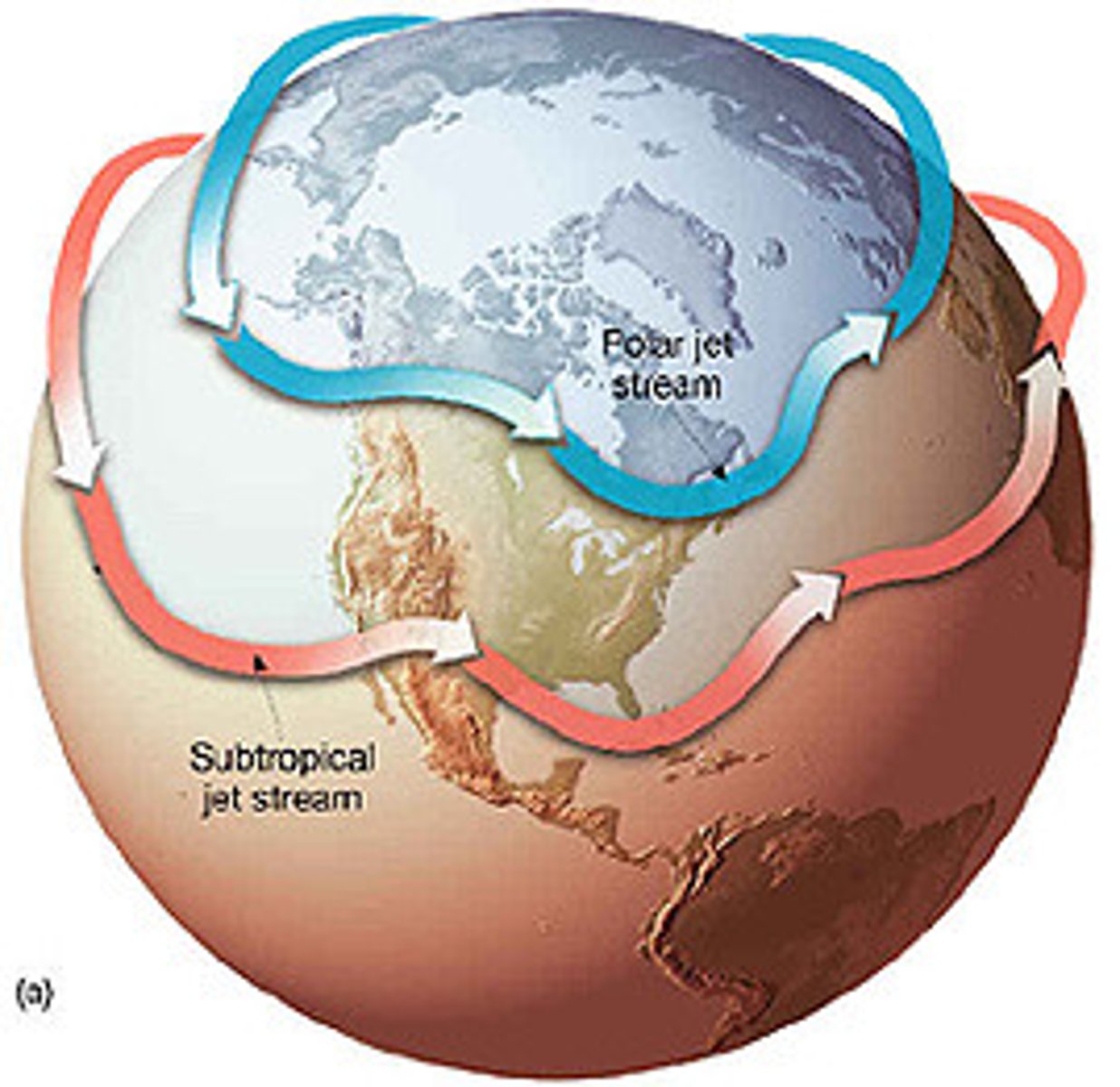
jet stream
a high-speed high-altitude airstream blowing from west to east near the top of the troposphere
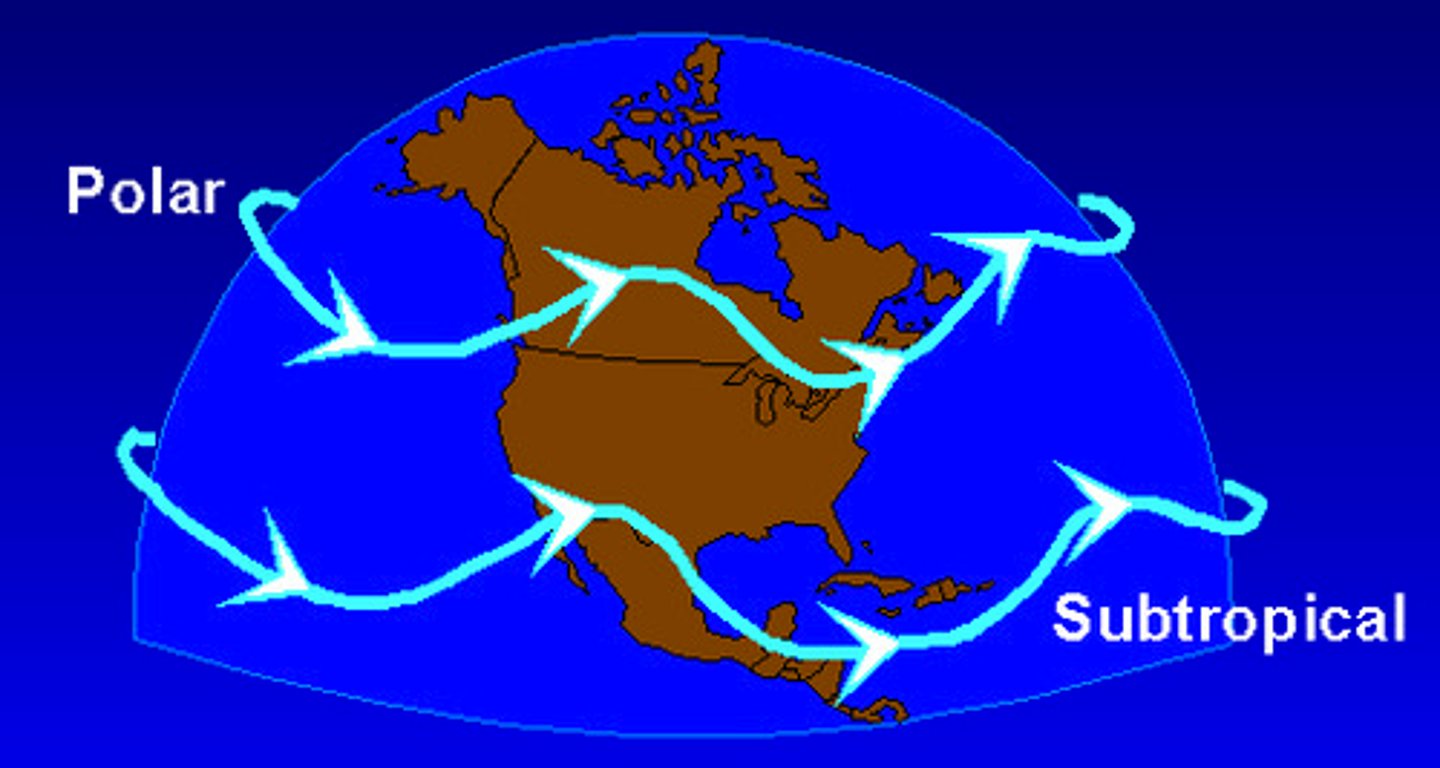
sub tropical jet stream
Jet stream found between the Hadley and Ferrel cells
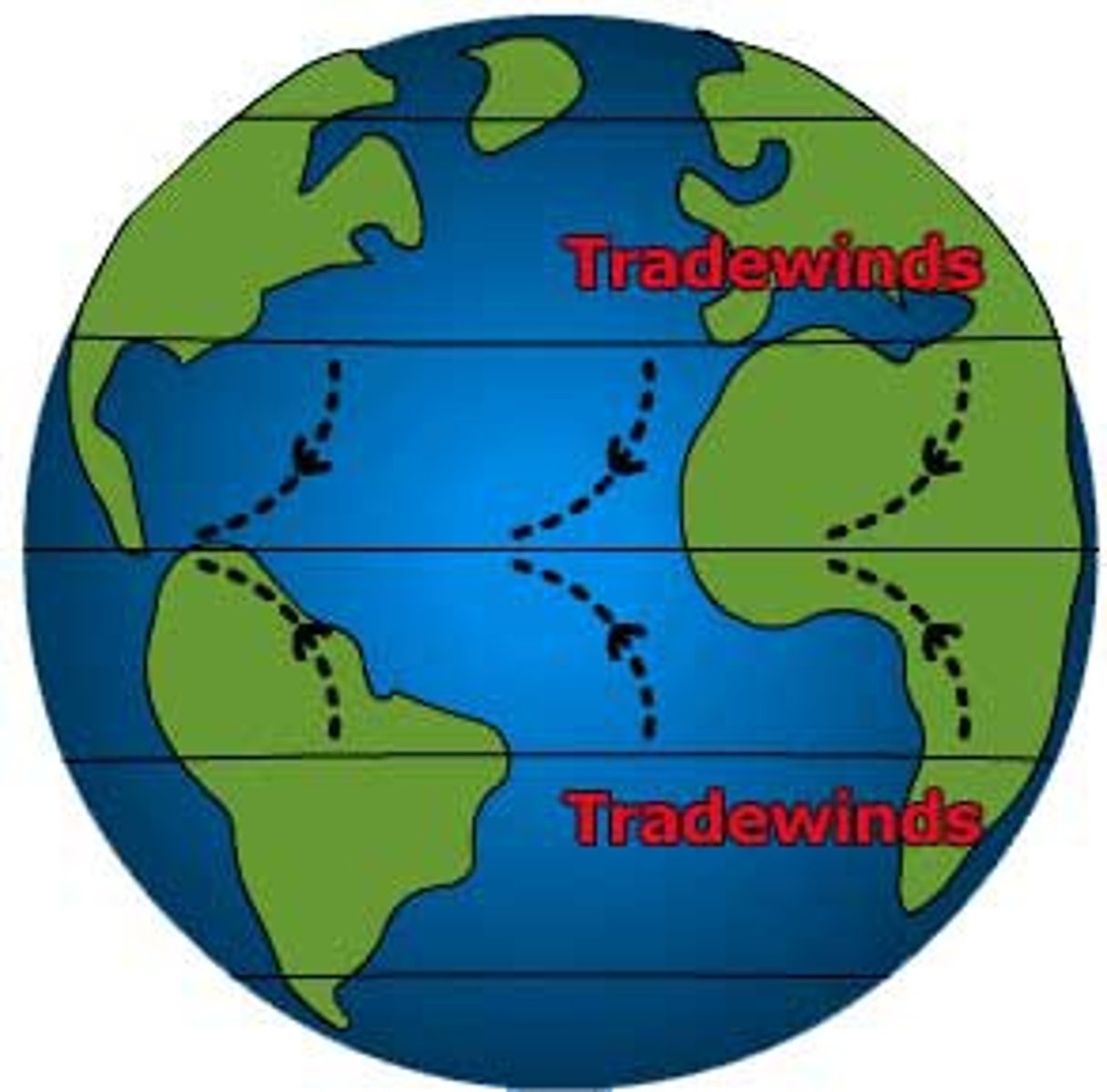
trade winds
prevailing winds that blow from east to west from 30 degrees latitude to the equator in both hemispheres
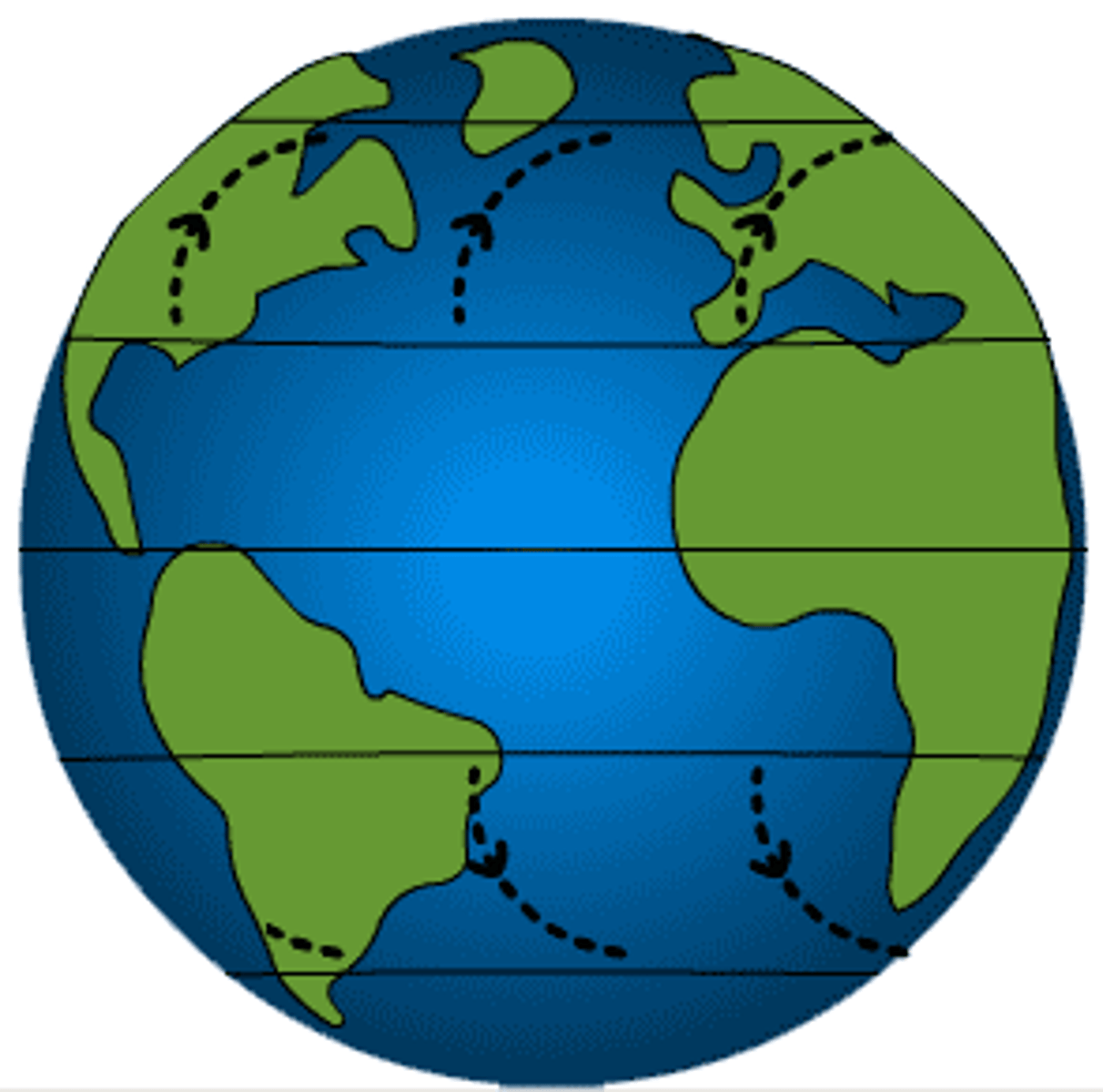
prevailing westerlies
winds that blow west to east between 30 and 60 degrees in the northern and southern hemispheres
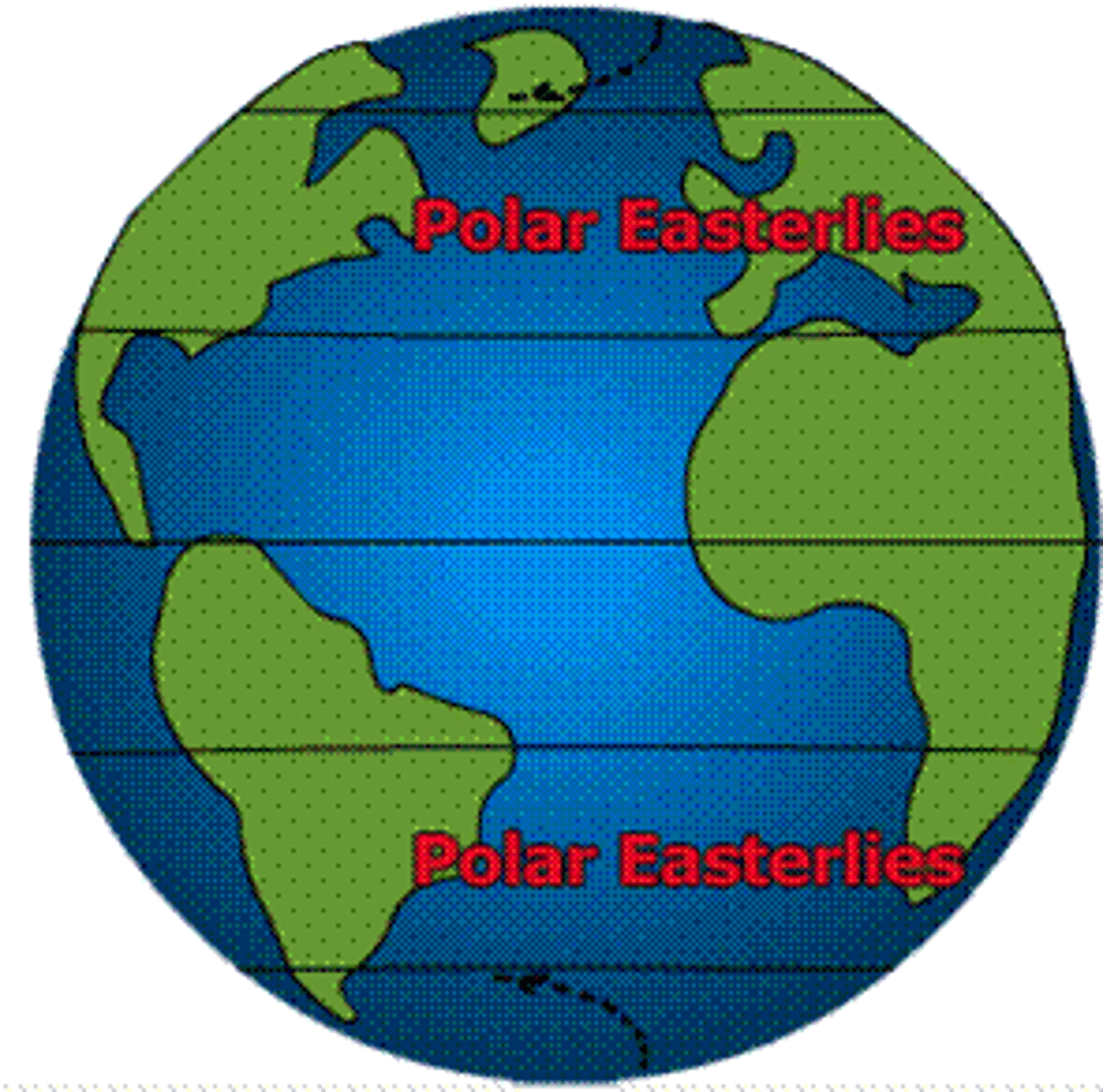
polar easterlies
cold winds that blow from the east to the west near the North Pole and South Pole
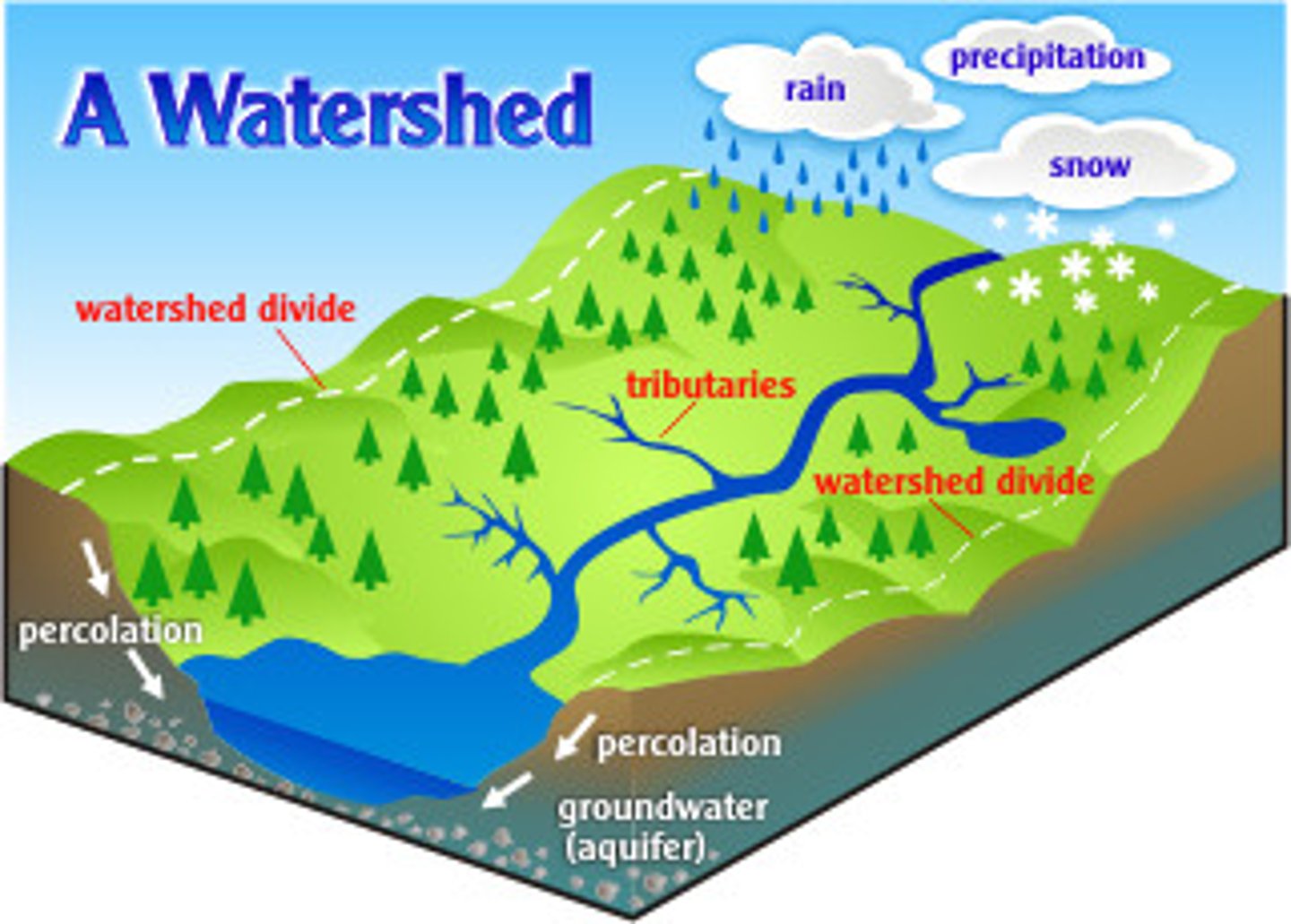
watershed (drainage basin)
land area that delivers runoff, sediment, and dissolved substances to a stream
Insolation
incoming solar radiation
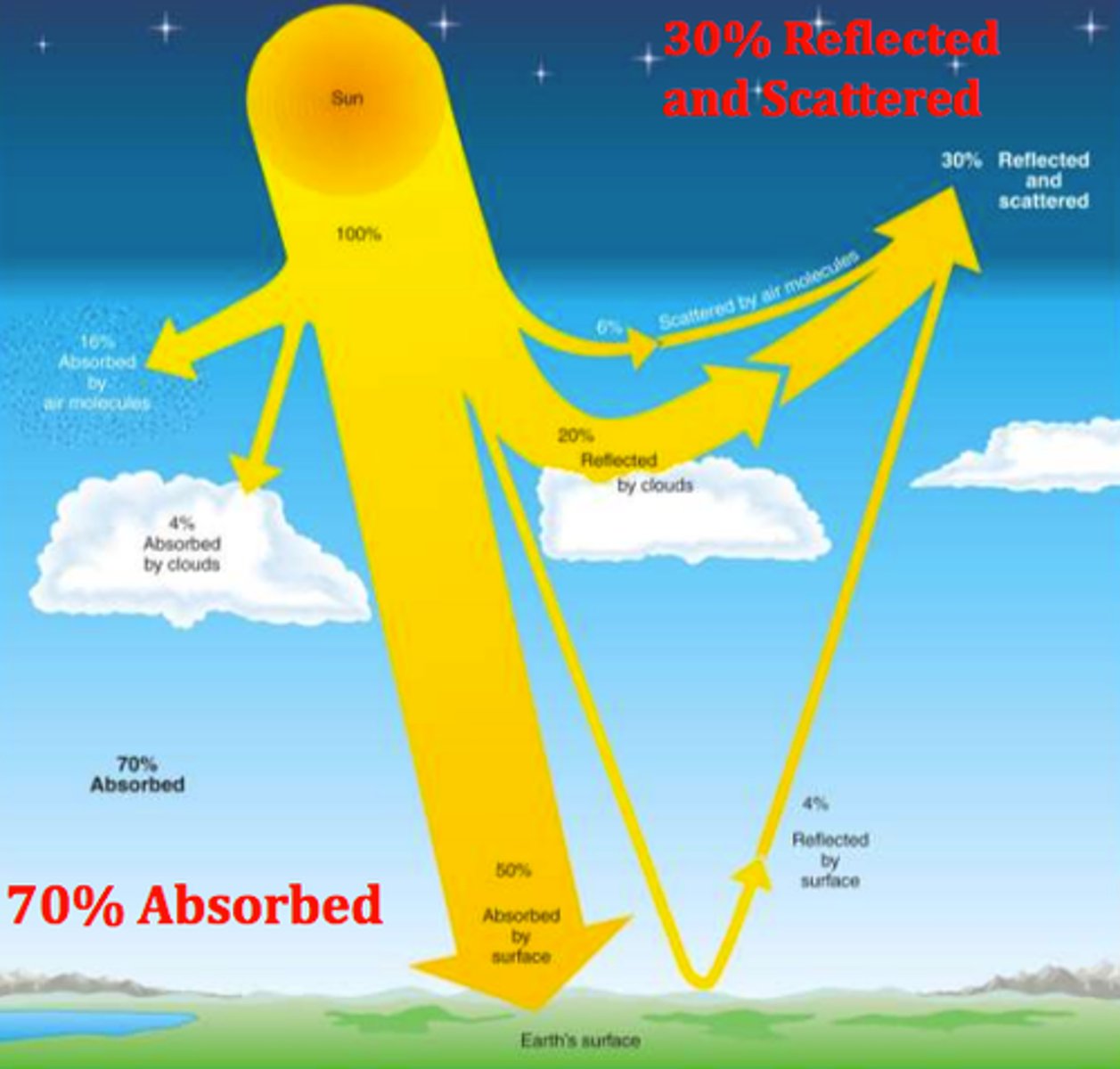
specific heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celsius
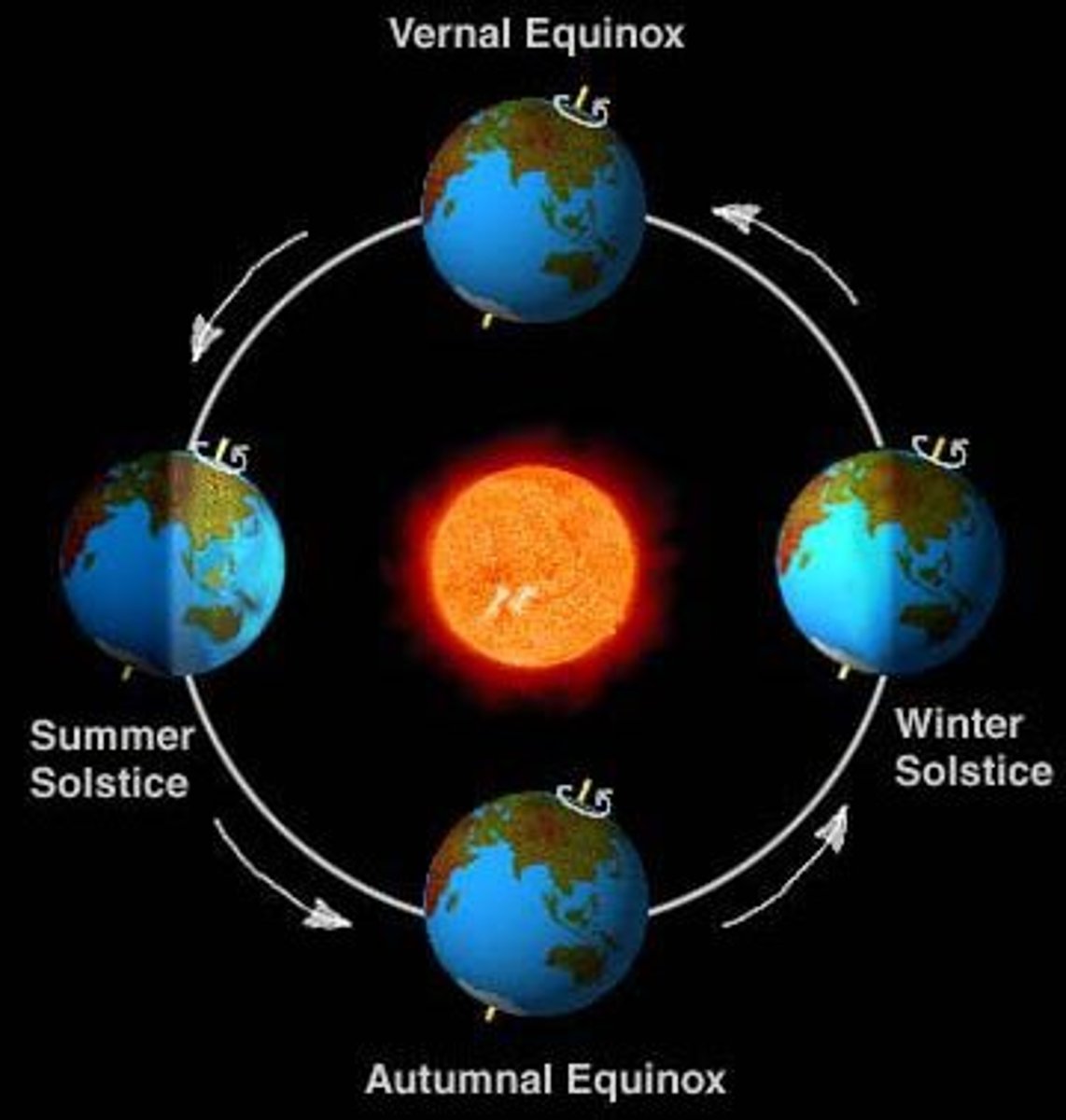
Solstice
The two days of the year on which the sun reaches its greatest distance north or south of the equator
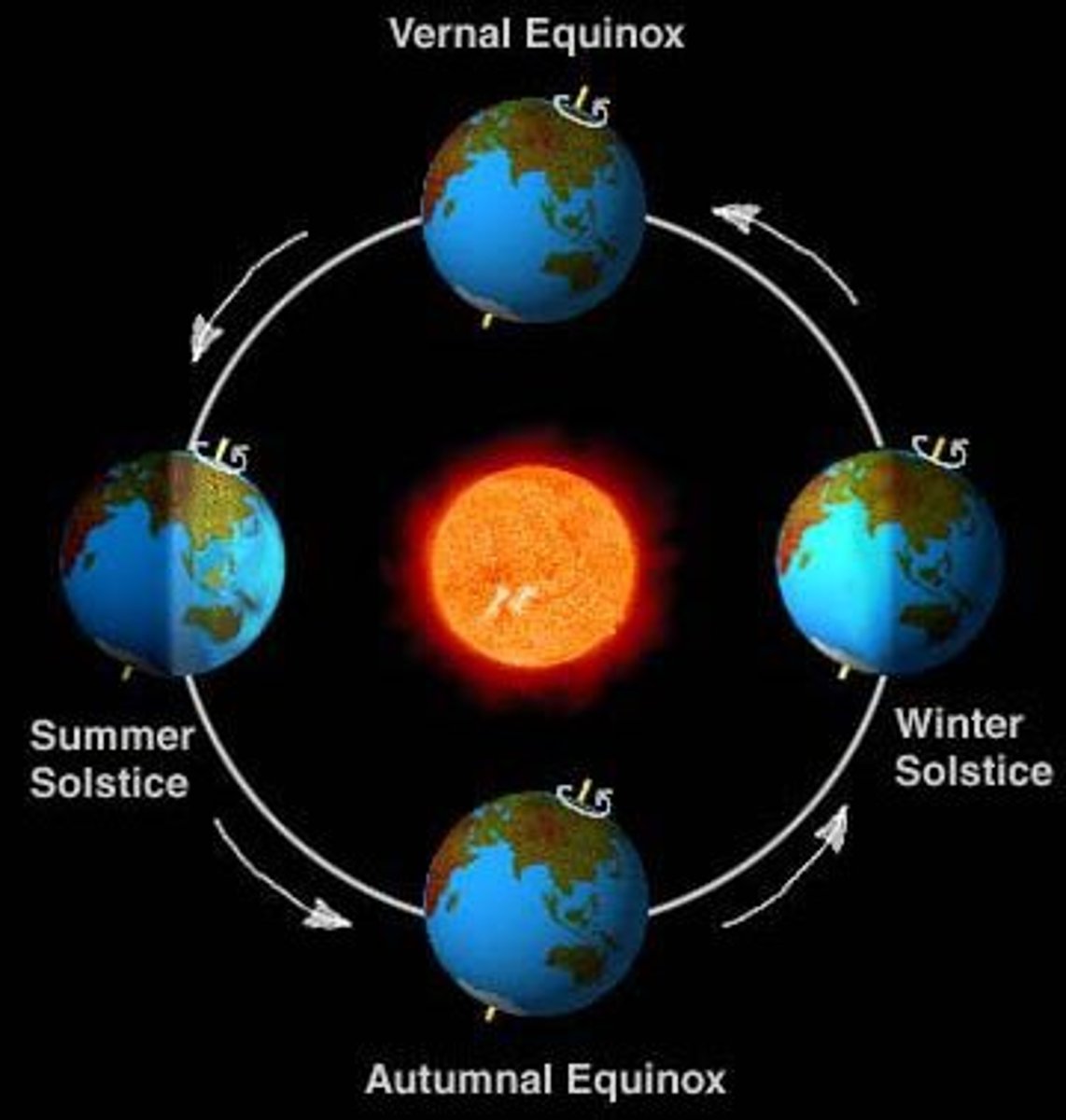
Equinoxes
the time or date (twice each year) at which the sun crosses the celestial equator, when day and night are of equal length (about September 22 and March 20).
weather
The condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place.
climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
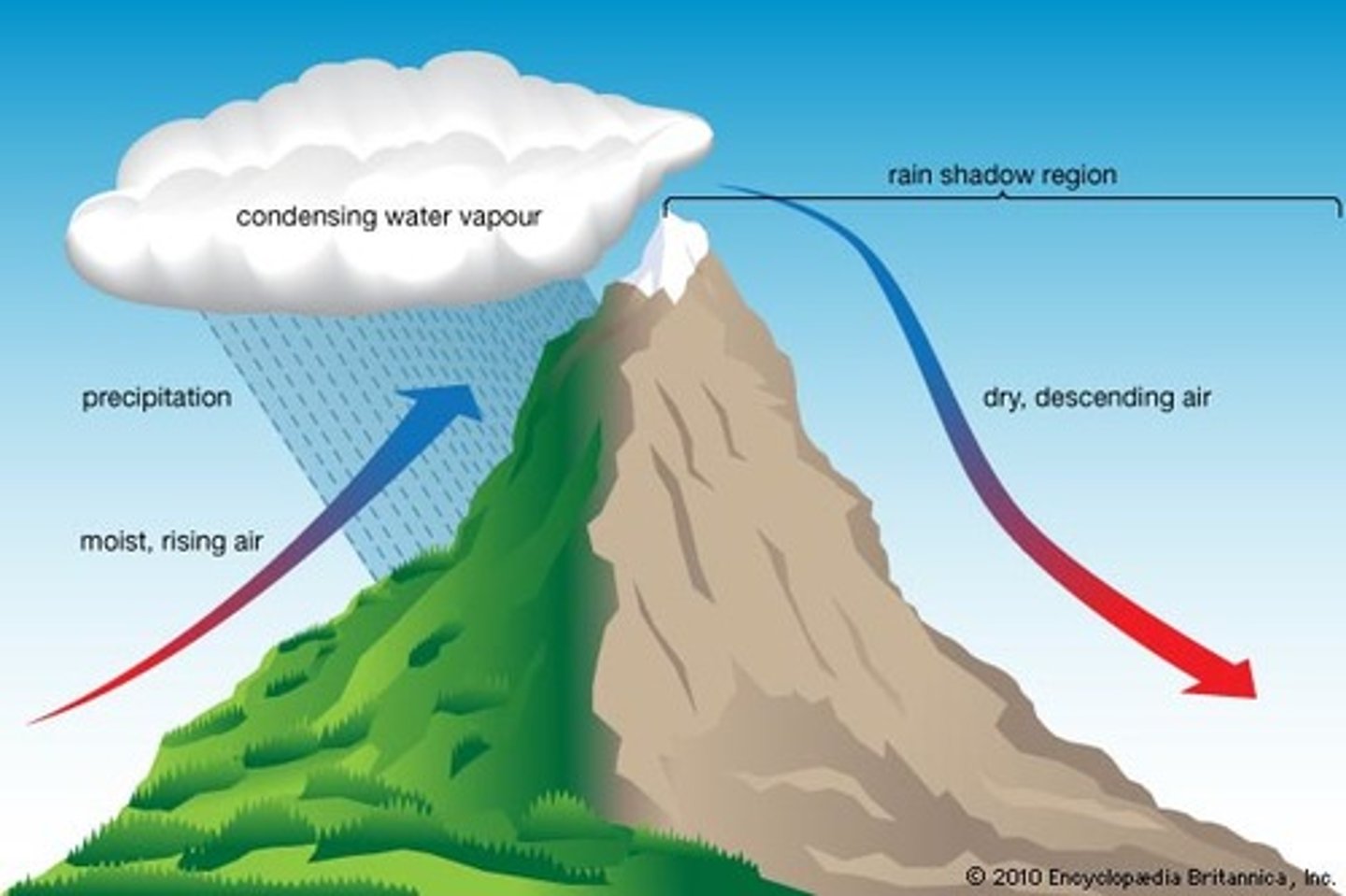
rain shadow effect
Precipitation falls on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on one side, but a desert area on the leeward side.
El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
The periodic changes in winds and ocean currents, causing cooler and wetter conditions in the southeastern United States and unusually dry weather in southern Africa and Southeast Asia.
La Nina Effect
a change in the eastern Pacific Ocean in which the surface water temperature becomes unusually cool
El Nino
an irregularly occurring and complex series of climatic changes affecting the equatorial Pacific region and beyond every few years, characterized by the appearance of unusually warm, nutrient-poor water off northern Peru and Ecuador, typically in late December.
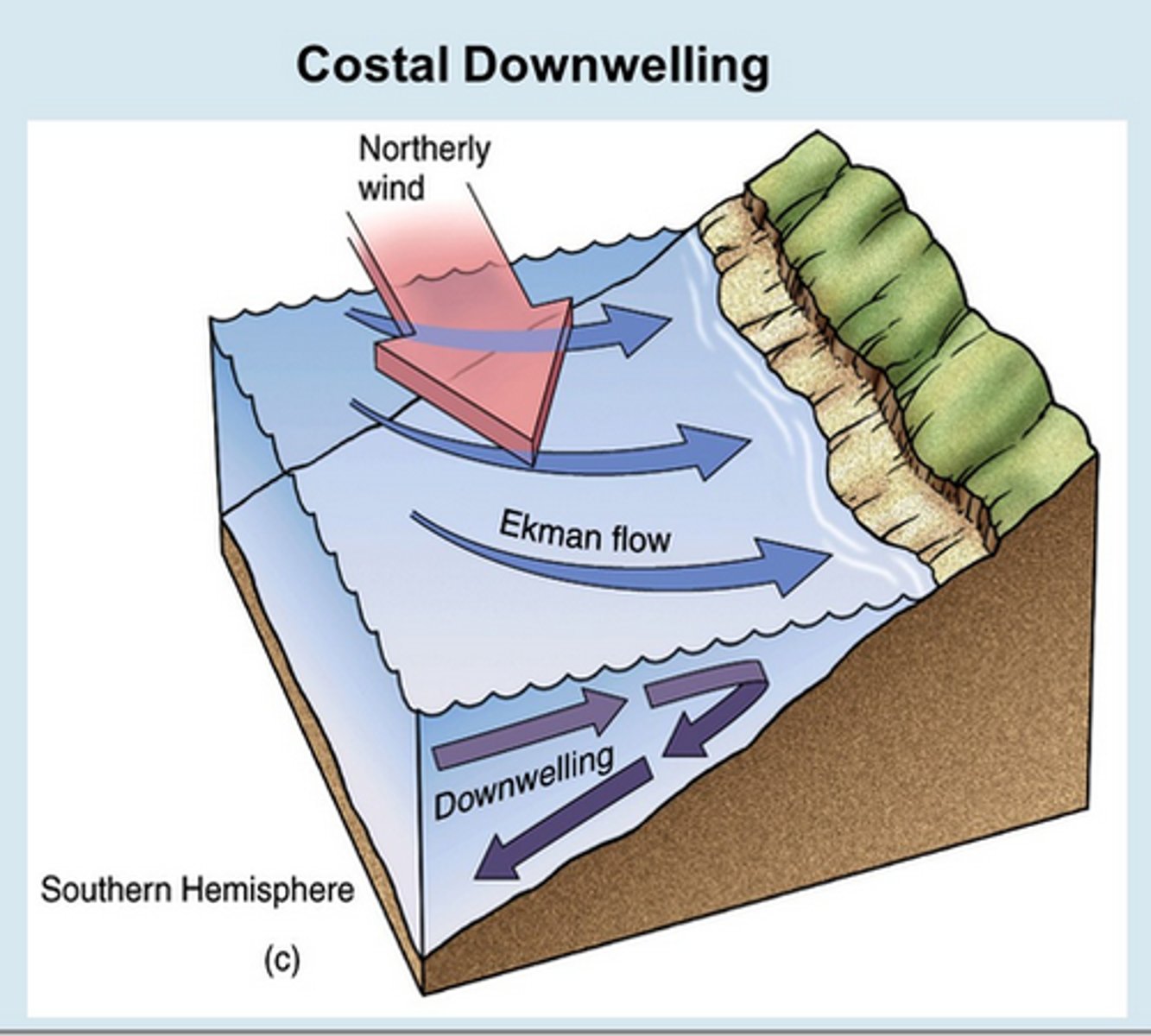
Downwelling
The movement of water from the surface to greater depths.
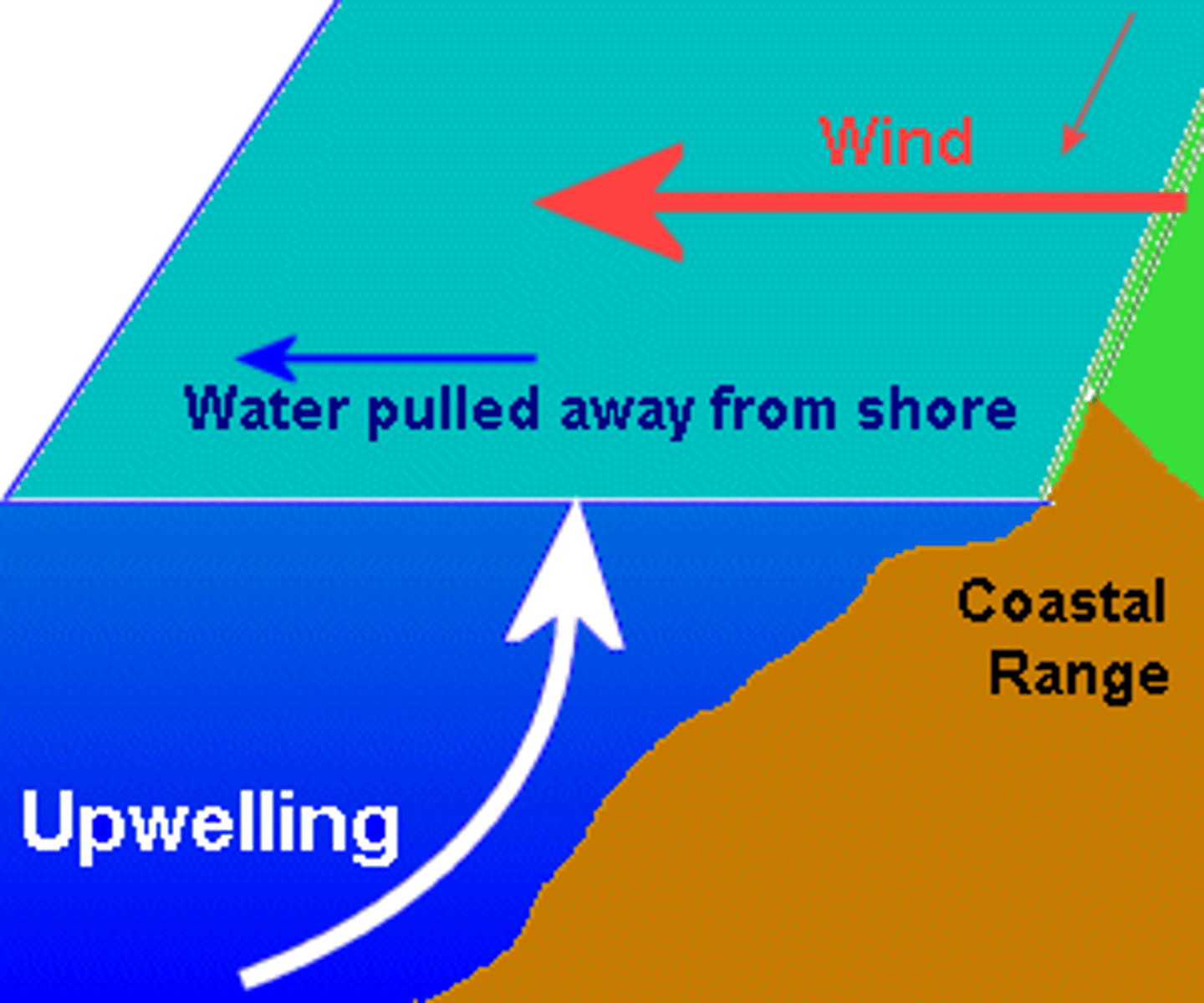
Upwelling
the upward movement of ocean water toward the surface as a result of diverging currents
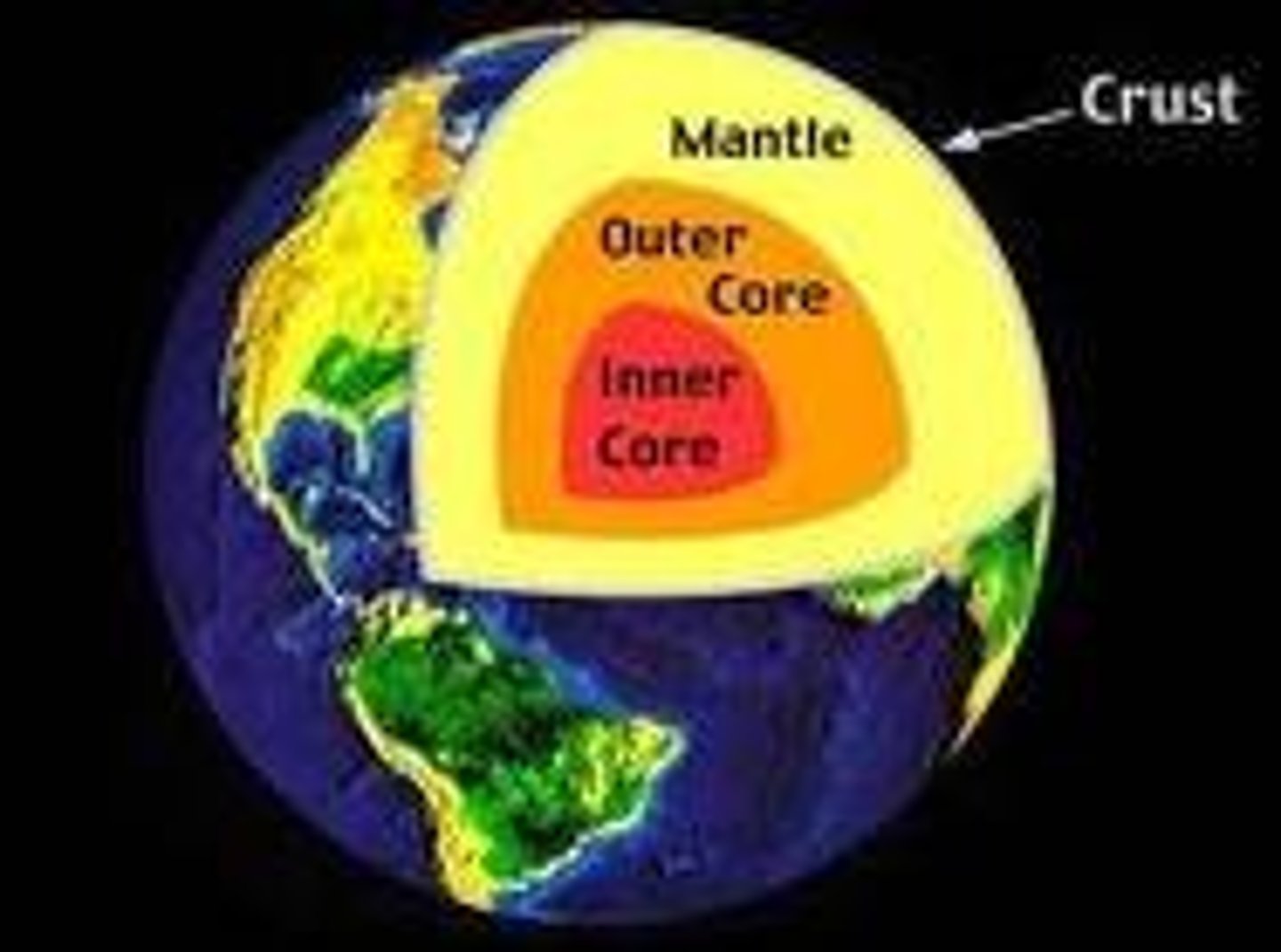
core
The central part of the earth below the mantle
Crust
Earth's outermost layer.
earthquake
Shaking and vibration at the surface of the earth resulting from underground movement along a fault
geology
Study of the earth
igneous rock
a type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface
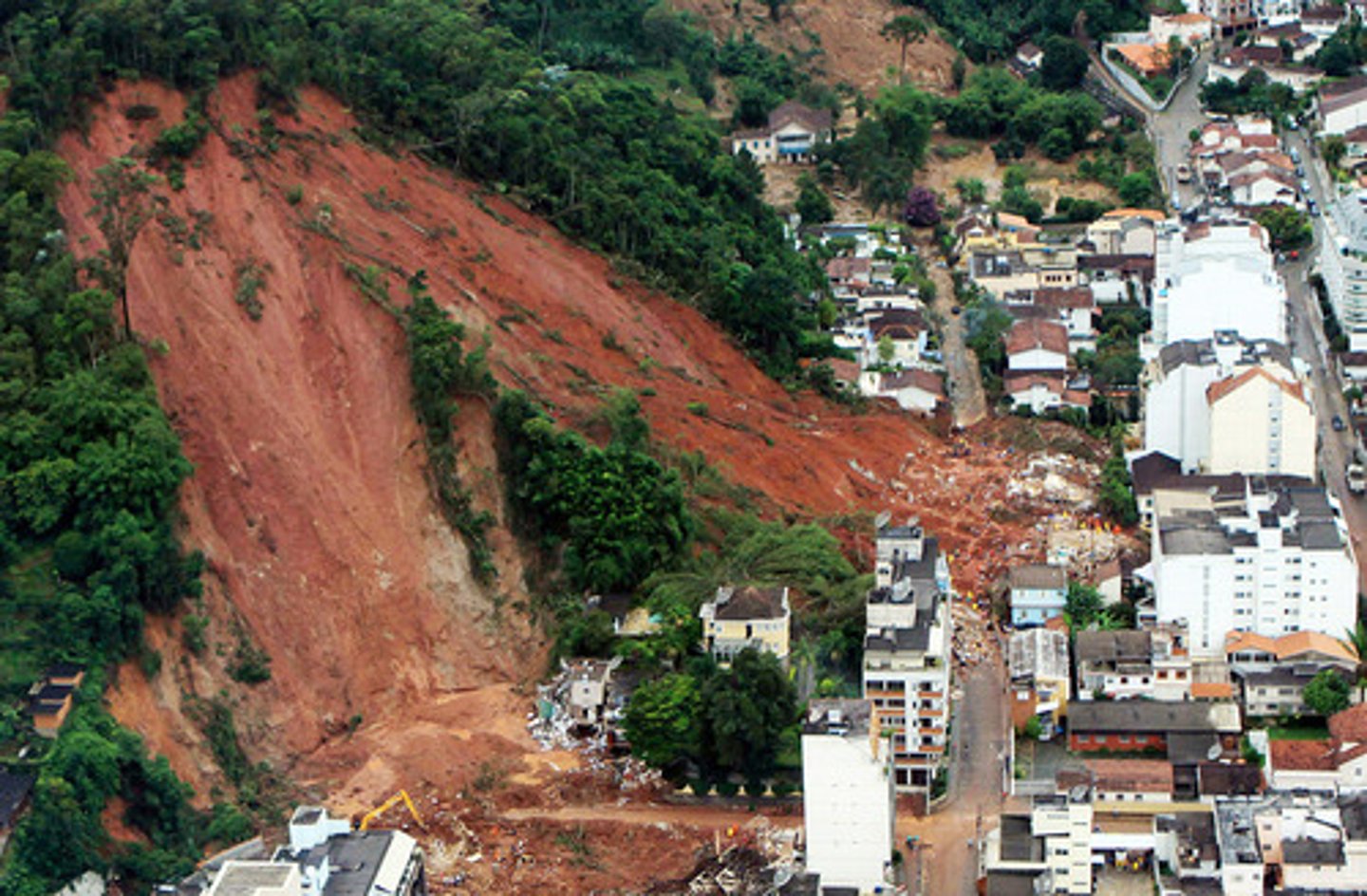
landslide
the sudden movement of rock and soil down a slope

Lava
Magma that reaches Earth's surface
Magma
A molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle
Mantle
The layer of hot, solid material between Earth's crust and core.
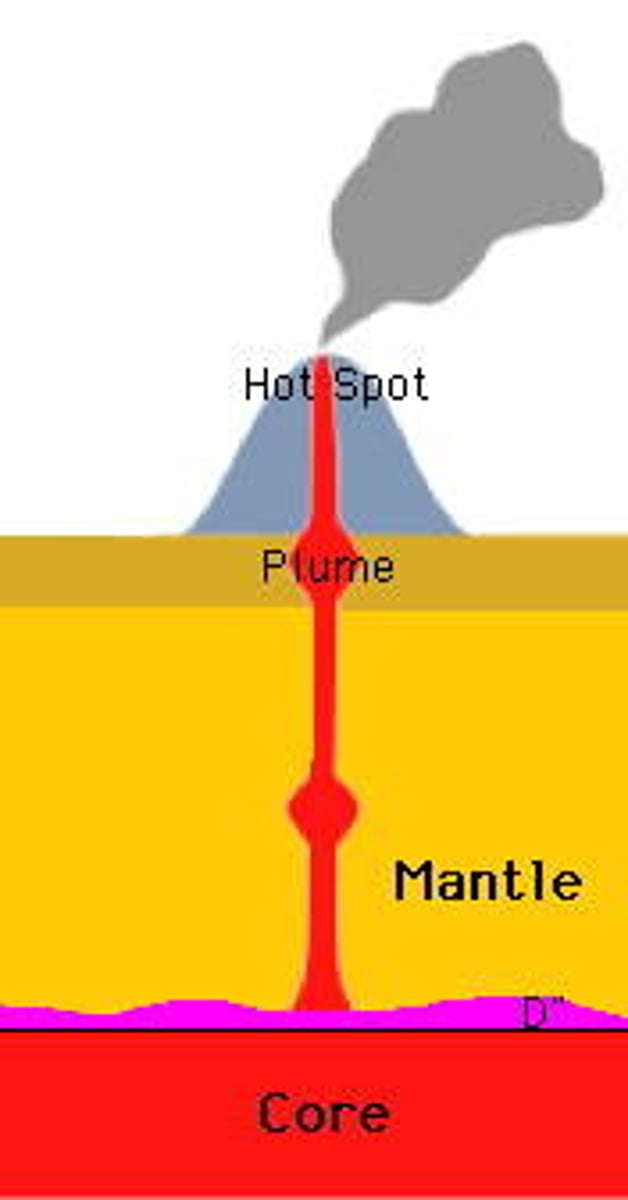
mantle plume
a column of very hot rock rising up through the mantle
mass wasting (mass movement)
occurs when soil and rock moves down a slope under the force of gravity
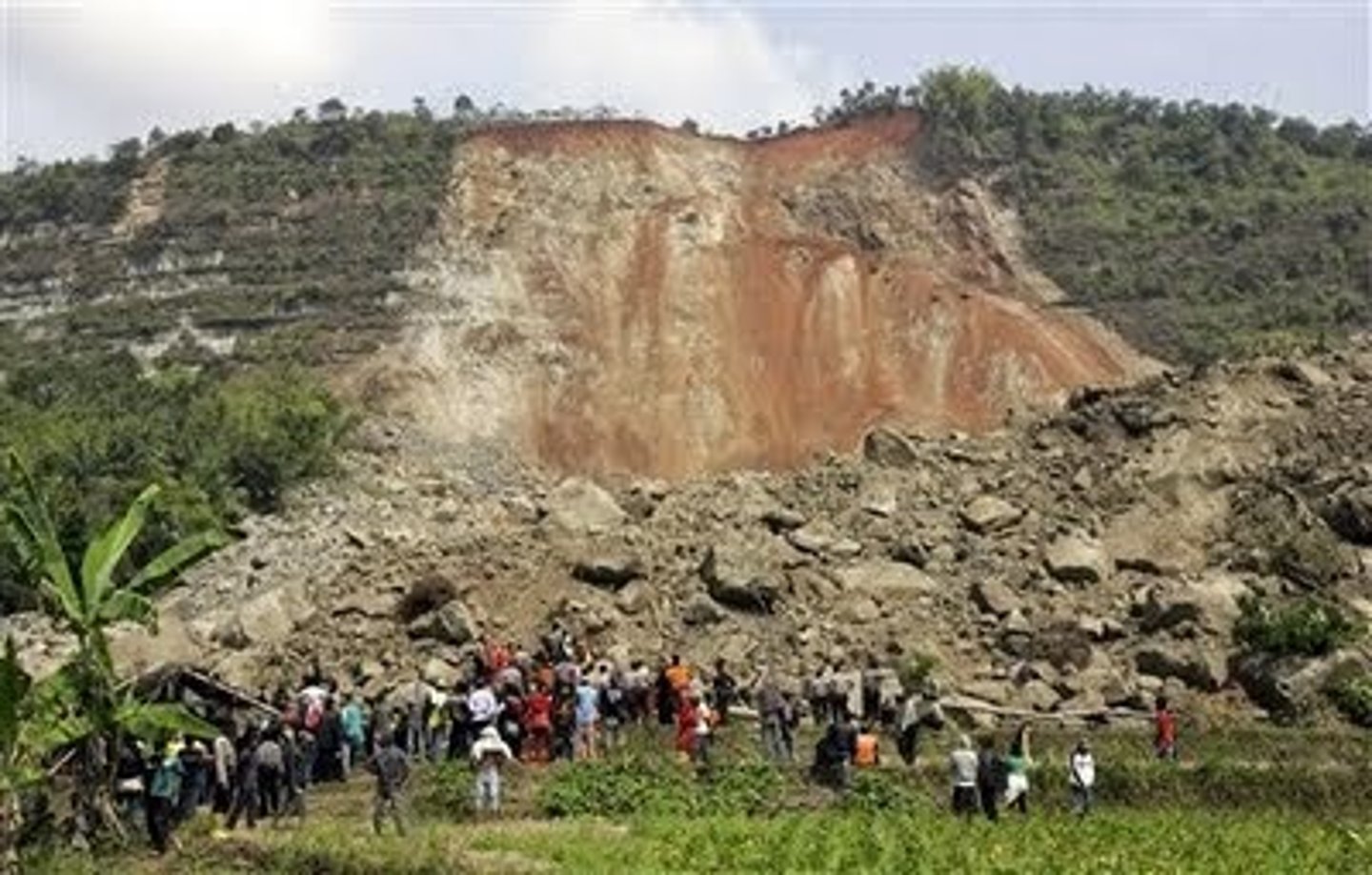

metamorphic rock
rock that has been changed by heat and pressure
Minerals
A solid inorganic substance of natural occurrence with a specific chemical composition, and an orderly crystalline structure.
ozone layer
Protective layer in atmosphere that shields earth from UV radiation.
Tsunami
A giant wave usually caused by an earthquake beneath the ocean floor.
volcano
a mountain or hill, typically conical, having a crater or vent through which lava, rock fragments, hot vapor, and gas are being or have been erupted from the earth's crust.
rock
A naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic matter
rock cycle
an idealized cycle of processes undergone by rocks in the earth's crust, involving igneous intrusion, uplift, erosion, transportation, deposition as sedimentary rock, metamorphism, remelting, and further igneous intrusion.
sediment
small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or living things
sedimentary rock
A type of rock that forms when particles from other rocks or the remains of plants or other organic parts that are pressed and cemented together
Subduction
The process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary.
bedrock
Rock that makes up Earth's crust; also the solid rock layer beneath the soil
clay
the finest soil, made up of particles that are less than 0.002 mm in diameter.
Humus
material formed from decaying leaves and other organic matter
fertilizer
a chemical or natural substance added to soil or land to increase its fertility
Loam
Rich, fertile soil that is made up of about equal parts of clay, sand, and silt.
sand
the coarsest soil, with particles 0.05,2.0 mm in diameter.
silt
fine particles of fertile soil with particles between 0.05 and 0.002mm in diameter
soil
The loose, weathered material on Earth's surface in which plants can grow.
atmospheric pressure
the pressure caused by the weight of the atmosphere
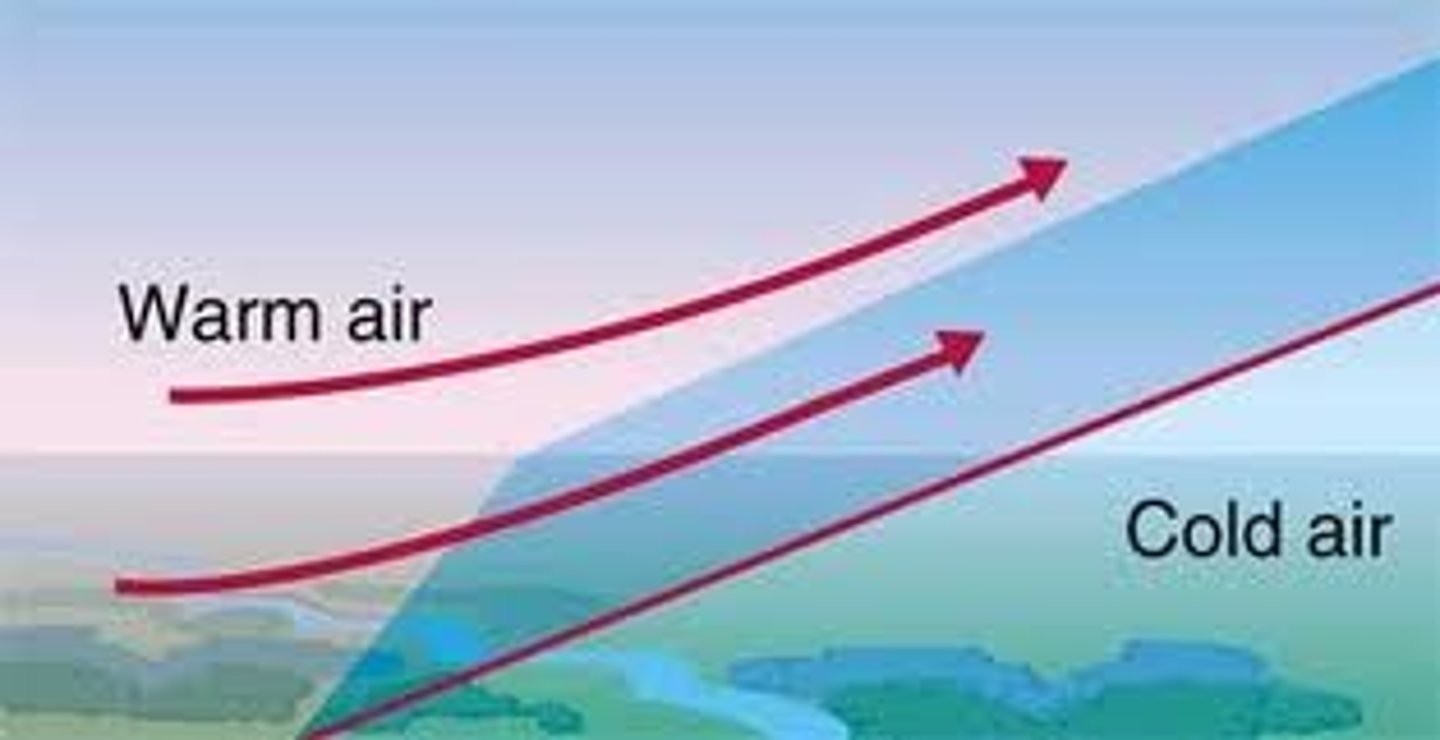
cold front
A front where cold air moves in under a warm air mass.
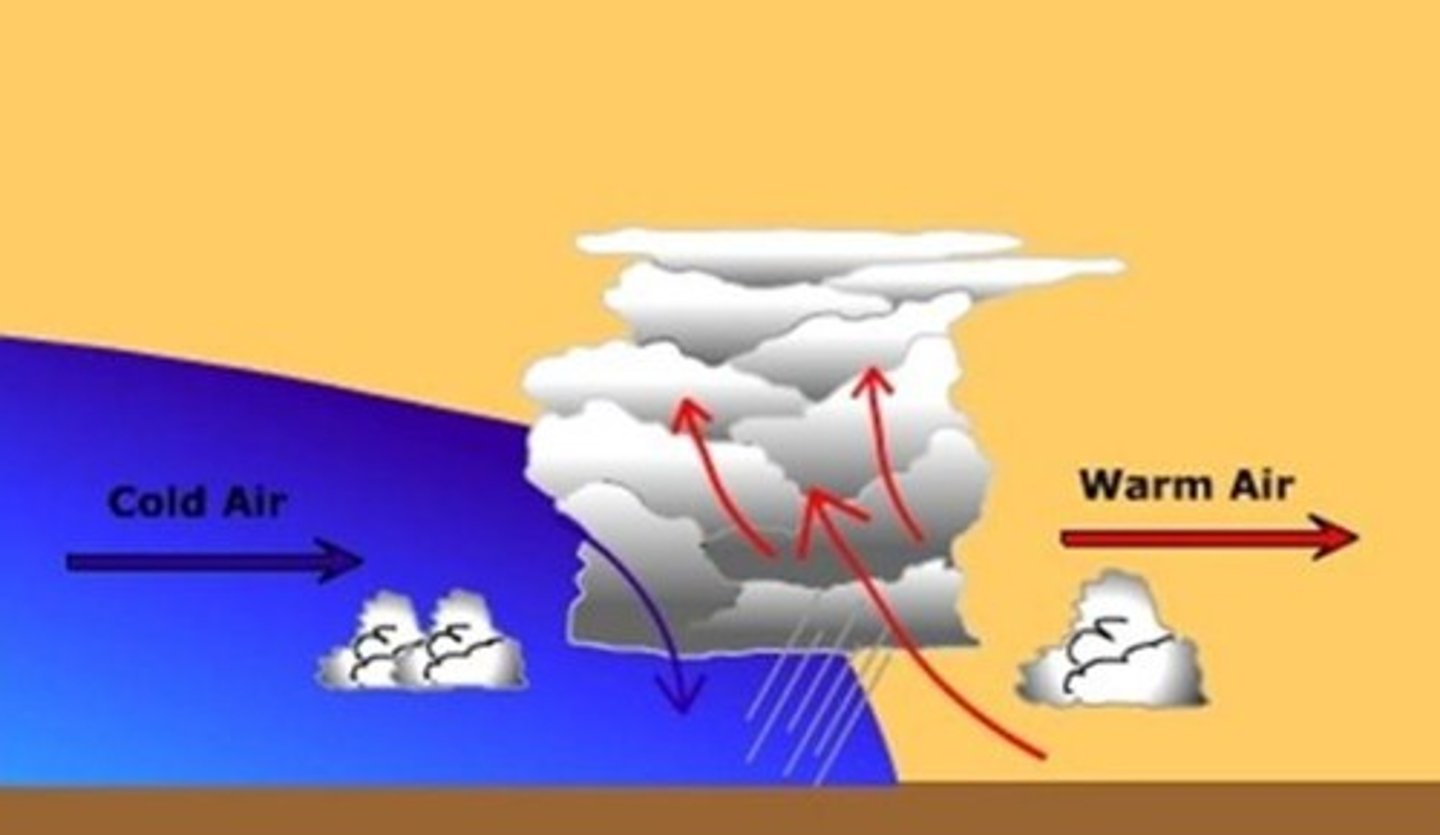
front
A boundary between two air masses
hurricane
A severe storm that develops over tropical oceans and whose strong winds of more than 120 km/h spiral in toward the intensely low-pressure storm center
low pressure
A mass of rising warm air that usually bring wet, stormy weather.
high pressure
A mass of sinking cool air that usually bring fair weather.
relative humidity
The percentage of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount of water vapor that air can contain at a particular temperature
warm front
a front where warm air moves over cold air and brings drizzly rain and then are followed by warm and clear weather
P waves
A type of seismic wave that compresses and expands the ground.
S waves
A type of seismic wave that moves the ground up and down or side to side
surface waves
seismic waves that travel along the Earth's surface
megathrust fault
The plate boundary between a subducting slab of oceanic lithosphere and the overlying plate
strike-slip fault
a type of fault where rocks on either side move past each other sideways with little up or down motion
plate boundary
the region where two tectonic plates are in contact
hot spot volcanoes
• A hot spot is an area where material from deep in the mantle rises and then melts, forming magma