Gavande NSAIDs lecture
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
the most used NSAIDS are _____________, accounting for almost 40% of global sales for _______(pathology)________.
ibuprofen, diclofenac. osteoarthritis
3 therapeutic activities of NSAIDs
analgesic (pain-relief)
anti-inflammatory
anti-pyretic (fever)
adverse effects of NSAIDs
gastric irritation
ulcer formation
stomach bleeding
longer bleeding (platelet inhibition)
cardiovasc events
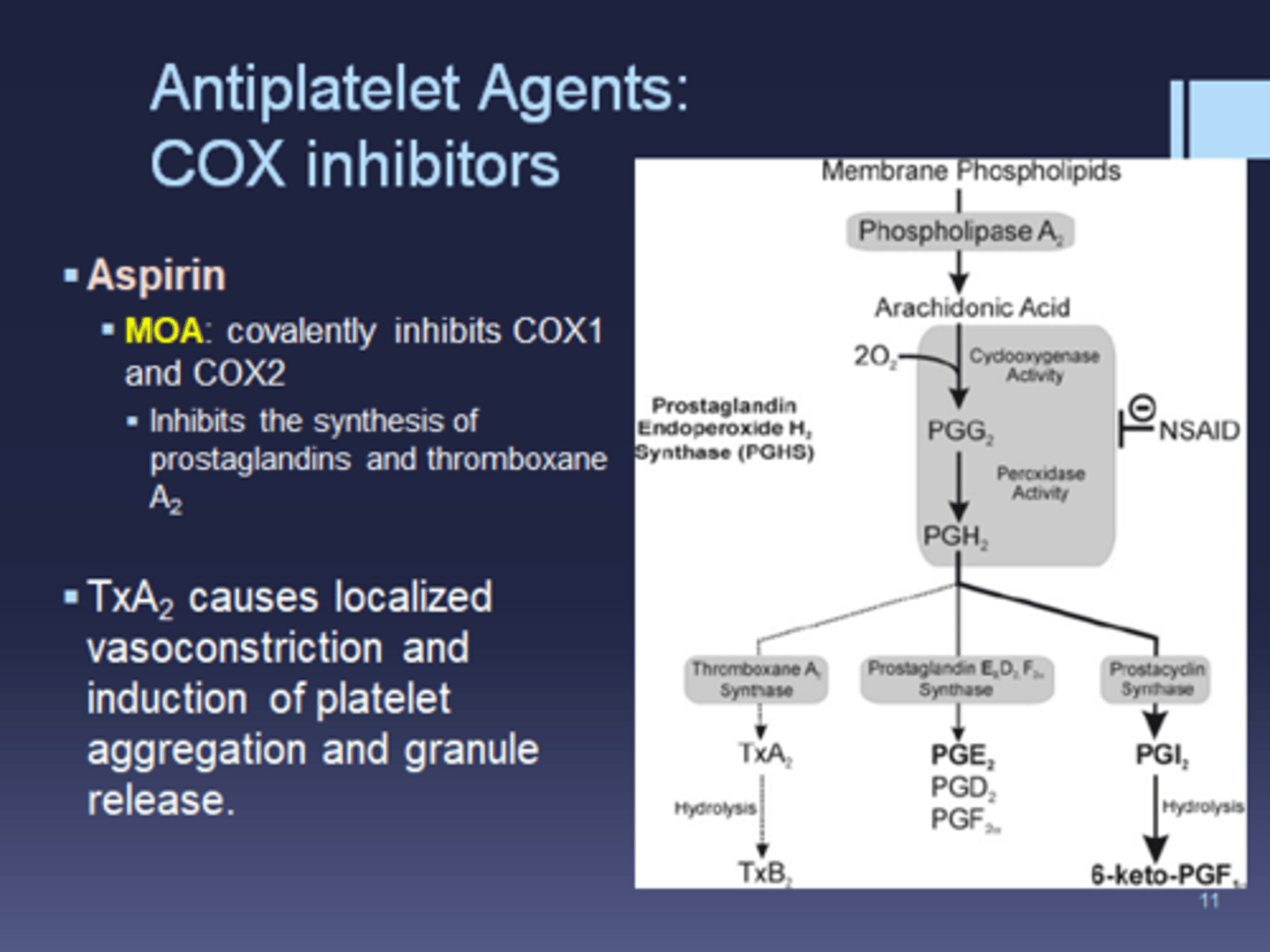
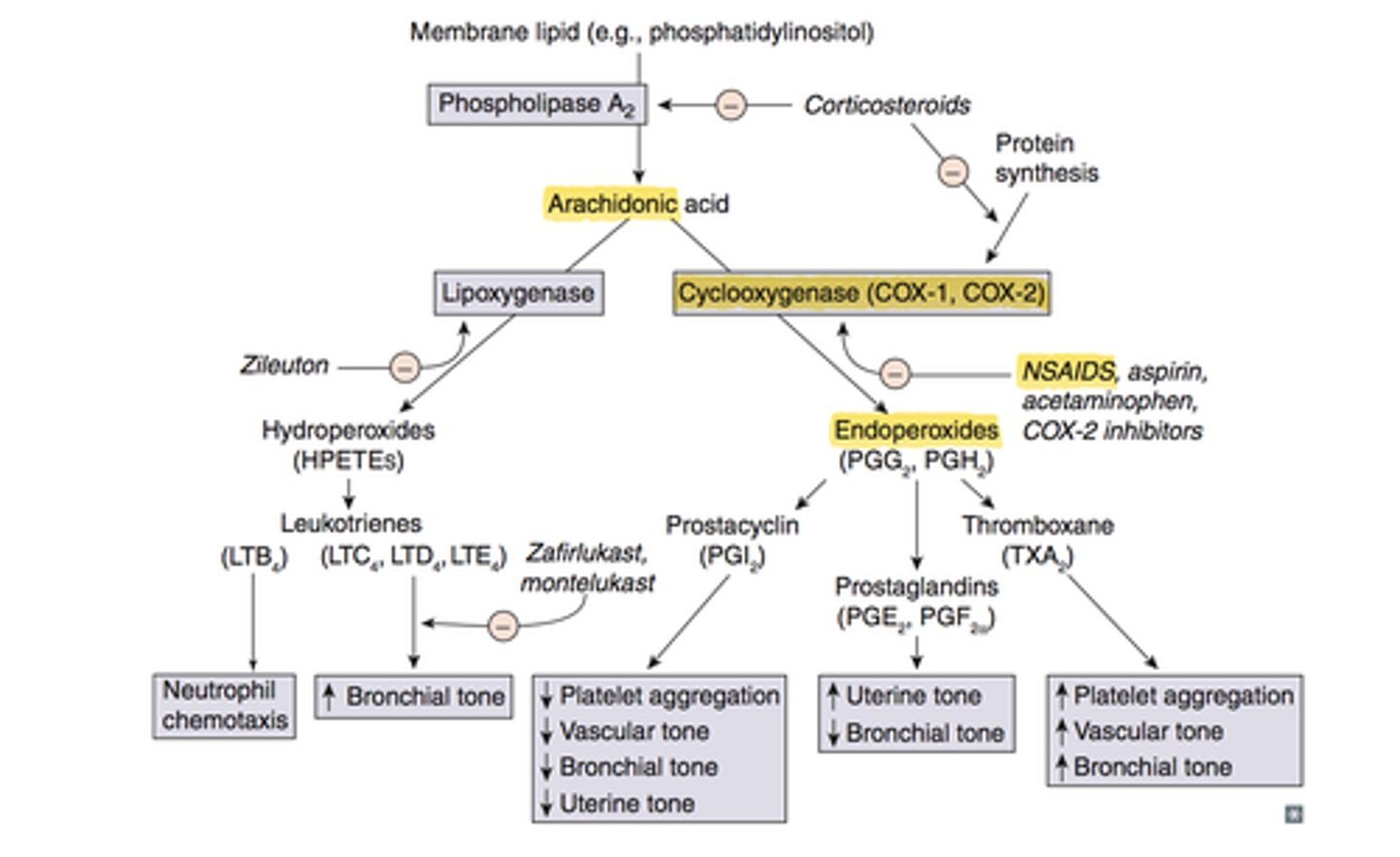
NSAIDs inhibit the biosynthesis of _____________
prostaglandins (by inhibiting COX enzyme)
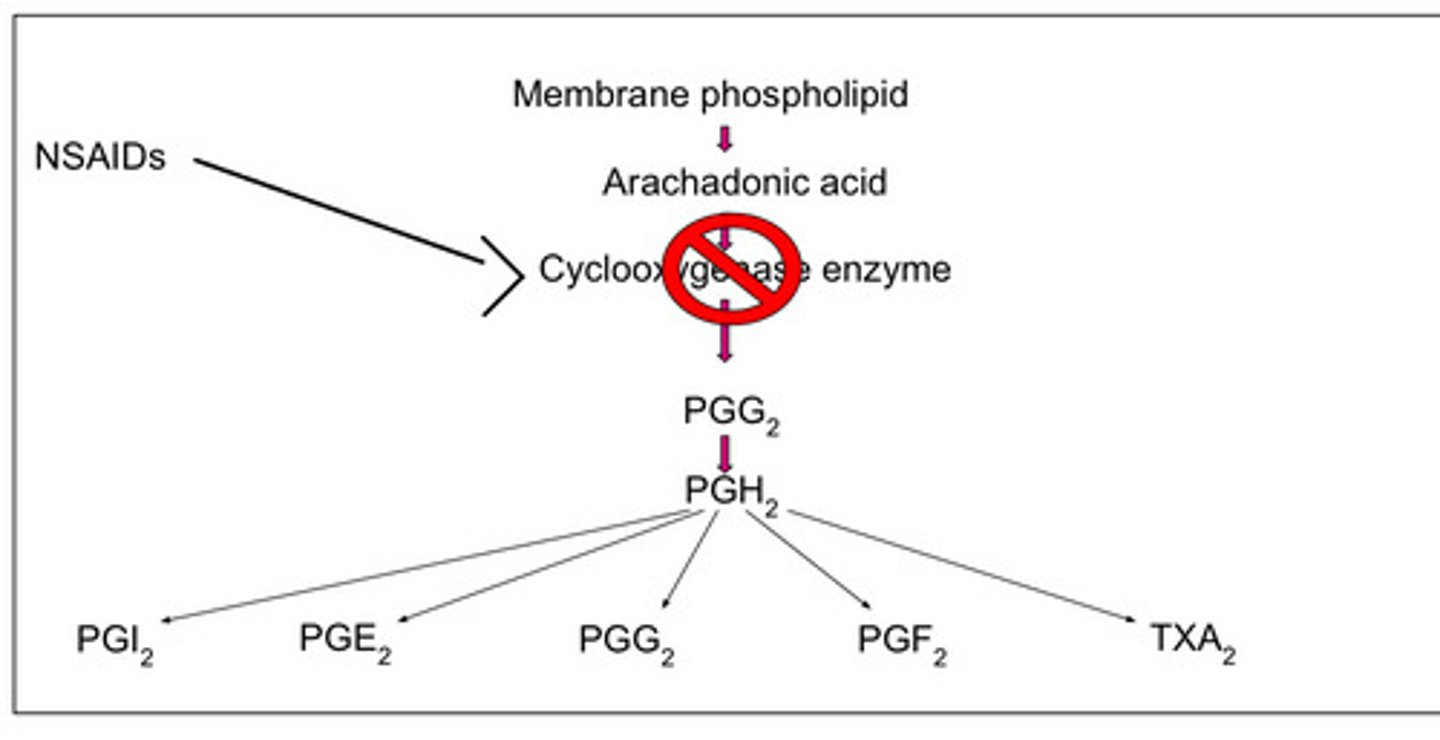
what do prostaglandins do
mediate inflammation, form protective layer in gut, transmit pain signal to brain, regulate internal temp
Which individual discovered that aspirin completely blocks prostaglandin production
Vane
which 3 individuals received Nobel prizes for their prostaglandin discoveries
Vane, Bergstrom, Samuelsson
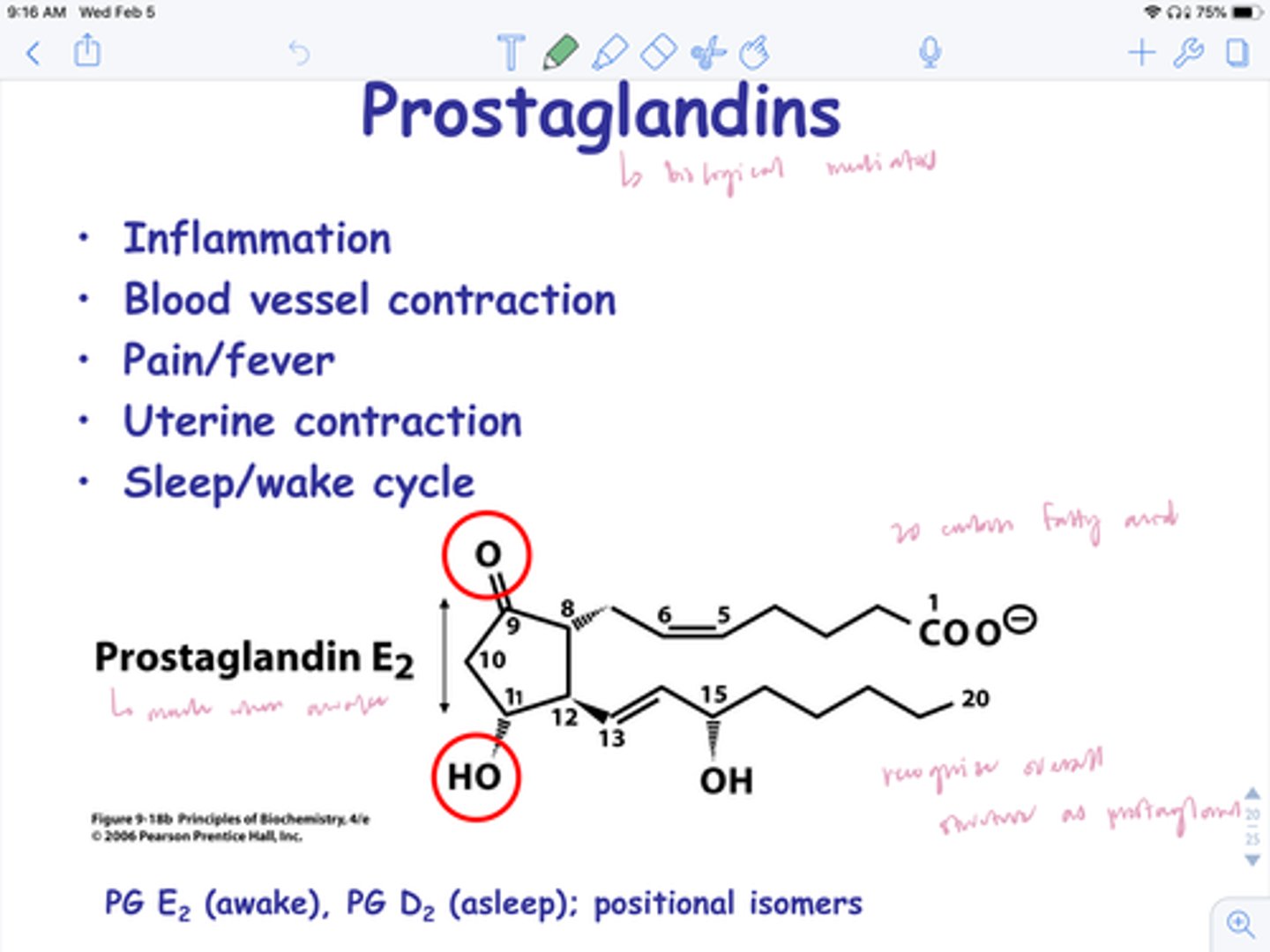
compare prostaglandins, prostacyclins, and thromboxanes
prostaglandins (PGE2): inflammation, fever, pain, GI mucous secretion
prostacyclins (PGI2): inhibits platelet aggregation, vasodilation
thromboxanes (TXA2): enhance platelet aggregation, vasoconstriction
t/f: PGE2 and TXA2 seem to have opposite biological effects regarding platelets
false. PGI2 and TXA2 do.
PGE2= prostaglandin
PGI2= prostacyclin (inhibit platelets/clots)
TXA2= thromboxane (enhance platelets/clots)
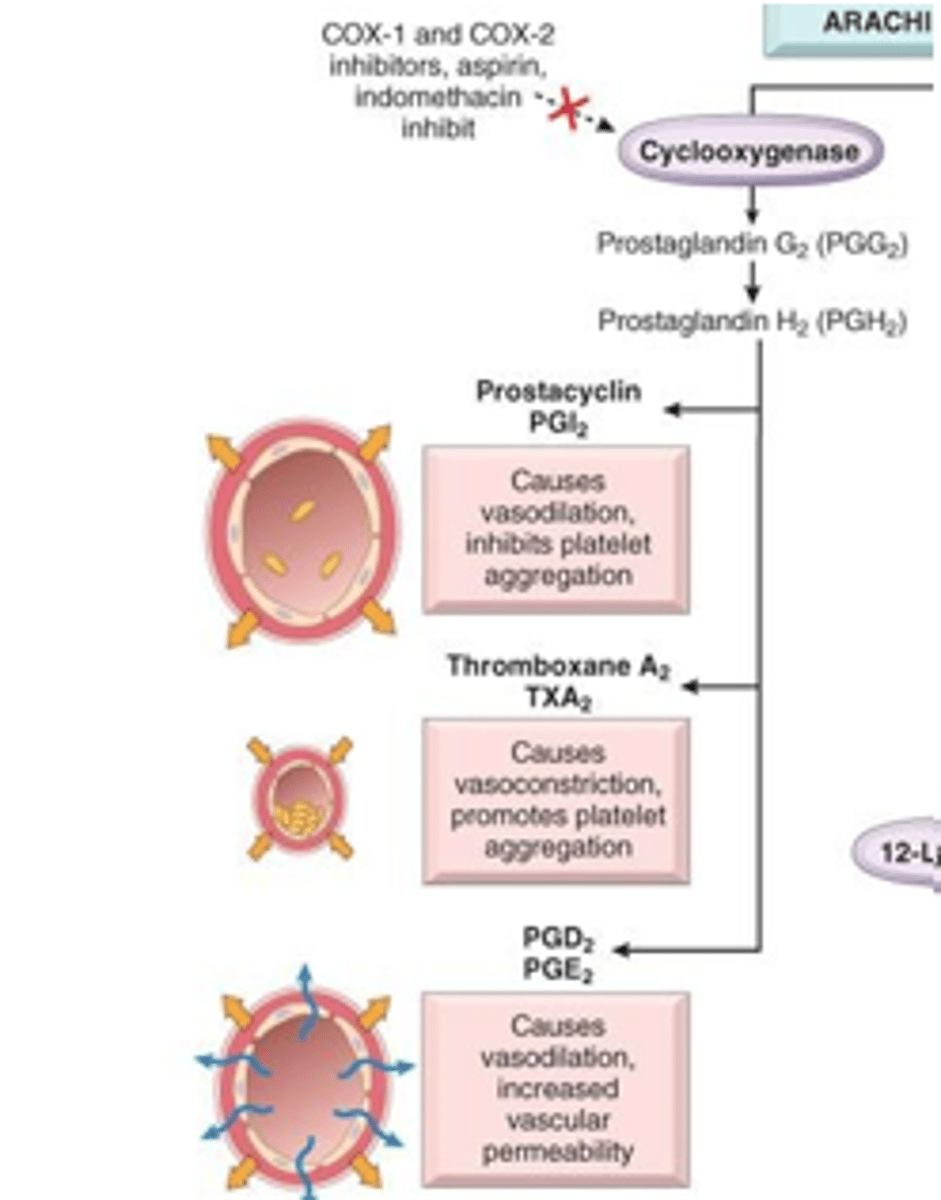
which enzyme is involved in biosynthesis of prostaglandins, prostacyclins, and thromboxanes
COX
the ________ enzyme is necessary to convert _________ into PGE2, PGI2, and TXA2
COX; arachidonic acid
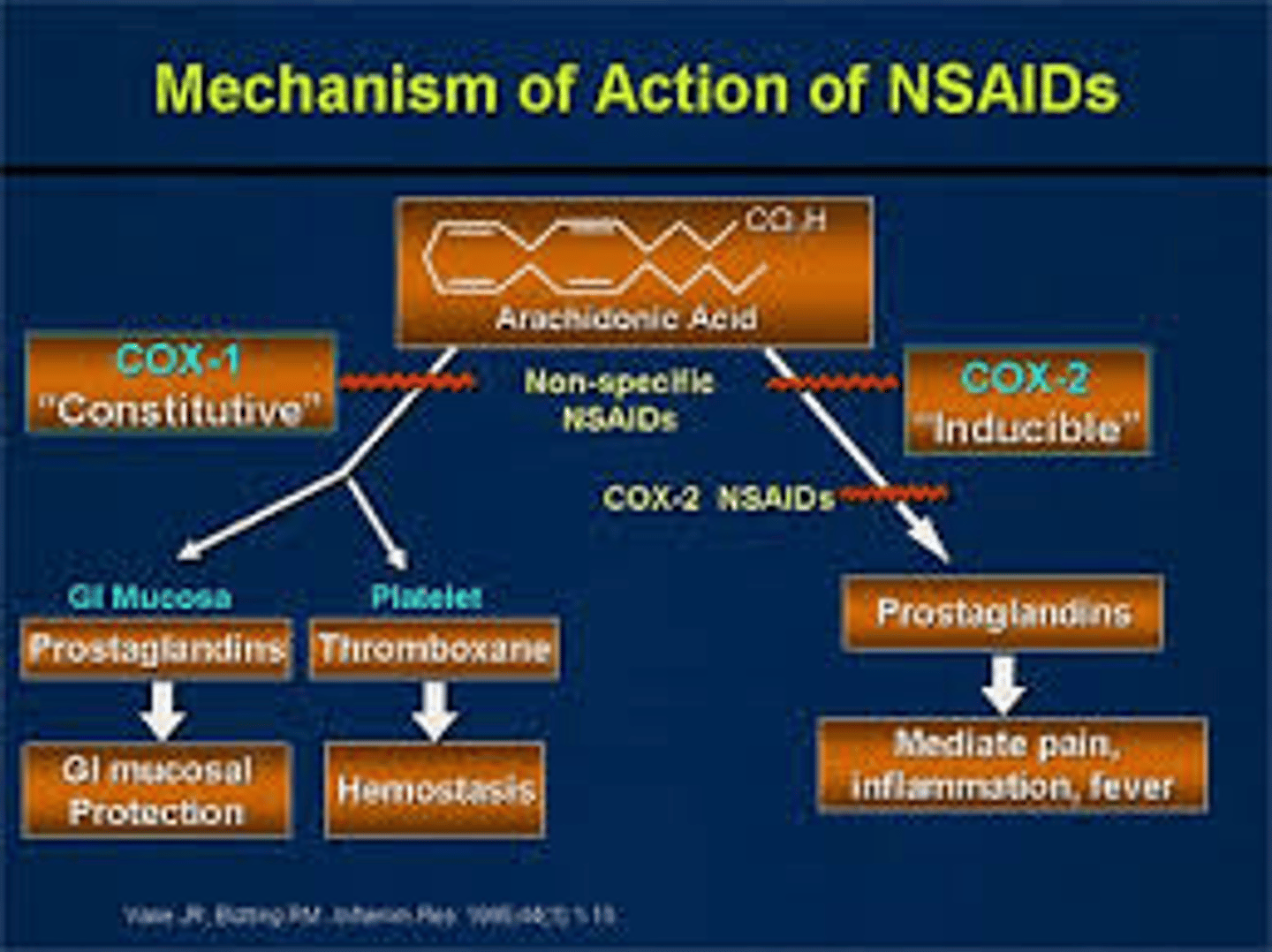
COX1 vs COX2
COX1: CONTINUOSULY expressed in gut, uterus, kidney, platelets
COX2: INDUCIBLE by cytokines, mitogens, and endotoxins; responsible for elevated production of prostaglandins during inflammation
which COX enzyme is continuously expressed and where
COX1- gut, uterus, kidney, platelets
which COX enzyme is inducible and when
COX2; inflammation (elevated prostaglandins)
NSAIDs general MOA
bind to COX active site, therefore blocking arachidonic acid
(can be nonselective or COX2 selective)
t/f: COX1 and COX2 are structurally similar and have the same binding pocket
false. similar, but different binding pockets
which COX enzyme is the intended target for NSAIDs
COX2
compare the COX1 and COX2 binding pockets
COX1: more restrictive to NSAIDs, steric hindrance
-cationic Arg120: binds to COOH of NSAID
-Ile 434 and Ile 523 interact w each other, making smaller binding site
COX2: less restrictive, celecoxib
- cationic Arg120: binds to COOH of NSAID
- Val 434 and Val 523 are smaller= less restrictive
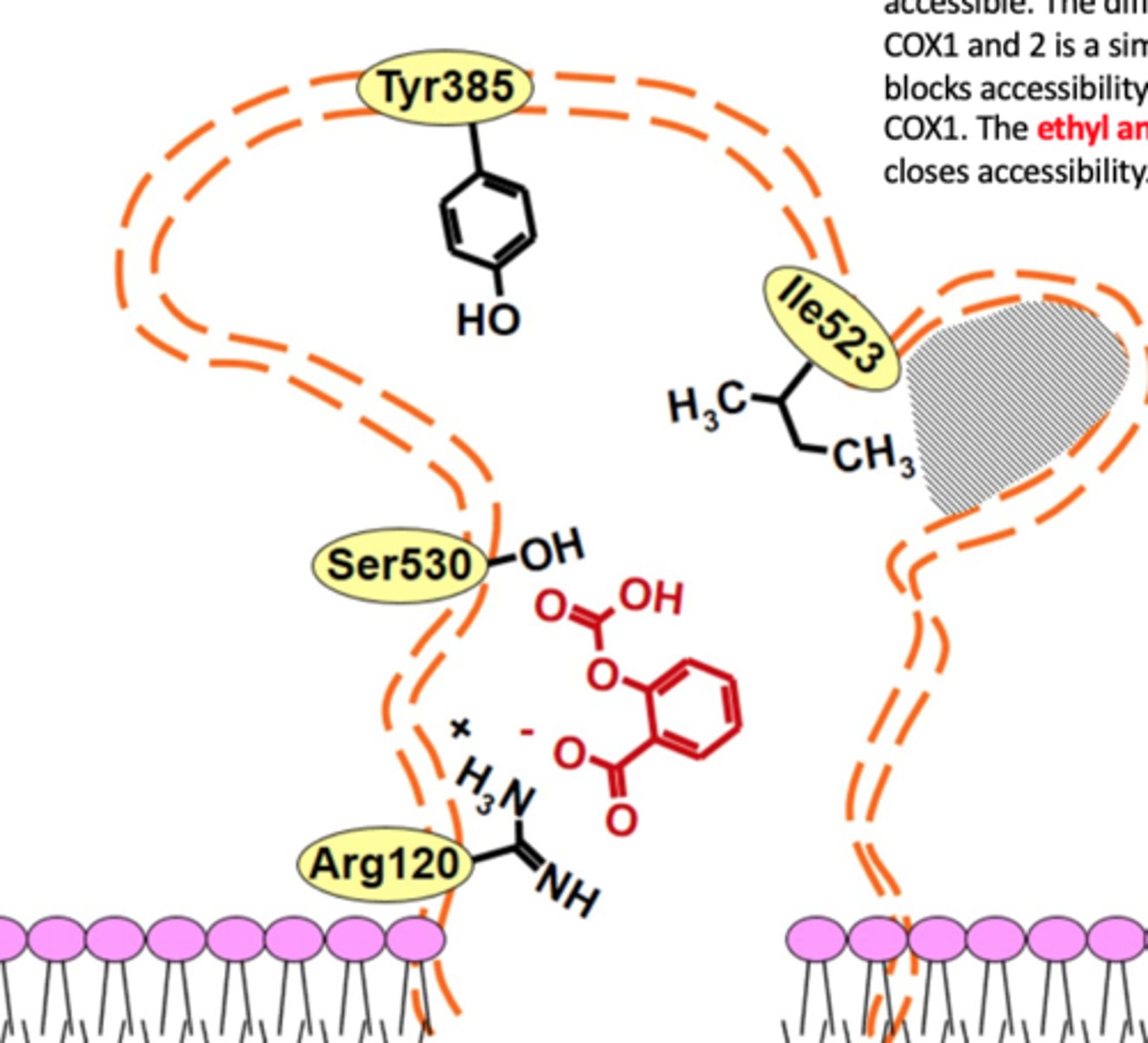
which amino acid do NSAIDs interact with in COX1 and COX2
Arg 120 (cationic)
Which amino acids make the COX1 enzyme more restrictive and which make COX2 less restrictive
COX1: bulky isoleucine (Ile 434 and 523)
COX2: smaller valine (Val 434 and 523)
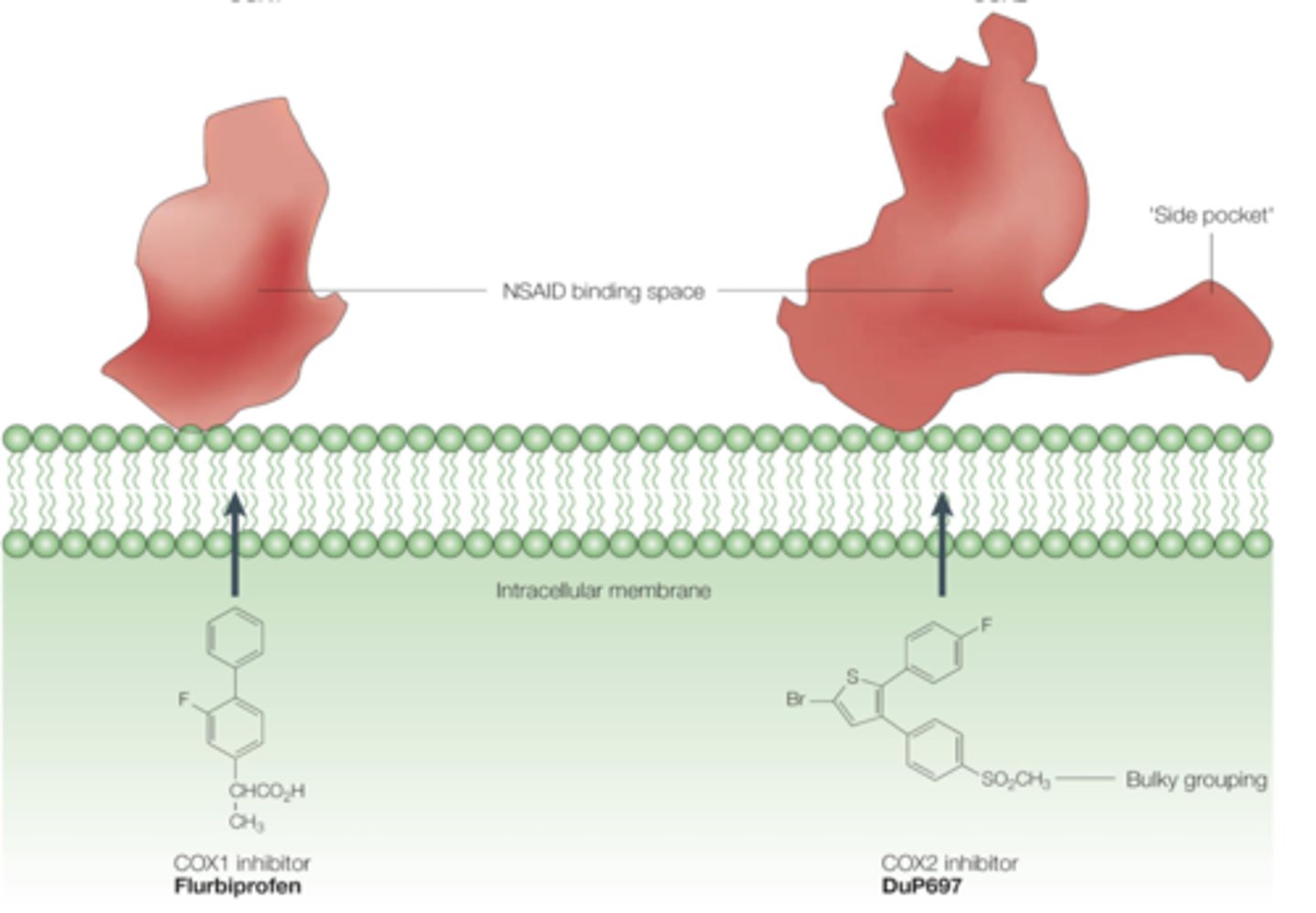
what prevented selective COX2 inhibitors from working
mutations of Val residue in COX2 back to Ile
The valine in COX2 enables access to a __________
side pocket (accommodates bulkier groups of COX2 selective inhibitors) [compare to COX1 that has bulkier Ile instead]
![<p>side pocket (accommodates bulkier groups of COX2 selective inhibitors) [compare to COX1 that has bulkier Ile instead]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6cf8fb33-2904-46b0-888f-0cca89ac3ff8.jpg)
general NSAID structure-activity relationship (SAR)
charge:
rings:
charge: anionic at pH 7.4 (to bind to Arg+)
rings: 2 aromatic rings mimic arachidonic acid double bond
- conjugated rings but assume NON-COPLANAR shape
t/f: structural features that force coplanarity block inactivating metabolism and increase lipophilicity, therefore increasing anti-inflammatory potency of drug
false. must force NON-coplanarity

substituting rings with stable functional groups increases _________ of drug
duration of action (ex: fluorine)
give an example of what non-planarity is in NSAIDs
the COOH and the aromatic ring are in different planes
(increase anti-inflammatory potency)
t/f: the majority of NSAIDs are selective for COX2 to reduce inflammation
false. majority is non-selective (except for celecoxib)
4 chemical classes of NSAIDs
1. salicylic acid derivatives
2. arylalkanoic acids
3. oxicams
4. selective COX2 inhibitors (celecoxib)
salicylic acids: inhibition of COX results in decreased levels of ___________
pro-aggregatory and vasoconstrictive thromboxanes (TXA2)
(so less TXA= less aggregation and constriction)
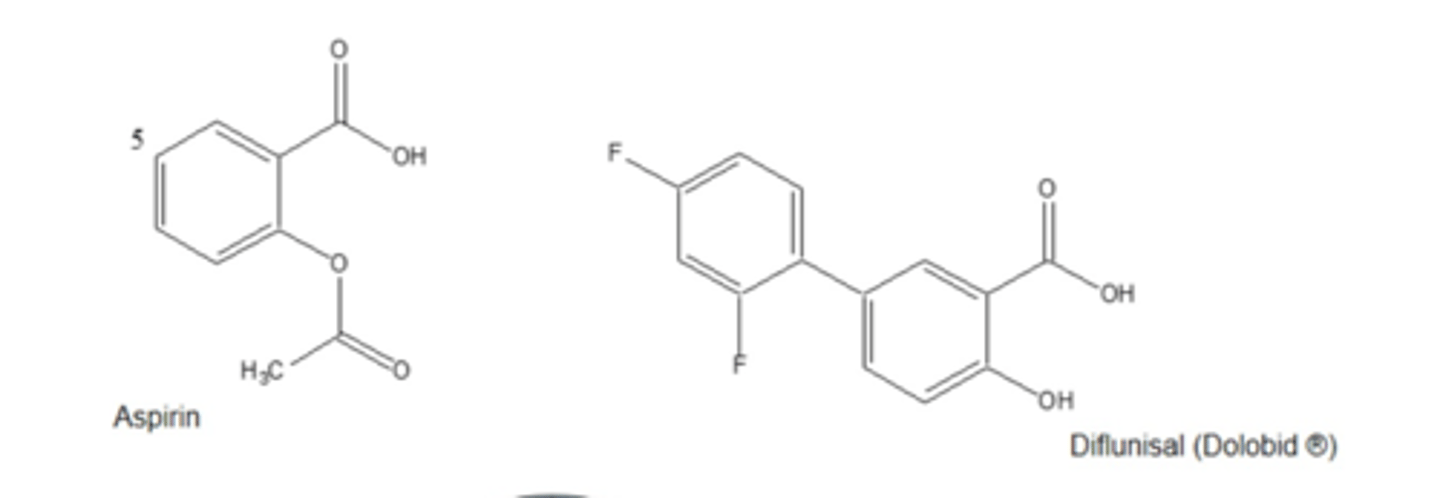
compare aspirin to diflunisal MOAs
both inhibit COX= less TXA2
aspirin: low dose IRREVERSIBLY inhibits COX1
high dose REVERSIBLY inhibits COX2
diflunisal: REVERSIBLE inhibitor of COX1/COX2
MOA of aspirin irreversible inhibition
1. COX1/2 enzyme has serine: OH= NU
2. aspirin has acetoxy (OCOCH3)= E
3. OH of serine attacks acetoxy= covalent bond
4. COX is now irreversible inhibited
aspirin SAR map
1. COOH group adjacent to acetoxy
2. aromatic ring= orients acetoxy
3. acetoxy= required for covalent interaction with Ser
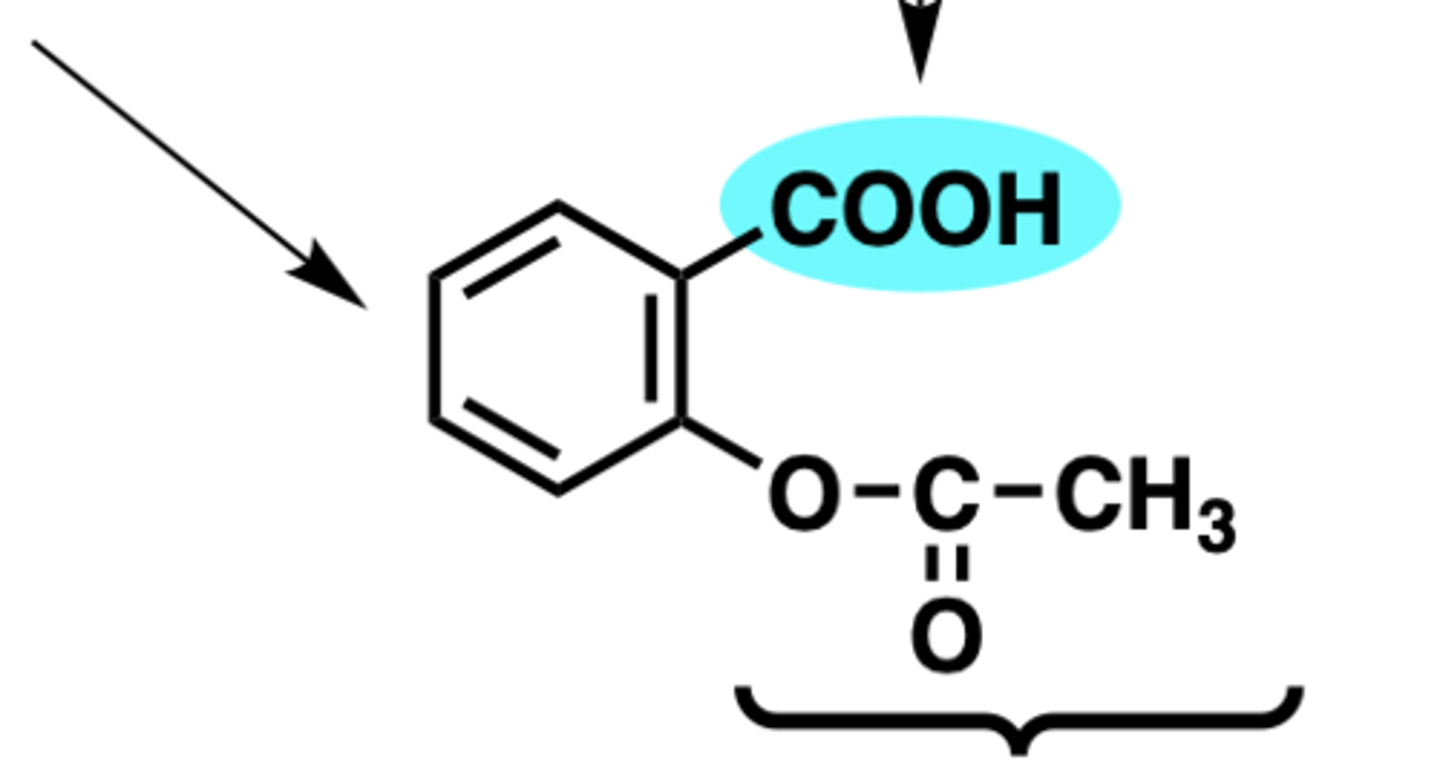
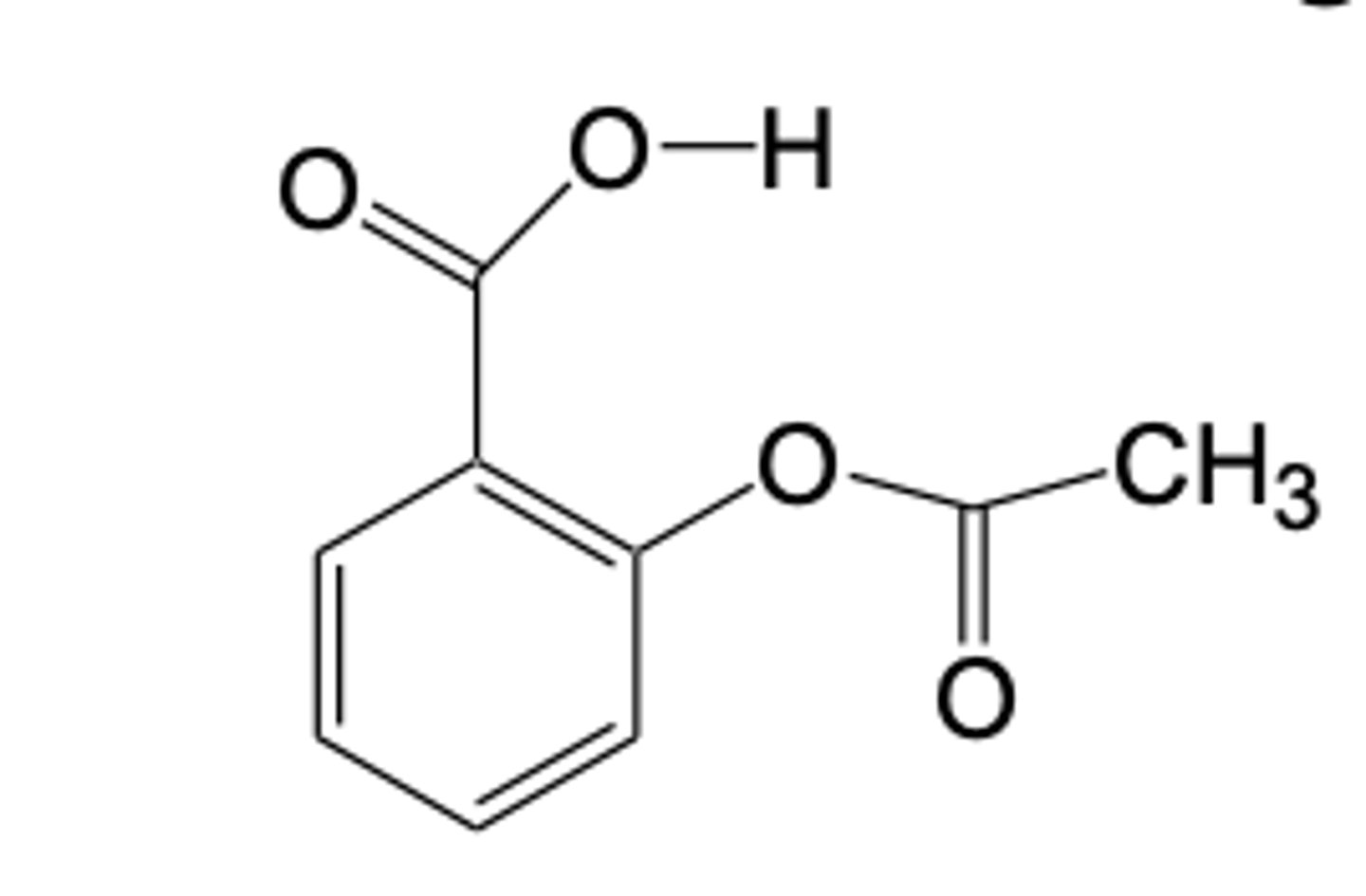
what is present in aspirin but not in diflunisal that allows aspirin to irreversibly inhibit COX
the acetoxy group= covalently bonds to Ser in COX
(diflunisal has COOH that reversibly interacts with Arg120)
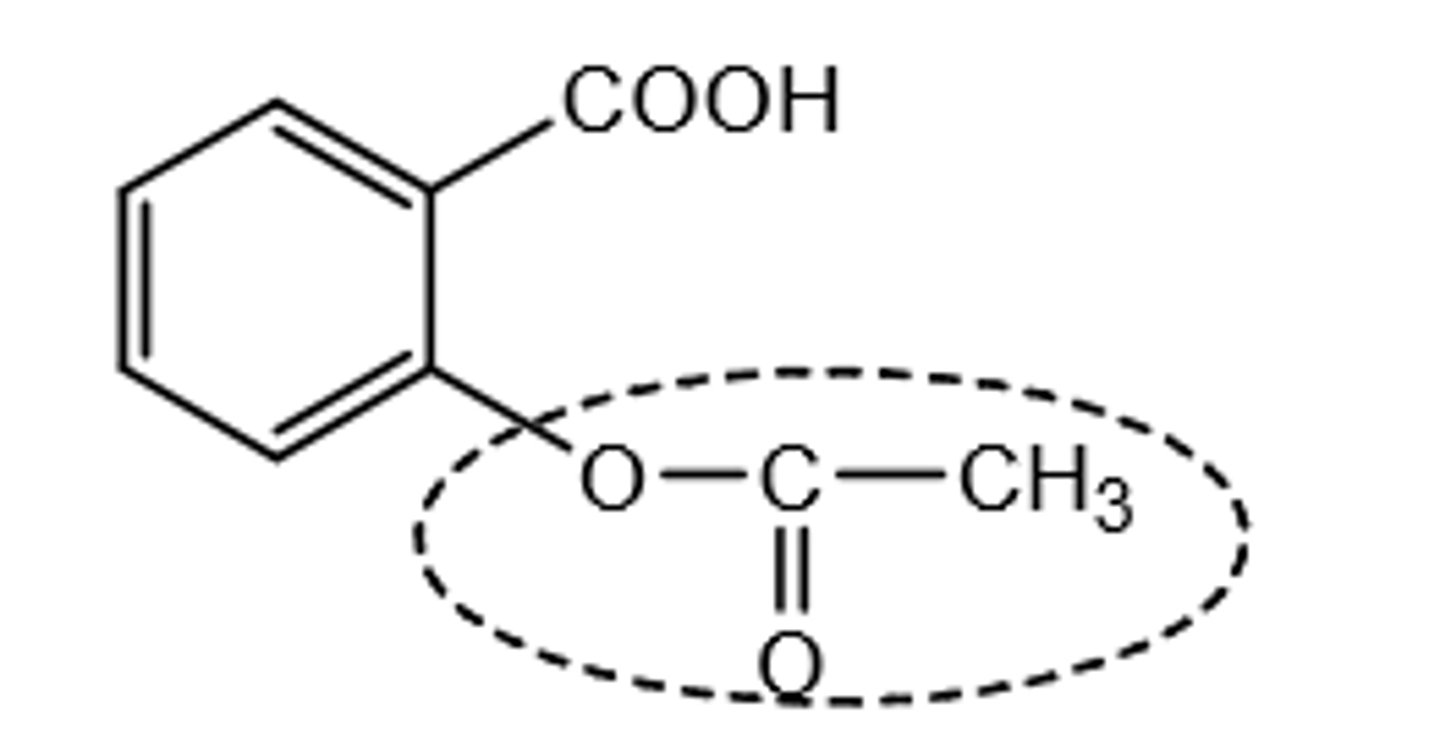
diflunisal SAR map
1. COOH group= reversible anchoring to Arg120
2. para-fluoro= prevents hydroxylation, increases duration
3. ortho-fluoro= promotes non-coplanarity of aromatic rings
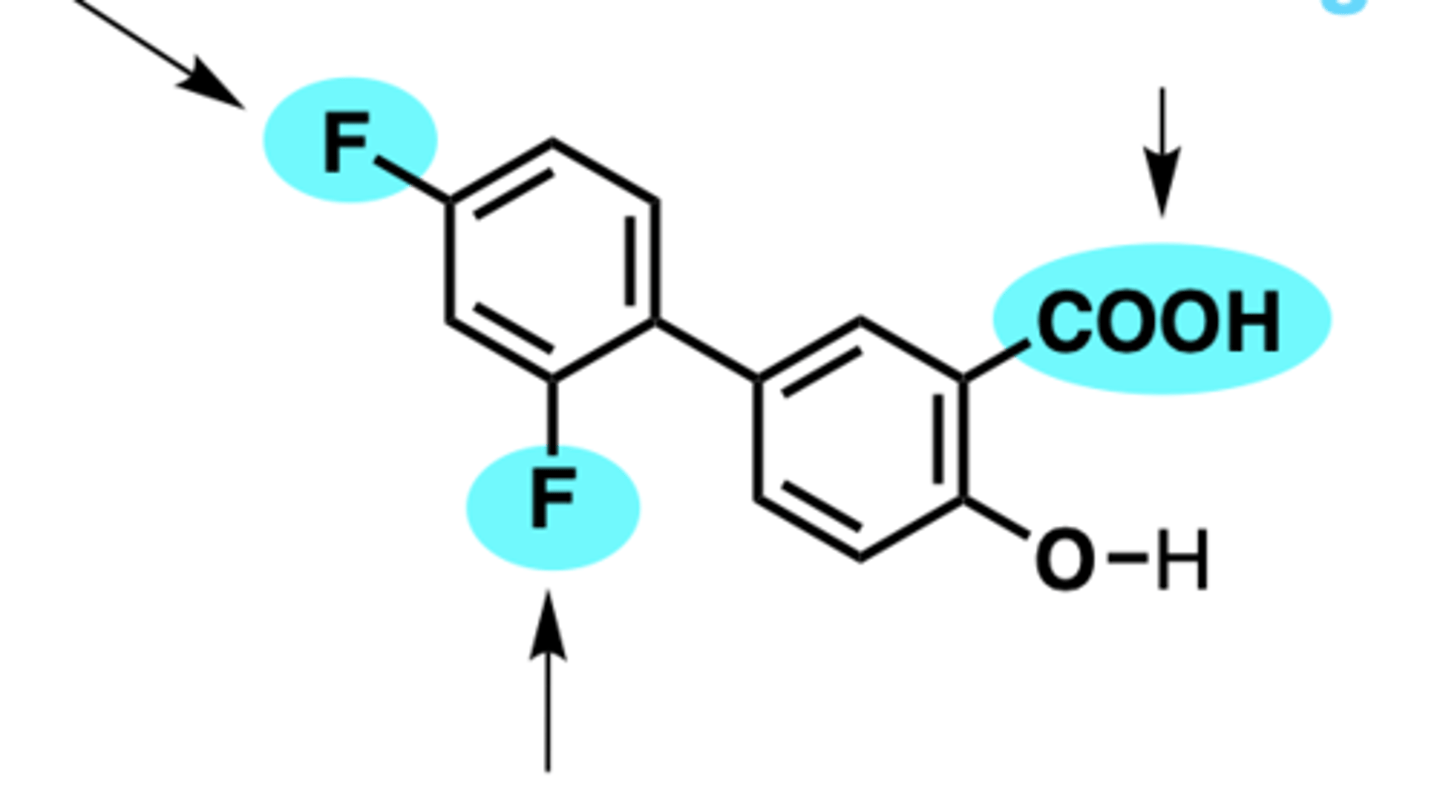
where is aspirin absorbed? pKa?
strongly acidic pKa= 3.5
-passively absorbed from the GI tract
effect of increasing gastric pH specifically around aspirin tablet on absorption
increasing pH around tablet= promotes dissolution-> later absorbed when pH lowers
= decreases GI distress
effect of increasing total gastric pH via PPIs on aspirin absorption
increasing total gastric pH= less gastric absorption bc increased ionization
t/f: the rate of aspirin absorption is dosage form dependant
true (faster if small particle size)
where is aspirin and diflunisal excreted? what form?
urine, glucuronide conjugate
how is aspirin metabolized
1. hydrolyzed in plasma before reaching COX
2. OH or COOH is conjugated with glucuronide (15% of urinary metabolism)
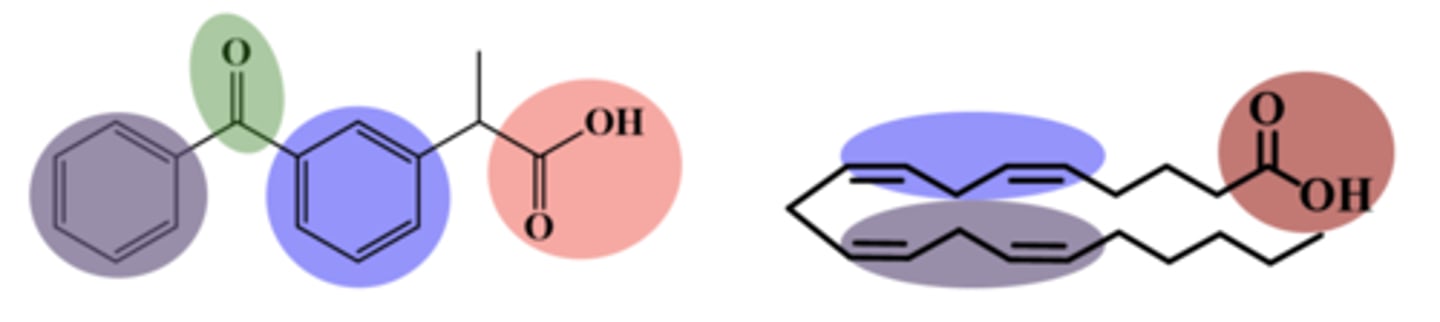
arylalkanoic acids general MOA
nonselective COX inhibitor
majority of marketed NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, belong to which class
arylalkanoic acids
arylalkanoic acid SAR
1. COOH one carbon away from ring= interacts with Arg
2. alpha carbon with or without groups
3. 2nd aromatic ring= forces non-coplanarity

purpose of the second aromatic ring in arylalkanoic acids
1. forces non-coplanarity
2. augments lipophilicity
3. inhibits inactivating CYP-mediated metabolism
IC50
concentration of inhibitor required to reduce enzyme activity by 50%
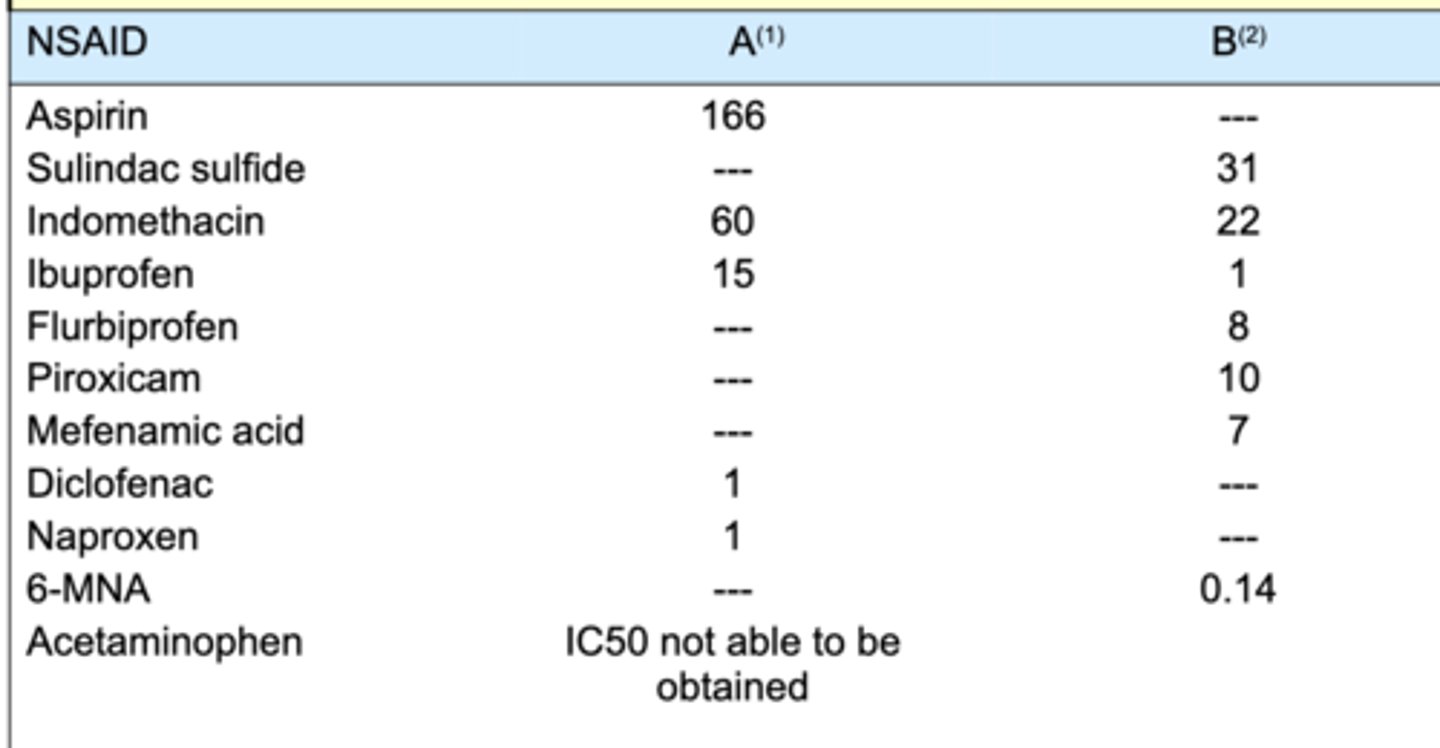
3 MOAs of diclofenac that make it so potent
1. inhibit COX (less prostaglandins and thromboxanes)
2. inhibits phospholipase A2 (inhibits arachidonic acid release)
3. inhibits lipoxygenase (less leukotrienes)
describe ibuprofen enantiomer activity
-S is more active than R
- administered as racemic mixture since R becomes S in vivo
t/f: all arylalkanoic acids are non-selective COX inhibitors
true (ex: diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen)
diclofenac metabolism
- extensive hepatic metabolism via CYP 3a4, 2c9= forms quinone imines
- rare but severe hepatoxicity bc quinones= electrophiles that may bind to tissue/DNA
t/f: ibuprofen undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism that induces a rare but severe hepatoxicity via quinone imines
false. that is diclofenac
ibuprofen metabolism
rapid inactivation via CYP2C9 and 2C19
- omega and omega-1 hydroxylation
t/f: ibuprofen has a relatively long duration of action
false. short bc of rapid inactivation via CYP2C9 and CYP2c19
indomethacin metabolism
major: CYP2C9 catalyzed O-dealkylation
minor: hydroxylation and glucoronidation
sulindac metabolism
PRODRUG!
-activated via reversible reduction sulfoxide-> active methylsulfide
- increases drug duration
which arylalkanoic acid is a prodrug with increased duration
sulindac
only class of nonselective NSAIDs that do NOT have COOH
oxicams (note celebrex also doesnt have cooh but it is selective)
oxicams general MOA
- anion is made though acidic enol proton loss
- anion is stabilized via resonance
NO COOH!
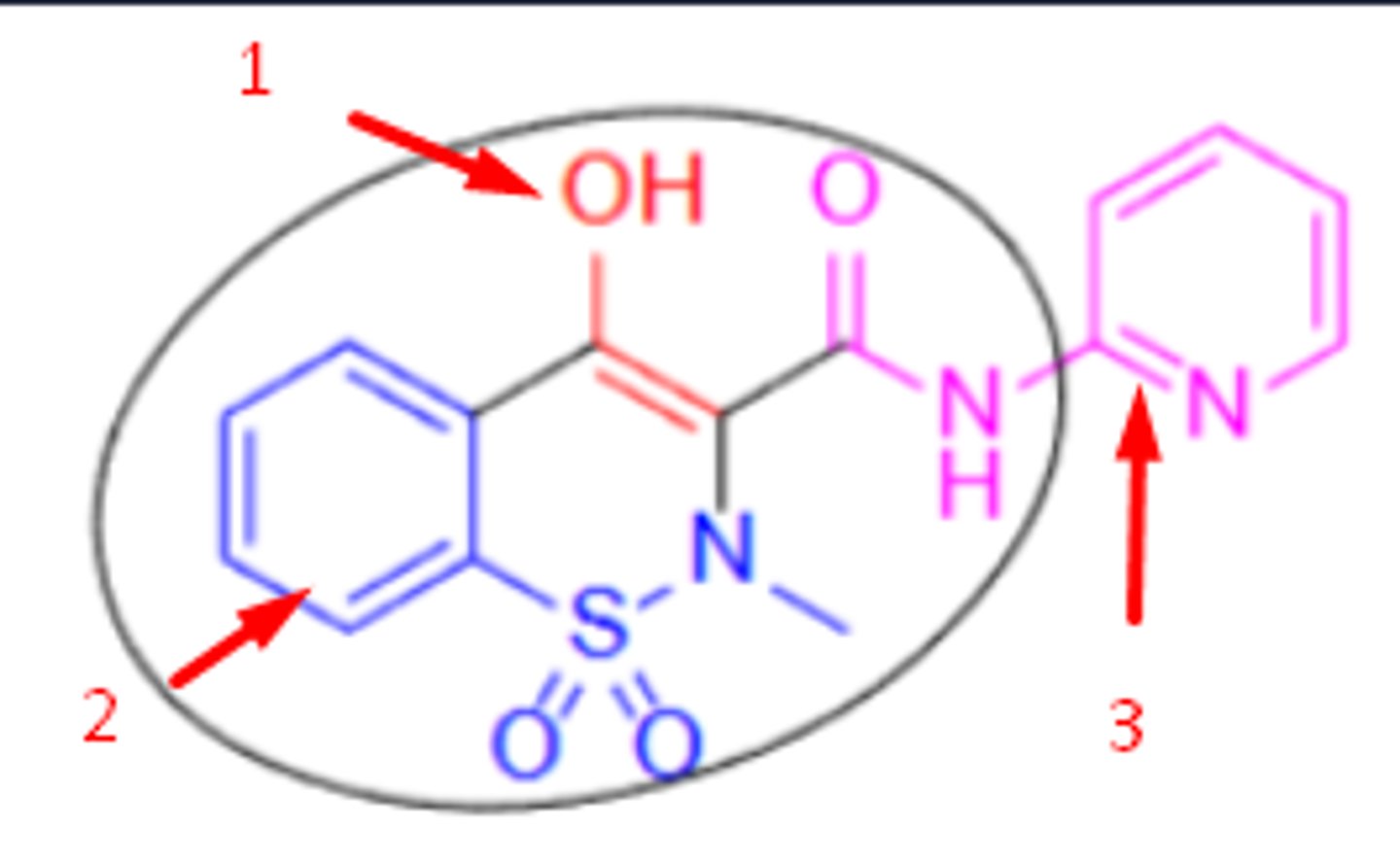
oxicams SAR
1. anion via deprotonation of enol= interacts with COX arg
2. non-coplanarity between 2 aryl rings
3. sulfoxide= influences COX1/COX2 preference
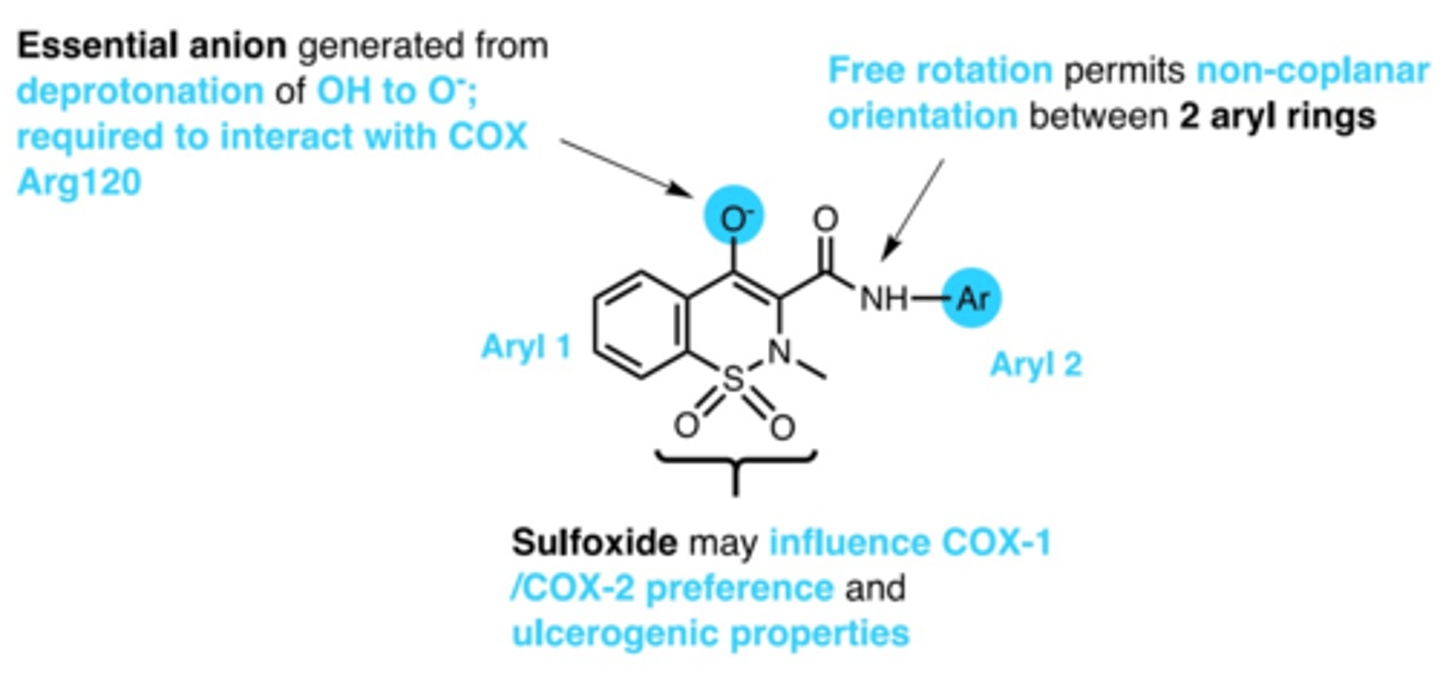
what extends the duration of action of oxicams
enterohepatic recycling (reabsorbed back into GI instead of secretion)
_____________ in inflamed tissue is the intended target of NSAIDs
COX2
COX2 inhibition in vessel wall causes
decrease in PG12-mediated vasorelaxation
= results in vasoconstriction/ strokes
which is the only COX2 selective inhibitor in US? which were withdrawn due to cardiovasc morbidity?
US= celecoxib
withdrawn= rofecoxib and valdecoxib
celebrex uses and side effects
use= arthritis, pain, familial adenomatous polyposis
side effects= vascular events, MIs, stroke, upper GI complications
which amino acid does celebrex bind to on COX2 enzymes
Arg153 (not Arg120)
celecoxib metabolism
CYP2C9; glucuronide conjugate
non-selective NSAIDs often have pKas of __________
3.5-4.5
t/f: all NSAIDs are orally active and bound to serum proteins
true
explain how inhibition of COX2 affects thrombotic cardiovascular events
COX1 = TxA2 formation (pro-aggregatory)
COX 2 =PGI2 in endothelial cells formation (vasodilator, anti-aggregatory)
if only COX2 is inhibited, there may be more pro-aggregatory= strokes/MI
3 things COX2 inhibition leads to
1. lower PGI2 (more aggregation)
2. lower nitric oxide
3. more leukotrienes (atherosclerosis, ischemic complications)
what could happen if heart-healthy patients take NSAIDs for prolonged periods of time
gradually increases risk of heart attacks and strokes by progressive artery hardening (more leukotrienes, less anti-aggregates)
NSAIDs black box warning
increased risk of adverse cardiovascular thrombotic events, including fatal MI and stroke
t/f: tylenol is an example of a non-selective NSAID
false. tylenol is NOT an NSAID, no anti-inflammation
tylenol MOA
unknown (analgesic/ antipyretic)
- both central and peripheral mechs
- augments endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligands
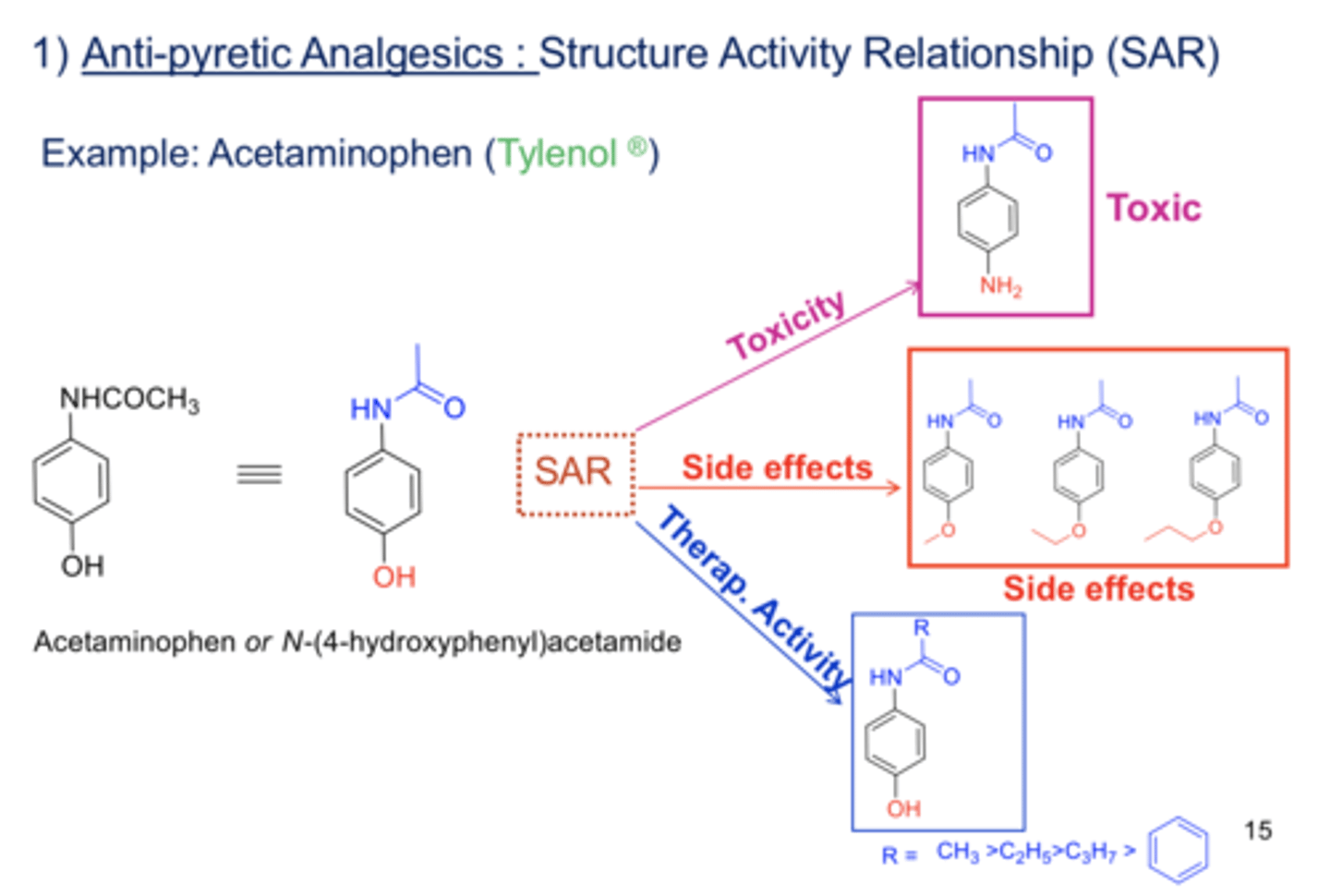
acetaminophen SAR
acetanilide
acetaminophen metabolism
via CYP2E1 and CYP3A4= forms NAPQI (N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine)= VERY ELECTROPHILIC/ toxic
-NAPQI is detoxified via glutathione
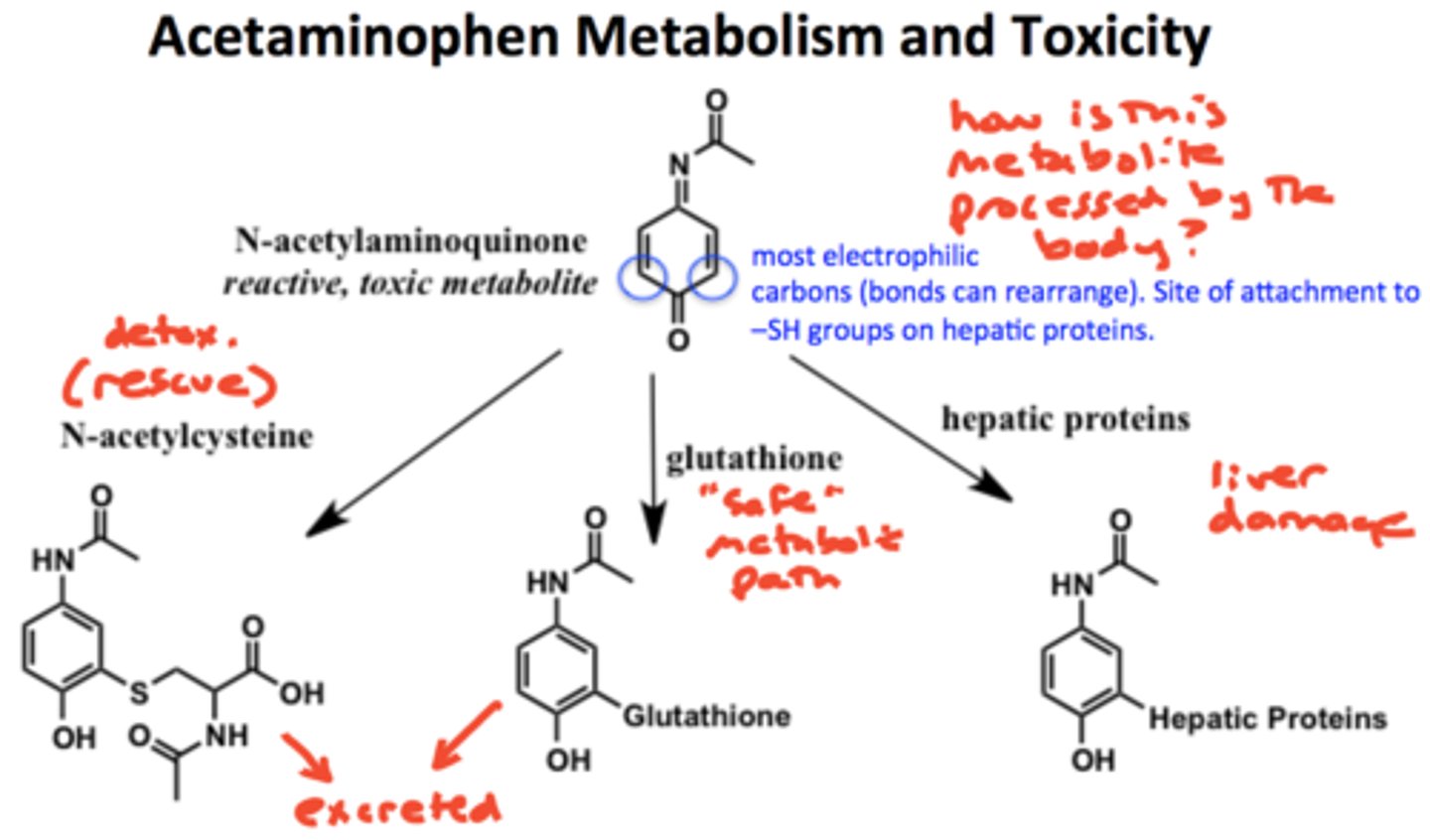
acetaminophen overdose. risk is increased by?
- overdose via toxic metabolite liver damage
- risk is increased by chronic alcohol abuse
acetaminophen max dose
650mg at once
(manufacturers: 325mg per dose)
dose/day: 2-4g