AP HUG Final
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
different ways to measure scale
global scale, regional scale, national scale, local scale
projection
the method used to represent the curved surface of the Earth on a flat map.
Mercator projection and limitations
shows the Earth with straight lines for latitude and longitude, making navigation easier but making landmasses near the poles look bigger than they really are.
limitations: sizes of places are distorted, especially near the top and bottom.
core and periphery countries
core countries: wealthy, developed nations with strong industries, technology, and economic power (USA, Japan)
periphery countries: poorer, less developed nations with weaker industries and economies (e.g., many countries in Africa, parts of Asia and Latin America).
concentration and density
concentration - the spread of people or things over a given area, how clustered or spread out they are.
density - the number of people or things per unit area (e.g., people per square mile).
different types of diffusion
expansion diffusion, contagious diffusion, hierarchical diffusion, relocation diffusion
expansion diffusion
Ideas or trends spread outward and grow bigger as they move to new places.
Example: A new song becoming popular worldwide.
contagious diffusion
Spread happens quickly and easily, like a disease passing from person to person.
hierarchical diffusion
Trends start in big or important places and then move to smaller places.
Example: Fashion trends starting in big cities and then reaching small towns.
relocation diffusion
People move to new places and bring their ideas, culture, or traditions with them.
Example: A family bringing their language or religion to a new country.
distance decay
The idea that as the distance between two places increases, the connection or interaction between them decreases.
space-time compression
The idea that advancements in technology (like cars, airplanes, the internet) make it easier and faster to travel and communicate, so places feel closer together even if they are far apart.
physiological vs. arithmetic vs agricultural density
Physiological Density: Number of people per unit of arable (farmable) land.
Arithmetic Density: Total number of people divided by the total land area.
Agricultural Density: Number of farmers per unit of arable land.
doubling time
The amount of time it takes for a population to double in size.
impact of development on birth and death rates
Development usually leads to slower population growth because fewer babies are born, and fewer people die.
health issues at different levels of development
Developed countries generally experience higher life expectancies, lower infant and maternal mortality rates, and better access to healthcare, while developing nations often face challenges like malnutrition, infectious diseases, and limited access to medical services.
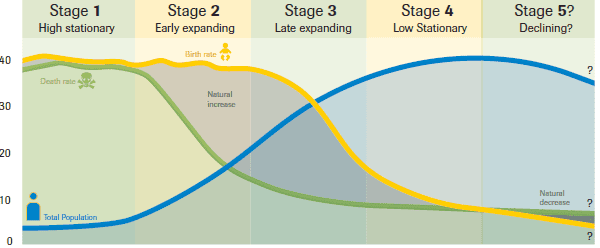
demographic transition model
a tool demographers use to categorize countries' population growth rates and economic structures. The model analyzes birth rates, death rates, and total population trends in a society at a given point of time.
immigration vs. emigration
Emigrate means to leave one's country to live in another. Immigrate is to come into another country to live permanently.
demographic groups most likely to migrate
Young adults, particularly those between 18 and 34.
brain drain
the emigration of highly skilled and educated individuals from a country, often to developed nations, seeking better opportunities, living conditions, or political stability.
pop culture vs folk culture
folk culture refers to traditional customs and beliefs of small, homogeneous groups in isolated areas, while popular culture is found in large, heterogeneous societies and is widely diffused through mass media.
culture and globalization
culture is what a group of people do and believe, and globalization is how the world becomes more connected and similar through trade, communication, and travel.
diffusion of pop culture
how entertainment, fashion, and trends spread quickly across the globe, mainly due to modern communication and transportation.
food taboos
are restrictions on eating certain foods that are often based on cultural, religious, or social beliefs.
culture landscape
is the visible human-made environment that reflects a culture's way of life, such as buildings, roads, and farms.
territory
defined area of land that belongs to a person, group, or country.
folk clothing and popular culture
Pop culture influences folk clothing by introducing new styles and trends, which can modernize or sometimes replace traditional outfits.
ethnic cleansing
is when a group tries to remove or eliminate another ethnic group from a certain area through violence or forced removal.
apartheid in South Africa
a system of racial segregation where the government separated people by race and kept non-white people, especially Black South Africans, under control and limited their rights from 1948 to the early 1990s.
centripetal vs. centrifugal forces
Centripetal forces are factors that unite people or regions together, while centrifugal forces are factors that pull people or regions apart.
characteristics of the shapes of the states
Compact: Round or square-shaped, easy to manage (e.g., Poland).
Prorupted: Have a long extension or projection (e.g., Thailand).
Elongated: Long and narrow (e.g., Chile).
Fragmented: Several disconnected parts (e.g., Indonesia).
Perforated: Surrounded by or perforated by another state (e.g., South Africa).
federal vs. unitary governments
Federal government shares power between a central government and smaller regions, while unitary government has most of the power in a single central government.
European union’s purpose
unite European countries by promoting economic cooperation, free trade, and peace among member nations.
landlocked states
are countries that do not have a coast or access to the ocean.
imported food from overseas
is when a country buys and brings in food products from other countries to sell and eat.
types of subsistence agriculture
Shifting Cultivation: Farming on small plots, then moving to new areas when soil gets tired.
Pastoral Nomadism: Moving with animals to find new pastures.
Intensive Subsistence: Farming large amounts of food on small land, using lots of labor.
Mixed Crop and Livestock: Growing crops and raising animals together on the same farm.
type of commercial agriculture
Crop farming: Growing crops like wheat, corn, and rice to sell.
Dairy farming: Raising cows for milk and dairy products.
Livestock ranching: Raising animals like cattle and sheep for meat and wool.
Plantation farming: Large farms in tropical areas growing crops like coffee, sugar, or tea for export.
assumptions of the Von Thunen Model
The land is flat and uniform in all directions.
There is one central city or market.
Land use is based only on transportation costs.
Farmers aim to maximize profit.
No other factors like climate or soil type affect land use.
Three dominan grais
Wheat
Rice
Maize (corn)
types of employment sectors
Primary sector: Involves gathering natural resources like farming, fishing, and mining.
Secondary sector: Involves making products in factories, like manufacturing and construction.
Tertiary sector: Involves services like teaching, healthcare, and retail.
maquiladoras
are factories in Mexico near the border that assemble goods, often using imported materials from other countries, mainly for export to the U.S. and other markets.
break of bulk points
are locations where goods are transferred from one mode of transportation to another, like from ships to trucks or trains.
human development index
is a number that shows how well a country is doing in terms of health, education, and income.
agglomeration
is when people, businesses, or industries gather close together in one area.
purchasing power parity
is a way to compare the value of money between countries, showing how much goods and services one unit of currency can buy in different places.
vertical integration
is when a company controls different stages of production, from raw materials to finished products, all within one company.
situation factors relating to industry
Proximity to markets: Being close to customers to sell products easily.
Access to resources: Nearness to raw materials needed for production.
Transportation: Easy access to roads, ports, or railways to move goods.
Labor supply: Close to workers or skilled labor pools.
site factors relating to industry
Land cost and availability: Affordable and suitable land for building factories.
Climate and environment: Favorable weather conditions for production.
Water supply: Reliable access to water needed for industrial processes.
Topography: Flat land that makes construction easier.
Natural resources: Presence of raw materials nearby.
transportation method for industries
road, rail, sea, and air
free trade zones in north America and Europe
are designated areas where goods can be imported, processed, and exported with reduced customs restrictions to promote trade and economic activity.