Computer science feedback flashcards
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1-64 unit 1.1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
what is meant by a clock speed of 3.6 GHz?
Carries out 3.6 billion instructions per second
Which of the following tasks is the ALU not responsible for ?
Storing the results of a calculation
Which of the following is NOT a component of the CPU ? (1)
RAM (1)
Cache memory is part of the CPU.
What does cache memory enable the CPU to do ?
Store data to be transferred bac to RAM
Where does the CPU fetch instructions from?
RAM - Instructions to be executed are stored in RAM
Out of the following CPUs, which can carry out the most instructions per second ?
3 GHz quad core CPU
What is the fetch-decode-execute cycle?
the process that the CPU uses to carry out instructions
Where in the FDE cycle is an instruction converted into a format the CPU can use ?
Decode
During program execution, the CPU checks the address in the program Counter.
What is the address that is stored ?
Address in RAM of the next instruction
The CPU is made up of a number of different components, including registers.
What are registers ?
small, high-speed storage locations within the CPU temporarily hold data and instructions for processing.
In the Von Neumann architecture of a computer system, which of the following components is used for storing data and instructions ?
RAM
In a computer system, which of the following is an example of a primary storage device ?
RAM
what is primary storage
the component of the computer that holds data, programs and instructions that are currently in use.
list the types of primary storage
ROM, RAM, flash memory, cache memory
how does a program counter work?
Holds the address of the next instruction to be processed. Passes the address to the MAR
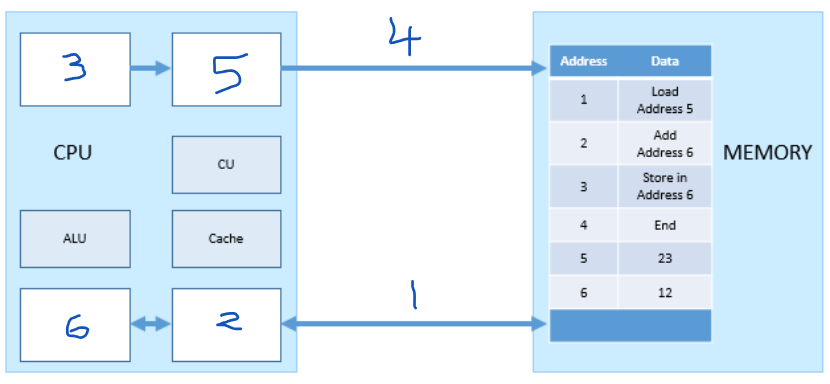
Which number represents the MAR?
5
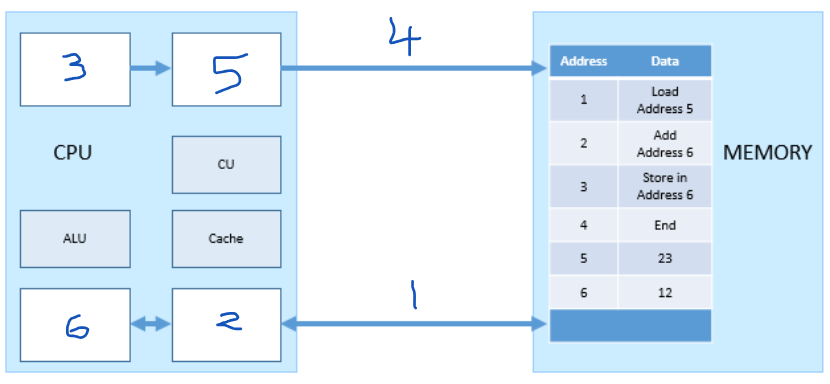
Which number represents the PC (program counter)?
3
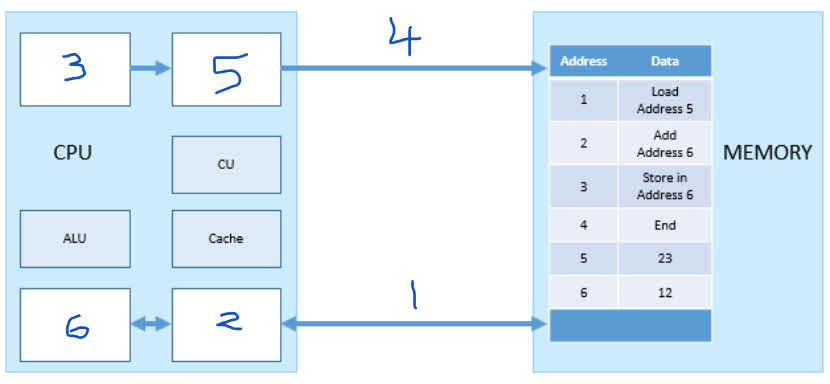
Which number represents the MDR?
2
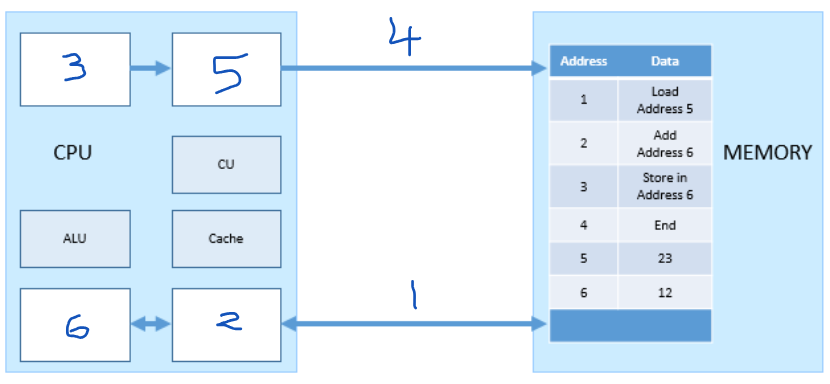
Which number represents the ACC?
6
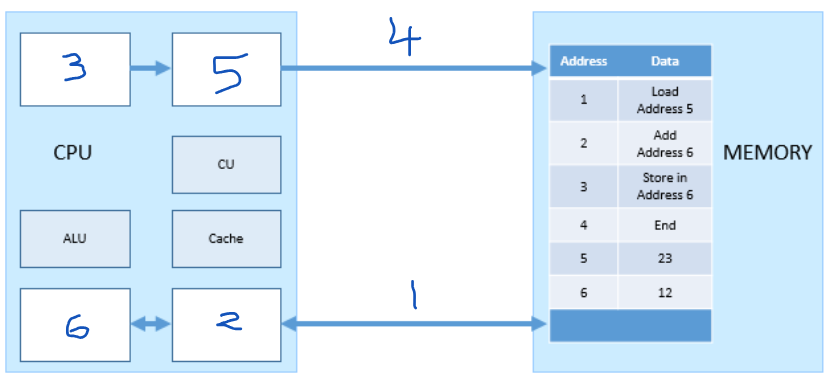
Which number represents the address bus?
4
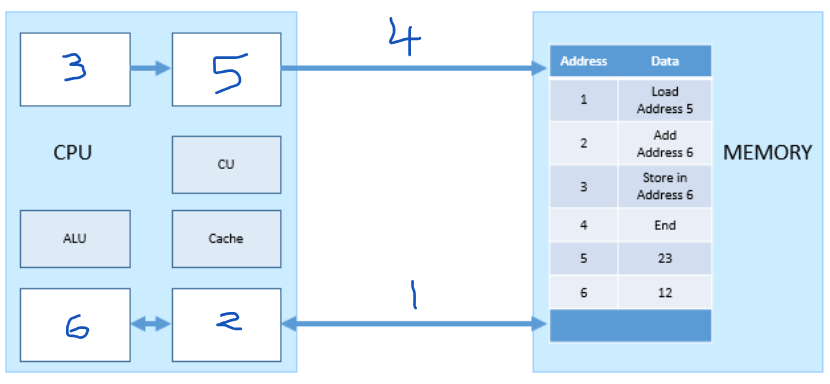
which number represents the data bus?
1
What is the purpose of the address bus?
Transfers the address to read/write data to/from from MAR to memory
what is the purpose of the data bus?
transfers data between the main memory and the MDR
What is the purpose of the PC (program counter)?
holds the address of the next instruction to be fetched from memory
what is the purpose of the ACC?
holds/stores the results of calculations made by the ALU
What is the purpose of the MAR?
Holds the address to read/write data to/from
What is the purpose of the MDR?
holds the data that has been read from memory or is about to be written to memory
What is the CPU?
The CPU is an internal piece of hardware that is responsible for executing/processing the instructions of programs
What happens during the fetch part of the FDE cycle?
The CPU gets the next instructions to be processed from main memory
What happens during the “decode” part of the FDE cycle?
The CPU examines the instruction that has been fetched and works out what action needs to be taken e.g. adding, subtracting, storing or loading
What happens during the execute part of the FDE cycle?
The CPU actually carries out the instruction e.g. it loads the data, it stores the data etc
List the components of a Von Newman Architecture
A Processor/ CPU, a memory unit, connections for input devices, connections for output devices
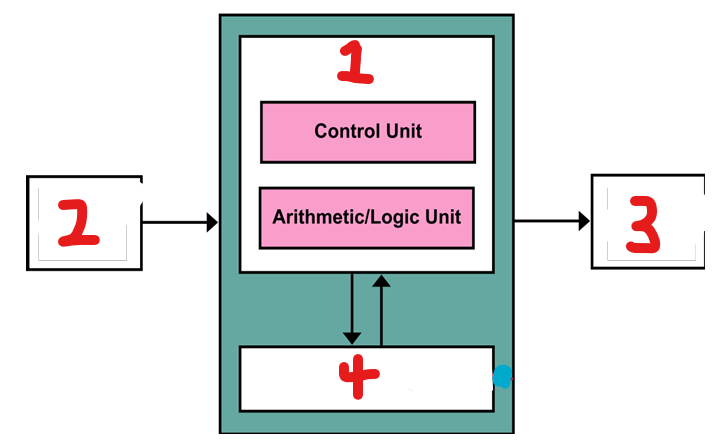
What component of the CPU is represented by number 1?
Processor
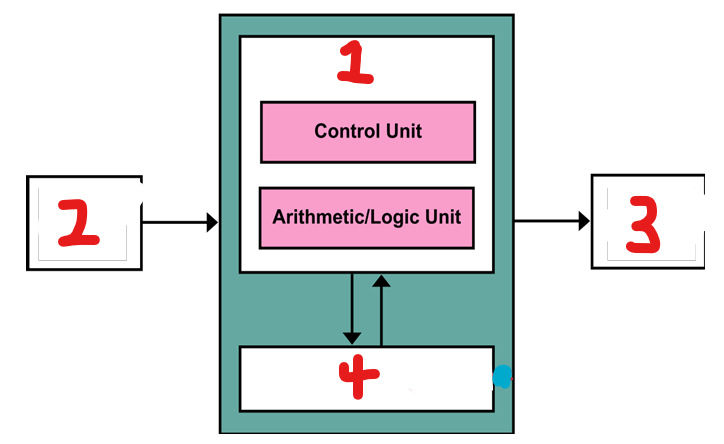
What component of the CPU is represented by number 2?
input
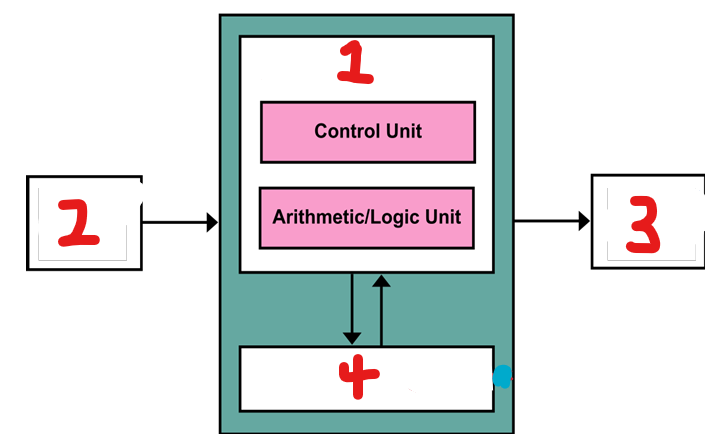
What component of the CPU is represented by number 3?
output
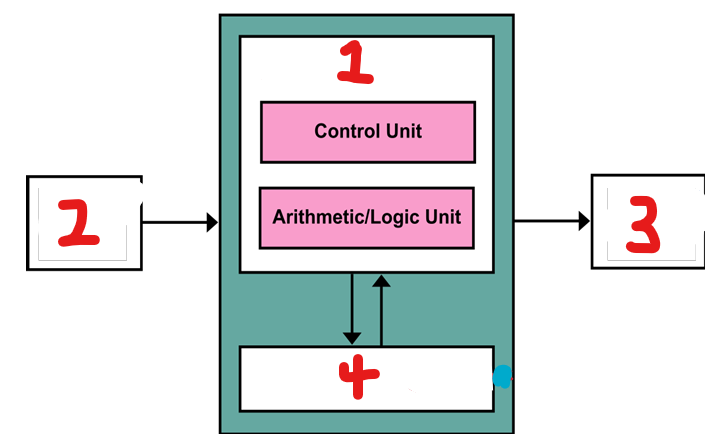
What component of the CPU is represented by number 4?
storage (cache)
how many memory units does the Von Newman architecture have?
The Von Neumann architecture has 2 memory units - one for instructions and one for data
What are registers?
Registers are locations of computer memory on the CPU that provide extremely fast access and store data temporarily
How do you think the clock speed of a CPU would affect the performance of a computer
it would determine how many FDE cycles can be completed by the CPU in a second, and therefore how fast the computer can run without overheating- a higher clock speed means the computer can run faster without overheating
How many fetch decode execute cycles can a single core CPU execute at one time?
3 billion
What are the key factors that govern the performance of the CPU in a computer?
lots of cache means lots of data can be transferred quicker to the processor;
Higher clock speed means more processes are executed per second;
Having more cores increases the clock speed since more cycles are being processed at once because there are more cores processing at the same time
according to the Von Neumann model, what are stored in memory?
data and instructions
explain what happens in the 'fetch' section of the Fetch Decode Execute cycle
The instruction and data required are fetched from RAM
what is the purpose of a ‘bus” in Von Neumann architecture?
to transfer instructions and data between the CPU and main memory
Which component acts as an intermediary between the processor and the main memory during the FDE cycle
Cache
state two advantages of using Von Neumann architecture
simplifies the design of the CPU
data and instructions are stored in the same area of memory so less components are required
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of more cores in a CPU ?
Processing data independantly
The CPU's first step is to fetch the next instruction to be executed.
The CPU will copy the memory address from where ?
The Program Counter (PC)
What is the role of the MAR register in the Von Neumann architecture?
Holds any of the memory addresses that are about to be used by the CPU
Which statement is a possible action during the 'execute' stage of the FDE cycle ?
The instruction stored in the MDR is decoded
What is the Control Unit (CU)?
a component of the CPU that synchronises data flow around the CPU
What is the Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)?
a component of the CPU that performs mathematical and logical operations
list the registers on a CPU
Program counter, MAR, Address bus, data bus, MDR, ACC
identify parts of a computer that could improve the performance of a computer
Clock speed, cache size, number of cores, RAM, SSD, HDD, graphics card
explain one reason why the cache size affects the performance of the CPU
data is transferred faster which makes the CPU more efficient
List the events that take place in the Fetch Decode Execute cycle
the address of the next instruction to be fetched from memory is sent from the PC to the MAR;
the PC increments by 1;
an instruction is fetched from memory and placed on the data bus and is carried to the processor and stored in the MDR;
the instruction is then decoded;
The decoded instruction is then executed so that the CPU performs continuously;
The process is repeated
what is an embedded system?
a computer system that is built into another device and has been created for one specific purpose.
list devices that contain embedded systems
dishwasher, MP3 player, washing machine, manufacturing equipment
list the characteristics of embedded systems
task specific
the task is performed in a certain time frame
do the same thing repeatedly
may respond to sensors
list the purposes/ advantages of embedded systems
to provide a specific, pre-defined function
cheaper than providing a full personal computer system
can be much smaller than a personal computer system
allows for a device to be automated/programmed
How does the number of cores affect the CPU’s performance?
More cores allow more instructions carried out simultaneously, and allow the processor to process more instructions at the same time. This allows batches of instructions to be executed more quickly, which allows for more programs to be run at the same time.
How does the clock speed affect the performance of the CPU?
A faster clock speed means more instructions carried out per second and so instructions are executed more quickly. This allows for more programs to be run at the same time. This also allows for more complex processing operations to be completed in real time.
What is level 1 (L1) Cache?
cache that is part of the CPU itself and is both the smallest and the fastest to access
What are L2 and L3 caches?
Extra caches built between the CPU and the RAM. L2 and L3 caches take slightly longer to access than L1.
what is volatile memory
memory where the data is lost when the power is switched off
what is non volatile memory
memory where the data remains when the power is switched off
list examples of volatile memory
RAM, cache
list examples of non-volatile memory
hard drive, ROM
what is the role of the hard drive?
a component of the main memory that holds the data not in use and when the computer is switched off; permanent storage
what is the role of cache
holds frequently used instructions, quicker to access than RAM
what is the role of RAM
holds data currently in use e.g. when a file is opened, this is moved from the HDD to RAM
what is the role of the CPU
this performs Fetch, Decode, Execute cycles to run programs on a computer
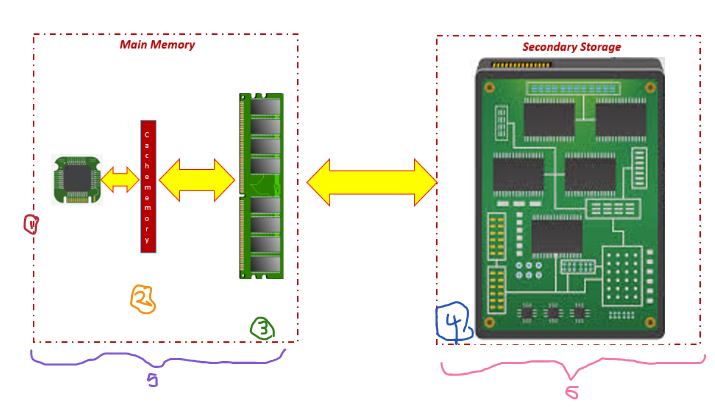
label the numbers on this diagram of parts of the main memory
1: CPU
2: Cache
3: RAM
4: Hard drive
5: Volatile Storage
6: Non Volatile Storage
what is flash memory
non-volatile, solid state memory that can be read from and written to
list characteristics of flash memory
non volatile - retains data when the power is turned off
solid state - contains no moving parts, making it an ideal storage medium for many modern devices e.g. smartphones, tablets
fast to access and write to, although not as fast when reading from or writing to RAM
requires little power, making it an ideal storage medium for many modern devices e.g. smartphones, tablets
also used as external secondary storage e.g. USB memory sticks and SSDs
define virtual memory
When RAM is full, a portion of the HDD (hard drive) is allocated to act like RAM. Data is moved between virtual memory and RAM when needed by the CPU.
What do you think would be the effect on the performance of the computer of using a lot of virtual memory rather than upgrading your RAM?
Using a lot of virtual memory would reduce the performance of the computer because secondary storage (such as a hard drive or SSD) is much slower than RAM. This means programs would take longer to load and run
what is the definition and role of secondary storage?
permanent storage of instructions and data not in use by the processor. Stores the operating system, applications and data not in use. Read/write and non-volatile.
list types of optical storage
CD/R, CD/RW, DVD/R, DVD/RW
list uses for optical storage
music, films, archive files
list characteristics of optical storage
low capacity
slow access speed
high portability
prone to scratches
low cost
list characteristics of magnetic storage
example: hard disk drive
uses: operating system and applications
high capacity
medium data access speed
low portability (except for portable drives)
reliable but not durable
medium cost
list characteristics of solid state storage
examples: memory cards and solid state hard drive (SSD)
use: digital cameras and smartphones
medium capacity
high portability
reliable and durable
no moving parts
fast data access speed
hich cost
what is storage capacity
the amount of data a storage device is able to store
wht is storage speed
the read/write access speed of a storage device
what is storage portability
how easy it is to transport a given storage medium. e.g; solid state and optical storage are designed to be highly portable, whereas more traditional magnetic storage is designed to stay in place
what is storage durability
how resistant to damage and wear and tear a storage device is. Devices with low durability will wear out easily over time
ehst is storsge cost
the relative price of a storage medium on a cost per GB
Alicia is using a helmet mounted camera to record footage whilst snowboarding. Suggest two reasons why a flash memory card is a good choice for secondary storage in this scenario, and two reasons why a hard disk would be unsuitable.
A flash card is a good choice because:
- it is very lightweight and portable and small – is inside the camera so it won't be damaged by impacts
- it has sufficient storage capacity for long videos like recordings of snowboarding footage
A hard disk is a bad choice because:
- it isn't durable and is damaged by impacts, which are inevitable when snowboarding
It isn't portable and is large and heavy – not suitable to be attached to a helmet
Gregg is considering whether to download games for his games console from an online store, or whether to purchase the physical disks instead.
Give reasons why he may choose one option or another.
Online store – console might not support disks, or disk reader may not work
Physical disk – can be used in places without internet
Matt wants to keep a backup of his photos, and is considering using DVD-R disks. Give two advantages and two disadvantages of this method
Advantages:
- cheap per GB
- can store lots of photos
Disadvantages:
- short lifespan
- can break/ get scratched easily