PHAR 202 - Tertiary structure of a protein
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
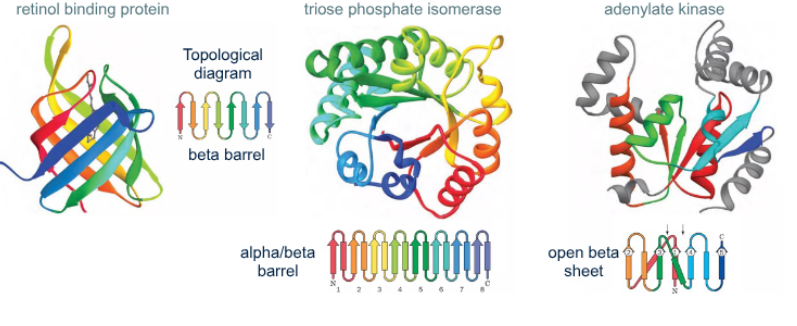
What is a tertiary structure
it’s a 3D arrangement of folded secondary elements together with the spatial dispositions of its side chains
Globular proteins are compact true or false?
true
Globular proteins have a packing density, what is that?
it’s the ratio of the volume enclosed by the van der waals envelope of the atom in a region TO the total volume of the region
the packing density for globular proteins is 0.75, what does that mean when it folds
it means that when it folds it’s tight and stable
There are 3 types of amino acid residues, what are they?
non polar residues
charged polar residues
uncharged polar residues
Where are non-polar amino acid residues found / occur?
interior of the protein
away from the aqueous solvent
Where are charged polar amino acid residues found?
surface of the proteins
they sometimes promote catalysis / metal ion binding
Where are uncharged polar residues found?
protein surface but frequently occur in the interior of the molecule
In the interior of the protein, there is an efficient packing due to Hydrogen Bonds. Nearly all buried hydrogen bond donos form hydrogen bond with….
burried acceptor groups
The formation of a hydrogen bond with a burried acceptor group ……… the polarity of the hydrogen bonding group (N—H or C=O)
neutralizes
Why is there efficient packing in the interior of the proteins
due to hydrogen bonds between burried acceptor groups and burried hydrogen bonding groups
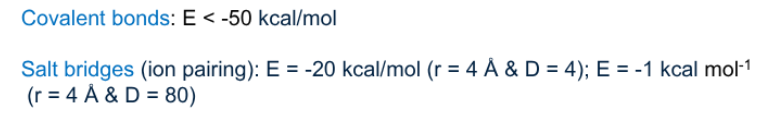
Why is ion pairing stronger in a protein in the interior but not the exterior
because it’s hydrophobic in the interior of the protein, the exterior has water on the protein surface that weakens ionic bonds, meanwhile proteins non-polar interior reinforces them
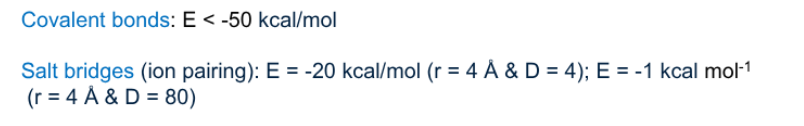
Which amino acid residues can make a salt bridge?
(+) amino acids: histidine, lysine, arginine
(-) amino acids: Glutamic acid, aspartic acid
Why can (+)/(-) amino acids form salt bridge
through their electrostatic attraction between their opposite charges along with hydrogen bonding between atoms within the charged groups
Hydrogen bonds are predominantly…….. between
electrostatic interactions (but with 10% covalent character)
acidic donor group and an acceptor than has a lone pair
Hydrogen bonds only weakly stabilize proteins, but provides….
a structural basis for its native folding pattern
In low medium (low dielectric constant), the E of the hydrogen bonding is…
-3 to -7
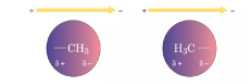
What force is a major influence in determining protein conformation
London Dispersion Force
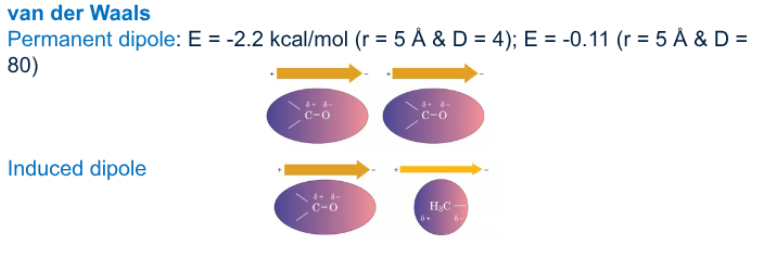
What is the difference between permanent dipole and induce dipole
Permanent dipole
permanent separation of charge in molcues
lasting positive and negative end
Induced dipole
temporary separation of charge form when an external electric field distorts the electron cloud of a neural molecule
momentary positive and negative end
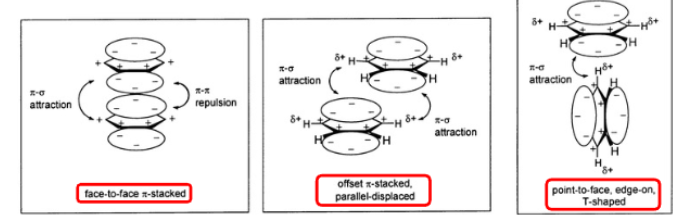
what is pi-pi stacking
when amino acids preferentially align their benzene rings
is pi-pi stacking weaker than LDF?
yes, but they are significant in controlling protein conformation and substrate binding properties
what is cation-pi interaction
when the cation attracted to negative electrostatic potential of a benzene ring (happens every 77 amino acids in PDB)
What is the hydrophobic effect
non-polar susbtances minimize their contacts with water + amphipathic molecules
why is the hydrophobic effect important in determining protein structure
because native proteins form an intracellular micelle
Why does transferring a hydrocarbon from water to a nonpolar solvent increase entropy (ΔS > 0)?
Water molecules form an ordered "cage" around them (low entropy).
If the hydrocarbon leaves water, the ordered water cage breaks → water becomes freer → entropy increases (ΔS > 0).
What is the enthalpy change (ΔH) for aliphatics when transferred from water to nonpolar solvent?
Positive (endothermic).
What is the enthalpy change (ΔH) for aromatics in the same transfer?
Approximately zero (athermic).
Is the hydrophobic effect mainly driven by enthalpy or entropy?
By entropy (ΔS).
What drives the spontaneity (negative delta G) of the process
the larg TAS component which is entropically driven due to the hydrophobic core collapsing
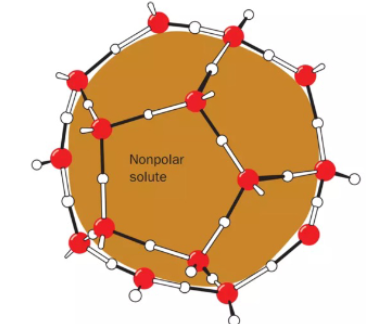
What is Clathrate
ordered water molecules (a water cage) that surround a nonpolar solute
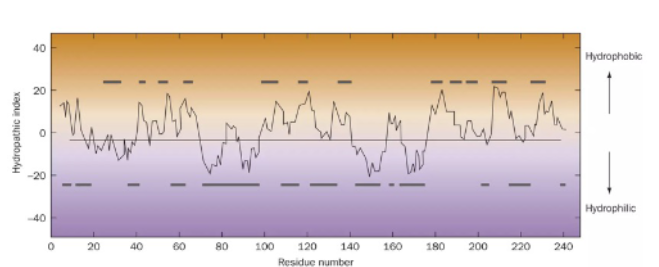
Explain this diagram
bars above: protein interior
bars below: protein exterior
as it goes up (+), it’s more hydrophobic
as it goes down (-), it’s more hydrophilic