A Level AQA 4.9 Fundamentals of communication and networking | 4.9.3 The Internet
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Define the Internet
A network of interconnected computer networks which uses an end-to-end communication protocol
Define what is a protocol
A set of rules that allows for communication between devices
What is the primary structure of the Internet
The Internet is mostly a wired network, with cables that pass under oceans to connect different continents.
What does ISP stand for
Internet Service Provider
What is an Internet Service Provider (ISP)
An ISP is a company which provides its customers with access to the internet
What are the largest ISP providers
The largest ISP providers are national companies
What are the largest ISP providers called
National Internet Service Provider
How do National Internet Service Providers provide access to the internet
They provide internet access to smaller regional and local ISPs, from whom homes and business can buy access to the internet
Define a packet
Is a container in which data is transmitted over networks.
What is packet switching
Packet switching is a method of transmitting data where messages are broken into smaller packets and sent individually over the network. Each packet is routed independently to the destination, where they are reassembled into the original message
What is the role of a router in packet switching
A router directs data packets between networks. It examines the header of each packet to determine the best path for it to reach its destination based on current network conditions.
How does a router determine the best path for a packet
A router uses routing tables and algorithms to decide the most efficient route for a packet based on factors like network congestion and distance.
What is a hop in networking
A hop is each time a packet passes through a router on its way to the destination. The number of hops a packet can take is limited by its Time to Live (TTL) value.
What is the Time to Live (TTL) value in a packet
The TTL value is a counter that decrements each time a packet passes through a router. When the TTL reaches zero, the packet is discarded to prevent it from circulating indefinitely.
What is the purpose of packet switching
Packet switching improves network efficiency and reliability by allowing multiple packets to take different paths to their destination, reducing congestion and ensuring data can still reach its destination even if some routes fail.
How do routers handle congestion
Routers use algorithms to manage congestion by selecting alternative paths for packets, prioritizing certain types of traffic, and sometimes dropping packets when the network is too congested.
What is the difference between packet switching and circuit switching
Packet switching breaks data into packets and sends them independently, while circuit switching establishes a dedicated path for the entire communication session.
What is the role of routing tables in routers
Routing tables store information about network paths and are used by routers to determine the best route for each packet.
How do routers contribute to network security
Routers can implement security measures like firewalls and access control lists (ACLs) to filter traffic and protect the network from unauthorized access.
What are the primary components of a packet
Senders address
Receiver’s address
Packet contents
Time to live (TTL)
Sequence number
What is the purpose of the Senders address in a packet
Identifies where the packet was sent from, and therefore where the response should be sent to.
What is the purpose of the Receiver’s address in a packet
Identifies the packet’s indented recipient, allowing it to be routed to the correct device.
What is the purpose of the Packet contents in a packet
Where the packet’s intended recipient, allowing it to be routed to the correct device
What is the purpose of the Time to live (TTL) in a packet
Holds the number of hops a packet can go through before being dropped
What is the purpose of the Sequence number in a packet
Contains the number of packets in a message and identifies a packet’s position in relation to others. This allows packets to be reassembled in the correct order and allows missing packets to be identified
What is the main job that both Routers and Gateways do
They connect different networks, allowing packets to reach their destination
Define routers
Where and why are routers used
Used in networks to direct data packets efficiently.
Define Gateways
A network point that acts as an entrance to another network.
Where and why are gateways used
Connect different networks and translate data between protocols.
How is routing achieved across the Internet
Routers use routing tables and protocols to find the best path for data packets.
What does URL stand for
Uniform Resource Locater
Define a URL (Uniform Resource Locater)
A reference to a web resource specifying its location and retrieval method.
What are the parts of a URL
https://
www
/news
/technology
/index
/html
What is the purpose of the https:// part of a URL
The protocol being used to access the file.
What is the purpose of the www part of a URL
Subdomain for world wide web. This will usually point to the web server hosted at the following domain.
What is the purpose of the bbc.co.uk part of a URL
A Domain. BBC is the name of the organisation. .uk is a top-level domain (TLD) and .co is a second-level domain (2LD)
What is the purpose of the /news part of a URL
Directory of the file being requested
What is the purpose of the /technology part of a URL
Subdirectory of the file being requested
What is the purpose of the /index part of a URL
Name of the file being requested
What is the purpose of the .html part of a URL
The file’s extension. Hyper text markup language (HTML) which is frequently used for creating web pages
Examples of top level domains (TLDs)
.com
.org
.net
Define Domain names
Identifies an organisation or individual on the Internet. They use alphanumeric characters which make them easy for humans to remember
What does 2LD stand for
Second level domain
How are domain names organized
Hierarchically: TLD (e.g., .com or .uk), 2LD (e.g., example or .co), and subdomains (e.g., news.example.com or bbc.co.uk ).
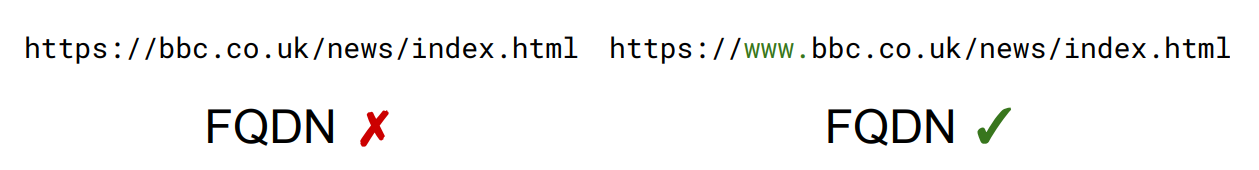
What does FQDN stand for
Fully Qualified Domain Name
Define the term Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)
Is a domain that specifies an exact resource and can be interpreted in only one way. An FQDN will always include the server’s host name.
What does IP stand for
Internet Protocol
Define the term IP address
Uniquely identifies devices on a network, such as the Internet. Since IP addresses are hard to remember, domain names are used to map to IP addresses. As they are a human-friendly representation of an IP address
True or False | Does every Computer have an IP address
True.
An IP address is assigned to every computer on the Internet and every device that communicates on a network
What does DNS stand for
Domain Name System
What is the purpose of the domain service and DNS system
Translates domain names to IP addresses using DNS servers.
What service does an Internet registry provide
Internet registries manage the allocation and registration of domain names and IP addresses.
What do Internet registries do
They ensure the uniqueness of domain names and IP addresses and maintain a centralized database to prevent conflicts.
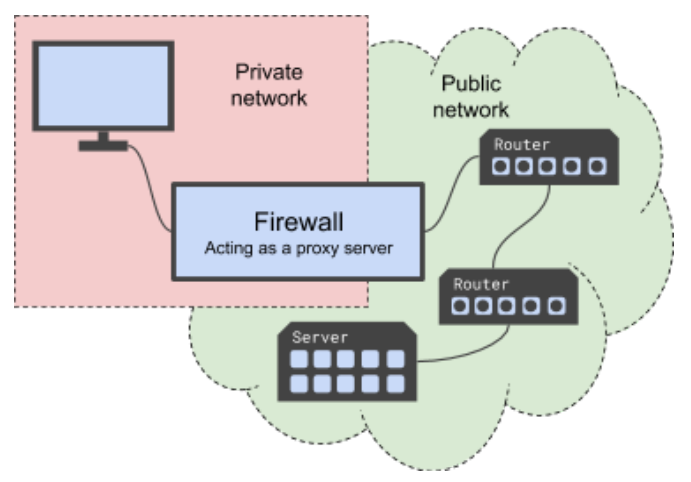
What is a Firewall
A firewall is a combination of hardware and software that isolates an organisation’s internal network from the Internet at large, allowing some packets to pass and blocking others.
Name 3 firewall techniques
Packet filtering
Stateful inspection
Proxy server
What is Packet filtering
A firewall technique used to accept or block packets based on their source IP address or protocol (determined by port number). Network administrators can specify IP addresses or protocol
What is Stateful inspection
Examines the contents of a packet before allowing it through the firewall. Some firewalls keep track of current network connections, filtering out packets that are not related to ongoing network activity.
What is a Proxy server
It is a server that sits between a public network and a privet network. They manage every packet that passes between the two networks
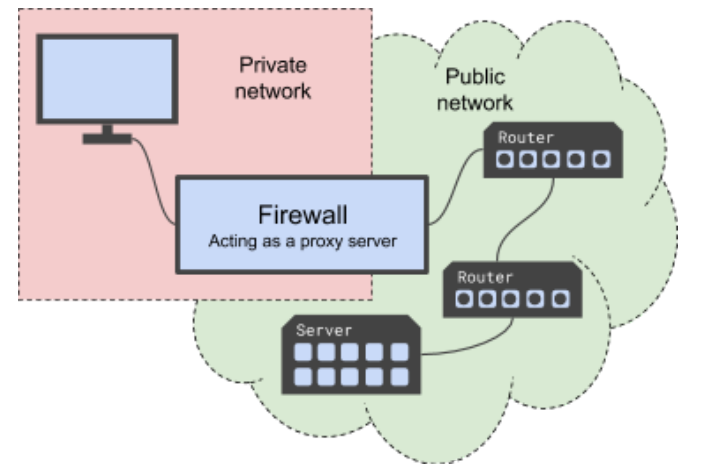
Firewalls are said to act as a proxy when …
They control the movement of packets between public and private networks.
Describe when a device in a private network sends a packet through a firewall and into a public network
The packet’s “sender” address is that of the firewall rather than the device’s private IP address. This provides some degree of anonymity to devices on probate networks as their private address is never sent beyond the private network
Define encryption
The process of scrambling data so that it can not be understood if intercepted
When is encryption used
When information needs to be transmitted securely over a network
Two types of encryption
Symmetric
Asymmetric
Define Symmetric encryption
Both the sender and receiver share the same private key. This key is used to both encrypt and decrypt data sent between the two parties
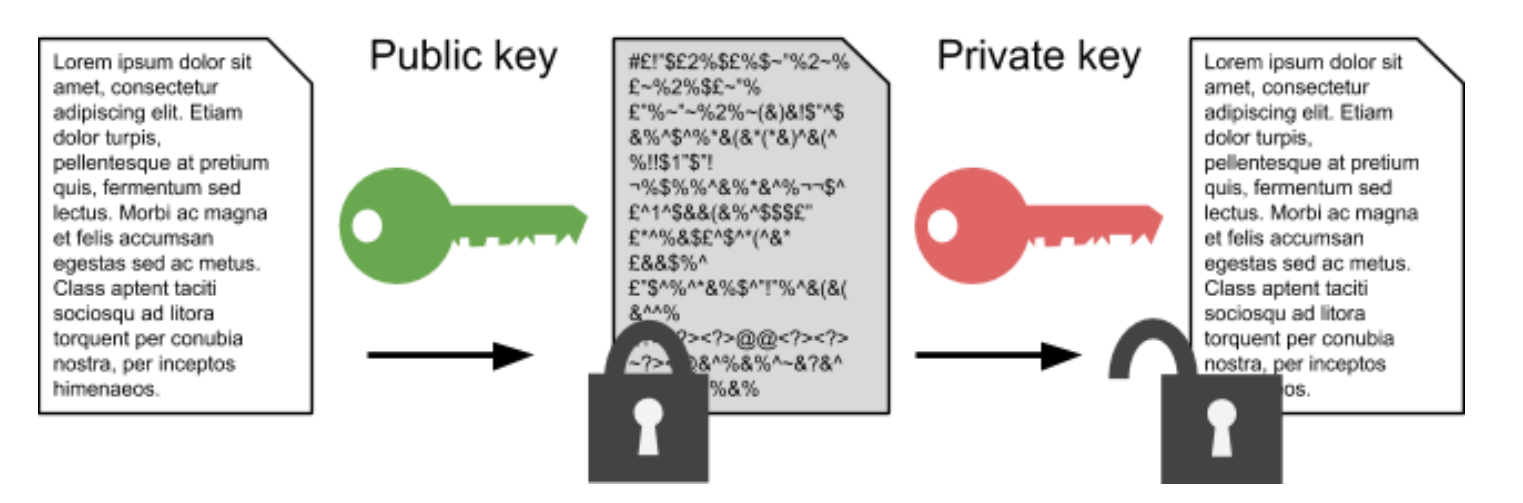
Define Asymmetric encryption
When there are two devices communicating using asymmetric encryption, four different keys are used. Each device has a pair of mathematically related keys, one of which is kept secret (the private key) and the other shared on the Internet (the public key).
The process of Symmetric
Before any information is sent. The sender and receiver must engage in a key exchange to ensure they both have a copy of the shared key.
What is a major flaw of Symmetric
Because the key needs to be shared, if it’s exchanged over a network it’s venerable to interception
The process of Asymmetric encryption
Before a message is sent, it’s encrypted by the sender using the recipients public key. This means only the corresponding private key can decrypt it and vice versa.
The recipients private key (which the recipient only has access too) means that only the recipient can decrypt the message
Define digital certificate
A digital certificate verifies ownership of a key pair used in asymmetric encryption. It ensures that a key pair is authentic and not being used by an imposter.
Define digital signature
A digital signature is a cryptographic technique used to verify the sender of a message and ensure the message has not been tampered with during transmission.
Explain how digital certificates are used and obtained
Digital certificates are issued by certificate authorities (CAs) and contain information such as a serial number, owner’s name, expiry date, owner’s public key, and the CA’s digital signature. They verify the authenticity of key pairs in asymmetric encryption.
Explain how digital signatures are used and obtained
A digital signature is created by hashing a message, encrypting the hash with the sender’s private key, and appending it to the message. The recipient decrypts the hash with the sender’s public key and checks if it matches a newly computed hash of the received message to verify authenticity and integrity.
Why are digital signatures important
Digital signatures provide authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation, ensuring that messages are from a verified sender and have not been altered.
What is the role of a certificate authority (CA)?
A certificate authority (CA) is a trusted organization that issues digital certificates to verify the legitimacy of key pairs in asymmetric encryption.
How does hashing relate to digital signatures
Hashing creates a unique fixed-length digest of a message, which is encrypted with the sender’s private key to form the digital signature. Any change to the message alters the hash, revealing tampering.
Types of malware
Worms
Trojans
Viruses
Define worms
Are a piece of malicious software that can self- replicate between computers, this can happen either within a network or by users downloading and running malicious software
Define Trojans
A type of malware that disguisesas a benign file that users tricked into opening. These are often spread as email attachments or downloaded from malicious websites
Define what is a benign file
A type of software that does not pose any malicious threat to the system or user data
Define viruses
Require a host file in which to reside. These files are typically executable files, meaning that viruses can lie dormant in a computer until their host file is opened or run.
Viruses can spread between computers over a private network, the Internet or even through the use of physical media like hard drives, flash drives and optical disks.
Vulnerabilities that malware might exploit
Exploit bugs in the code
Out of date software
Poor security (lack of good security features)
Lack of anti-virus software
Ways to prevent malware
Anti-virus software
No out of date software
Good security (so good security features)
Good code quality
What are anti-virus software
Specialist pieces of software that scan the files on a computer and remove any suspicious files
How does malware exploit out of date software
The primary issue lies in the undressed security features and out of date protection/ security
How does malware exploit poor security
Malware takes advantage of weak passwords, outdated software, and misconfigured settings to gain unauthorized access and spread infections.
How does malware exploit bugs in the code
Malware exploits coding flaws, such as buffer overflows and injection vulnerabilities, to execute malicious code and compromise systems.