Lens Materials and Manufacturing, Glazing
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
In this session you will learn about spectacle lens materials, manufacturing process as well as surfacing and glazing of spectacle lenses.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms

What Do We Expect From a ‘Good’ Ophthalmic Lens?
The ideal ophthalmic lens:
Corrects refractive error with….
No aberrations (spherical and chromatic aberration) and no “light loss”
UV-protection
Cosmetically appealing (as thin as possible, as invisible as possible)
Light weight
Resistant to mechanical impact and scratches
No change in lens material due to liquids (i.e. opacification of the material)
Resistant to changes in temperature
Optical properties - reflectance (R), Absorption (A) and transmission (T); Refractive Index (n or RI) and Abbe number (Vd)
Mechanical properties - Specific Gravity (SG), Impact resistance (IR) and scratch resistance (SR)
Absorption (A) is an optical property. True or False?
True
Opthalmic Lens Information and Practical Implications
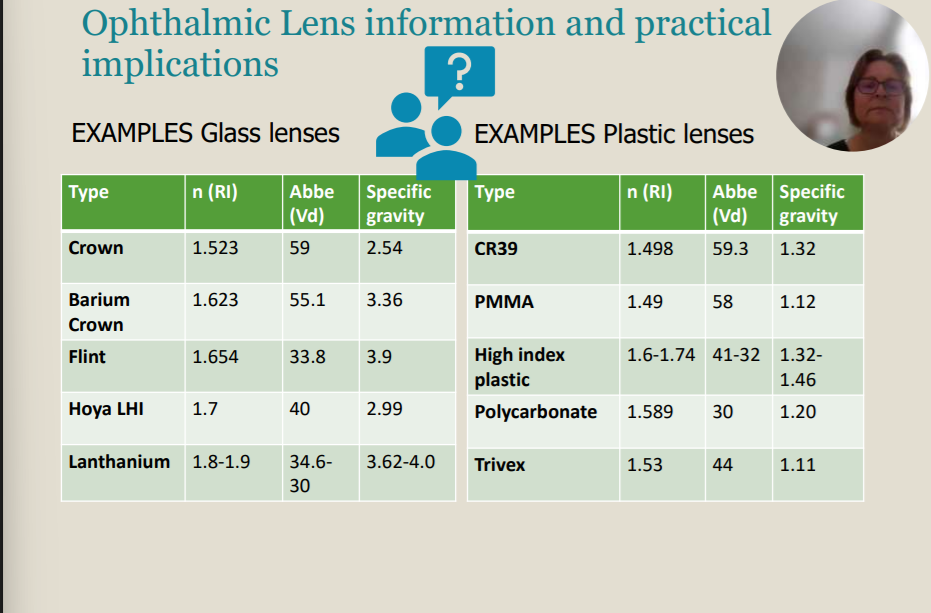
The crown glass had a refractive index (n), Abbe (Vd) and specific gravity (SG) are _____, _______ & _______.
1.523; 59; 2.54

Opthalmic Lenses Properties
The Abbe number (Vd) - optical quality
The refractive index (RI, n) - mechanical property (weight, thickness)
The Specific gravity / Density – mechanical property (weight)
The ________ is for optical quality, _______ is the mechanical property (weight & thickness) and ______ is a mechanical property (weight).
Abbe Number (Vd); Refractive Index (n); Specific Gravity (SG)
Refractive Index (n or RI)
= ratio of velocity of light in air vs velocity of light in the medium
Classification of material according to n:
n =1.5 → standard lens material
n 1.5 to 1.7 → mid-index material
n>1.7 → high-index material
Higher n means a lens has a greater ability to refract light: results in a thinner lens despite having the same power as a lens with lower n → Curve variation factor (CVF)
CVF = 0.523 / nd - 1
Increased refractive index is achieved as a direct result of increasing the density of the material (specific gravity = the heaviness of a substance compared to water (no units).
Higher _______ means a lens has a greater ability to refract light.
Refractive Index (n or RI)
Opthalmic Lens Thickness - Glass
Effect of increasing refractive index, n:
n = 1.56 11% thinner then n=1.523
n = 1.60 17% thinner then n=1.523
n = 1.67 25% thinner then n=1.523
n = 1.70 29% thinner then n=1.523
n = 1.74 32% thinner then n=1.523
n = 1.80 37% thinner then n=1.523
n = 1.90 44% thinner then n=1.523
CVF = 0.523 / nd - 1
Thickness saving = 7%
0.523 / 1.523 -1 = 1.00
0.523 / 1.56-1 = 0.93
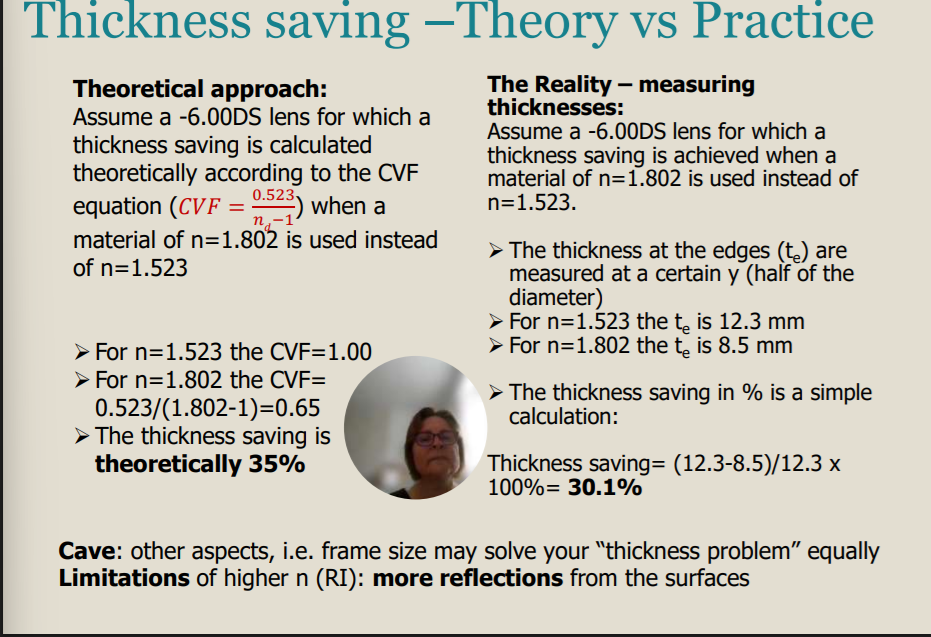
Thickness Saving
Thickness saving - xmm - x1mm / xmm x 100% = x%
Thickness saving= (12.3-8.5)/12.3 x 100%= 30.1%
Specific Gravity or Density
=The heaviness of a given volume of material/substance compared to water [no unit]
Another way of describing the heaviness of a given volume of material is “density”
Density (gcm-3) = Mass (g) / Volume (cm3)
Increased refractive index is achieved as a direct result of increasing the density of the material.
greater density means higher refractive index => thinner lenses (less mass)
Increased refractive index is achieved as a direct result of increasing the density of the material.
Increased refractive index is achieved as a direct result of increasing the density of the material. True or False?
True
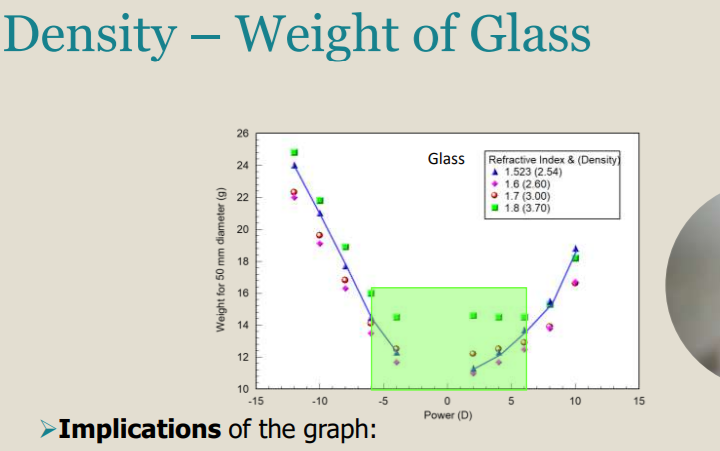
Density - Weight of Glass
Implications of the graph:
For low powers a lens of higher refractive index will be thinner but heavier than crown glass.
for high powers a lens of higher refractive index will be thinner and lighter than the equivalent crown glass lens
For _____ powers a lens of higher refractive index will be _____ and _____ than the equivalent crown glass lens.
High; Thinner; Lighter
Specific Gravity - Glass vs Plastic
In Glass lenses specific gravity increases significantly with increasing refractive index, n).
In Plastic lenses Specific gravity does not vary significantly.
Plastic Lenses are at least 50% lighter than glass lenses
In Plastic lenses an increase of n results in a reduction of weight (25-33%) due to the reduction in lens volume (thinner lens).
Plastic lenses are at least ______ lighter than glass lenses.
50%
The Abbe Number - Vd
= measure of the material ability to hold the spectrum together.
Specifies axial and “transverse chromatic aberration”
The greater the dispersion, the greater the dioptric difference between the red and blue foci (i.e. the wider and more noticeable the spectrum)
The degree of chromatic aberration is dependent on the prismatic effect at a given point on the lens in addition to the lens material
The lower the Abbe Number, the greater the transverse chromatic aberration
Abbe number of the eye: 45
Range of Vd in lenses: 30 - 60
Patients are prone to notice the dispersion when Vd < 40 particularly when wearing large diameter lenses
Cave when: dispensing n> 1.7 => possibility of colour fringes OR dispensing prism by decentration
Glass lenses have better optical performance (less dispersion) for the equivalent refractive index
The Abbe Number (Vd) is the measure of the material ability to hold the ________ together.
Spectrum
Other Mechanical Properties Ophthalmic Lenses
Impact resistance: = the ability of a material to withstand a high force or shock applied to it over a short period of time.
Test FDA approved: 5/8 inch steel ball onto the lens from a height of 50 inches
Polycarbonate is the most impact resistant lens material followed by high index plastic lenses, CR-39 and glass lenses.
➢Scratch resistance:
= the ability of a material to withstand abrasions
Bayer abrasion test: abrasion from oscillating "sand “ (alumina zirconia),
Glass is the most scratch resistant material, and Polycarbonate is the least scratch resistant plastic lens type
Hard coatings are mandatory for Polycarbonate, mid-index plastics and Trivex
________ is the most impact resistant lens material followed by high index plastic lenses, CR-39 and glass lenses.
Polycarbonate
Calculate theoretically the achievable thickness reduction (compared to crown glass) possible for barium crown glass and Lantal 1.9 glass.
CVF = 0.523/ nd - 1
Crown Glass - 1.523
Barium Crown - 1.623
Lantal 1.9 - 1.9
0.523 / 1.523 - 1 = 1.00
0.523 / 1.623 - 1 = 0.84
0.523 / 1.9 - 1 = 0.581
100% - 58.1% = 41.9% = 42%
The thickness saving theoretically for barium crown glass is 16% and for lantal 1.9 is 42%
The raw materials to a finished pair pf spectacles is _______ for glasses and ______ for plastic.
Sands; Resins
Lens Material - Glass
Glass Lenses
Quartz - SiO2 (sand): Historically quartz was used to make spectacle lenses since 5000 BC
Naturally occurring transparent materials such as quartz have a crystalline structure, i.e. the atoms are arranged in a regular lattice formation
Glass has an amorphous structure, i.e. the atoms are arranged in an irregular manner.
Glass is a supercooled liquid
Glass materials (not natural ones): soda lime silica glass
Crown = 70% silica (from sand with a silica content minimum of 99.5%), 12% calcium oxide, 15% sodium oxide, Small % of potassium, borax, antimony, arsenic (improve the quality of the glass
Refractive index (n or RI) of 1.523
Abbe (Vd) of 58.9
Specific gravity of 2.54
UV absorption up to 280 nm
Glass materials (not natural ones): soda lime silica glass
Barium Crown = 30% silica, 35% barium oxide, Small % of lime, zinc, aluminium, boron, antimony, zirconium
Refractive index (n or RI) of 1.523
Abbe (Vd) of 55.1
Specific gravity of 3.36
Glass materials (not natural ones): soda lime silica glass
Dense Barium Flint = 30% silica, 60% lead oxide, 8% soda and potash, small % of arsenic, antimony (quality)
Refractive index (n or RI) of 1.654
Abbe (Vd) of 33.8
Specific gravity of 3.9
UV absorption up to 330 nm
Glass materials (not natural ones):
Titanium = Titanium oxide base, developed in the 1970’s with aim to increase n (RI = 1.7)
Refractive index (n or RI) of 1.701
Abbe (Vd) of 42
Specific gravity of 3.2 g/cm3
UV absorption up to 330 nm
Lanthanum = Lathanum base, developed in the 1980’s with aim to increase n (RI = 1.8-1.9)
Refractive index (n or RI) of 1.805 to 1.885
Abbe (Vd) of 35-31
Specific gravity of 3.6 -4.2 g/cm3
UV absorption up to 350-340 nm
Glass is a supercooled liquid. True or False?
True
Lens Material - Plastic
In the UK, Glass lenses account for < 10% of the market. Plastic (resin) lenses account for the remainder
Plastics are organic molecules derived principally from the oil industry and are manufactured by polymerisation
Original plastic lenses were made from Perspex (polymethylmethacrylate or PMMA) moulded under heat and pressure in a glass die of the appropriate curvature, before polishing to optical quality
Less weight than glass material (specific gravity/ density)
Better impact resistance then glass material due to chemical structure
First plastic used in ophthalmic lenses was CR-39 (Columbia Resin; 39th formulation) in 1950’s
a thermosetting polyester resin (allyl diglycol carbonate).
The liquid monomer, allyl alcohol undergoes polymerisation into CR-39
Refractive index (n or RI) of 1.498
Abbe (Vd) of 59
Specific gravity of 1.3 g/cm3
UV absorption up to 350 nm
Polycarbonate is a synthetic material (thermoplastic) from a petroleum polymer and a plastic polymer
initially developed (1970’s) for aerospace application due to its UV-absorption properties (up to 380 nm) and flexible molecular structure (impact resistant)
Used in ophthalmic lenses since the 1980’s
Refractive index (n or RI) of 1.586
Abbe (Vd) of 30
Specific gravity of 1.2 g/cm3
UV absorption up to 385 nm
Trivex (also known as phoenix or triology) is a urethanebased pre-polymer
similar to polycarbonate, but with better optical properties
More rigid than Polycarbonate – use for rimless mounts, scratch sensitive
Lighter in weight then CR-39, but thinner than Polycarbonate
Refractive index (n or RI) of 1.532
Abbe (Vd) of 43-45
Specific gravity of 1.1 g/cm3
UV absorption up to 395 nm
Polycarbonate is the most impact resistant and the least ________.
Scratch Resistant
Need to Know:
The ideal Ophthalmic lens:
Corrects refractive error with…
No aberrations (spherical and chromatic aberration) and no “light loss”
Best optical quality can be achieved with glass
Higher n result in increased chromatic aberration
Polycarbonate exhibits the worse optical quality within plastics
Full UV protection (also in lecture tints & coatings)
Plastic lenses provide better UV protection (100% for Polycarbonat, high-index and Trivex) then glass lenses (<280nm)
Cosmetically appealing (as thin as possible)
For high powers an increased n (glass material) will result in a lighter and thinner lens than the equivalent crown glass.
Light weight
Plastic lenses are 50% lighter than glass lenses
Resistant to mechanical impact and scratches
Glass has a greater abrasion resistance than plastic despite having the least impact resistance; Polycarbonate has the lowest abrasion resistance of all plastic lenses: Hard coating mandatory
No change in lens material due to liquids (i.e. opacification of the material)
Resistant to changes in temperature:
CR-39 more fog resistant than glass lenses;
Polycarbonate exhibits the worse optical quality within plastics. True or False?
True
Raw Materials to a Finished Pair of Spectacles - RoadMap
Manufacturing
Continuous flow process - glass
Polymerisation - plastic
Surfacing
Traditional surfacing/ Free - form surfacing
Tinting; Coating
Glazing
Pair of Spectacles
Raw Materials → Manufacturing → Surfacing → Glazing → Pair of Spectacles. True or False?
True
From the Raw Ingredients to An Opthalmic Lens
Manufacturing: The manufacturing process up to an unfinished blank is a continuous flow process → unfinished blank
Surfacing: Traditional lens surfacing produces the lens blank which is ready to be glazed
Digital lens surfacing takes over more and more, enabling for producing “Free form” lenses
Glazing: produces the finished spectacles for an individual according to the "needs"
Correcting the refractive error and achieving the individual centration values of the spectacle wearer
The manufacturing process for glass is ___________ process and for plastic it is _____.
Continuous Flow; Polymerisation
Manufacturing Glass Lenses
Glass lenses
The manufacturing process up to an unfinished blank is a continuous flow process
Glass formation = melting (1000-1500oC) carefully weighted raw materials.
Refining = temperature increased to 1600oC in order to eliminate gases and purify glass melt (fluid).
Conditioning = slowly cooling down the glass melt to make it viscous and thus, suitable for the next stage. (glass melt is stirred throughout)
Moulding and = glass melt (consistency of treacle) is moulded into lens blanks before passing immediately to a glass press
Annealing = slowly cooled to room temperature in order to avoid internal stresses.
The unfinished blank has a finished front (spherical) and unfinished back curvature, but is not transparent; the maximum achievable power is determined by the thickness of the lens
The maximum achievable power is determined by the ________ of the lens.
Thickness
Manufacturing Plastic Lenses
Original plastic lenses are moulded under heat and pressure in a die of appropriate curvature, before polishing to optical quality.
Manufacturing:
Liquid monomers and other substances, e.g. initiator and UV absorber are added into a mould (glass dies with sealing rings)
Polymerisation = application of heat activates the initiator and triggers the chemical reaction. The chemical reaction is exothermic and leads to hardening of the resin
Plastic lens is separated from the die and further heat treatment process reduces strain in the lens matrix.
During the hardening process the volume of material in the mould shrinks
In plastic lenses with the refractive index 1.501 this shrinkage totals as much as 14%
For plastic resins of higher refractive index, different monomers are used
High-index resins often require more than one monomer and the resin is produced by polyaddition.
The production process for the high-index resins is considerably longer and may take up to 48 hours to complete
The hardening process of plastic lenses the volume of the material _______ and this is by a total of 14% for a n = 1.501 plastic lens.
Shrinks
Lens Surfacing
After manufacturing the unfinished blanks a quality inspection is carried out on samples
Traditional lens surfacing produces the lens blank which is ready to be glazed (produces the power)
Blocking = unfinished blank attached to a metal button using soft metal alloy as adhesive, for plastic lenses a protective plastic film is applied to the lens surface before blocking
Generating = blank surface is brought to its approximate curve and thickness by a diamond impregnated cutting wheel (named lathe)
Grinding+ Polishing = progressively finer grinded abrasive surfaces smoothen the front surface of the lens until optical quality is achieved; after quality control, the blank is removed from the metal button
Laser ID engraving
Coating and tinting process.
Limitation: produces desired power onto ONE surface of a lens (backsingle vision, front – varifocal/progressive lenses)
Digital surfacing – removes the limitations of the traditional surfacing process (limited base curves).
produces unlimited shapes and exceptional accuracy (0.01D) on one or two surfaces of the lens to achieve the intended design – freeform lenses.
Reduction of lens aberrations
________ is the unfinished blank attached to a metal button using soft metal alloy as an adhesive.
Blocking
Glazing of Opthalmic Lenses
Also named Lens edging:
The completed lens blank needs to be cut into the frame, matching the lens wearers centration needs (PD, heights)
Transferring required centration onto the lens (marking the DVP; DVP=OCD if no prismatic effect is required)
Blocking the Lens
Transferring the frame shape onto the uncut (blank) lens
Grinding the lenses to match into the frame
Glazing is also called _______.
Lens Edging
Glass Benefits and Constraints
Benefits
Very scratch resistant
Thinnest lens available (1.9)
Very high levels of optical quality
Constraints
Brittle unless toughed (not impact resistant)
Heavy
In varifocal lenses the designs are relatively old
Not used for children
Not for rimless frames
Working with acid could opacify the lens
The thinnest, scratch-resistant and highest optical quality lens can be made from glass. True or False?
True
Plastic Benefits and Constraints
Benefits
Light weight
Flexible used (suitable for most frame types)
More robust than non-toughened glass
Constraints
Easier to scratch than glass unless hard-coated
Plastic lenses are less ________ than glass lenes.
Scratch Resistant
Polycarbonate Benefits and Constraints
Benefits
The most impact resistant
Inherent UV protection
Low density so lighter weight than plastic or glass
useful for children as it is low budget and can be used for sports
Constraints
More distortion than glass, plastic or hybrid lenses of a similar refractive index
Much softer surface - easily scratched unless coated
Some coatings and tints will not adhere to the lens surface properly
Limited tints / coatings available in sunglasses
Polycarbonate is easily scratched unless coated. True or False?
True
Safety Environment
British standards (BS EN 166:2002) specifies the requirements for safety eyewear
British standards (BS EN 207: 2017): Specification for laser radiation filters
Laws:
The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974
The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998
Personal Protective Equipment Regulations 2002
Health and Safety (Display Screen Equipment) Regulations 1992
Workplace (Health, Safety and Welfare) Regulations 2002
British standards (BS EN 166:2002) specifies general requirements for safety eyewear
4 categories: safety spectacles, goggles, visors/face shields and sunglasses.
BS EN 167 defines the required optical tests for safety eye-protection:
Regarding field of vision, transmission and diffusion (UV), and refractive properties.
Styles of frames, the lens materials and types are defined by these standards
lenses and frames not produced accordingly are not acceptable – check for kite mark
BS EN 207 (2017): Specification for laser radiation filters
Specified by optical density (log of the attenuation factor at a given wavelength) AND damage threshold of protective device
Eye-wear marking: e.g., ‘DI 750 – 1200 L5, R 750 – 1200 L6, M 750 – 1200 L4’
D,I,R and M refers to continous wave (D) or different pulse lengths: I=long pulse, R=‘Q-switched’ and M=‘femtosecond’
750-1200 nm refers to wavelength range
L4, L5, L6 refer to the maximum power or energy density.
Glass lenses are often toughened/tempered – safety glass
Chemical process – lenses placed in a bath of a potassium salt at 400℃ changing some of its characteristics
Heating process - the lenses are heated to a high heat, cooled rapidly changing some of the characteristics
BS EN 207 (2017) provides specification for ________ filters.
Laser Radiation