types of trade protection
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
trade protection
government intervention aiming to limit imports and/or encourage exports by setting up trade barriers that protect from foreign competition
tariff
a tax that is placed on imports to protect domestic industries from foreign competition and to raise revenue for the government
quota
an import barrier that set limits on the quantity or value of imports that may be imported into a country
production subsidy (international)
an amount of money paid by the government to a firm, per unit of output, to encourage production and provide the firm an advantage over foreign competition
export subsidy
payments made by the government to exporting firms on the basis of the number of units exported
administrative barriers
trade barriers in the form of regulations that aim to limit imports into a country. these barriers may take the form of product safety standards, sanitary standards or pollution standards
why countries might not want to engage in free trade
protect infant industries
national security
environmental standards
anti-dumping
unfair competition
government revenue
domestic job protection
ELDC diversification
winners from tariffs
domestic producers are better off
domestic employment in protected industry increases
government gains tariff revenues
losers from tariffs
domestic consumers are worse off
domestic income distribution worsens (regressive tax)
increased inefficiency in production
foreign producers are worse off
global misallocation of resources
calculations: consumer expenditure from tariffs
consumer expenditure = P x Q
consumer expenditure before tariff = Pw x Q2
consumer expenditure after tariff = (Pw + T) x Q4
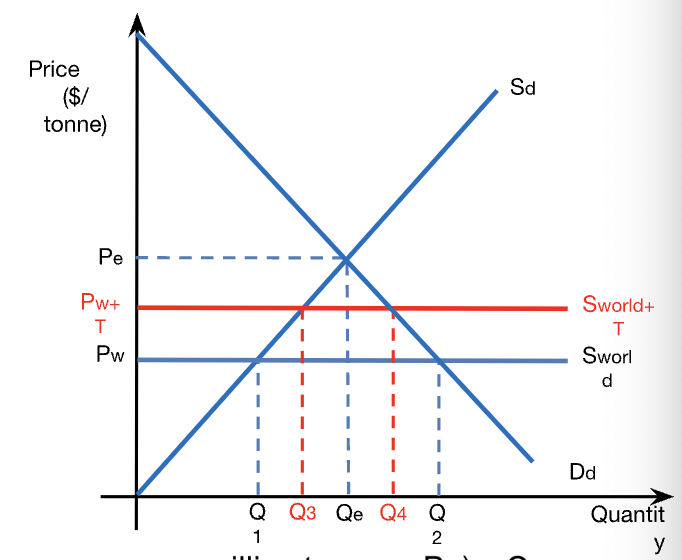
calculations: consumer surplus from tariffs
consumer surplus before tariff = (max price consumers pay - Pw) x Q2 / 2
consumer surplus after tariff = (max price consumers pay - (Pw - T)) x Q4 / 2
calculations: domestic producer revenue from tariff
domestic producer revenue = P x Q
domestic producer revenue before tariff = Pw x Q1
domestic producer revenue after tariff = (Pw + T) x Q3
calculations: producer surplus from tariff
producer surplus before tariff = (Pw - min price to sell) x Q1 / 2
producer surplus after tariff = ((Pw + T) - min price to sell) x Q3 / 2
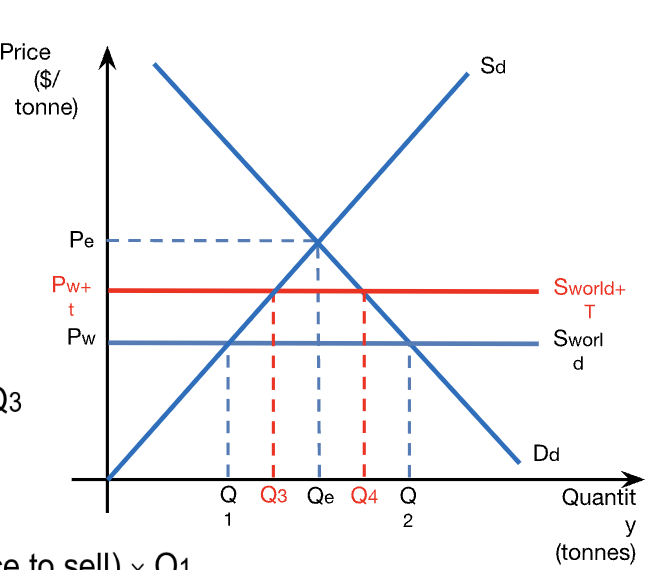
calculations: foreign producer revenue from tariff
foreign producer rev = Pw x import quantity
foreign producer rev before tariff = Pw x (Q2 - Q1)
foreign producer rec after tariff = Pw x (Q4 - Q3)
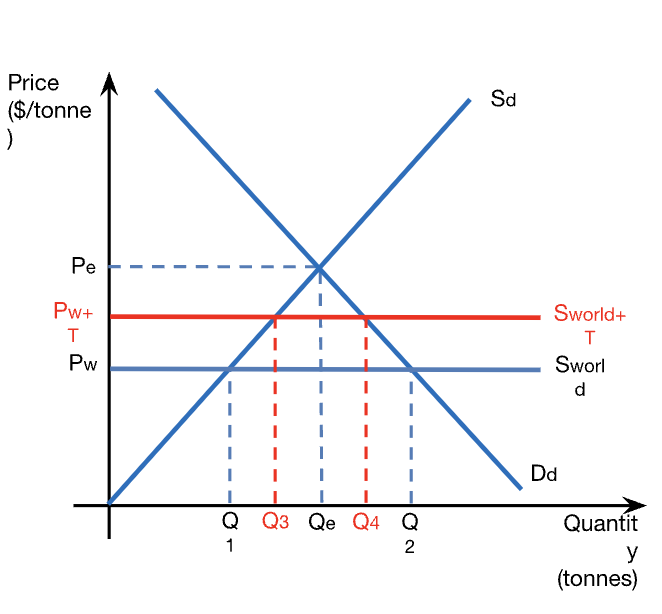
calculations: gov’t revenue from tariff
gov’t rev = tariff x import quantity
gov’t revenue = T x (Q4 - Q3)
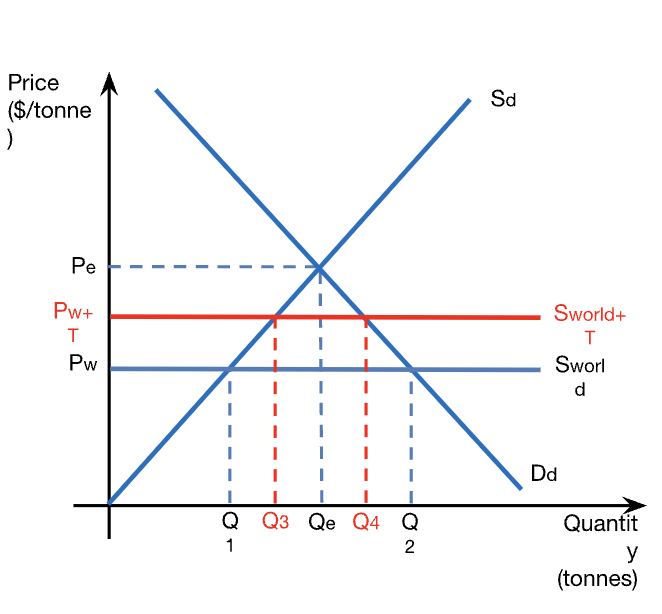
anti-dumping
tariffs that aim at raising the artificially low price of a dumped imported good to the level of the higher domestic price
dumped good: one that is exported at a price below cost of production
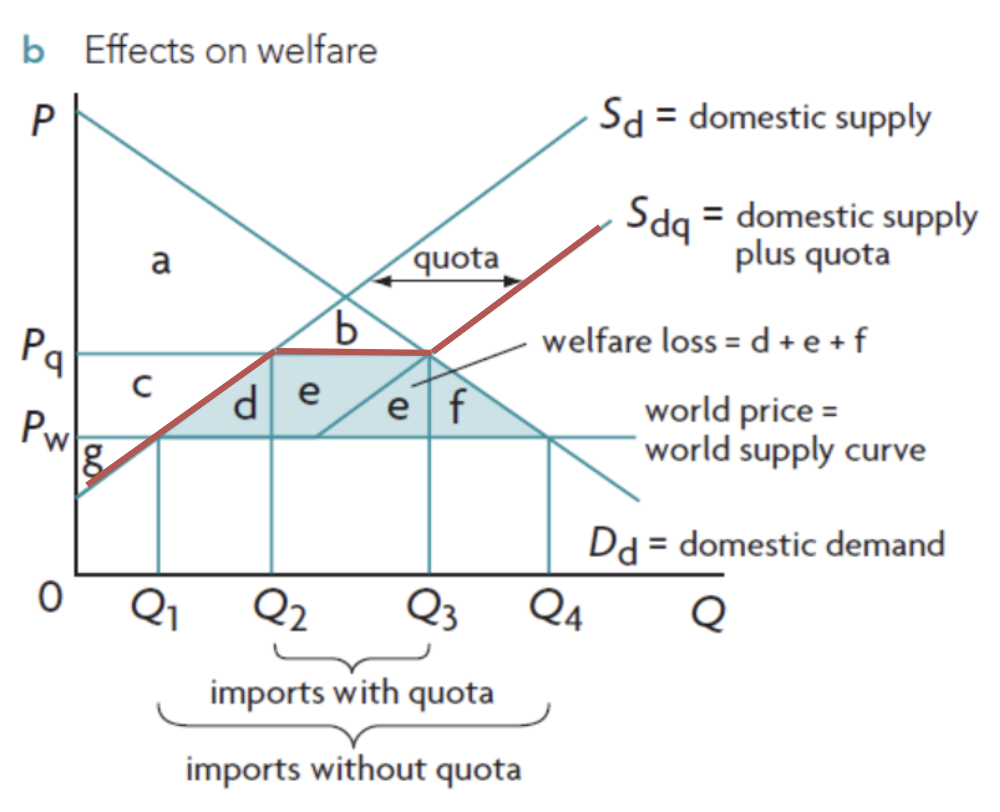
winners from quota
domestic producers are better off
domestic employment in protected industry increases
neutral impact from quota
the gov’t = no gain or loss
losers from quota
domestic consumers worse off
domestic income distribution worsens (regressive)
increased in efficiency in production
foreign producers are both worse and better off
global misallocation of resources
quota diagram
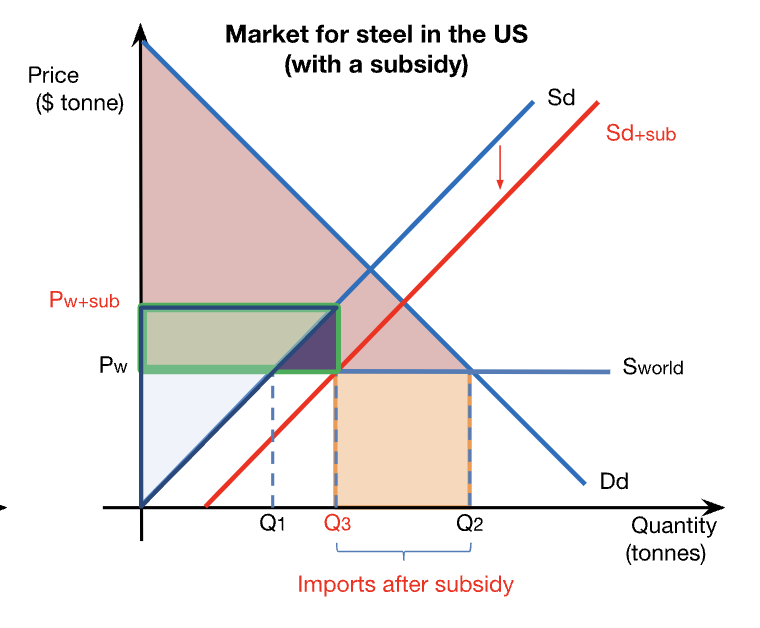
winners from production subsidies
domestic producers are better off
domestic employment in protected industry increases
consumers are not affected
losers from production subsidies
gov’t budget loses
taxpayers are worse off
increased inefficiency in production
exporting countries are worse off
global misallocation of resources
export subsidy diagram
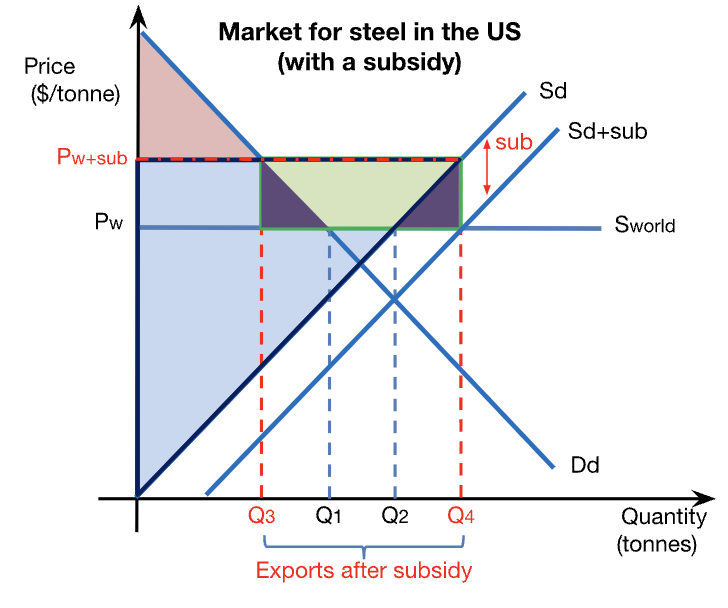
winners from export subsidies
producers better off
domestic employment increases
losers from export subsidies
consumers are worse off
gov’t budget loses
taxpayers worse off
domestic income distribution worsens
exporting countries worse off
global misallocation of resources
production subsidy diagram