Paracetamol Poisoning and Carbon monoxide Flashcard
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and details regarding carbon monoxide and paracetamol poisoning, including mechanisms of toxicity, liver damage, treatment options, and biochemical alterations.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is carbon monoxide often referred to as?
The Silent Killer
What is the primary reason for hepatic damage during paracetamol poisoning?
Liver glutathione stores become depleted.
What factors can reduce glutathione stores?
Elderly,
malnourished,
anorexia nervosa,
short-term starvation due to concurrent illness.
How is paracetamol primarily metabolised in the body?
Conjugation (60-90%)
forms paracetamol glucuronide and sulphate.
•Oxidation (5-10%) – P450 system
Forms N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine (NAPQI)
NAPQI is very reactive and damaging
What is the percentage of paracetamol that undergoes oxidation?
5-10% via the P450 system
to form
N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine (NAPQI).
What is the effect of administering acetylcysteine within 8 hours after paracetamol ingestion?
It results in 0% death from hepatic failure.
What happens if acetylcysteine is given more than 8 hours after ingestion?
It results in a 5.3% death rate from hepatic failure.
Why are blood glucose levels low following paracetamol overdose?
The liver's ability to breakdown glycogen is reduced.
What happens to the conjugation pathway during paracetamol overdose?
It becomes saturated, leading to more paracetamol being converted to NAPQI.
What are some biochemical abnormalities seen in paracetamol poisoning?
BIG increase in AST/ALT,
increase in bilirubin,
decrease in blood sugar,
decrease in phosphate,
metabolic acidosis,
increase in amylase,
increase in PT (INR),
decrease in clotting factors and platelets.
What organs are affected by NAPQI?
Liver and kidneys.
What is the AST/ALT value indicating severe hepatic damage?
1000 IU/L.
What causes metabolic acidosis in paracetamol poisoning?
Massive indigestion - reduced aerobic respiration.
Reduced hepatic clearance of lactate
hypoperfusion leading to anaerobic respiration.
How is acetylcysteine administered?
Intravenously (I.V.) for 21 hours.
What are the antidotes to paracetamol poisoning?
Glutathione precursors.
What substance does NAPQI alter the regulation of?
Calcium.
What occurs during days 3-5 of severe paracetamol poisoning?
•Jaundice > Liver failure > Encephalopathy
•Back pain > Renal angle tenderness > Renal failure
This can happen in the absence of hepatic failure
•DIC – from liver failure
•Cardica arrhythmias – acid/base and electrolyte disturbance
What is the most common antidote for paracetamol poisoning?
Acetylcysteine.
Why is INR increased and platelet levels decreased in paracetamol overdose?
•Hepatic failure causes reduction in antithrombin
More thrombin causes DIC
DIC uses up all platelets
•Clotting factors + platelets are used up > bleeding
What factors influence hepatotoxicity in a paracetamol overdose?
•Dose of paracetamol ingested
•Plasma paracetamol concentration
•Time of administration of antidotal therapy
•Nutritional status
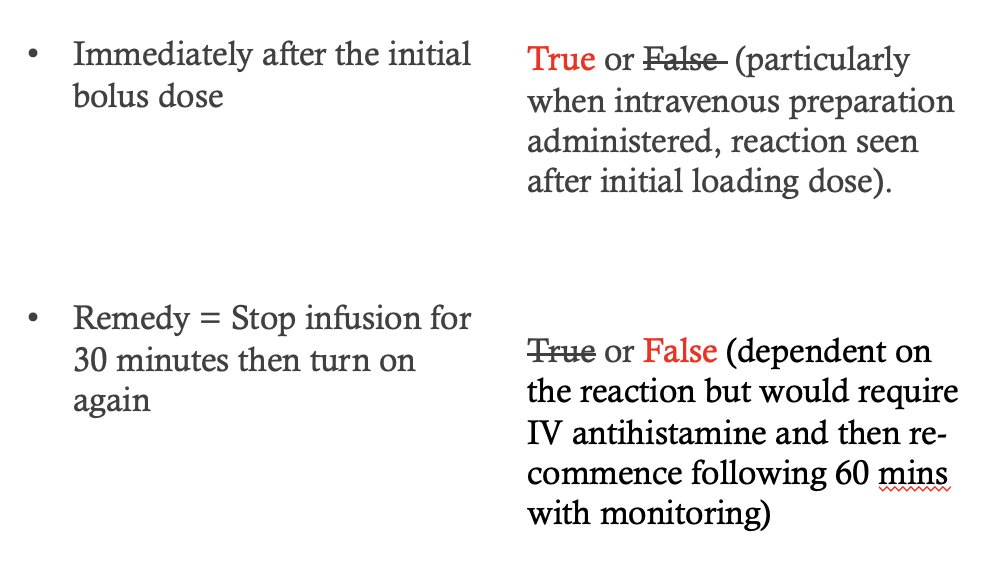
What adverse events can occur with acetylcysteine administration?
Why does phosphate decrease in paracetamol poisoning?

How does NAPQI damage the liver?
By depleting glutathione, which protects hepatic cells from oxidative damage.
How is NAPQI removed from the body?
Through conjugation with glutathione,
forming cysteine and mercapturate conjugates.
What happens to the conjugation pathway during paracetamol overdose?
It becomes saturated,
leading to increased conversion to NAPQI.
What should be monitored during acetylcysteine infusion?
Adverse events
occurring immediately after the initial bolus dose.
What are the two main mechanisms for paracetamol metabolism?
Conjugation and oxidation.
What are the potential outcomes of severe paracetamol poisoning?
Jaundice,
liver failure,
encephalopathy,
DIC, and cardiac arrhythmias.