OTH 5217–Exam 3: Discharge and Settings
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Continuum of healthcare
variety of settings form a continuum of care
patients may enter at any point
progress is not always sequential
available services vary across settings
The Delivery of OT services in each setting are influenced by?
OT ethical principles
other stakeholders
accrediting organization and agencies
-ACHA, CMS, TJC, CARF
government regulations/reimbursement
-medicare PPS: set fee per patient on the basis of the patient’s diagnosis-related group (DRG), regardless of the actual cost of services
quality
-HCAHPS: Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems Survey measures patient satisfaction, discharge information, responsiveness of hospital staff, and physician–nurse communication
-patient protection and ACA: law to improve quality of care and reduce readmissions
The primary risk factors for patient readmission within 30 days of discharge include:
-living alone
-having unmet ADL and IADL functional need
-lacking skills necessary for carryover of health and medical regime and recommendations
-having limited education
T or F: Approximately 25% of Medicare patients return home with un-met ADL needs, which are defined as not having the necessary help, needing more help, or having to wait to perform basic ADLs and functional mobility until help arrives.
true
OT CAN HELP reduce readmission rates!!!!
Modifiable readmission risk factors
-Functional status, including poor prior level of function with ADLs and mobility status
-Falls
-Depression before, during, and after a hospital admission is associated with impaired cognition, an inability to retain discharge education, and poor compliance with medical recommendations such as medication or diet regimens
-Inadequate family education when preparing for discharge
-Cognitive impairment (especially memory) leads to multiple issues, including poor adherence to medical discharge instructions because of poor retention, decreased quality of life, caregiver distress, delirium, and poor pain control.
Non-modifiable readmission risk factors
-Advanced age is associated with malnutrition and more falls.
-Obesity is associated with higher risk for chronic conditions that lead to recurrent hospitalizations such as diabetes, coronary events, and hypertension.
-Medications, especially polypharmacy, complex regimens, and medications that are sedating (e.g., tranquilizers or hypnotics).
-Multiple comorbidities (e.g., chronic disease, age, and psychological issues).
-Shorter and longer lengths of stay in the hospital.
-Social factors
Tor F: Longer stays are associated with physical decline, which leads to a functional status decline. Shorter stays are associated with patients being discharged "quicker and sicker".
true
True of F: Although some barriers for discharge are non-modifiable and the therapist has no control over those issues (e.g., illegal resident status, no insurance, no family), occupational therapy practitioners can control documentation that does not sabotage the hospital's efforts to successfully discharge the patient to the next level of care.
true
documenting recommendations is an important aspect in discharge process
What is discharge planning?
Coordinating, planning, and arranging for the transition from one health care setting to another
What is the goal of discharge planning?
to transition patient to the safest and least restrictive environment
What are disposition sites?
places/settings to which a patient might be discharged
The next level of care (disposition site) is based on.......
-functional level
-safety and risk avoidance
-economic reality of reimbursement rules
If disposition is to the home environment, the OT shoulder consider..........
accessibility
-ramps, doorway and hallway width, bathroom, etc
caregiver abilities
-physically able? part-time or full-time?
safety
-is the home safe and accessible? can the client perform ADLs/IADLs safely?
When looking at disposition sites, the OT should consider......
prior level of function
current level of function
disparity between prior and current functional levels
patient and family matters (values, roles, beliefs)
patient's cognitive function*
rehab potential
patient competency
patient decision-making capacity
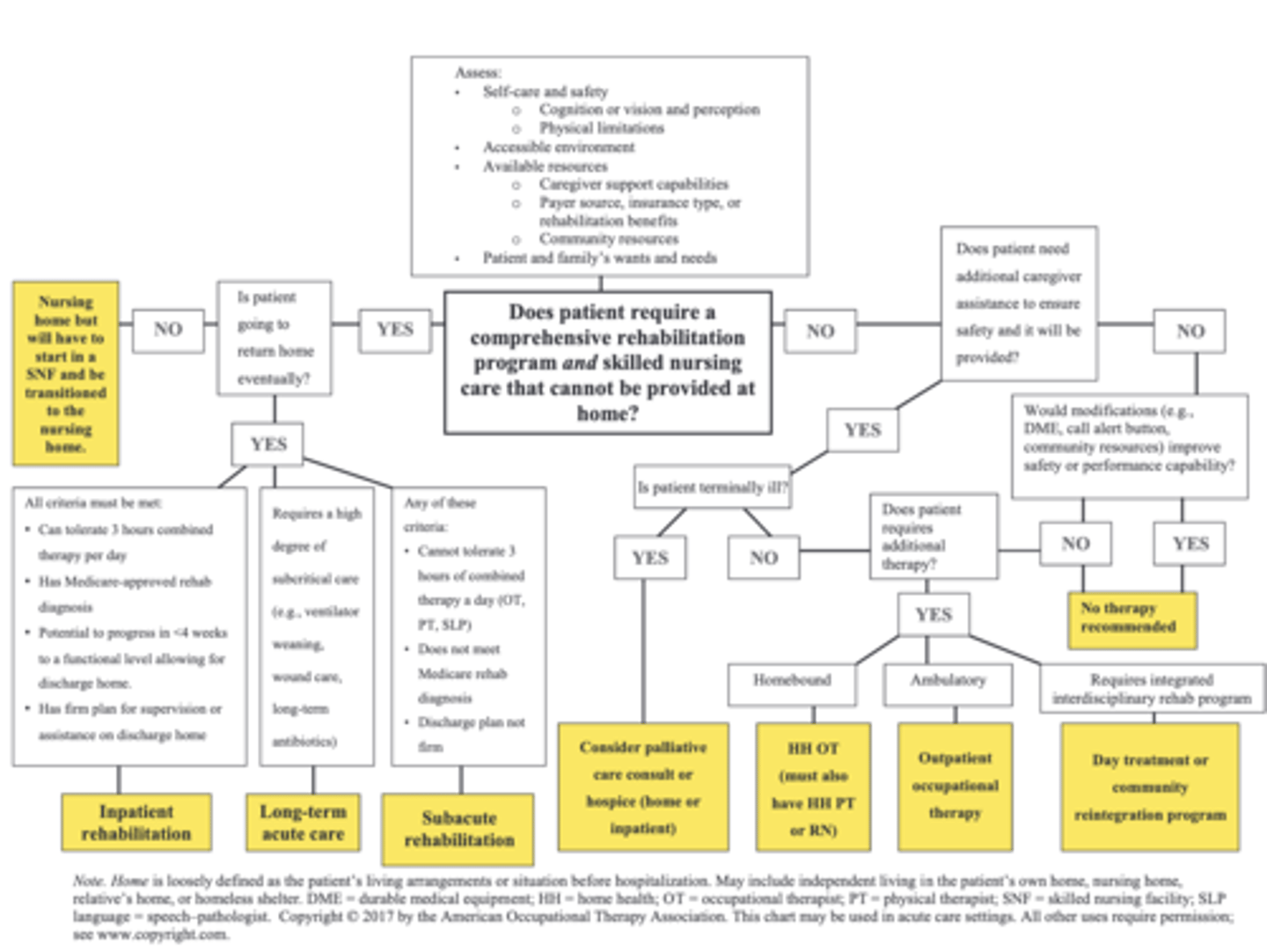
What is prior level of functioning? How is it assessed?
how the patient performed ADLs prior to admission
assessed by exploring the patient's:
-home environment
-motivation to engage in life versus just existing
-prior IADL and BADL status
-fall risk
-support systems, including the caregiver's realistic capabilities to physically, emotionally, and logistically provide care
What is current level of functioning? How is it assessed?
focuses on BADLs and functional mobility
assessed by extrapolating details from the patient's:
-task performance and their safe and effective use of adaptive equipment or techniques
When looking at if there is a disparity between prior and current functional levels, the OT should consider.......
How has the patient’s illness actually affected his or her ability to function?
Did the patient accurately report a realistic prior level of function immediately preceding his or her admission? Were some important details left out?
example
a patient has clearly demonstrated an inability to put on underwear, socks, and shoes over the feet, asking how they accomplished dressing at home may permit the patient to share that family members always help, even though the patient reported being independent.
T or F: Because time is so limited in an acute care setting, cognition is generally assessed for basic occupations with a detailed activity analysis of the skill components involved in the task. If there are deficits in mild executive functioning skills (difficulty problem-solving obstacles, cognitive flexibility, higher reasoning) or if high-level cognitive deficits are noted, continued outpatient services with occupational therapy, speech-language pathology, and neuropsychology are recommended.
true
(this refers to deciding disposition site and looking at patient's cog function)
________________ is a legal decision a judge makes after considering the testimony of health care providers and evaluating medical information
competency
Patient competency
therapy staff does not directly make competency decision but rather provides information to the physician (psychiatrist typically)
only courts can declare incompetence
-laws vary by state
_______________ is the ability to understand and make rational decisions when presented with the facts
decision-making capacity
What is an important factor to look at when evaluating a a patient's decision making capacity?
their ability to make rational decisions based on facts i.e.
-understanding options
-reasoning and appreciation: insight of consequences
-expressing and making choices: executive functioning
To determine competency, the health care team must establish the patient's capacity for decision making, which has the following requirements:
understanding: must have the ability to clearly understand the options and ramifications of each option; patients must be able to make an educated decision after being informed of all the options
reasoning and appreciation: must have a stable and competent set of values upon which decisions are generally made; being able to articulate why a specific decision was made and how their choices will affect them
expressing and executing a choice: must be able to actually make decisions, autonomously and without coercion; must also be able to demonstrate executive function sufficient for implementing a solution
What is the general flow/order of settings?
1) inpatient settings
-acute care
-inpatient rehab facility
-subacute rehab or SNF
2) home health services
3) outpatient settings
-day treatment programs
-outpatient facility
4) other
-hospice
-LTACH
Inpatient settings include
acute care
inpatient rehab
acute rehab
subacute rehab
SNF
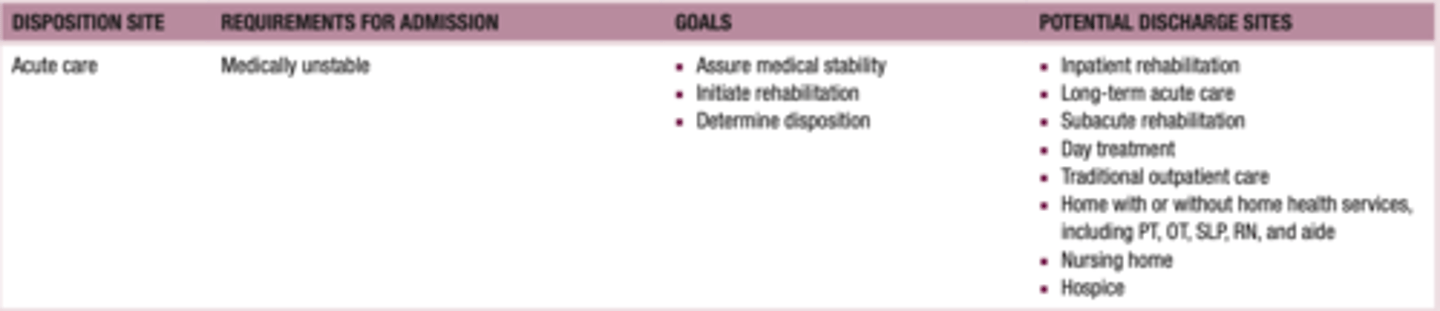
What is acute care?
24-hour skilled care for short-term illnesses or injuries; generally given in hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers
hospitalization due to:
-new medical condition
-exacerbation of chronic condition
initiates the rehab process
focus on clients' needs after DC from acute
-disposition to: inpatient, SNF, home health, outpatient, hospice, etc.
Inpatient rehab facility: Admission requirements
discharge plan is identified
-home, family's home, or ALF
-nursing home is unacceptable disposition
patient's must tolerate
-at least 3 hours of intensive therapy/day
-at least 5-7 days per week
-day (1) starts with the day of admission
-requires 24-hour nursing care but is medically stable
-must qualify under 1/13 diagnostic categories (CMS 60% rule–stroke, SCI, TBI)
must require more than 1 type of therapy
-any combo of OT, PT, SLP
usual LOS = 7-28 days
-average = 13 days

Inpatient rehab facility: Goal and and discharge disposition
goal is to discharge to community
disposition sites
-home w/ or w/o health services
-ALF
-traditional outpatient
-day treatment center

Subacute rehab or SNF: Admission requirements
-therapies are provided at an intensity of <3 hr/ day (usually closer to 1.5 hr/day)
-usually housed in a nursing home in a separate department
-allows for slower progression (slow paced rehab)
-LOS: may be up to 100 days
not permanent residents
Subacute rehab or SNF: Discharge disposition
home w/ or w/o home health
day treatment
traditional outpatient
inpatient rehab (rare!!!!!!!)
Skilled nursing facilities
-institution that meets CMS criteria for skilled nursing care, including rehab services
-may 'house" subacute rehab services
those receiving services, but not in subacute
-considered "residents" not patients
-preferred consumer label for people who live in LTC facilities
may have goals to increase participation or maintain current level (prevent further decline)
long-term placement of residents (subacute rehab not)
Home health: Admission requirements
-client must be homebound
-provided within the clients home
-most natural context for intervention
-support occupational participation in the home environment
-OT now acts a "stand alone" therapy for HHS
not as intensive as rehab facility
-patients not seen daily
-2-3 times per week
Home health: Discharge disposition
Day treatment
Traditional outpatient
What is included in outpatient settings?
includes
-day treatment
-outpatient facilties
What are outpatient services?
-freestanding facilities or hospital based
-patients are medically stable
-able to travel within community to receive services
-OT must ascertain level of performance and occupational engagement in different environments (home, work, etc.)
Day treatment programs: Admission requirements
-community-based intervention setting
-provides intensive interdisciplinary interventions
-clients are community-dwelling individuals
-provides further recovery after serious acute injury (TBI, CVA, progressive neurodegenerative disorders)
Day treatment programs: Goals
focuses on patient's awareness and tx of his or her impairments
emphasis on return to function
-community re-integration
-return to work or school
-IADLs
-basic ADLs
not as affected by time constraints
ex: plan functional outings, day trips
Outpatient facility: Admission requirements
-medically stable
-living at home
-may require a single discipline or multidisciplinary approach
-extensive patient/family education (improves carryover; prepare for final DC from therapies)
-typically, last level of continuum of care
What are other disposition settings?
hospice
LTAC
Hospice: Admission requirments
Inpatient hospice requirements:
-terminally ill with <6 mo to live
-acute medical intervention or nursing care for palliation of symptoms
In-home or nursing home hospice requirements:
-terminally ill with <6 mo to live
Hospice: Goals
-comfort measures
-usually minimal to no provision of rehabilitation
-family education to ensure patient's needs and desires are being met
Long-term acute care (LTAC): Admission requirements
-hospital-level inpatient care for those who require extended stays
-subcritical care provided; the patient still requires a high level of skilled care because of medical complexity of illness but is not critically unstable
Requirements for admission:
-may be ventilator dependent initially but admitted for ventilator weaning
-or is on ≥ 2 antibiotics
-or has complex wound care requirements
-most patients are referred from ICU—stable, but too sick for general floor care
-nurse or social worker in conjunction with the medical director evaluates patient referrals in conjunction with medical director of long-term acute care
LTAC: Discharge disposition
Hospice
Nursing home
Inpatient rehabilitation
Subacute rehabilitation
Home with or without home health services,
including PT, OT, SLP, RN, and aide
Outpatient