MSK non neoplstic bone & cartilage
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
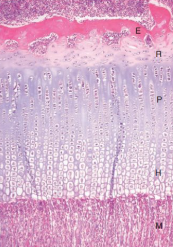
What does R, P and H represent?
reserve, proliferative and hypertrophic zones of the physis/growth plate
What are the biomarkers for bone and explain their levels
ALP - present in all tissue but mainly liver, kidney, placenta and bone. Raised in young animals and in animals with bone-forming tumours
Calcium - raised in diseases involving bone metabolism. Hypercalcaemia of malignancy.
Two examples of congenital chondrodysplasia in farm animals
Bulldog calves
Spider lamb syndrome
Cause, Gross and histo features of bulldog calves
Affects Dexters and other minatures
Caused by 2 different mutations in ACAN gene
Gross:
aborted before 7th month of gestation. Small calves, short limbs, protruding mandible, domed head, cleft palate, normal size tongue protruding from mouth
Histo:
lacks distinct growth plates
densely packed chondrocytes in physeal cartilage with no orderly arrangement. Fibrillar eosinophilic intercellular matrix

Cause, gross and histo pathology of spider lamb syndrome
Affects Suffolk and Hampshire sheep.
Caused by autosomal recessive mutation of FGFR3 gene
Gross:
long limbs and neck, shallow body, scoliosis/kyphosis of thoracic spine, concave sternum and other sternal deformities
Valgus deformity of forelimbs causing knocked-kneed appearance
Histo:
abnormal ossification centres in bone developed by endochondral ossification
What breeds of cat get osteochondrocysplasia, its cause and gross and histo pathological features
Scottish fold, American curl
Autosomal dominant fold-eared gene
Gross:
irregular size and shape of tarsal, carpal., metatarsal, metacarpal, phalanges and caudal vertebrae
secondary degenerative arthropathy
Histo:
defective endochondral ossification in physes beneath articular cartilage

Signalment, pathogenesis and gross and histo pathology of physeal dysplasia in cats
Male overweight Siamese and Maine Coons
usually 2-4 years, older than expected age of physeal closure (7-9 months)
Unknown pathogenesis
Physeal dysplasia affects all growth plates but only proximal femur fractures (due to force)
Gross = avulsed head of femur
Histo: dysplastic growth plates = disorganised clusters of chondrocytes surrounded by abundant matrix
Gross and histo pathology of osteogenesis imperfecta. What is the pathogenesis.
Gross:
marked joint hypermobility causes inability to stand
dentinogenesis imperfecta
normal shape bones but very brittle
Histo:
variable osteoblast numbers and activity
calcified cartilage spicules in primary spongiosa lined by very thin layer of basophilic bone matrix
little osteoclastic resorption or trabecular realignment. woven bone may line deeper secondary spongiosa
caused by collagen chain mutations in goldies and beagles (COL1A1 and COL1A2)
autosomal recessive mutation of SERPINH1 in dachshunds of collagen chaperone HSP47
Breed predisposition: holstein-friesians, charolais, angus, Romney lambs, the dog breeds mentioned above
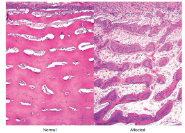
Name this pathology and what causes it? Explain the pathogenesis. Describe the histology.
Lead line (band of sclerosis), caused by lead toxicity - a toxic osteodystrophy
Pathogenesis: impaired osteoclastic resorption. May contain acid-fast intranuclear inclusions.
Histo = persistence of mineralized cartilage trabeculae in the metaphysis
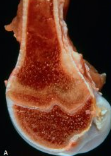
Cause of this toxic osteodystrophy in a cat. Explain the pathogenesis and gross and histo appearance.
Vitamin A toxicity, seen in cats fed liver.
Pathogenesis:
inhibition of chondrocyte proliferation and reduction in RNA and protein synthesis
Gross hallmark = osteophyte formation = deforming cervical spondylosis
Histo
physeal lesions = reduced chondrocyte proliferation = narrow growth plates
osteoporosis = decreased osteoblasts and thinner osteoid seams
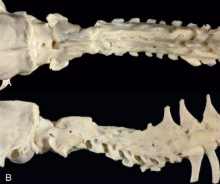
What is this condition and explain its pathogenesis. Describe the main gross and histo features.
Rickets = defective endochondrial ossification
Caused by insufficient dietary phosphorous or calcium/inappropriate ratio of the two, insufficient availability of activated vitamin D.
Gross:
bowed legs, swollen joints. mostly at sites of rapid growth (long bone metaphysis, costochondral junction = rachitic rosary)
Histo:
hypertrophic chondrocytes at physes and beneath articular cartilage = hallmark
Compare the histology of rickets and osteomalacia
Rickets shows pathology in the growth plates, while as osteomalacia affects adults it involves points under the most mechanical stress, such as where tendons intersect. These areas show localised accumulation of osteoid too.
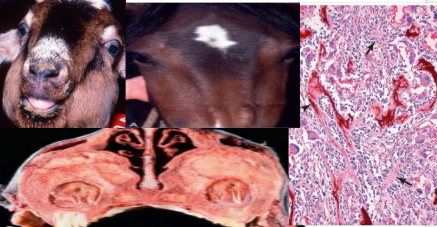
What is this condition? Explain its pathogenesis. Describe the main gross and histological pathology.
Fibrous osteodystrophy
Pathogenesis: Persistently elevated parathyroid hormone (usually secondary to chronic renal disease or calcium/phosphorous dietary imbalance) eventually leads to generalised bone resorption.
Herbivores on high bran/concentrate diet, or carnivores on meat and offal only diets.
Gross: bilateral enlargement of skull bones, including maxilla and mandible
Histologically has 3 key features:
osteoclastic bone resorption
fibrosis
osteoblastic deposition of new woven bone
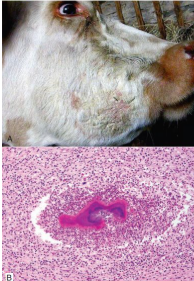
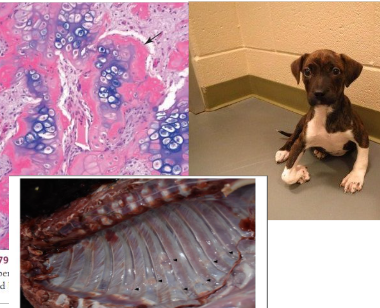
Cause of mandibular osteomyelitis in calf. Describe the gross and histological features.
Actinomyces bovis bacteria
Gross = honeycomb appearance due to pockets of inflammation surrounded by reactive bone
Histo = A.bovis colonies surrounded by Splendore-Hoeppli material, suspended in neutrophilic exudate
What is the cause of atrophic rhinitis in pigs and describe the pathogenesis.
Pasteurella multocida and Bordetella bronchiseptica produce toxins
Toxins inhibit osteoblast differentiation and stimulate osteoclastic activity = bone loss
What bacteria are involved in vertebral osteomyelitis in large animals? what is the most common?
Trueperella pyogenes = most common
Staphylococcus aures = invades osteoblasts
E.coli
Salmonella enterica Typhimurium
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Mannheimia haemolytica ….
Haematogenous infection of bone is the most common
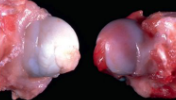
Pathogenesis of avascular necrosis of the femoral head and its gross and histo features.
Affects westies aged 4-8 months
Pathogenesis = autosomal recessive trait
ischaemia = delayed incorporation of blood vessels into femoral head
Gross = fracture and collapse of necrotic trabecular bone, and flattened femoral head
Histo = subchondral epiphyseal osteonecrosis