4.2 Unit circle and Values and tricks
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
UNIT CIRCLE FORMULA
x²+y²=1
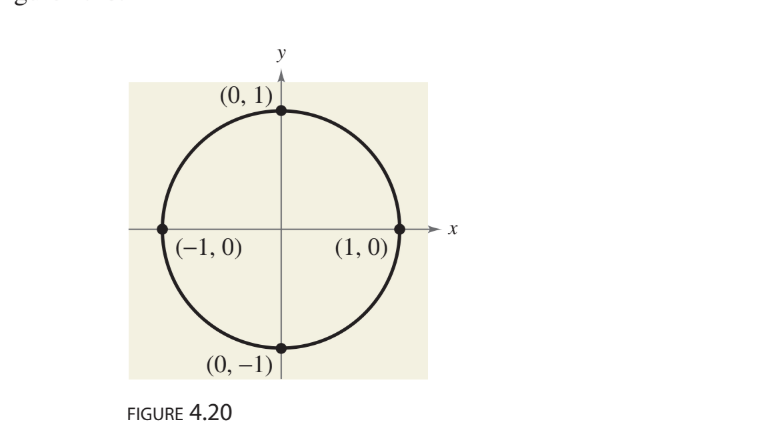
On Unit circle what are Sin and Cos
Sin=y-value
Cos-x-value
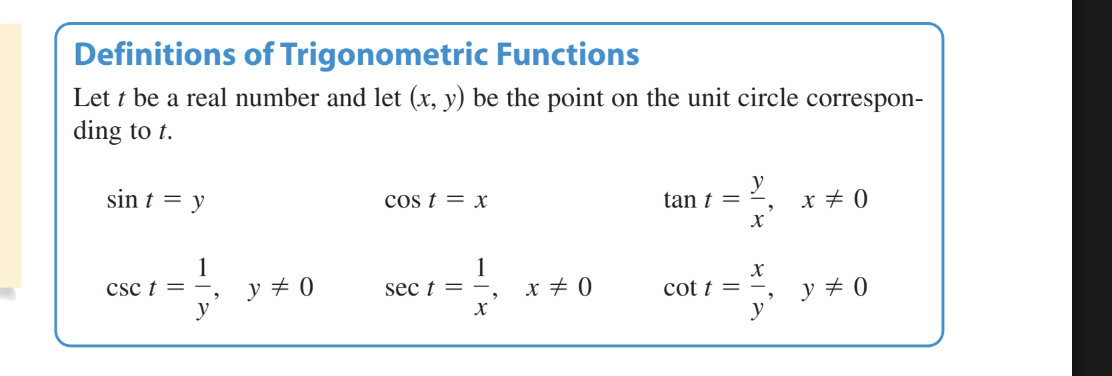
ON UNIT CIRCLE WHAT ARE VALUES FOR ALL TRIG FUNCTIONS IN X and Y terms
sinx=y cosx=x tanx=y/x. x cannot equal 0. cotx= x/y. y cannot equal 0. secx= 1/cos. cos cannot be 0. cscx=1/sin. sin cannot be 0
Practice problem: Find 4 values of theta (2 + and 2- ) that satisfy the following equation: cos theta =( -square root 3 /2) Give your answer in radians
5π/6, 7π/6, -5π/6, -7π/6
Practice problem: evaluate the six rtrig functions where sec(theta)=-17/8 and sin theta >0
sin(theta)=15/17
cos(theta)= -8/17
tan(theta)=-15/8)
sec(theta)=-17/8
csc(theta) = 17/15
cot(theta) -8/15
0°
Radians: 0, sin θ: 0, cos θ: 1, tan θ: 0, csc θ: undefined, sec θ: 1, cot θ: undefined
30°
Radians: π/6, sin θ: 1/2, cos θ: √3/2, tan θ: √3/3, csc θ: 2, sec θ: 2√3/3, cot θ: √3
45°
Radians: π/4, sin θ: √2/2, cos θ: √2/2, tan θ: 1, csc θ: √2, sec θ: √2, cot θ: 1
60°
Radians: π/3, sin θ: √3/2, cos θ: 1/2, tan θ: √3, csc θ: 2√3/3, sec θ: 2, cot θ: √3/3
90°
Radians: π/2, sin θ: 1, cos θ: 0, tan θ: undefined, csc θ: 1, sec θ: undefined, cot θ: 0
120°
Radians: 2π/3, sin θ: √3/2, cos θ: -1/2, tan θ: -√3, csc θ: 2√3/3, sec θ: -2, cot θ: -√3/3
135°
Radians: 3π/4, sin θ: √2/2, cos θ: -√2/2, tan θ: -1, csc θ: √2, sec θ: -√2, cot θ: -1
150°
Radians: 5π/6, sin θ: 1/2, cos θ: -√3/2, tan θ: -√3/3, csc θ: 2, sec θ: -2√3/3, cot θ: -√3
180°
Radians: π, sin θ: 0, cos θ: -1, tan θ: 0, csc θ: undefined, sec θ: -1, cot θ: undefined
210°
Radians: 7π/6, sin θ: -1/2, cos θ: -√3/2, tan θ: √3/3, csc θ: -2, sec θ: -2√3/3, cot θ: √3
225°
Radians: 5π/4, sin θ: -√2/2, cos θ: -√2/2, tan θ: 1, csc θ: -√2, sec θ: -√2, cot θ: 1
240°
Radians: 4π/3, sin θ: -√3/2, cos θ: -1/2, tan θ: √3, csc θ: -2√3/3, sec θ: -2, cot θ: √3/3
270°
Radians: 3π/2, sin θ: -1, cos θ: 0, tan θ: undefined, csc θ: -1, sec θ: undefined, cot θ: 0
300°
Radians: 5π/3, sin θ: -√3/2, cos θ: 1/2, tan θ: -√3, csc θ: -2√3/3, sec θ: 2, cot θ: -√3/3
315°
Radians: 7π/4, sin θ: -√2/2, cos θ: √2/2, tan θ: -1, csc θ: -√2, sec θ: √2, cot θ: -1
330°
Radians: 11π/6, sin θ: -1/2, cos θ: √3/2, tan θ: -√3/3, csc θ: -2, sec θ: 2√3/3, cot θ: -√3
360°
Radians: 2π, sin θ: 0, cos θ: 1, tan θ: 0, csc θ: undefined, sec θ: 1, cot θ: undefined
Quadrant I
sin: +, cos: +, tan: +
Quadrant II
sin: +, cos: -, tan: -
Quadrant III
sin: -, cos: -, tan: +
Quadrant IV
sin: -, cos: +, tan: -
Trick for knowing what is positive and negative
ALL STUDENTS TAKE CALCULUS
All are positive in first quadrant
Only Sin is positive in second quadrant
Only Tan is positive in 3rd quadrant
Only cos is positive in 4th quadrant
What is a refrence angle
The angle that is made with the x-axis, use angle with that to find out.
What are coterminal Angles
and why do they matter
Coterminal angles are angles that share the same initial and terminal sides on the unit circle, meaning they end in the same position. You find them by adding or subtracting full rotations: 360 degrees or 2π radians.
All trig function values (sin, cos, tan, etc.) are the same for coterminal angles because they land at the same point on the unit circle.
30° Family (30 degree refrence angle)
30°, 150°, 210°, 330°; π/6, 5π/6, 7π/6, 11π/6; sin: ±½, cos: ±√3/2, tan: ±√3/3
45° Family (45 degree refrence angle)
45°, 135°, 225°, 315°; π/4, 3π/4, 5π/4, 7π/4; sin: ±√2/2, cos: ±√2/2, tan: ±1
60° Family (60 degree refrence angle)
60°, 120°, 240°, 300°; π/3, 2π/3, 4π/3, 5π/3; sin: ±√3/2, cos: ±½, tan: ±√3