Cell-cell communication: Neurons
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
what is the nervous system consisted of?
brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves
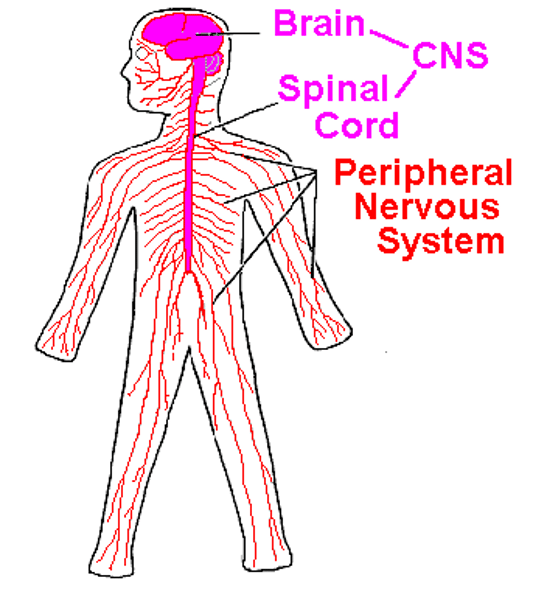
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
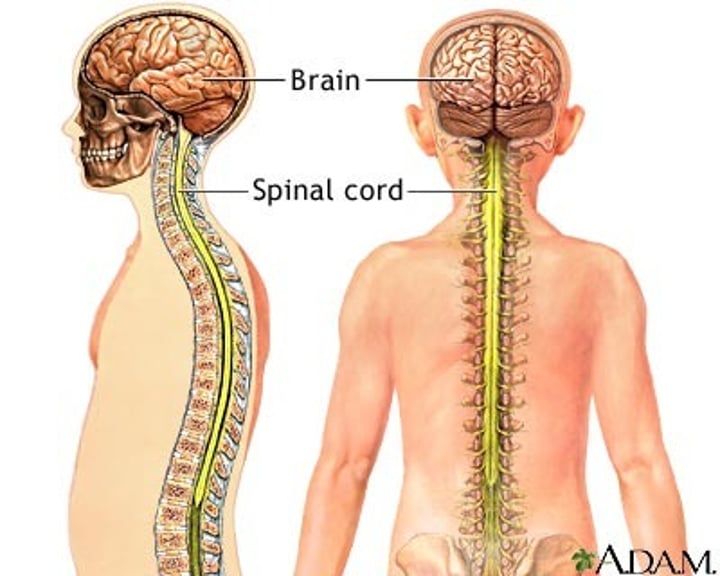
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles; controls voluntary activity
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs such as the heart; controls involuntary activity
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations (fight or flight)
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy (rest and digest)
reflex
a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus
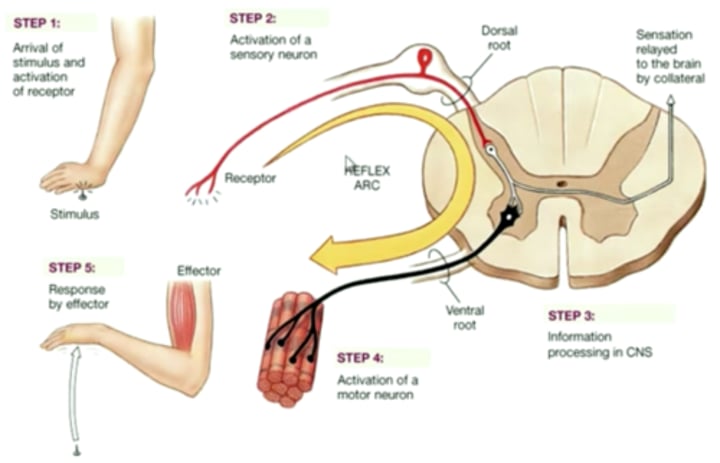
what are the 3 types of neurons?
sensory (afferent), motor (efferent), interneurons
sensory neuron
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
afferent neurons
Nerve cells that carry impulses towards the central nervous system
efferent neurons
Nerve cells that conduct impulses away from the central nervous system
motor neurons
control the activity of muscles
interneurons
pass signal from one neuron to another
Neuroglia
cells that support and protect neurons; can divide but cannot transmit cell signals
components of a neuron
cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin
cell body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
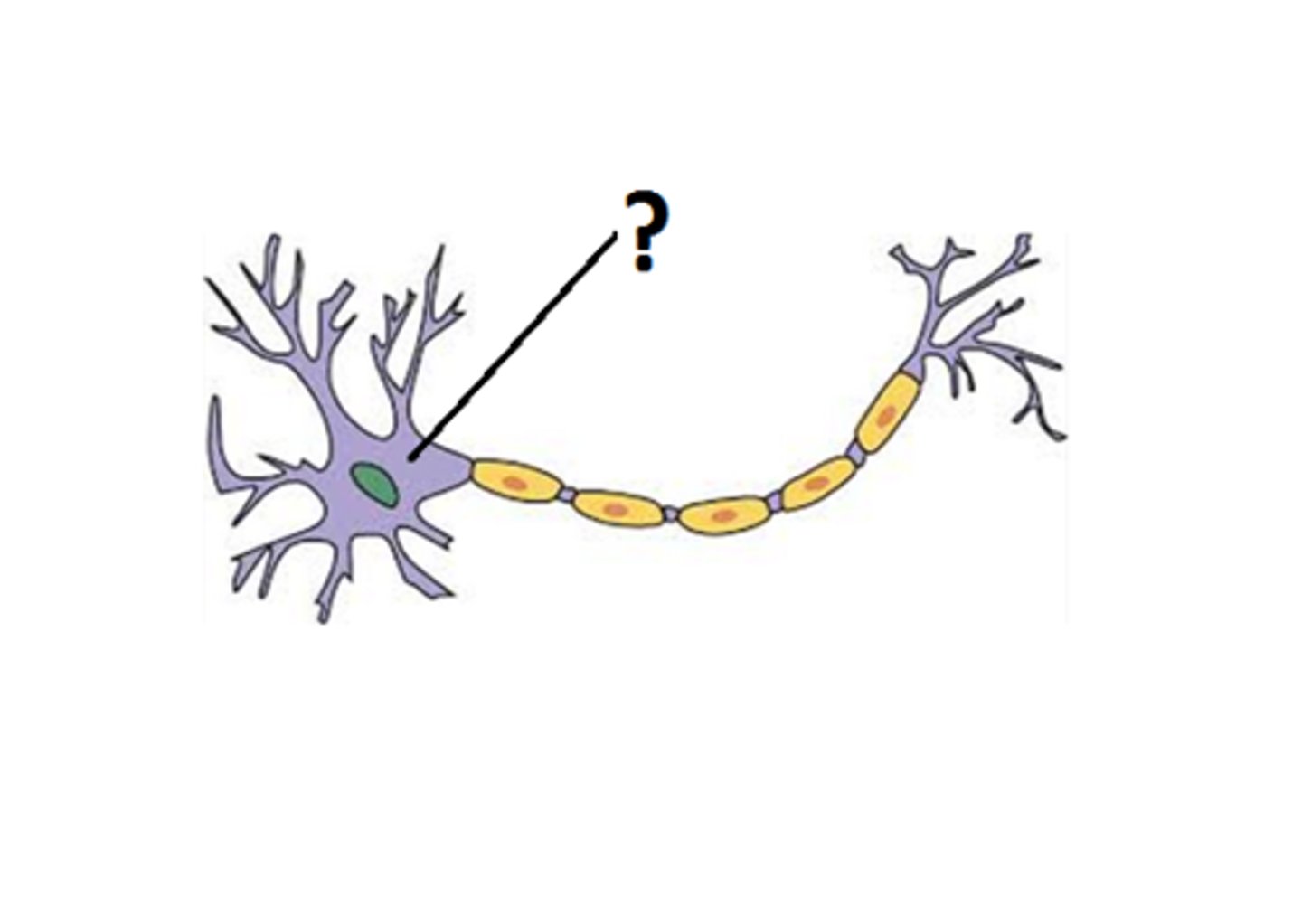
dendrites
receive chemical signals from other neurons and convert them into electrical signals
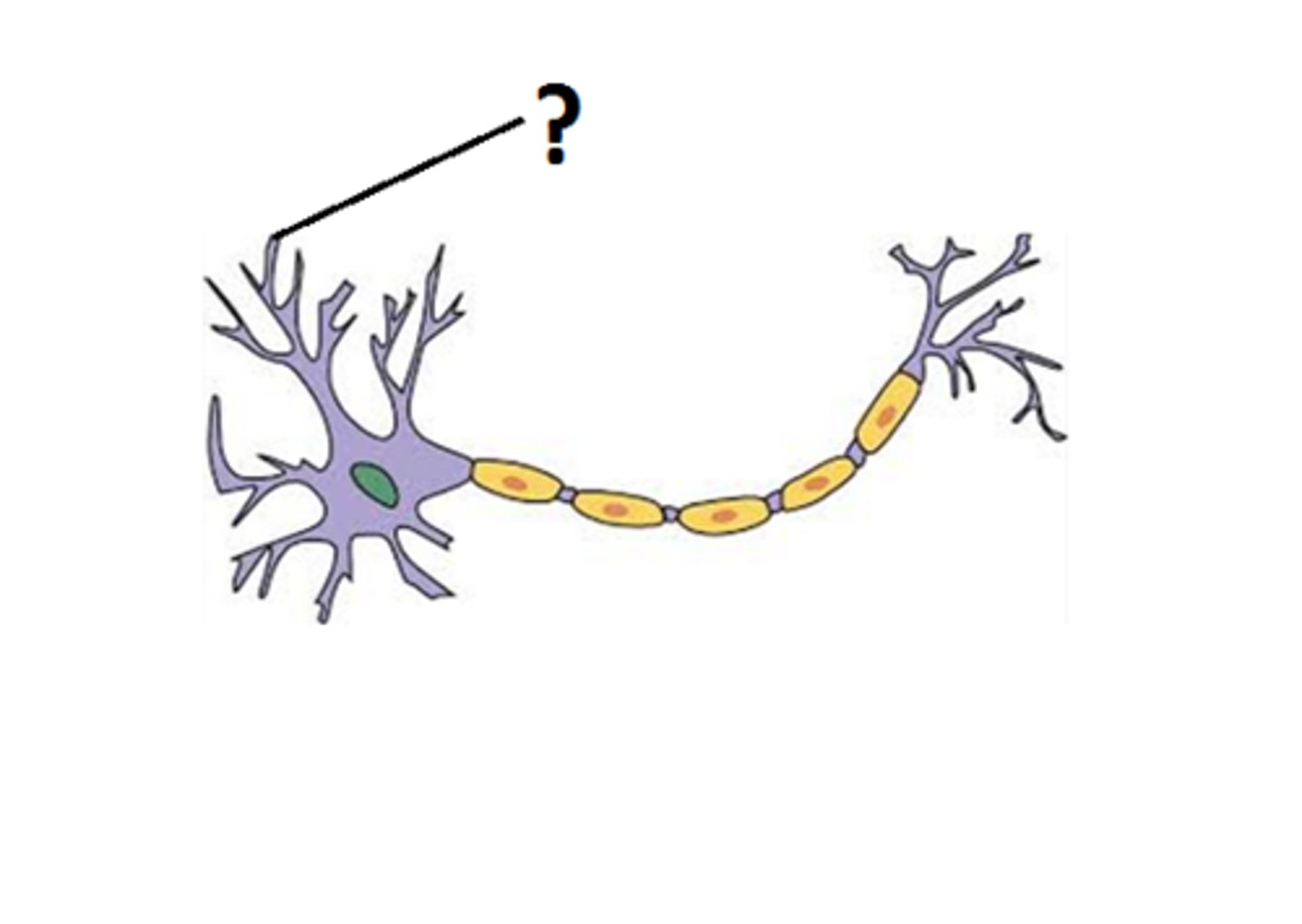
axons
a part of a neuron that carries impulses away from the cell body
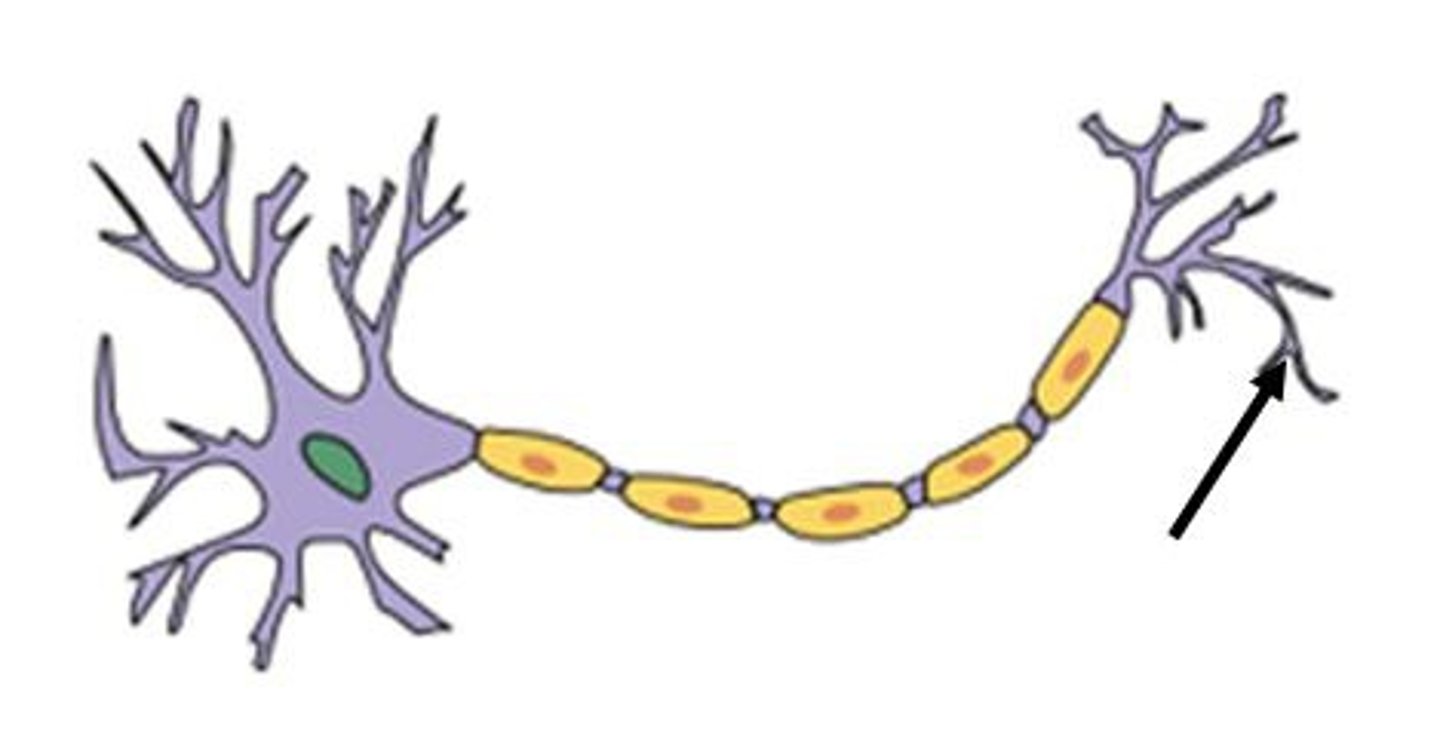
axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
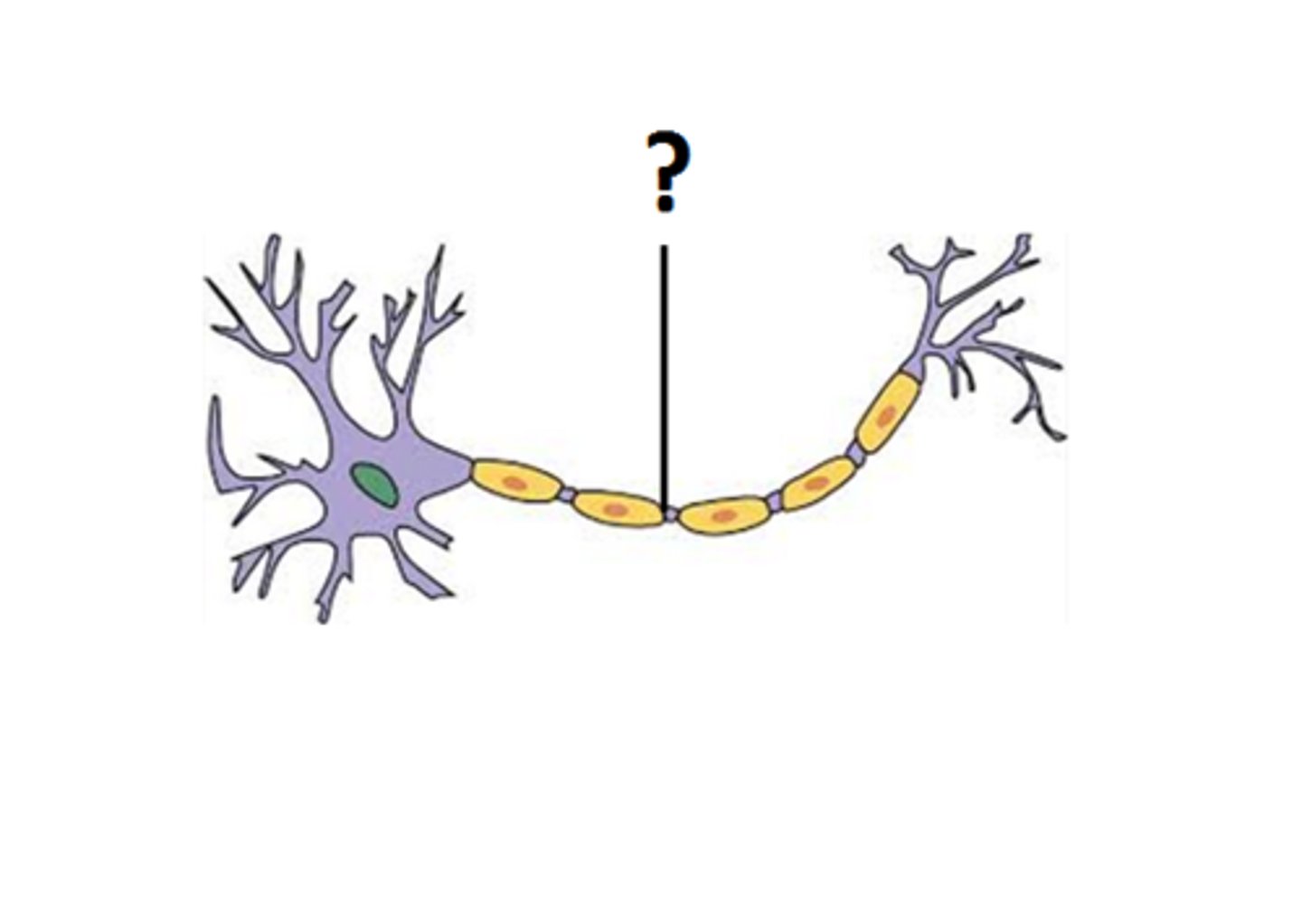
myelin sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
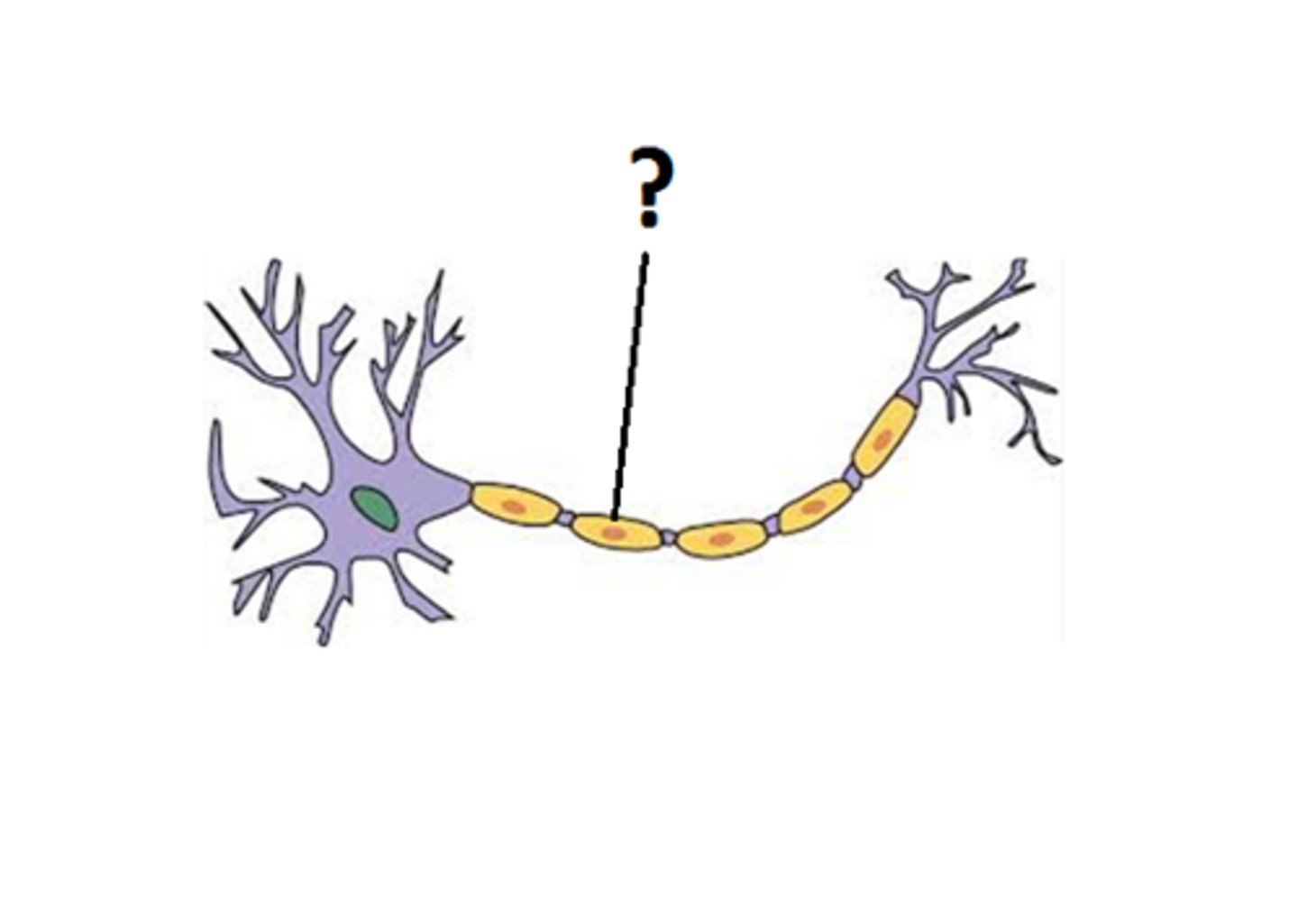
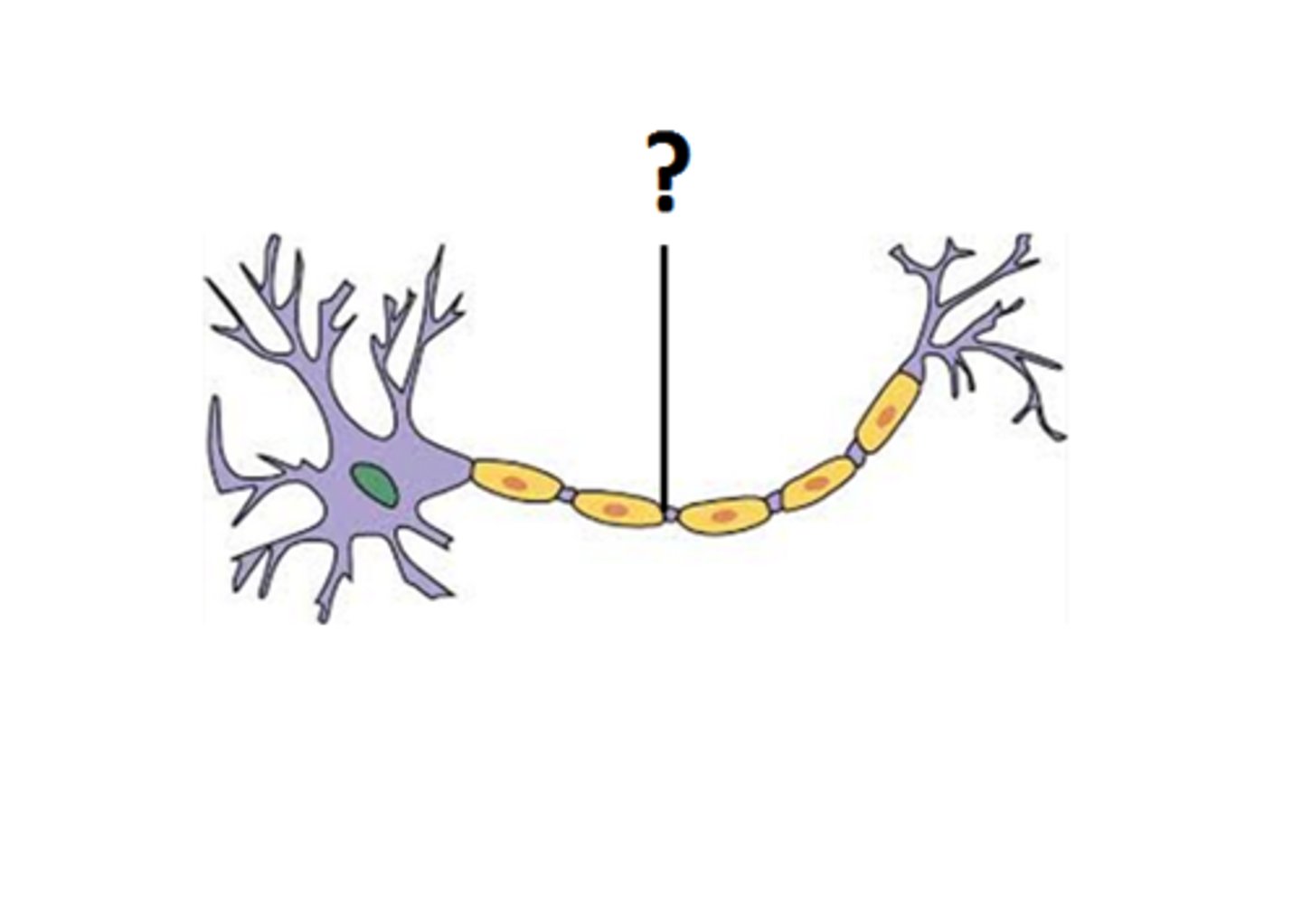
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in myelin sheath along the axon
membrane potential
the voltage difference across a membrane
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
resting potential of a neuron
stable, negative charge when the cell is inactive
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Electrical vs. chemical signals
Inside neuron - electrical
In between neurons - chemical
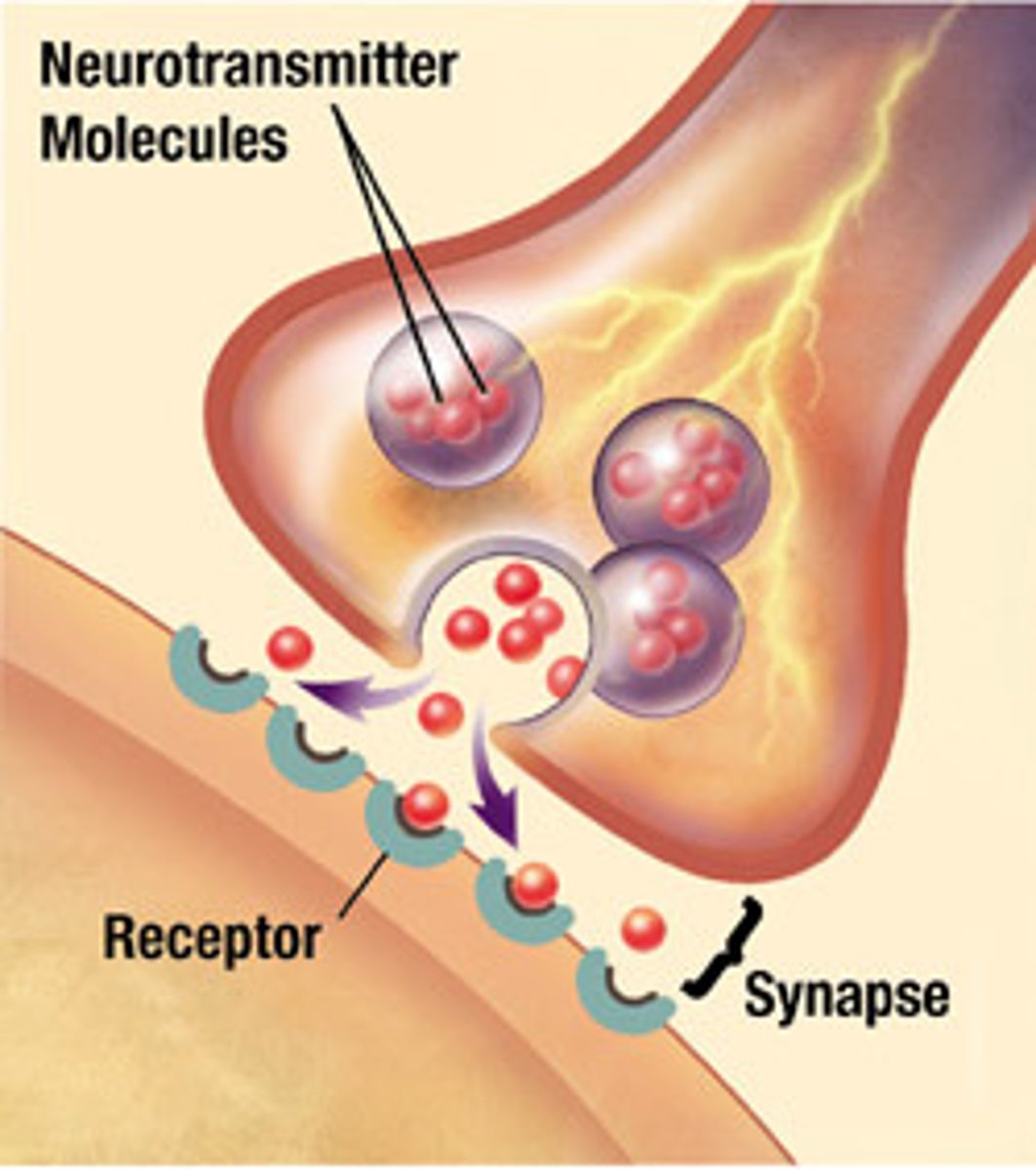
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
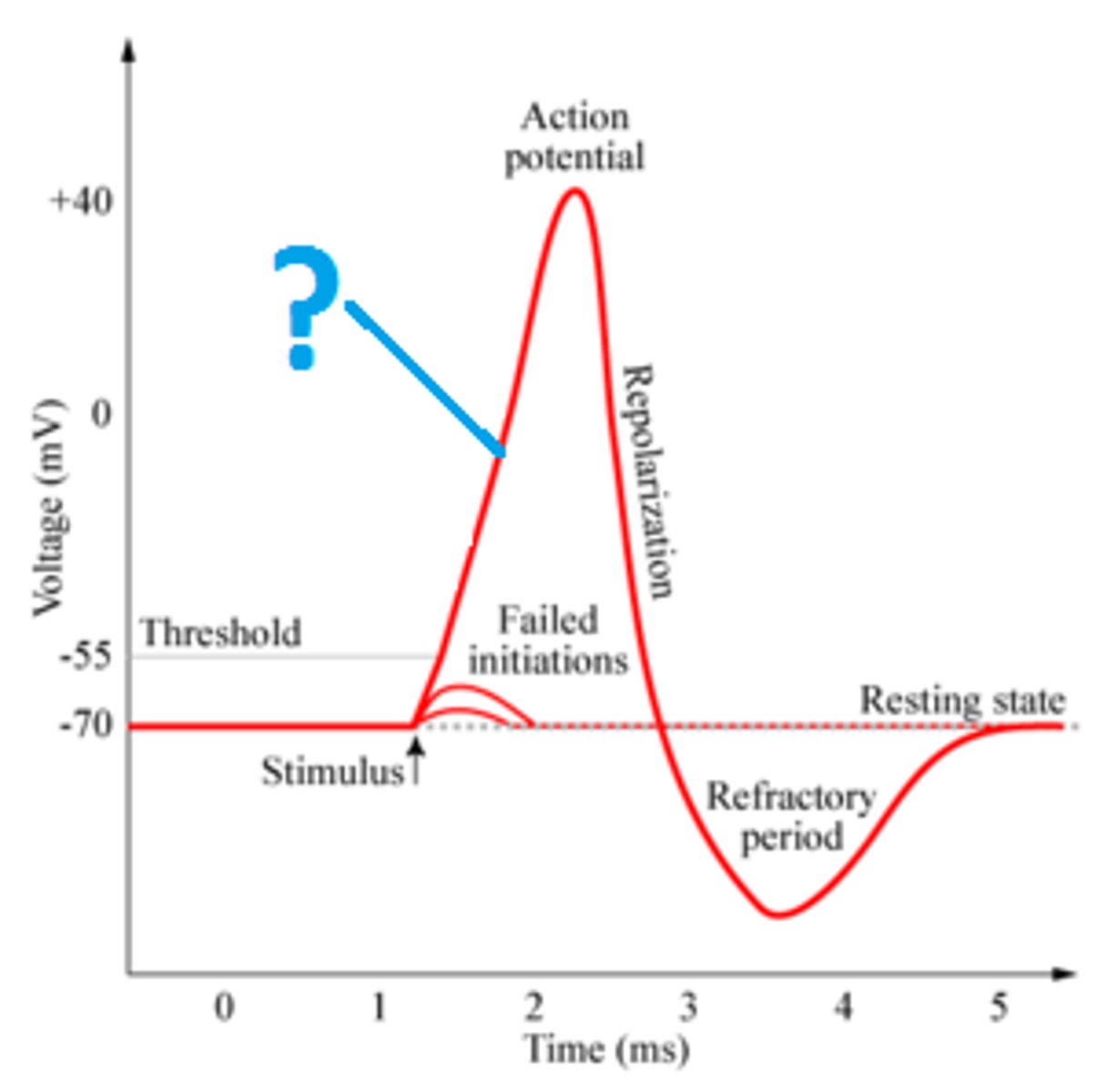
Depolarization
The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive.
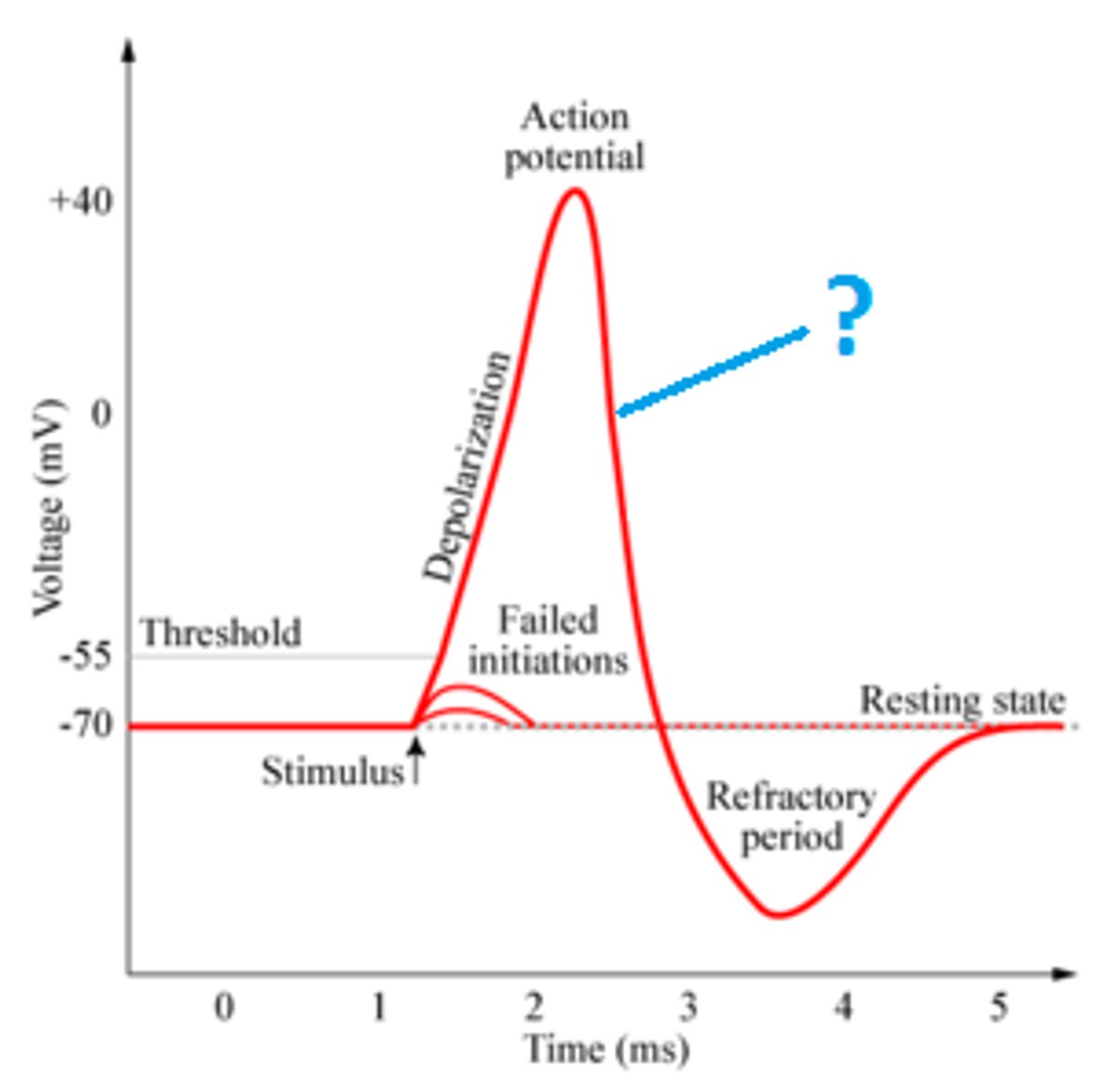
Repolarization
Return of the cell to resting state
Synapse
the junction between the axon terminal of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath