Polarity and Intermolecular Forces in Molecules
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
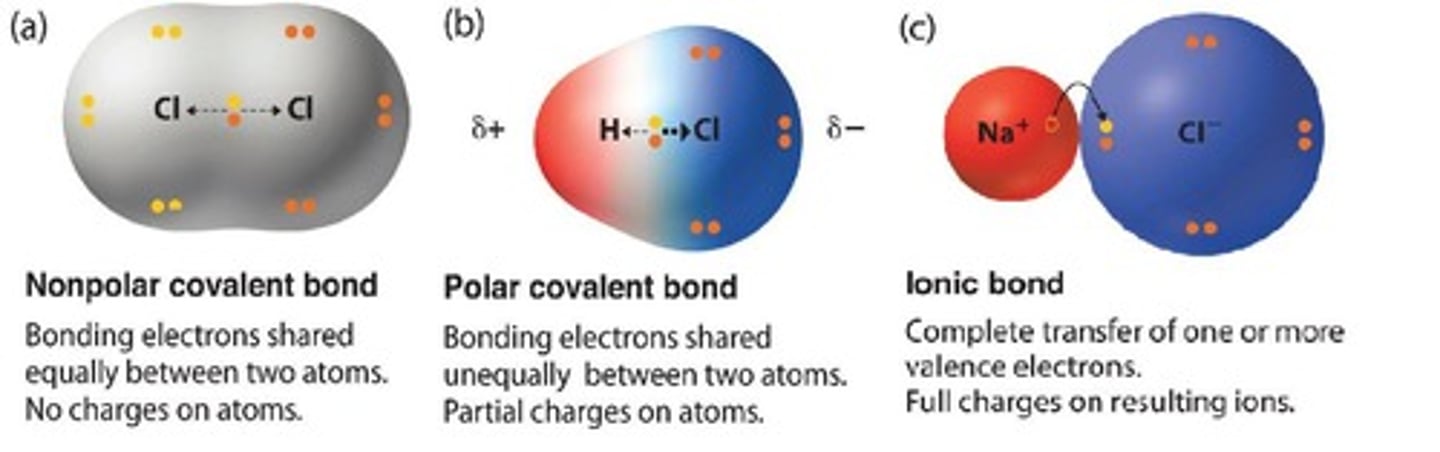
Polarity
Unequal sharing of electrons in a molecule.
Covalent Molecule
Molecule formed by sharing electrons between atoms.
Polar Molecule
Molecule with a net dipole moment due to unequal charge distribution.
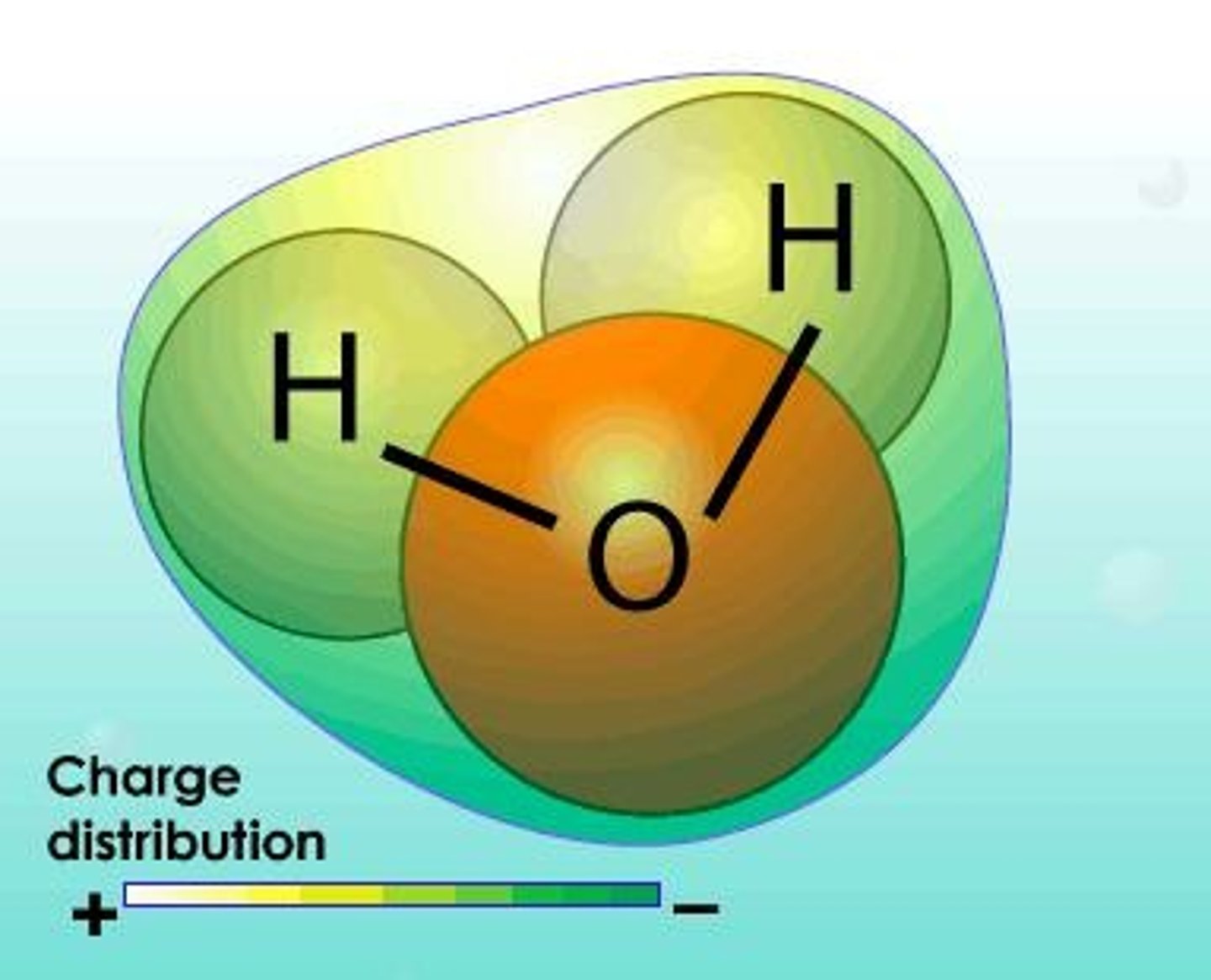
Non-Polar Molecule
Molecule with symmetrical charge distribution, no net dipole.
Dipole
Separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule.
Electronegativity
Tendency of an atom to attract electrons.
Partial Positive Charge
Slight positive charge on an atom in a polar bond.
Partial Negative Charge
Slight negative charge on an atom in a polar bond.
Symmetry
Balanced arrangement of atoms leading to non-polarity.
VSEPR Theory
Predicts molecular shape based on electron pair repulsion.
Intermolecular Forces (IMFs)
Forces between neighboring molecules affecting physical properties.
Intramolecular Forces
Forces holding atoms together within a molecule.
London Dispersion Forces
Weak, temporary forces due to electron movement.
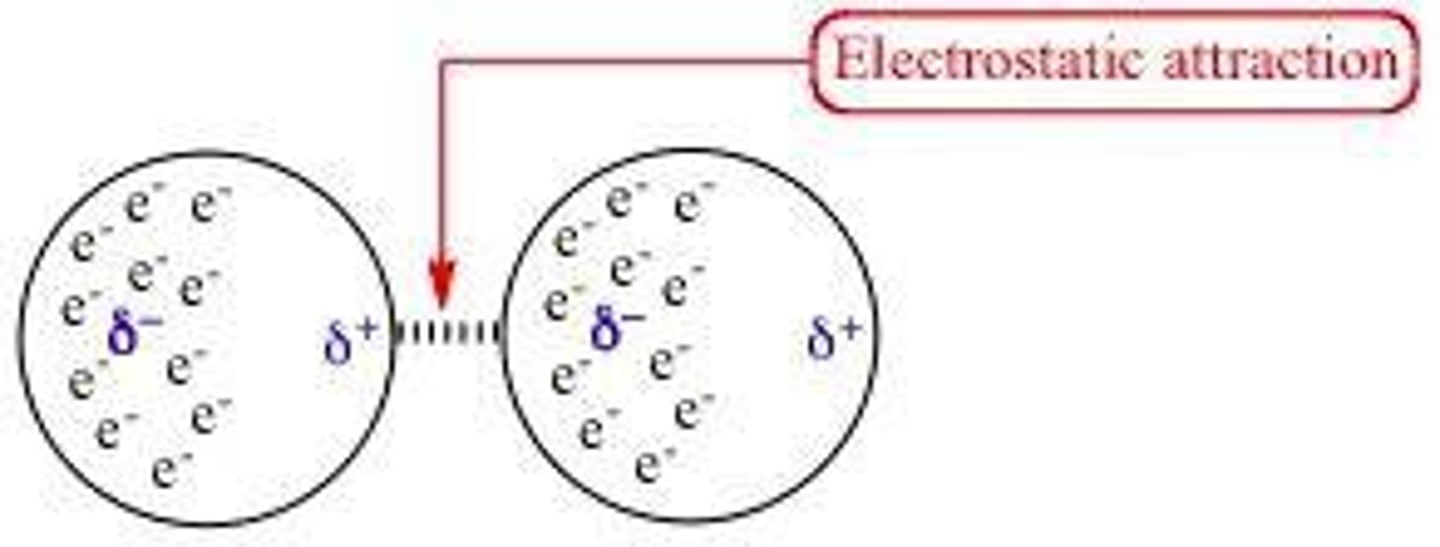
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Attraction between polar molecules' positive and negative ends.
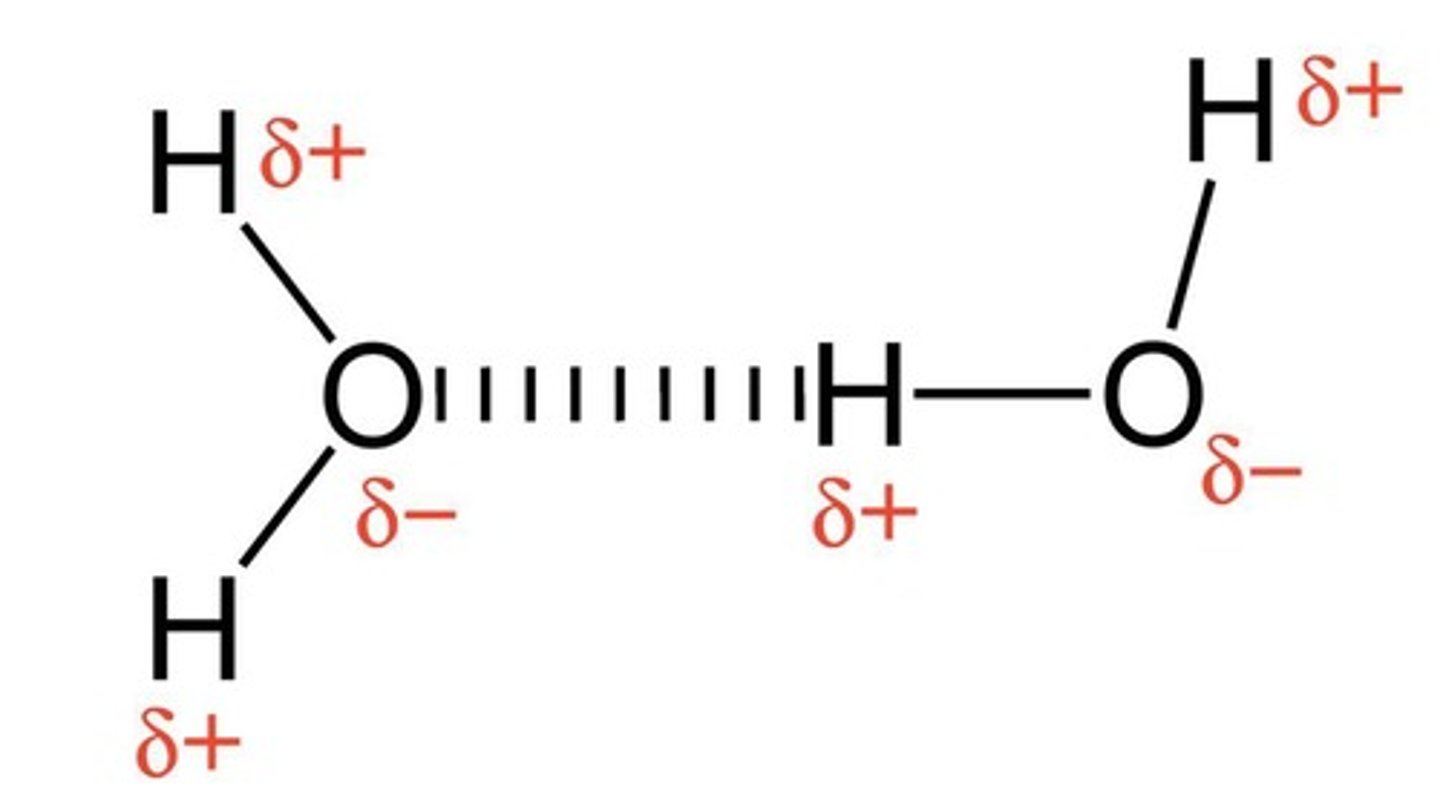
Hydrogen Bonding
Strong dipole-dipole interaction involving H and N, O, or F.
Boiling Point
Temperature at which a liquid turns to gas; influenced by IMFs.
Melting Point
Temperature at which a solid turns to liquid; influenced by IMFs.
Viscosity
Resistance of a liquid to flow; affected by IMFs.
Surface Tension
Energy required to increase surface area of a liquid.
Miscibility
Ability of substances to mix; polar with polar, non-polar with non-polar.
Ionic Compound
Compound formed by ionic bonds between charged ions.
Metallic Bonding
Bonding due to attraction between metal ions and delocalized electrons.
Network Covalent Bonding
Strong bonds forming a continuous network, e.g., diamonds.
Ionic Lattice
Ordered arrangement of ions in a crystal structure.
