BIOL 2153 - Angiosperms
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is the Phylum of flowering plants or Angiosperms?
Phylum Anthrophyta: includes 300k -450k species and largest phylum of plants
What are the unique characteristics of Angiosperms?
Flowers, Fruits and Lifecycle (double fertilization)
What are the MAJOR CLASSES of Angiosperms?
Two major classes:
Monocotyledonae: includes familiar plants such as grasses, lilies, orchids, and palms
Eudicotyledonae: many familiar trees such as apples, shrubs, and many herbs
A few species of angiosperms are ____ or _____
Parasitic: 200 parasitic monocots and 2800 parasitic eudicots. Form a specialized organ that penetrates tissues of the host (in the form of haustoria)
Myco-heterotrophic: plants that lack chlorophyll, they obligate relationships with mycorrhizal fungi (that also associates with another plant)
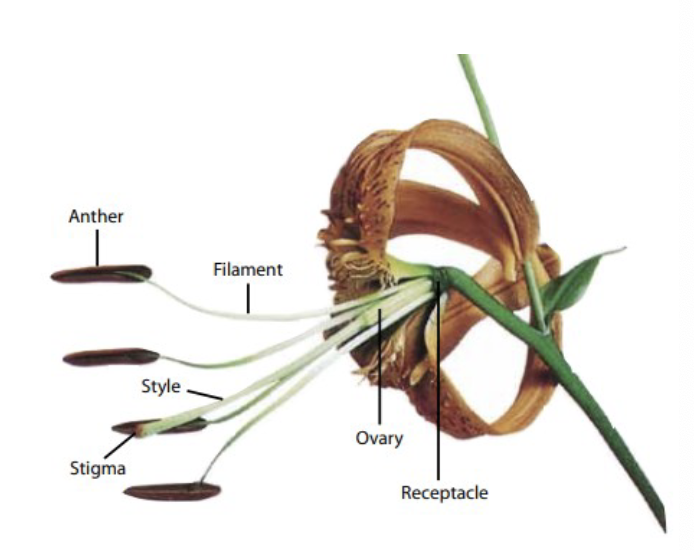
What is the Stamens?
AKA Androecium: male portion of the flower, Contains:
Anther: hosts the pollen
Filaments: elevates and supports the anther
What is the Carpels?
(PISTIL) AKA Gynoecium: female portion of the flower, Contains:
Ovary: holds ovule
Stigma: Traps pollen grains
Style: Connects stigma and ovary, provides a pathway for the pollen tube.
What are Inflorescences of a Plant?
the arrangement of flowers on a floral axis “flower stem”. The
What is the Peduncle and Receptacle of a plant?
Peduncle: The main supporting stalk of the whole inflorescence. The stalk supporting single flowers are called pedicels
Receptacle: the point of attachment to the flower stalk
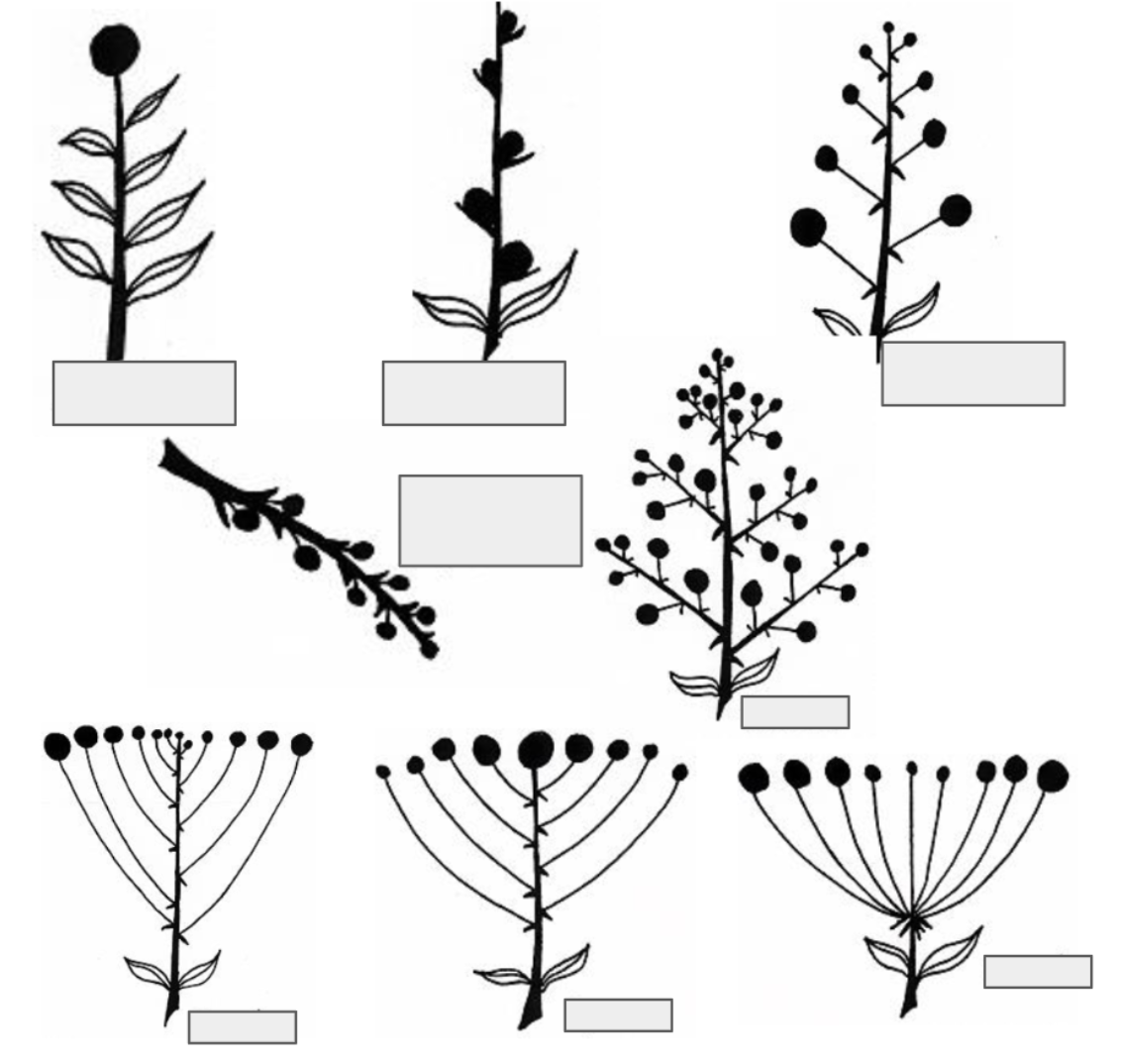
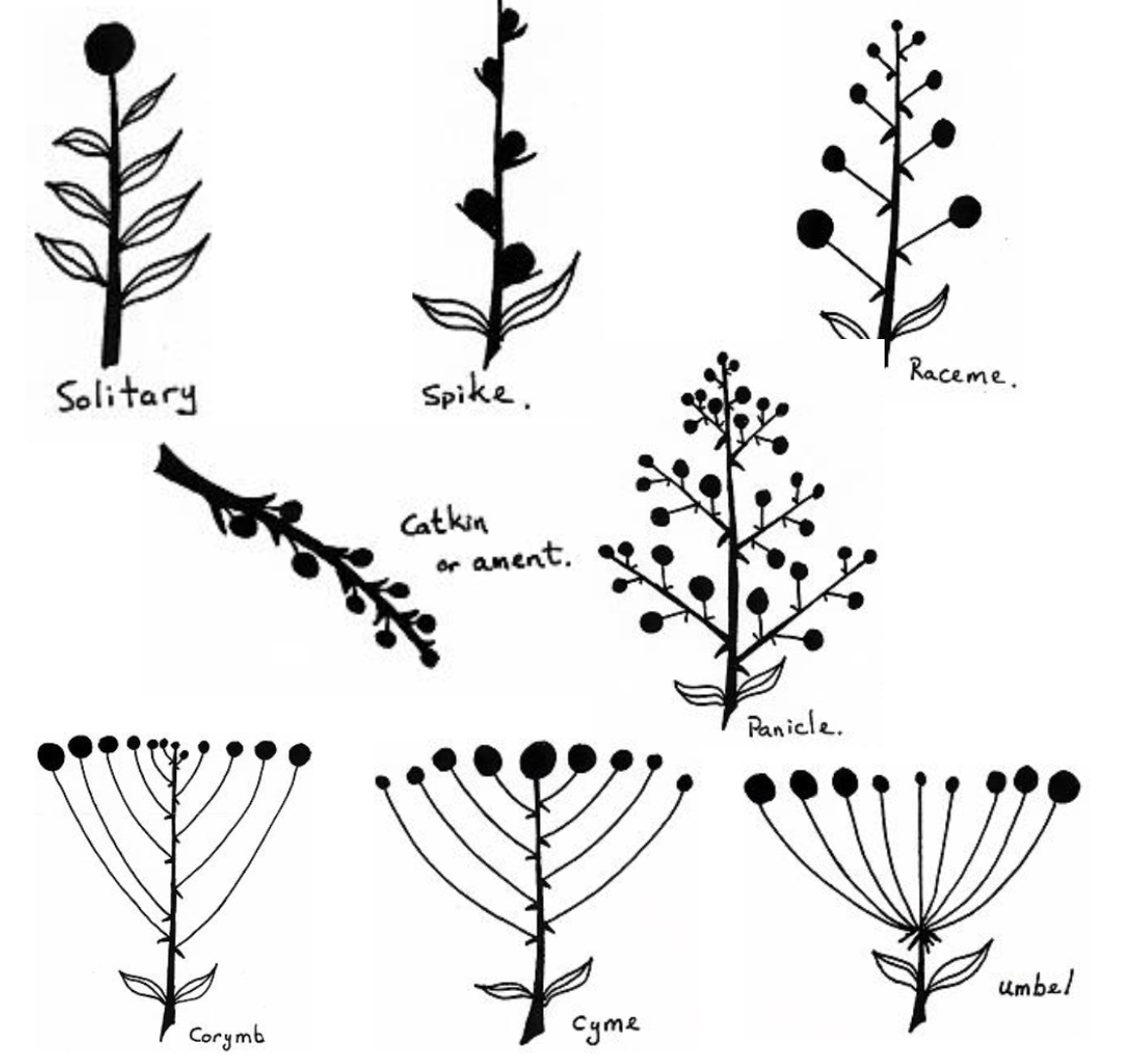
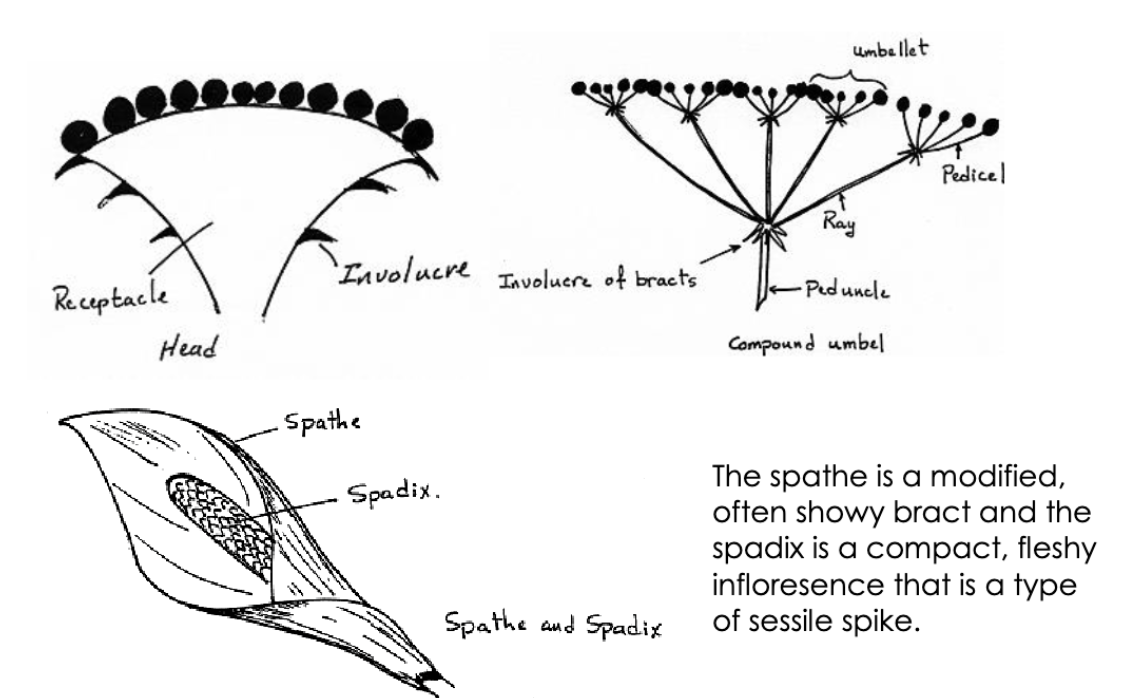
What are the types of Inflorescenses?
Solitary
Spike
Raceme
Catkin or ament
Panicle
Corymb
Cyme
Umble
Head
Spathe and Spadix
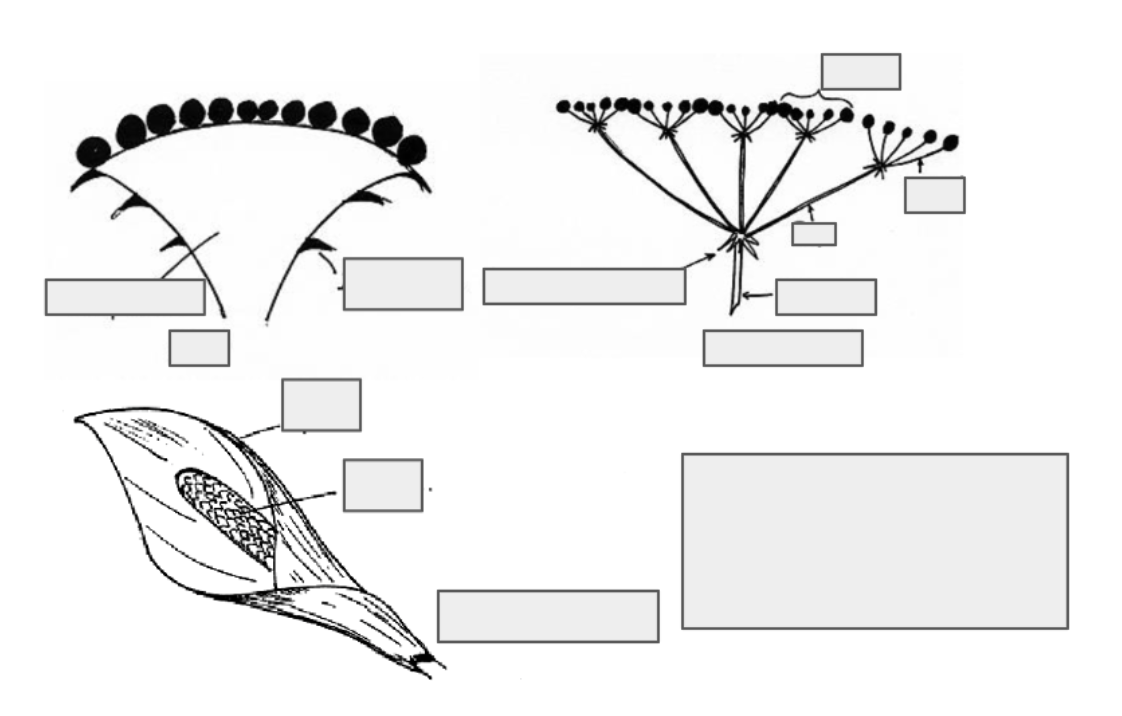
What are the two sets of sterile appendages in flowers and their function?
Sepals: protect developing bud and support petals when flower blooms (collectively called calyx)
Petals: protect reproductive structures and attract pollinators (collectively called corolla)
What is the Perianth?
Calyx and Corolla together
What defines a “Perfect Flower”?
If a flower has both stamens and carpels
What is an Imperfect flower?
If the flower doesn’t have either stamens or carpels.
Unisexual flowers are imperfect flowers (staminate or pistallate flowers)
If both staminate and pistillate flowers are on the same plant,
The species is monoecious
If the staminate and pistillate flowers are on separate plants,
the species is dioecious
A “WHORL” represent what?
the sepals, petals, stamens and carpels
Incomplete vs. Complete flowers

What are the various Ovary positions of a flower?

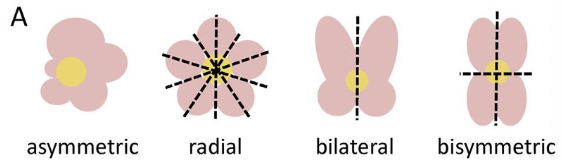
What are the symmetry in flowers?
Radially symmetrical flowers: multiple planes of symmetry due to the parts of each whorl being similar in shape and radiating from the center
Bilaterally symmetrical flowers: at least on member of one whorl is different from the other members of the same whorl (AKA irregular flower)
Define Microsporogenesis and Microgemetogenesis
Sporo: makes the microspores
Gameto: later development of the microgametophyte to a three-celled stage
Explain the production of Pollen
In the anther, there consists of a uniform mass of cells, the the four columns of sporogenous cells, the tapetum coats the developing pollen grain with a lipid rich coat. each microsporocyte gives rise to a tetrad of haploid microspores. The end is marked by the formation of the pollen grain
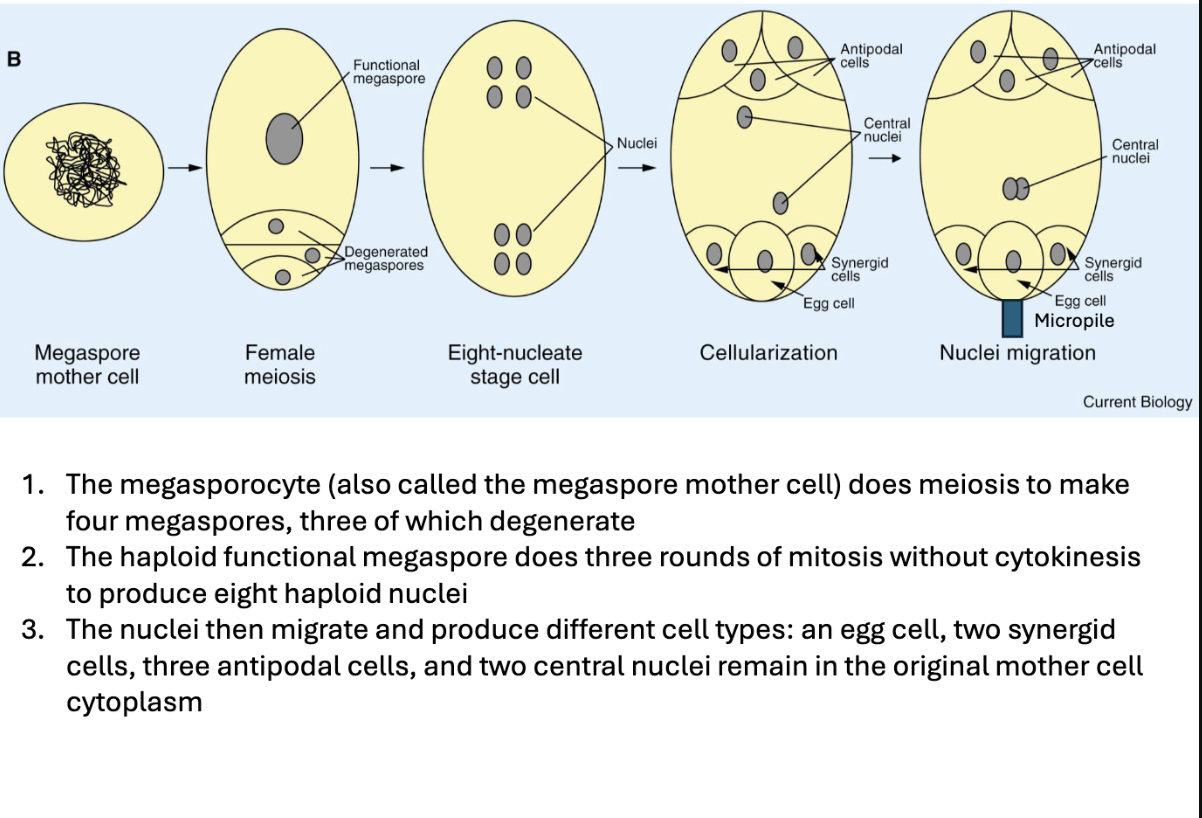
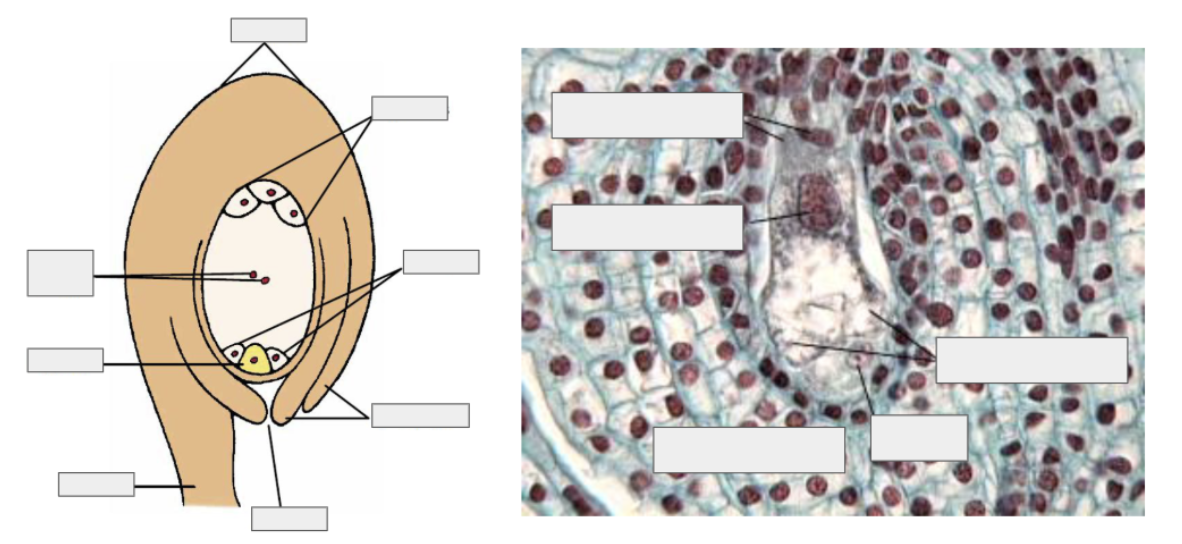
Megasporogenesis vs. Megagametogenesis

Explain the megagametophyte development of Angiosperms
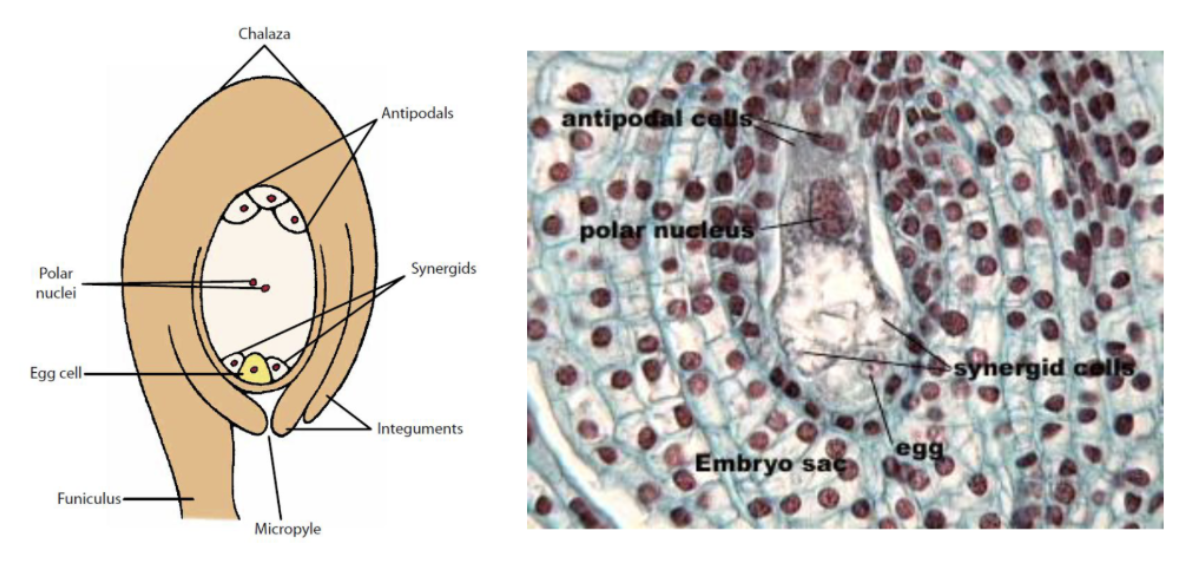
Define Pollination
the transfer of pollen to the stigma
Dry Stigma vs. Wet Stigmas

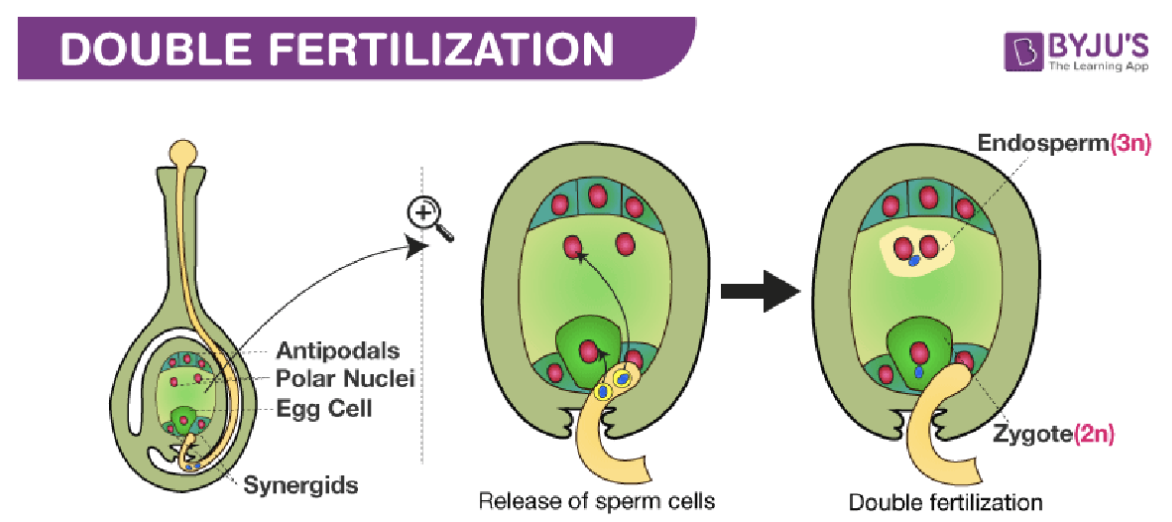
Explain the double fertilization of Angiosperms
One of the sperm fertilizes the egg to form a zygote. But there is a second fertilization that occurs, the other sperm fertilizes the central cell with the polar nuclei to form a triploid (3n) endosperm tissue. This tissue fills up with nutrients as the seeds develop which will feed the growing seedling once it germinates.
What is the earliest records that gave the “rise” of angiosperms?
Smallest number of changes to develop a carpel:
Caytoniales: mesozoic seed ferns where their capules is similar to carpels
Bennettiales: had flower like bisexual strobili, also had separate ovulate and pollen0bearing sporophylls
What is the Anthophyte Hypothesis?
Gnetophytes are the closest relative of angiosperms, Morphologically similar but DNA places gnetophytes within conifers. Angiosperms and extant gymnosperms are monophyletic.
What are the UNIQUE features of Angiosperms?

What is the first well preserved angiosperm called?
Archaefructus sinensis, approx 125 million years old, had carpels positioned above stamens
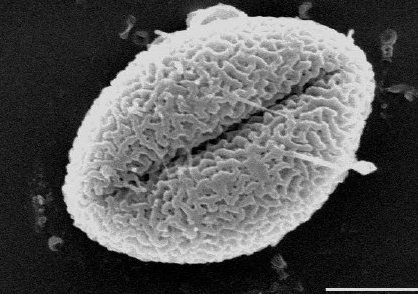
What is Monocolpate?
The pollen has a single aperture, the ancestral stae of pollen is found in the basal angiosperms and monocots
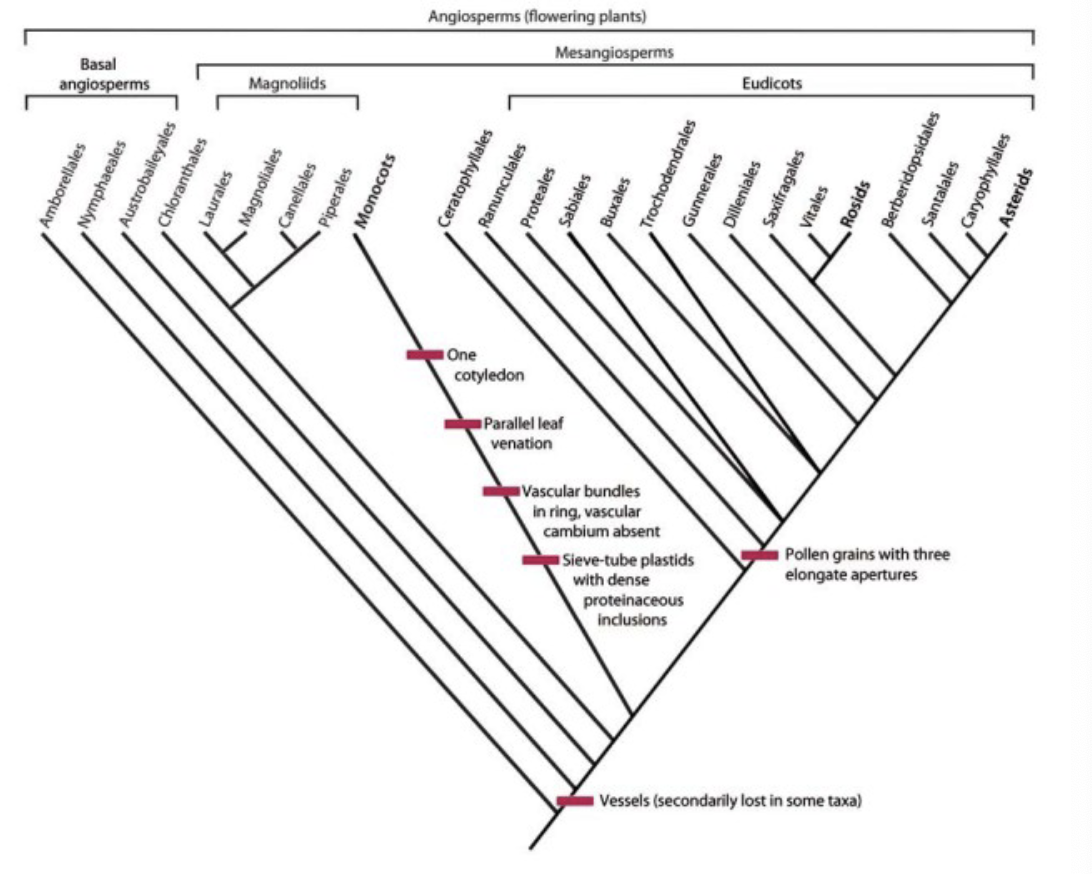
What is the common ancestors characteristics of Monocots and Eudicots
Mono: single cotyledon (or no secondary growth)
Eudi: tricolpate pollen and their derivatives
What are the BASAL angiosperms?
Ex: Amborellaceae, Nymphales, Austrobaileyales. They have a monocolpate pollen or a modification. All sister groups to all other flowering plants (grouped as the Mesangiospermae)
what is Satminodes?
Carpellate flowers contain sterile stamens
What is the Amborella
A shrub-like plant found on the island of New Caledonia. Its flowers are Imperfect, lack petals and sepals, with staminate and carpellate flowers on separate plants

What are the Magnoliids?
the first lineage to diverge within the messangiospermae, which includes:
Magnoliales (magnolias)
Laurales (laurel)
Piperales (black pepper)
Canellales (winter’s bark)
Monocots retain some basal angiosperm features, What are they?
Monocolpate pollen
3-merous flowers
Mesangiosperms consists of _____? While Angiosperms as a whole consists of ___?
Magnoliids and Eudicots.
Basal Angiosperms + Mesangiosperms
What does Tepals refer to?
During early evolution of Angiosperms, their perianth (calyx + corolla) were not distinct, so they were termed “Tepals”
what are Nectaries?
in some species, sterile stamens may exist as Nectaries which produce nectar to attract pollinators
What are the Four Major trends of Among Flowers?
Flowers diversed from having few parts or many indefinite parts to having few parts with definite numbers
Floral axis is shorter, no more spiral arrangement, and floral parts often fuse
Ovary is often inferior rather than superior (perianth also differentiated into distinct calyx and corolla)
Radial symmetry of early flowers has given way to bilateral symmetry in more recently evolved species
What are the Evolutionary Agents of the Angiosperms?
Animals: evident from the coevolutoon between flowers and insects (like how many features of flowers are directly linked to insect attraction)
Birds and Bats: often associated with plants that produce copious amounts of nectar
What is a fruit?
A matured ovary, more broadly, matured ovary with accessory tissues
What are the types of fruits?
Simple Fruits: develop from a single carpel or from two or more united carpels (cherry, tomato)
Aggregate Fruit: formed from a gynoecium each carpel retain its identity (each carpel is referred to as a fruitlet)
Multiple Fruits: derived from inflorescences from combined gynoecia of many flowers
What are the forms of Fleshy Fruits?
berries: one → many seeds, all parts are fleshy except the exocarp which may be a skin or rind (tomato, grapes)
Drupes: generally one seed, thin exocarp, fleshy mesocarp, stony endocarp (cherries)
Pomes: develop from a compound inferior ovary, flesh derived from floral tubes, tough cartilaginous endocarp. (apple)
What are Dehiscent fruits?
Fry fruits that break open at maturity:
Follicles
Legume
Siliqua
Capsule
What are Follicles?
Dry Dehiscent Fruit: derived from one carpel, they split along one side (ex magnolias)
What are Legumes?
Dry Dehiscent Fruit: similar to follicles, but split along both sides (like peas)
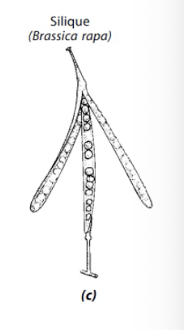
What are Siliqua
Dry Dehiscent Fruit: fruit of the mustard family, from two carpels and split in two halves with persistent partition
What are Capsules?
Dry Dehiscent Fruit: most common, derived from a compound ovary, release seeds in various ways.

What are Indehiscent fruits?
They are dry fruits that do no break open at maturity
What is the Achene?
Most common Dry Indehiscent Fruit: one seeded fruit attached to the pericarp by a funiculus
what are Samaras?
winged achenes
What are Cypsela
Dry Indehiscent Fruit achene fruits, in the asteraceae, that develop from an inferior ovary
What are Caryopsis or Grain
Dry Indehiscent Fruit Achene, in the poaceae
What are Nuts?
Dry Indehiscent Fruit Achene, with. a hard stony exterior
What are Schizocarp?
in Apiaceae and Sapindaceae, and some other fruit: splits at maturity into two or more seeded potions called mericarps