MOD 4 - Hereditary, Congenital, Degenerative Disorders
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Pathologies Covered
scoliosis
non-accidental injurt
osteogenesis imperfecta
delayed/advanced bone age
disc herniation
spondylosis
achondroplasia
DDH
Scoliosis Definition
A lateral deviation of the spine that’s greater than 20 degrees from the MSP
Classification - Scoliosis
degenerative or traumatic
Etiology - Scoliosis
80% structural = fixed and fails to correct with lateral bending
20% functional (non-structural) = fluid and corrects with lateral bending
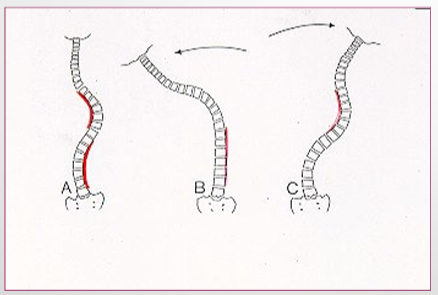
Types of Structural Scoliosis
idiopathic 80%
congenital - defect in VB construction
neuromuscular - disorders that cause spinal deformity
radiation-induced
trauma
degenerative joint disease - destruction of disc/facets
miscellaneous - tumors/surgery
Non-structural Scoliosis Causes
unequal leg lengths, herniated disc, muscle spasm
Complications - Scoliosis
cardio pulmonary = pressure on heart and lungs
degenerative spinal arthritis = due to pressure
curvature progression = double curve (compensatory), rapid growth spurt in adolescence
radiation exposure = for diagnosis and F/Us
difficult labor
Reason to perform Scoliosis Radiographs
Cobb Method = to evaluate curve site, magnitude and flexibility
Assess bone maturity for treatment planning, or for treatment planning itself
Monitoring progression/regression
Spinal Bone Maturity Imaging Areas
LT hand/wrist = VB epiphysis
VB ring epiphysis = spinal maturation
IC = final spinal maturation
Treatment - Scoliosis
Observation: x-rays every 3 months
Bracing: curves that are flexible
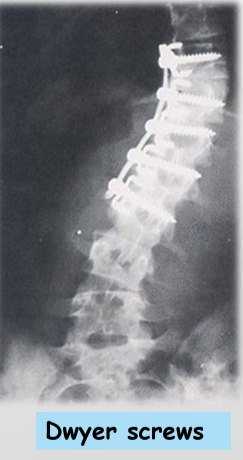
Surgical: curves>40degrees, when underlying abnormality can be treated, attachment of corrective instruments (rods, screws, wires)
Non-Accidental Injury (NAI) aka
child abuse
non-accidental trauma
suspected physical abuse (SPA)
Classification - NAI
traumatic
Etiology - NAI
Deliberate physical harm to a child
Pathogenesis (how to tell) - NAI
suspicious/abnormal fx on certain ages
injury doesn’t match hx
multiple fx in varying healing stages
Radiographic Images for NAI
skeletal survey > babygram
CT Head
Radiographic Appearance - NAI
metaphyseal / spinal fx = caused by shaking
rib fx = caused by squeezing chest/ direct blow
skull fx
brain injury
scapular fx
high energy trauma type injuries
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Definition
Genetic disorder commonly known as “brittle bone disease”
Classification - Osteogenesis Imperfecta
hereditary
Etiology - Osteogenesis Imperfecta
body can’t produce strong bones due to lack of collagen
Pathogenesis - Osteogenesis Imperfecta
disease progresses with few to many hundreds of fractures over lifetime → as it heals the large disproportionate callus leaves a deformity
S&S - Osteogenesis Imperfecta
pain due to fxs
blue sclera of the eye (instead of white)
loose joints and muscle weakness (due to immobility, w/c bound)
Radiographic Appearance - Osteogenesis Imperfecta
osteoporotic bones, thin cortices
callus formation
widened sutures, multiple wormian bone
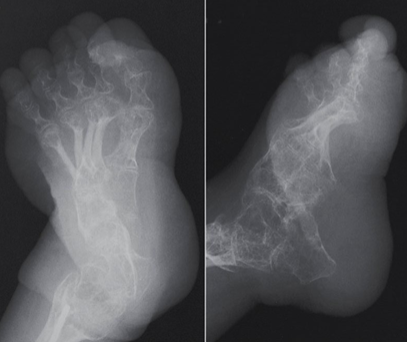
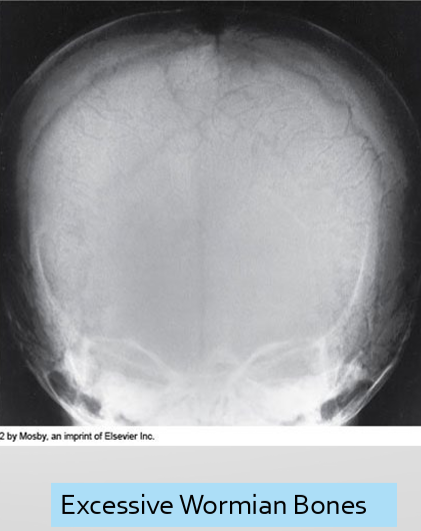
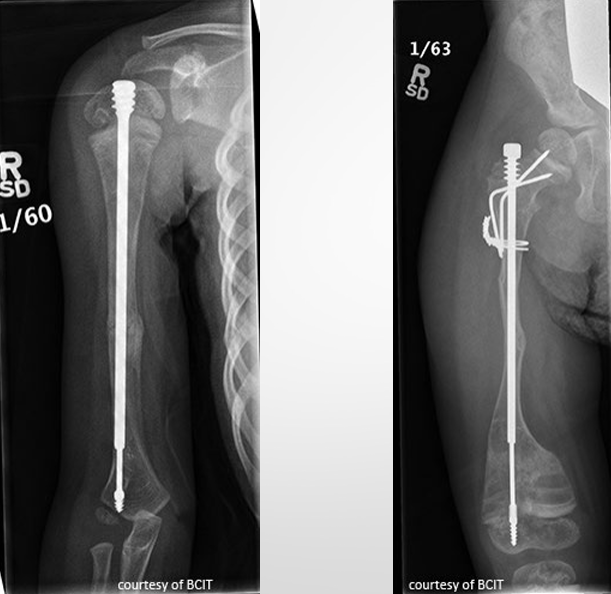
Treatment - Osteogenesis Imperfecta
focus is to prevent fx → extendable rods in long bones
medications to reg. osteoclast formation
Classification - Delayed/Advanced Bone Age
congenital
metabolic
Reason for Radiographs - Delayed/Advanced Bone Age
assessment of growth and evaluation of endocrine disorders
used to investigate: short/tall stature, early/late puberty, to predict height
Advanced vs. Delyaed Bone Age
Advanced
2 years advancement from chronologic age, concern is underlying pathologies
Delayed
2 years behind child’s chronologic age, concern is underlying pathologies
Constitutional delay of growth and puberty (CDGP)
Pathogenesis (cause) - Advanced Bone Age
elevated sex steroid (androgen, estrogen)
endocrine disorders
childhood obesity
Pathogenesis (cause) - Delayed Bone Age
endocrine disorders (decreased hormone levels)
systemic diseases (heart, urinary, digestive)
chromosomal disorders
idiopathic
Radiographic Appearance - Delayed/Advanced Bone Age
taller/shorted than average
carpal ossification ages
cap 1-3 months
ham 2-4 months
tri 2-3 years
lunate 2-4 years
scap/trap/trap - 4-6 years
pisi - 8-12 years
Classification - Disc Herniation
degenerative (common) or traumatic (rare)
types:
protrusion = annular fiber intact
extrusion = annular fiber tear but nucleus intact
sequestration = nucleus is severed
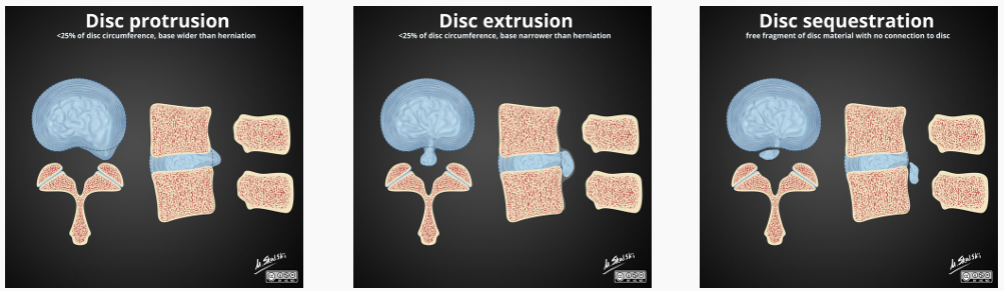
Etiology/Pathogenesis - Disc Herniation
inner disc bulges past outer disc
hereditary = collagen
congenital = spinal deformity
increased age = dehydration and instability
trauma or repetitive strain
poor posture
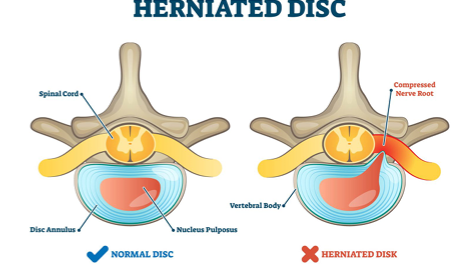
S&S - Disc Herniation
back/neck pain
radiculopathy (due to nerve compression)
Rad - Disc Herniation
narrowed disc space
osteophytes
best seen in MRI (required for diagnosis), CT is also valued when MRI is contraindicated
Treatment - Disc Herniation
rest, NSAIDS, physiotherapy, steroids
microdiscectomy, laminectomy, spinal fusion, artificial disc replacement
Classification - Spondylosis
degenerative
spinal arthritis that can also affect ST
osteophyte growth types
spondylosis deformans (ant/lat growth)
intervertebral osteochondrosis (post growth)
Etiology - Spondylosis
normal age related condition
common in CSP and LSP
increased chance with more stress applied to the spine
Pathogenesis - Spondylosis
disc breakdown
vertebral end plates break down
disc can bulge into post. annulus and joint space narrow compressing nerves and causing stenosis
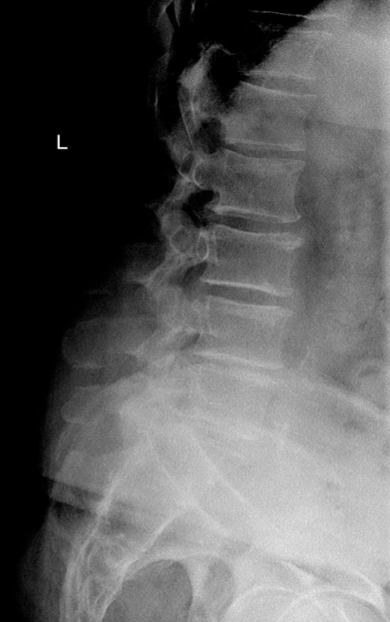
S&S - Spondylosis
asymptomatic
crepitus (feeling/sound of spine crunching)
Rad - Spondylosis
ant or post osteophytes
narrowed disc space
scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis
MRI, CT, X-ray
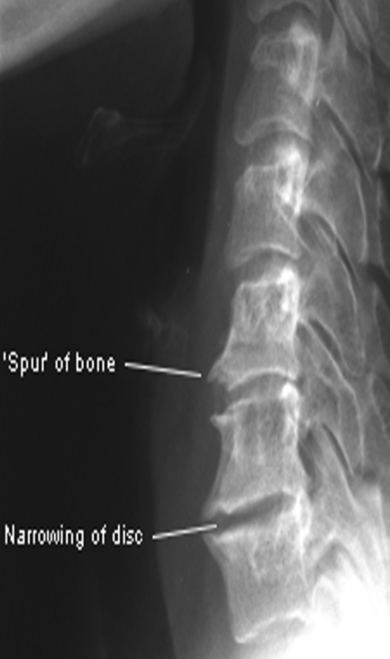
Treatment - Spondylosis
physiotherapy
NSAIDS, epidural injections
surgery
Classification - Achondroplasia
condition that affects bone growth → short stature and shortened limbs (dwarfism)
congenital/hereditary
Etiology - Achondroplasia
caused by the variant in the FGFR3 gene
does not affect cognitive developement
Pathogenesis - Achondroplasia
overactive FGFR3 inhibits prevents chondrocytes to covert into bone cells
delayed bone growth
S&S - Achondroplasia
macrocephaly/frontal bossing
trident hand
exaggerated lordosis
sleep apnea, numbness, diff swallowing
Rad - Achondroplasia
fetal US can show shortened limbs and enlarged head
genetic test can confirm diagnosis
long bones appear short and thick with a wide metaphysis
long fibula
bowing legs
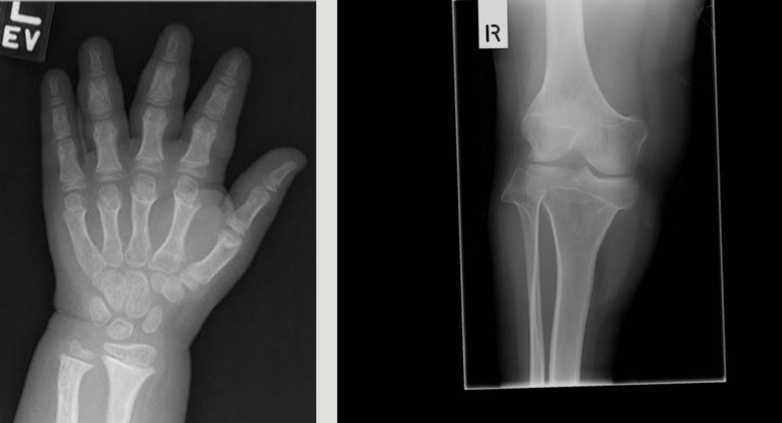
Treatment - Achondroplasia
no cure
goal is to manage complications = meds, growth hormone, surgery (limb lengthening)
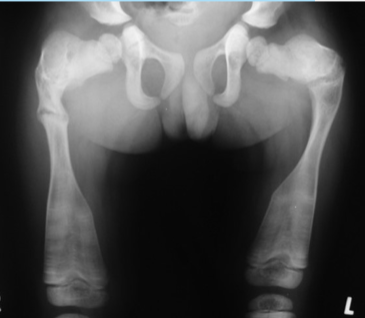
Classification - Developmental Dysplasia of Hip
congenital, depends on cause
types
dislocated = FH completely out of socket
disloc-able = high chance of dislocation
sublux-able = FH is loose in socket
Etiology - DDH
structural defects in the acetabular region
risk factors: first born, females (increased progesterone), breech position
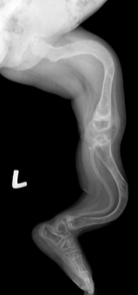
Pathogenesis - DDH
poor alignment leads to cycle of deformity
delayed ossification
deformed FH
early OA
S&S - DDH
galeazzi sign = asymmetric shortening
decreased hip abduction
hip pain
limp
Rad - DDH
AP views
evaluated with Perkin’s, Hilgenreiner’s, Shenton’s line
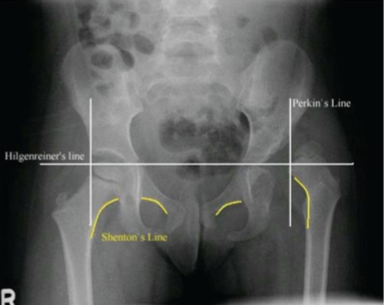
Treatment - DDH
palvik harness
close/open reduction