25 SQ: Recycling
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is the definition of recycling?
Using a material again after it has served its original purpose
Downcycling: recycling but the recycled item has lower quality

What are the main materials composing an aircraft?
Composites (50%), Aluminum (20%), Titanium (15%), Steel (10%), others (5%)
Name 2 reasons why the recycling of aircraft aluminium is more complex than recycling aluminium form the automotive and car industry
Anti-corrosion coating needed for aerospace applications, whcih is toxic as fuck to remove and dispose
High concentrations of alloying components not present in automotive or food industry
Why is a “Smart disassembly and dismantling“ of an aircraft needed for recycling aluminum?
To facilitate scrap sorting and scrap refining of the aluminum
To achieve an efficient and effective aluminum recycling and minimize contamination
To be able to get high-value alloys out of the Al scraps
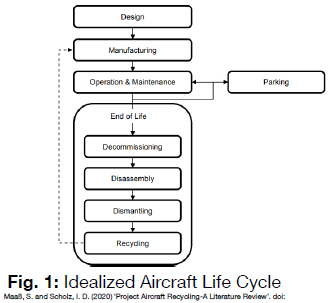
How does an ideal aircraft life cycle look like?
Design → Manufacturing → Operation and Maintenance → (End of Life) → Decomissioning → Disassembly → Demantling → Recycling → Manufacturing → …
What are the advantages and drawbacks of the mechanical recycling of CFRP components?
+ Recovery of fibers and matrix
+ No use of harmful substances
- Significant degradation of mechanical properties
- Unstructured, coarse and heterogeneous fiber architecture
- Limited use possibilities
Name 2 methods to recover carbon fibers from used CFRP parts
Pyrolysis
Solvolysis
What are the advantages and drawbacks of oxidation during the pyrolisis process?
+ Good retention of mechanical properties
+ No use of hazardous solvents
- Possible deposition of char on the fiber surface
- Polluting exhaust gas
Why can recylced CF not always be used in high-performance applications?
The recycling processes of CFRP usually degradate the fibers to a certain degree, which prevents that high FVR, sufficient fiber length and coherent fiber alignment is achieved