Taxonomy of Flowering Plants Test 1
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
genus
subfamily
family
order
class
phylum
name the taxonomy classes from largest to smallest (6)
taxonomy
what is the term for how thing in science are classified by genus, subfamily, family, order, class, phylum?
Systematics
what is the term used to show how things are related via evolution (not a tree dumbass)
classification based on the relationships with one another
phylogenetic tree
it is easier to represent systematics in a ______ ______
Fragaria
in the phylogenetic tree, which species is the most closely related to rosa
you can tell which species is closely related by their recent ______ ______
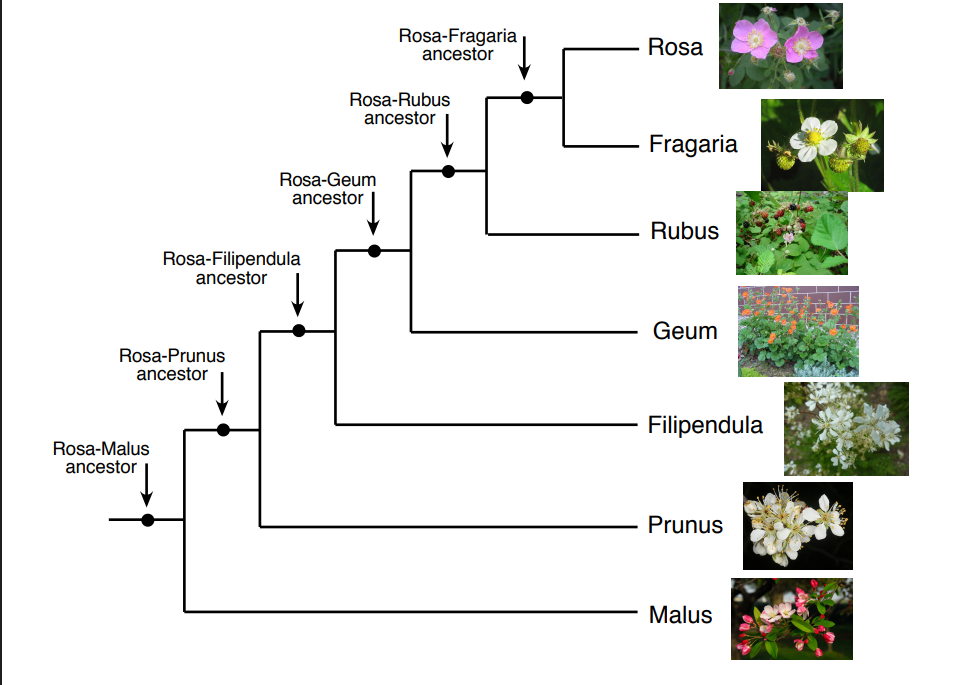
Malus
in the phylogenetic tree, which species is the least related to rosa?
nomencalture
what is the term for naming things binomial _______
binomial nomenclature
naming an organism by genus and species
the authority or the first person to name the species
in Rosa Carolina L. what does the L stand for
A. Gray was the first person to name the species and then SF Blake put in viguiera which kicked off proski
Helianthis porteri (A. Gray) Proski
Viguiera porteri (A. Gray) S.F Blake
what happened to these nomenclatures?
yes
can some authorities have two names?
anything with a standard ending that sounds Latin
Davidii
what are the rules for naming a genus or species
change David into an appropriate genus/species name
must be named after a genus that’s in it
must have a standard ending associated with the taxonomic category
what are the rules for naming anything above genus?
oideae
aceae
ales
opsida
phyta
what are the standard endings for the following:
subfamily
family
order
class
phylum
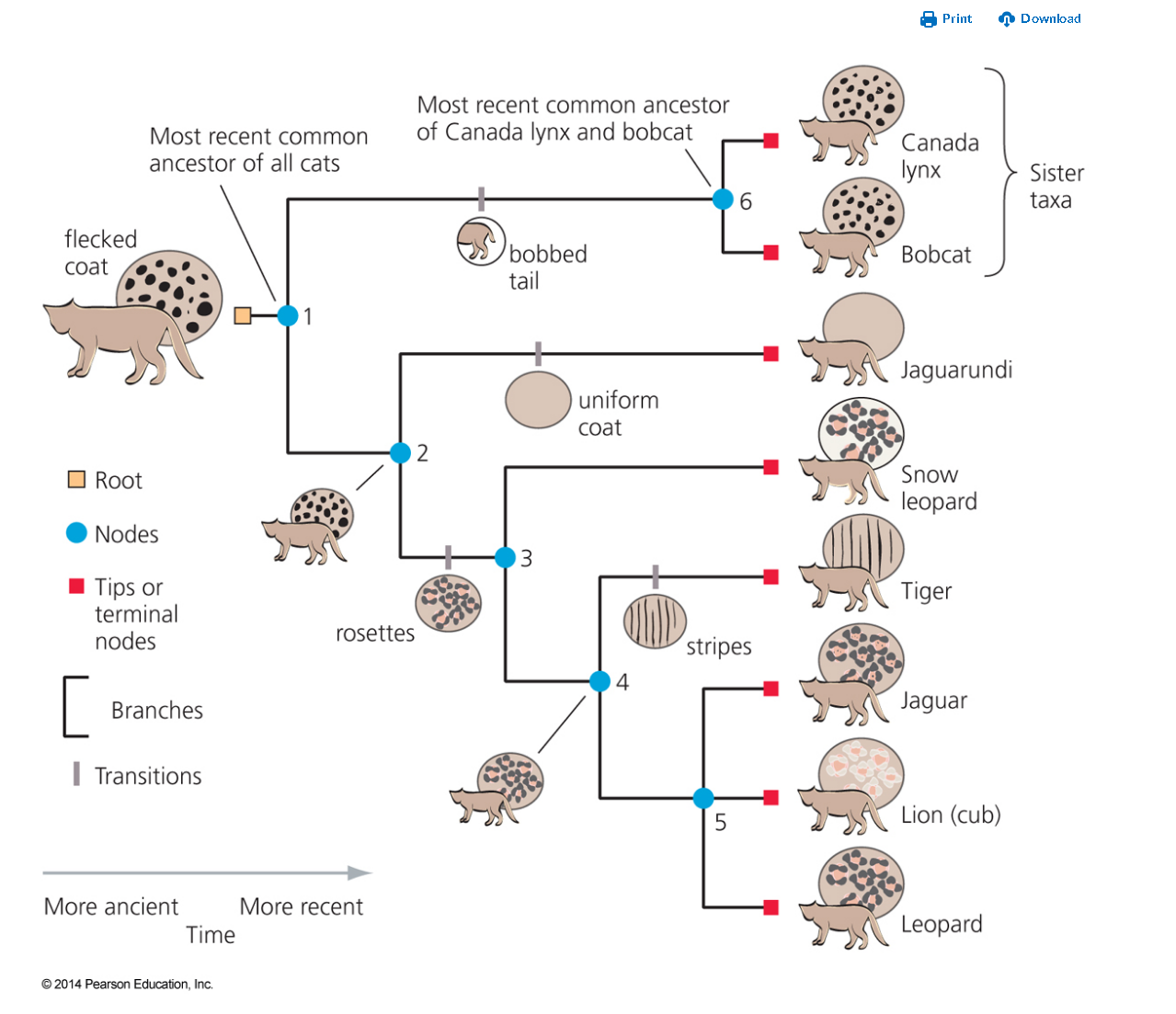
branches
what part of phylogenic tree
Linear sequence of ancestors
node
what part of phylogenic tree
part that one branch splits into 2 or more
Most recent common ancestor
root
what part of phylogenic tree
Ancestor of all members of the phylogeny
clade
what part of phylogenic tree
Any ancestor and all of its descendants
transitions
what part of phylogenic tree
Is also known as character
Character = any trait or attribute that can be evaluated (things you can count, measure ect.)
Character state = what you get when you evaluate a character, or description of the character
5
how many clades are present?
character
any trait or attribute that can be evaluated (things you can count, measure, ect)
character state
what you get when you evaluate a character or the description of a character
Petal …pink…whatever color
Petal number: 1,2,3,4,5….
Sepal Number: 1,2,4,5….
Cam photosynthesis: absent or present
DNA sequences
ATGC
Protein Sequences
20 amino acids
Zero of a character can be a _____
spot type
simple, rosettes
rosettes, simple
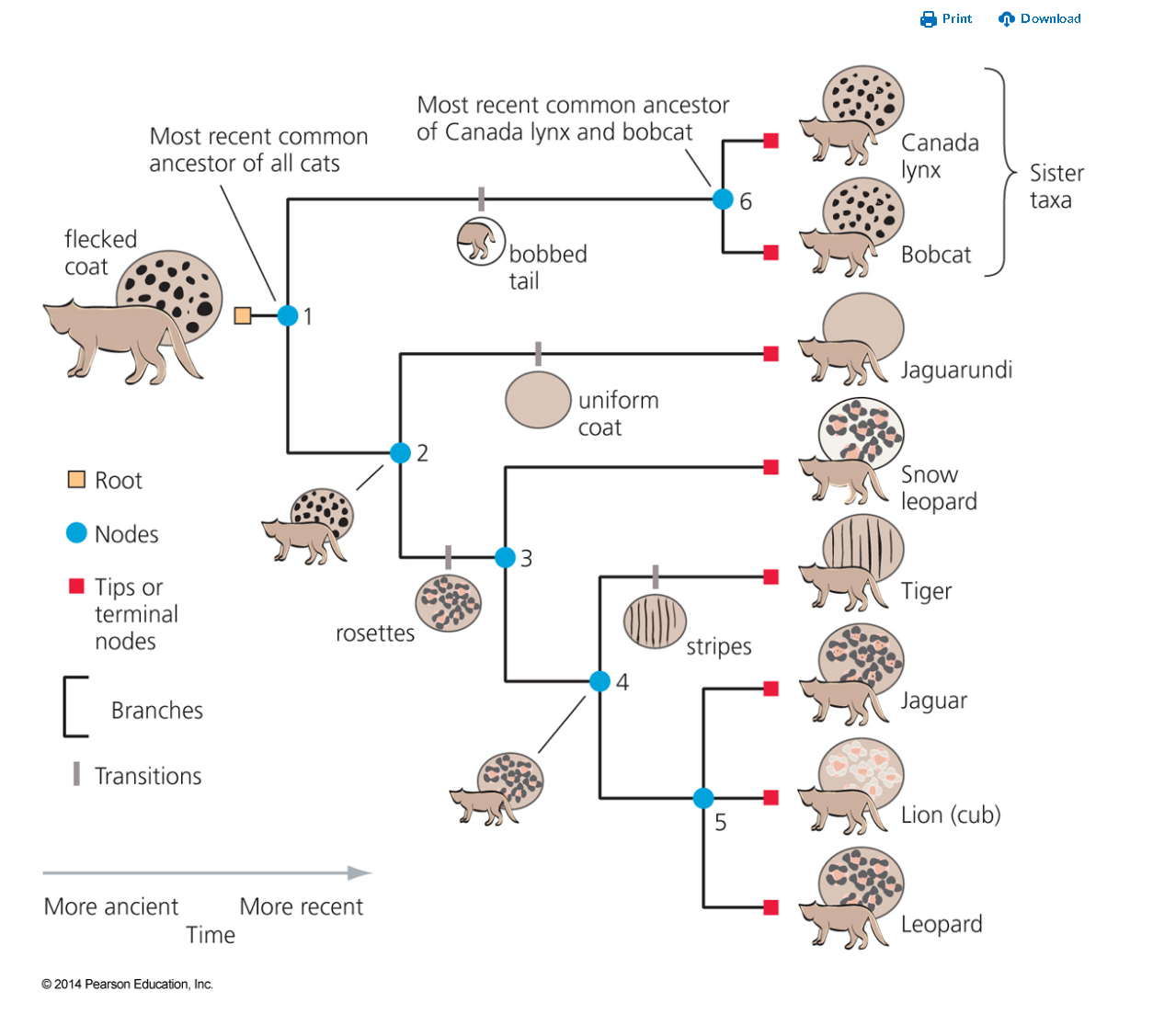
in this tree only focus on the spots
what is the character
what are the 2 character types?
which character type would be derived? which one would be ancestral?
produce phylogeny
observations
are all the group members of the same clade—yes
does the clade have members of any other taxonomic group—no
monophyletic
what are the 2 steps to the procedure of testing classifications
what are the 2 observation questions to ask about the clades and members and their preferred answers
if the preferred answers apply what type of taxonomic group is it?
yes
does monophyletic groups only apply to the taxonomies, not the clades?
biogeography
where species occur, why they occur, and how they got there
example:
Haplopappus
Is a species that occurs in chile
Hazadia california
Both this and haplopapus have very similar morphology
How did we get two very similar species in very different places?
They are closely related with a common ancestor
How did this common ancestor move so far?
Birds migration
Silverswords
Occur on hawaiian islands (big island)
Something from north america must've went to the hawaiian islands so we have to use DNA sequencing because nothing else looks like silverswords
Closest ancestor
Ralliardippsis + madie = tarweeds california
medicine
phylogenies also have uses in _______
Diseases caused by RNA viruses
Retroviruses = latch to cells and injects rna and then it gets transcribed into dna which makes the cell produce more dna cells of the virus
Rapidly evolving (influenza, ebola, hiv, west nile, yellow fever, covid-19)
HIV
Influenza
Covid-19
Came from Wuhang China and is related to bat covid
There was an outbreak in 2003 on the same place and grom bats but it didn't make it out of asia (2003 SARS)
Not as easily spread and more deadly than covid-19
character and character states
which character state is ancestor and which is derived
when building a phylogeny, what are the 2 requirements needed?
what do you have to find out about these?
directly from ancestor
with outgroup
how can character states be determined to be derived or ancestral by observing the character and character states?
Outside and directly related to group of intent (ingroup)
Represents the ancestor
Closest living to ancestor
As ancestral character states
outside and directly related to group of intent
represents the ancestor
closest living to ancestor
has ancestral character states
what are the 4 things needed to pick an outgroup
characters in data matrix
phylogenetic analysis
what are the two procedures to produce a phylogeny
assemble into clades based on share and derived character states
when it comes to phylogenetic analysis how does one do the general approach
Example: bird
5 derived character states: color on head, wing, stripe on tail, grey tail, long beak
Shared character states: orange wing tips, color on head, stripe on tail
So clades are birds with orange wing tips, color on head, and stripe on tail
clade support
percentages on phylogenies that show how well each clade are supported by data
biological species concept
what type of species is this?
based on reproduction, if 2 populations reproduce and produce fertile progenyy they are the same species
morphological species
what type of species is this?
individuals in different species should have distinguishable morphological characteristics = not successfully mating with each other
indicates no gene flow between them
phylogenetic species
what type of species is this?
all species should ne monophyletic in order to be able to mate successfully
no
if two species have different morphological characteristics they indicate ___ gene flow
experimental hybridizations
reproduction specific characters
evidence for or against gene flow
phylogenetic analysis
what are the 4 ways that one my test species concepts?
experimental hybridizations
maybe
probably
what type of species concept test is this
test bio species concept
If they can successfully mate they ______ the same species until is replicated in natural conditions
If they cannot they are ______different species
reproduction specific characters
what type of species concept test is this
Isolating mechanisms prevent successful interbreeding
Prezygotic
Prevent fertilization (2 steps in plants)
Prepollenation
Prevents interspecific pollination
Different flowering times
Different pollinators
Flowering parts and animals parts don't fit (humming bird beak example)
Pollinators of some species may not be active when the other is flowering
Flower parts of one species don't fit pollinators of other species
Pollen from one species gets on stigmas of another species
Recipient plants can interact with the pollen and the pollen tube chemically to determine if the pollen is compatible for pollination
Stigma and style can prevent pollen tube growth from other species
Postzygotic
Prevent the zygote from becoming a fertile adult
Different haploid numbers (# of chromosomes in 1 set)
We have 23 so if another organism had 20 we couldn't create a viable zygote
Meiosis I fails, no gametes produced—individual sterile
Mule example (donkey 31 horse 32)
Hinny (made with female donkey instead of female horse)
Different Ploidy (number of chromosome sets–anything >2 polyploid) levels
Hybridization between a diploid and a tetraploid (2n x 4n) = 1n gametes and 2n gametes = 3n progeny = sterile meiosis I fails–no gametes
isolating mechanisms
prevent successful interbreeding
two types: prezygotic and postzygotic
prezygotic
prevent fertilization
postzygotic
prevent the zygote from becoming a fertile adult
prepollenation
prevents interspecific pollination
different flowering times
different pollinators
flowering parts and animal parts don’t fit
flower parts of one species doesn’t fit pollinators of another species
what step of feralization does isolating mechanism prevent for prezygotic? name the 5
ways plants do this
chemically
stigma and style
Pollen from one species gets on stigmas of another species
Recipient plants can interact with the pollen and the pollen tube ________to determine if the pollen is compatible for pollination
______and ______ can prevent pollen tube growth from other species
different haploid numbers
different ploidy
what are th 2 ways postzygotic mechanism take place
different haploid numbers
what type of postzygotic isolating mechanism
We have 23 so if another organism had 20 we couldn't create a viable zygote
Meiosis I fails, no gametes produced—individual sterile
Mule example (donkey 31 horse 32)
Hinny (made with female donkey instead of female horse)
Meiosis I
infertile (sterile)
when there is different haploid numbers _________ fails, no gametes produce and the individual is _____
different ploidy
what type of postzygotic isolating mechanism
Hybridization between a diploid and a tetraploid (2n x 4n) = 1n gametes and 2n gametes = 3n progeny = sterile meiosis I fails–no gametes
allopatric speciation
Gene flow is interrupted by a geographic interbreeding barrier and the populations become genetically different ( become 2 separate species)
Like mountains, canyons
Example: A. Harrisi( South) and A. leucurus (North)
sympatric speciation
Genetic barrier divides a species in two
Polyploidy is usually the genetic barrier
Process:
Failure in meiosis I or II
Result: 2 diploid cells
2n spore = diploid (2n) gametaphyte = (2n) diploid gametes
2n sperm x 2n ovum = 4n progeny tetraploid
2n plant = 1n gametes X 4n plants = 2n gametes = 3n progeny–no gametes (sterile)
Creates interbreeding barrier
Identifying sympatric speciation:
Count the chromosomes in everything
Phylogeny of everything
Determine if there are characteristics of sympatric speciation
Pairs of sister species
They have different ploidy levels
Identifying potential of sympatric multiple ploidies in the same species
meiosis I or II
2 diploid cells
2n 2n 4n
2n 1n 4n 2n 3n
process of sympatric specieation
Failure in_______ or __
Result:_________
2n spore = diploid (2n) gametaphyte = (2n) diploid gametes
____sperm x ____ ovum = ___ progeny tetraploid
____ plant = ____ gametes X ___ plants = ____ gametes = ___ progeny–no gametes (sterile)
Creates interbreeding barrier
reticulate evolution
involves two different species that produce a progeny contain DNA from both
introgression
hybrid backcrosses to one or both parents
drift from one species transferred into the other
no
because the backcrossing with one of the original parent species will result in that original hybrid DNA being replaces with the parent species
are introgression species hybrids
why or why not
progeny does not mate with either parent
hybrid progeny cannot reproduce with parents
what are the two ways that introgression in hybrid species is avoided
no gene flow
no introgression
when it comes to introgression
if progeny don’t mate back with parents = _____ _______ ____
if prezygotic or postzygotic isolating mechanisms work well = __________________ _______
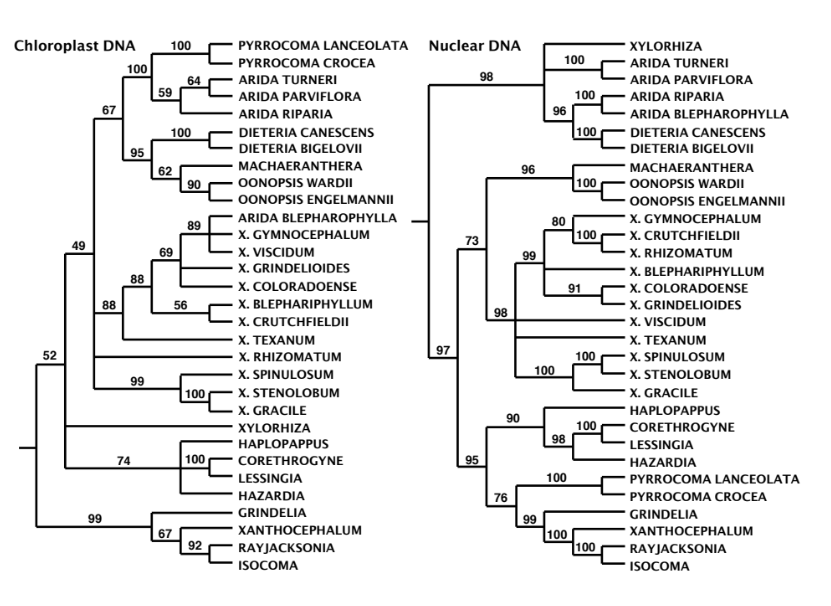
both phylogenies containing species of interest (using different sources of different sequences)
compare the two phylogenies and observe the relationship of species of interest
detailed stidy of nuclear genome
what are the 3 steps to identifying reticulate evolution
its DNA came from 2 different ancestors and is reticulate evolution
no
when looking for reticulate evolution and comparing the phylogenies, what does it mean when the relationships of the species have two different relationships?
do we know if its hybridization?
hybrid speciation
introgression
when looking at the nuclear genome, if there is a substantial amount of both ancestors it means ______
if most comes from one ancestor and little comes for the other ancestor it means ______
false
T/F you can tell a species is a hybrid by the phylogenetic tree alone
arida blepharophylla and X.
what two species may have reticulate evolution in these phylogenies? if it is multiple just put the first letter
remember to see which species group with what