Industrialization, Capitalism, and Social Reform Movements
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Industrial Development
Growth of industries using mechanization and resources.
Textile Industry
First sector to mechanize in the US.
Railroads
Key infrastructure driving industrial expansion in America.
Corporations
Businesses owned by stockholders sharing profits.
Capital
Initial money needed for business investments.
Standard Oil
Oil company founded by John D. Rockefeller.
Carnegie Steel Company
Steel company founded by Andrew Carnegie.
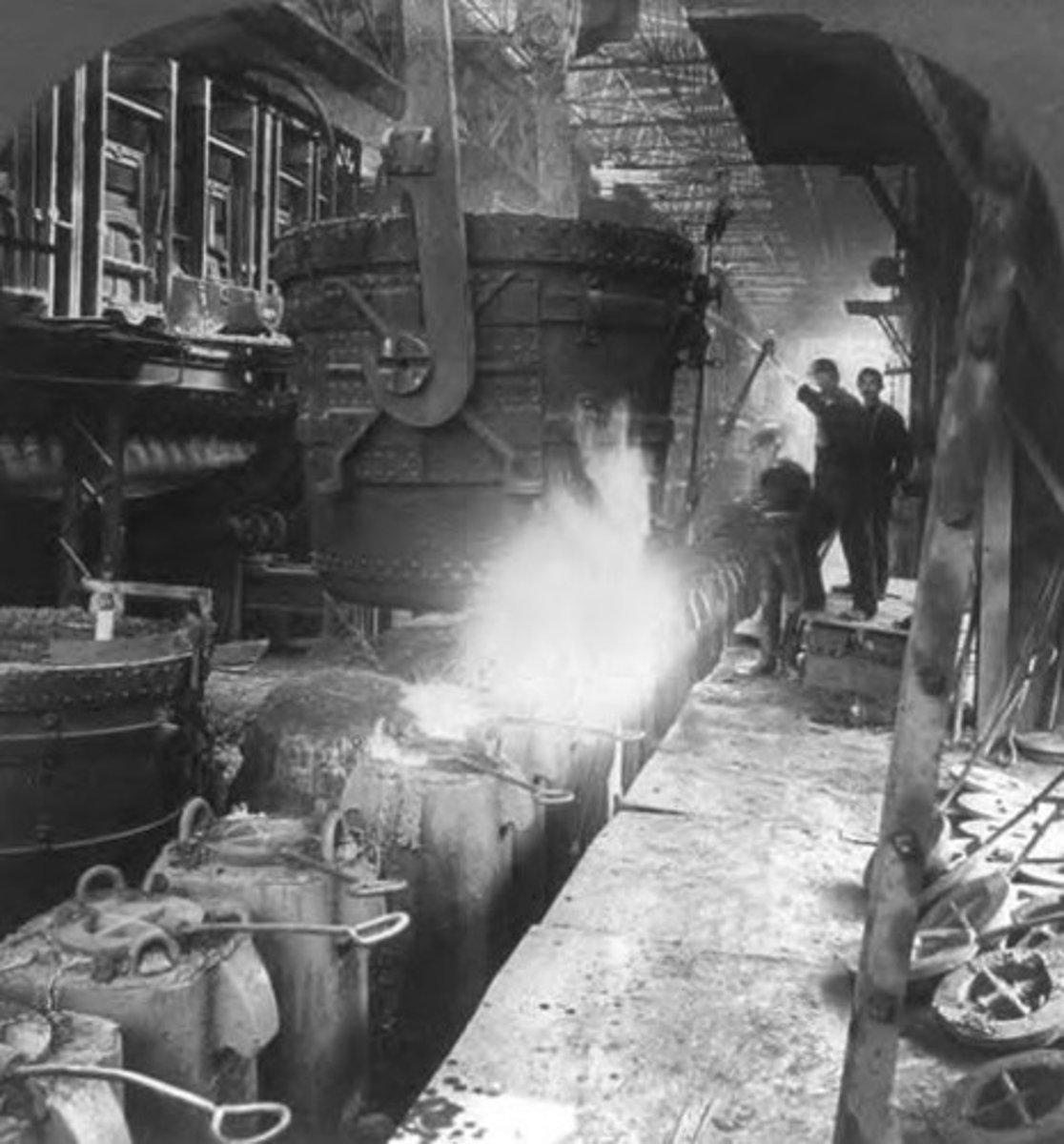

Big Business
Large corporations controlling entire industries.
Mechanization
Process of using machines for production.
Middle Class
Social class emerging from industrialization opportunities.
Social Reform
Movement aimed at improving societal conditions.
Industrialization
Transition from agriculture to industrial economies.
Immigration
Movement of people contributing to labor supply.
Economic Power
Wealth generated from industrial activities.
Labor Conditions
Work environment affecting wages and hours.
Entrepreneurs
Individuals who start and manage businesses.
Stockholders
Investors owning shares in a corporation.
Technology Boom
Rapid advancements in technology during the late 1800s.
Agricultural Revolution
Changes in farming leading to increased productivity.
Napoleonic Wars
Conflicts disrupting European industrialization progress.
Belgium's Industrialization
Started with secret spinning machinery plans.
Geographical Barriers
Natural obstacles hindering industrial development.
Social Structure
Societal organization affecting industrial growth.
Laissez faire
Economic policy allowing free market without government interference.
Adam Smith
Philosopher advocating free economy in 'The Wealth of Nations'.
Three natural laws of economics
Principles governing economic life according to Smith.
Capitalism
Economic system with privately owned production factors.
Thomas Malthus
Economist arguing population grows faster than food supply.
Permanent underclass
Ricardo's theory of always existing poor population.
David Ricardo
Economist who expanded Malthus's population theory.
Utilitarianism
Philosophy judging actions by their usefulness to society.
Jeremy Bentham
Philosopher who introduced utilitarianism in the late 1700s.
John Stuart Mill
Philosopher advocating for workers' rights and wealth equality.
Socialism
Economic system promoting public ownership for welfare of all.
Marxism
Radical socialism introduced by Karl Marx and Engels.
The Communist Manifesto
Pamphlet outlining Marx and Engels' socialist ideas.
Economic progress
Advancement in economic conditions and standards of living.
Free trade
Unrestricted commerce between countries without government interference.
Government intervention
Action taken by authorities to improve social conditions.
Social justice
Fair distribution of wealth and opportunities in society.
Cooperative agriculture
Farming system promoting shared ownership and benefits.
Public ownership
Government control of key industries for public welfare.
Warring classes
Marx's concept of societal divisions based on class conflict.
Legal reforms
Changes aimed at improving justice and legal systems.
Education reforms
Improvements in educational systems for better access and quality.
Industrialization effects
Negative consequences of rapid industrial growth on society.
Bourgeoisie
Middle class 'haves'; employers in society.
Proletariat
Working class 'have nots'; laborers.
Industrial Revolution
Period of rapid industrial growth affecting class dynamics.
Conflict
Struggle between bourgeoisie and proletariat.
Marx and Engels
Philosophers advocating for worker revolution.
Pure Communism
Final phase where all property is communally owned.
Means of Production
Resources used to produce goods and services.
Collective Bargaining
Negotiation process between workers and employers.
Labor Unions
Voluntary associations advocating for workers' rights.
Strikes
Workers' refusal to work in protest.
Abolition of Slavery
Movement to end slavery and promote rights.
William Wilberforce
Key figure in British abolition movement.
Emancipation Proclamation
1863 declaration freeing slaves in Confederate states.
Reform Movements
Efforts to improve social and political conditions.
Women's Rights Movement
Advocacy for women's equality and rights.
Economic Forces
Factors influencing society's structure and dynamics.
Socialism
Economic system with collective ownership of production.
Classless Society
Society without class distinctions or hierarchies.
Higher Wages
Increased pay offered for factory work.
Factory Conditions
Often harsh environments faced by workers.
Democratic Reform
Changes aimed at improving democratic governance.
Revolutionary Leaders
Figures like Lenin and Mao adapting Marxism.
Slavery in the Americas
Continued enslavement until late 19th century.
Public Education
Movement for accessible education for all.