Renaissance Art Study Guide
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Early Renaissance
Approximately 1400-1500, characterized by naturalism and the study of classical antiquity.
High Renaissance
Approximately 1500-1520, marked by a peak in artistic achievement and idealized forms.
Mannerism
Approximately 1520-1600, characterized by elongated figures and exaggerated emotional expression.
Humanism
A Renaissance intellectual movement emphasizing human potential, individualism, and secular subjects.
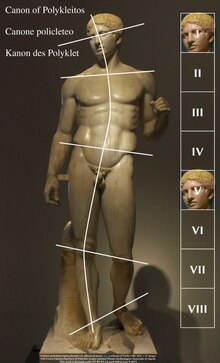
Contrapposto
A stance in sculpture where the figure's weight is shifted onto one leg, creating a naturalistic posture.

Chiaroscuro
The use of light and shadow in art to create depth and volume.
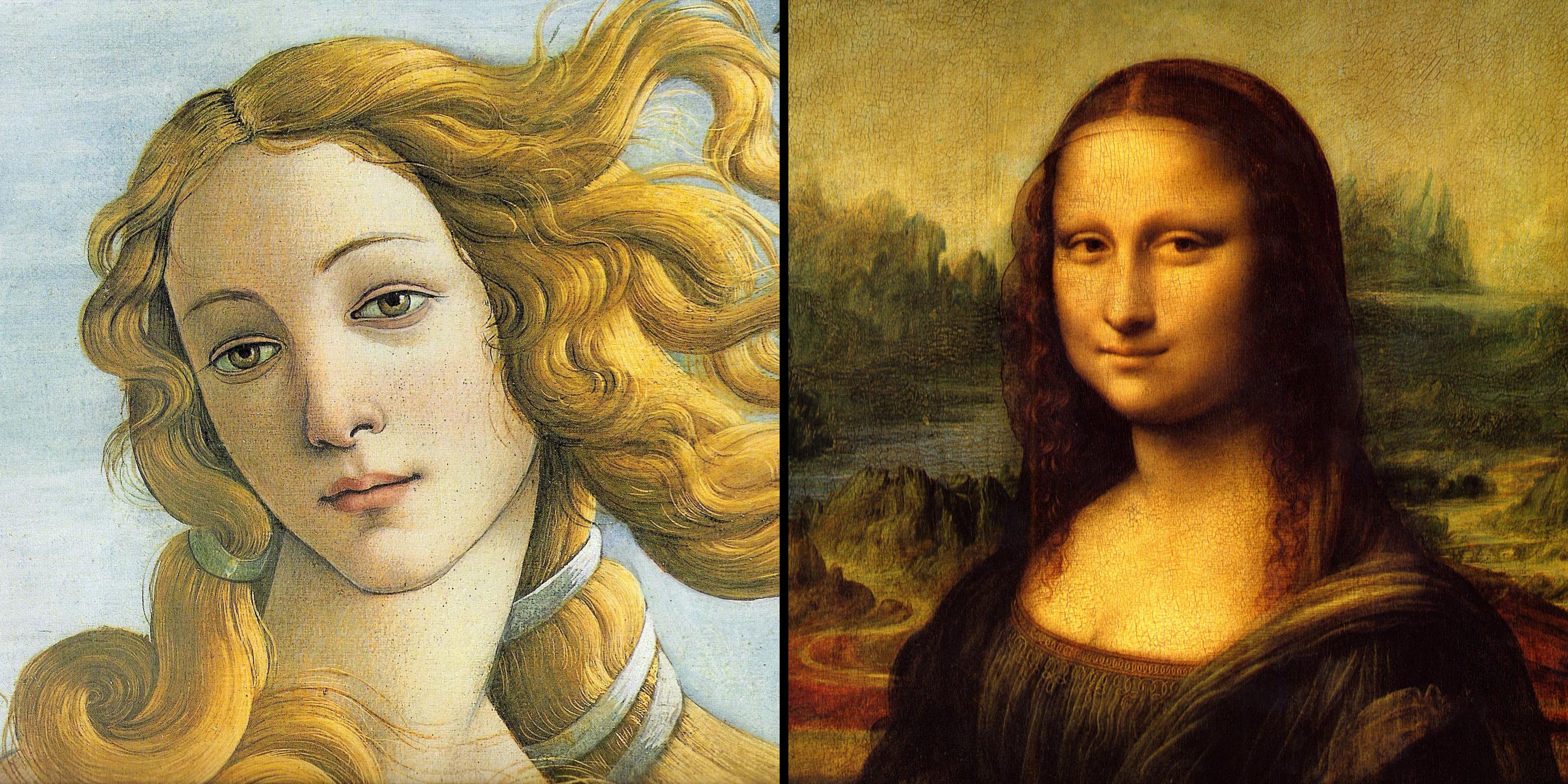
Sfumato
A painting technique blending colors and tones seamlessly without harsh outlines, notably used by Leonardo da Vinci.
Canvas
A strong, durable fabric used as a medium for oil paintings.
In situ
Latin for 'in place', refers to art or architecture remaining in its original location.
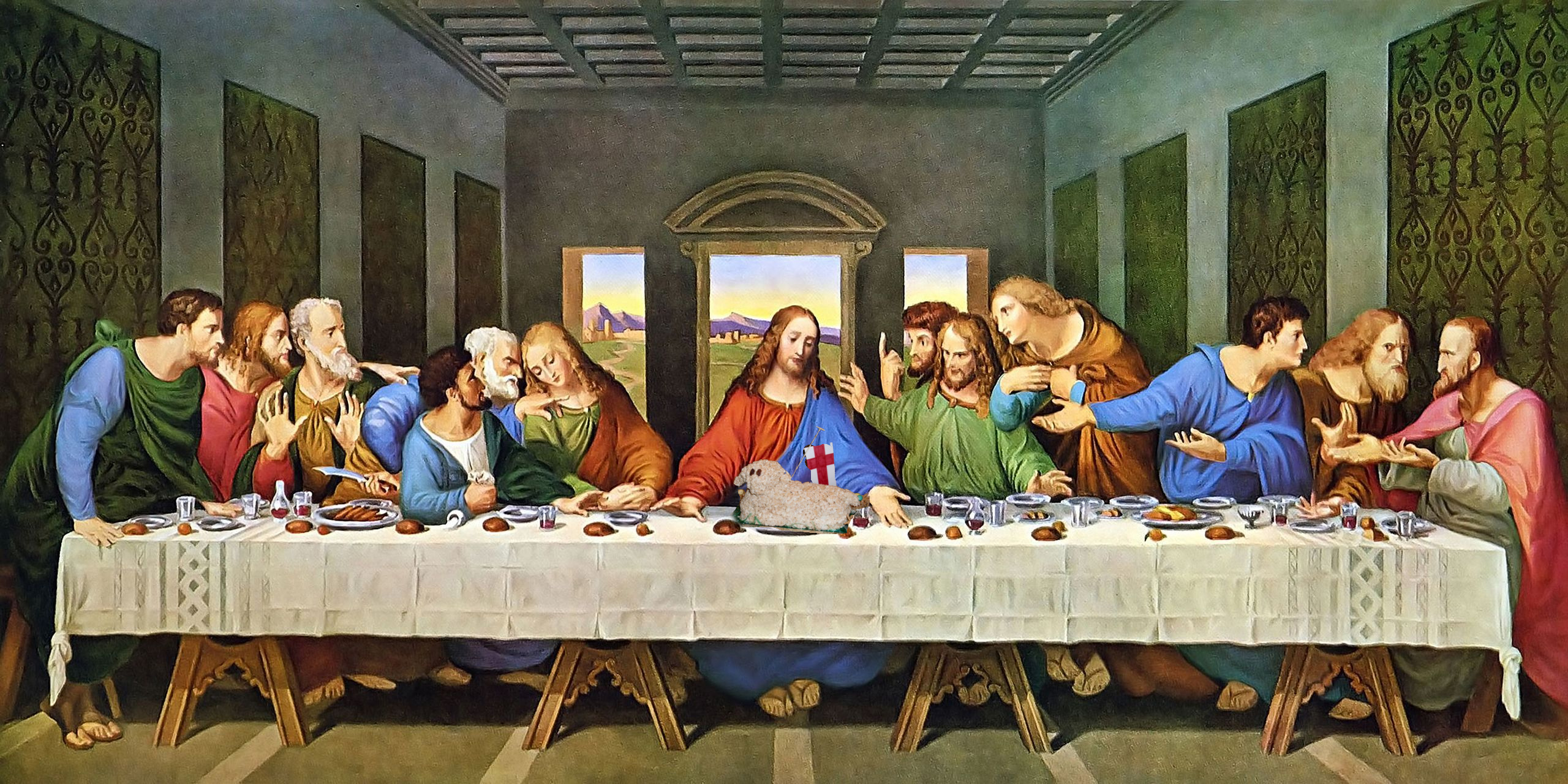

Last Supper
The final meal shared by Jesus and his disciples before his crucifixion; a popular subject in Christian art.

Pietra Serena
A type of gray sandstone used in Renaissance architecture, especially associated with Florence.
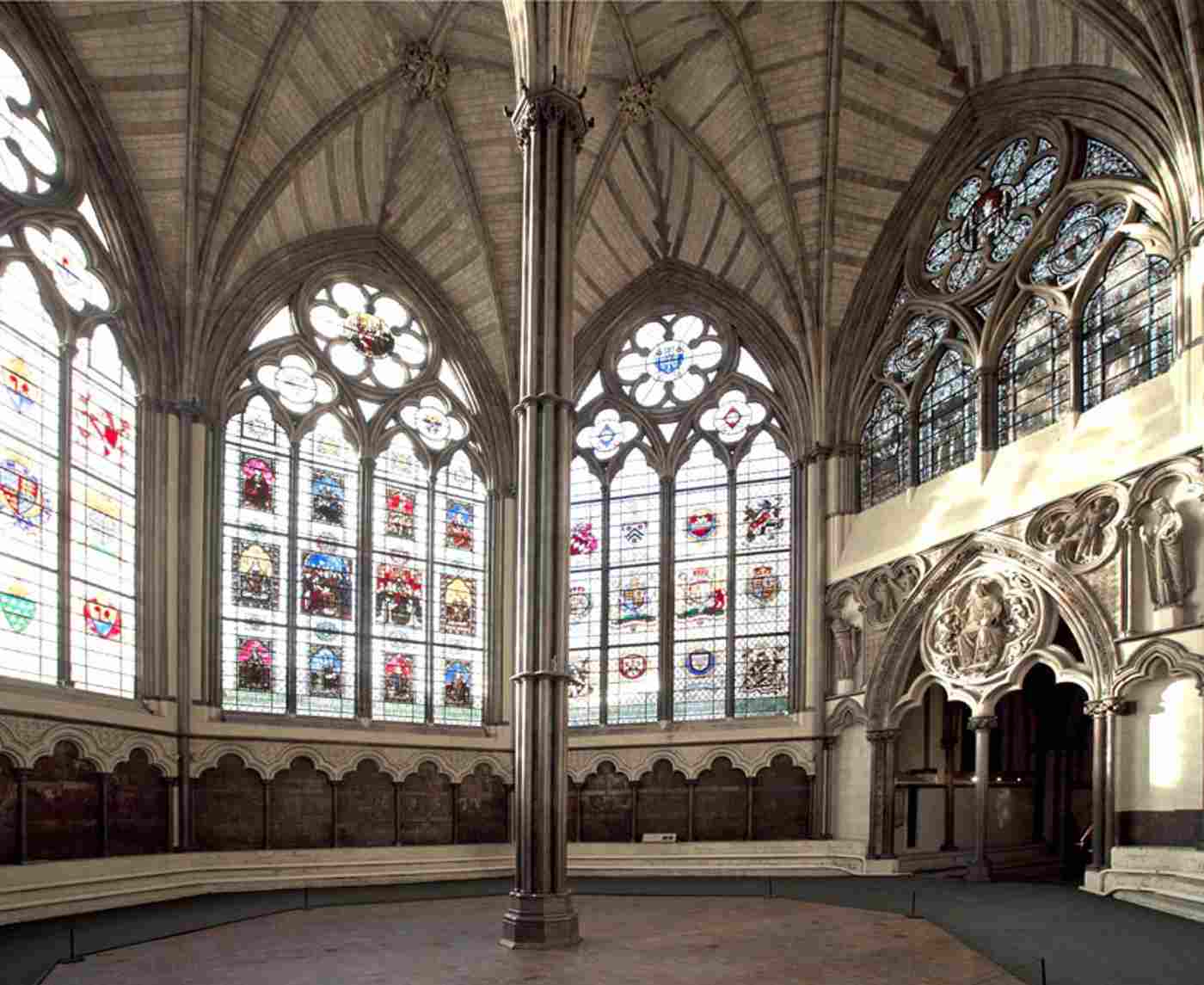

Chapter House
A room in a monastery or convent used for meetings, often decorated with religious art.
Madonna
Depiction of the Virgin Mary, often with the infant Jesus, in art.
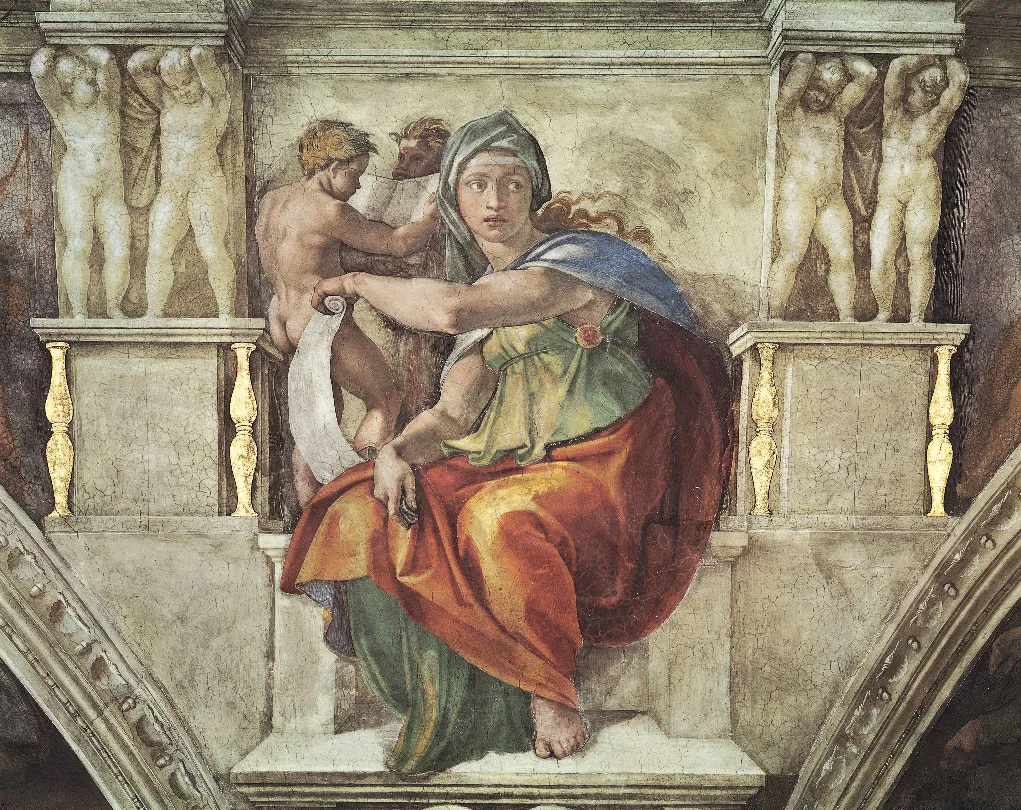

Sibyl
A prophetess or oracle depicted in classical mythology and Renaissance art.
Filippo Brunelleschi
Architect known for the Pazzi Chapel, featuring simplicity and harmony with classical elements.
Leon Battista Alberti
Architect of Palazzo Rucellai, noted for its classical order and innovative façade.
Fra Filippo Lippi
Artist known for naturalistic figures, exemplified in 'Madonna and Child with Two Angels'.
Sandro Botticelli
Artist known for 'Birth of Venus', emphasizing idealized beauty and mythology.
Donatello
Early Renaissance sculptor known for his bronze 'David', the first freestanding nude statue since antiquity.
Michelangelo
High Renaissance artist known for 'David' and the Sistine Chapel Ceiling, representing the idealized human form.
Raphael
High Renaissance artist known for the 'School of Athens', focusing on classical philosophers.
Titian
Venetian Renaissance artist known for 'Venus of Urbino', focusing on sensuality and rich colors.
Jacopo da Pontormo
Mannerist artist known for 'Entombment of Christ', characterized by elongated figures and emotional expressiveness.
Fresco
A technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid wet plaster.
Temperas
A fast-drying painting medium made of colored pigments mixed with a water-soluble binder.
Bronze
A metal alloy used in sculptures, such as Donatello's and Verrocchio’s 'David'.
Marble
A metamorphic rock commonly used in sculpture, notably Michelangelo's 'David'.
Venetian style
Art characterized by rich colors, sensuality and emotional depth, prominently used by Titian.
Pope Julius II
Patron of Michelangelo's Sistine Chapel, intending to glorify the church.
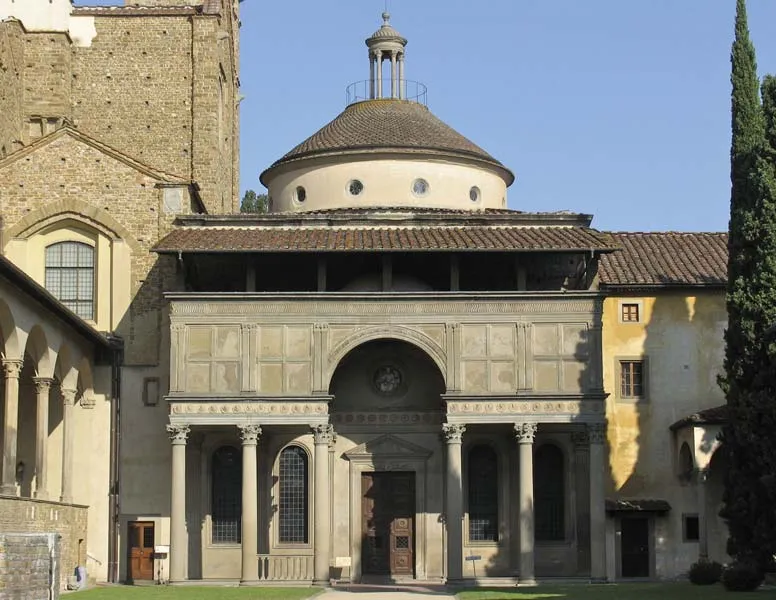

Filippo Brunelleschi, Pazzi Chapel (architectural style)
Renaissance, with classical elements such as columns and arches.
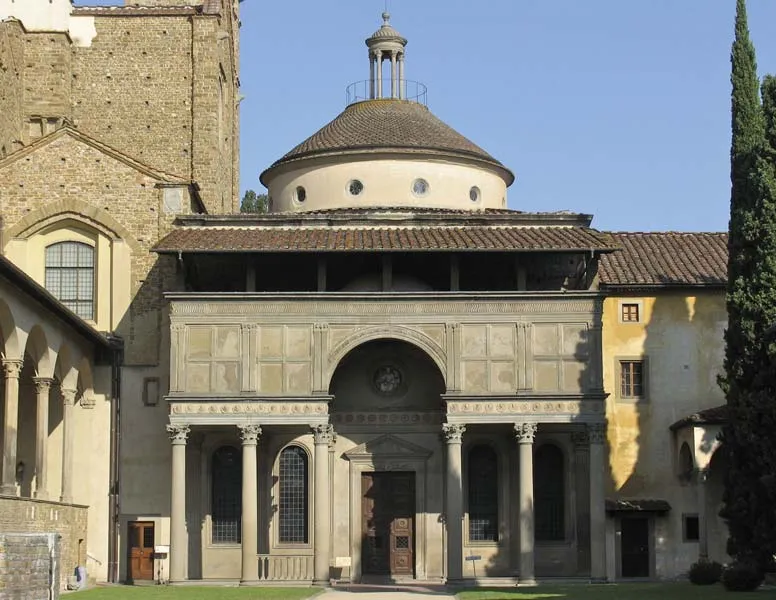

Filippo Brunelleschi, Pazzi Chapel (interior)
Simplicity and harmony, focusing on geometry and balance.
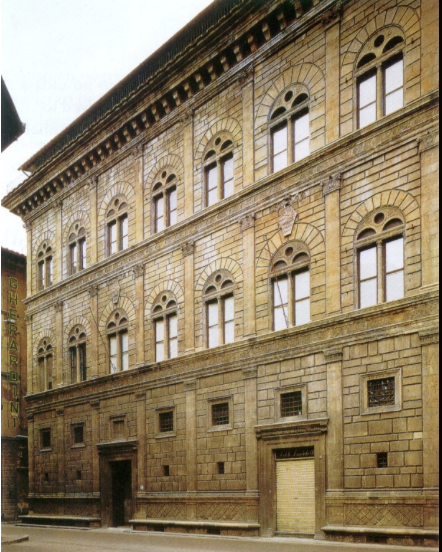

Leon Battista Alberti, Palazzo Rucellai (First Floor)
Rusticated stonework, used for strength and to support the building.
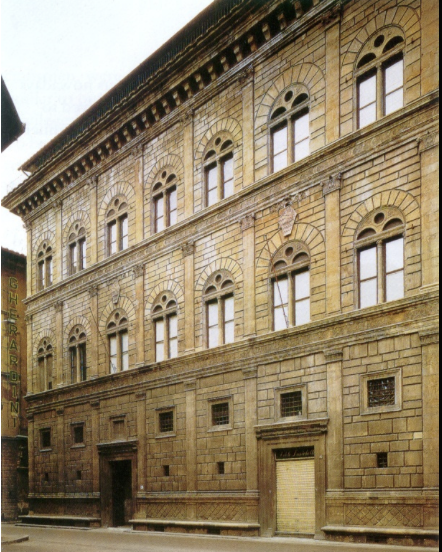

Leon Battista Alberti, Palazzo Rucellai (Second Floor)
Smooth masonry with decorative pilasters, focusing on classical order.
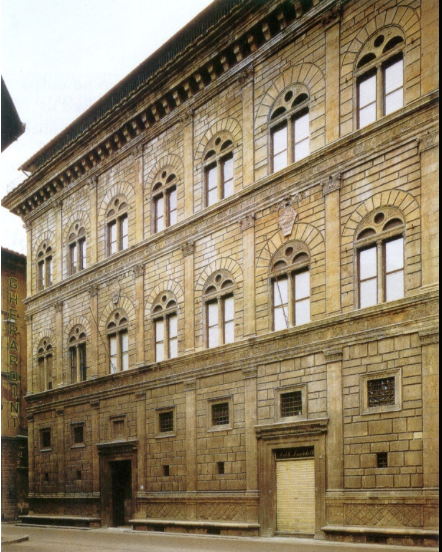

Leon Battista Alberti, Palazzo Rucellai (Third Floor)
Lighter masonry, signifying elegance and refinement.

Fra Filippo Lippi, Madonna and Child with Two Angels
Early Renaissance style, characterized by naturalistic figures and delicate use of color.
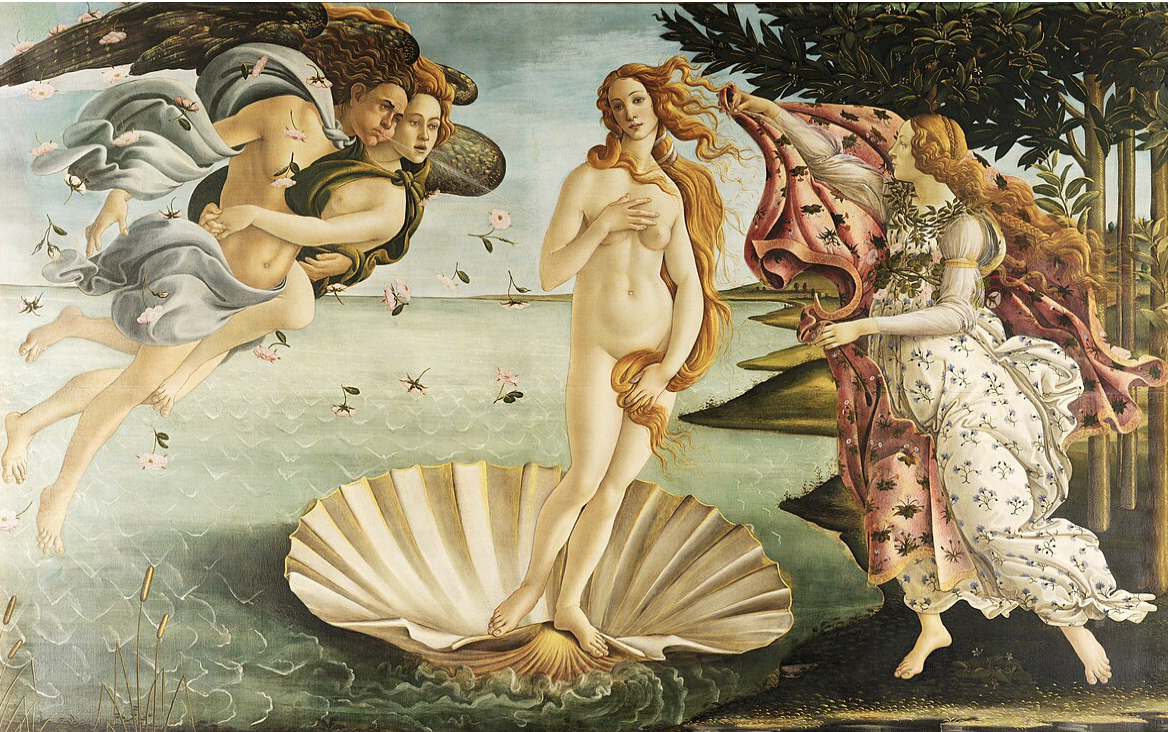
Sandro Botticelli, Birth of Venus
Early Renaissance style, with an emphasis on mythology, idealized beauty, and flowing lines.
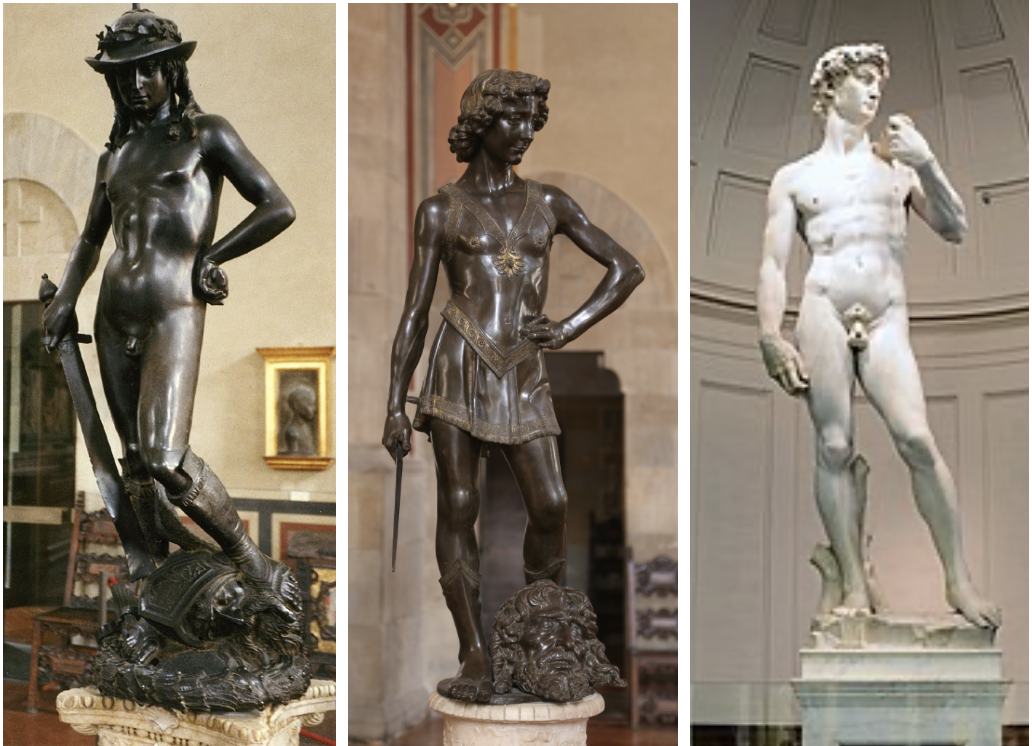

Donatello, David
Early Renaissance style, first free-standing nude statue since antiquity; emphasizes youth and naturalism.
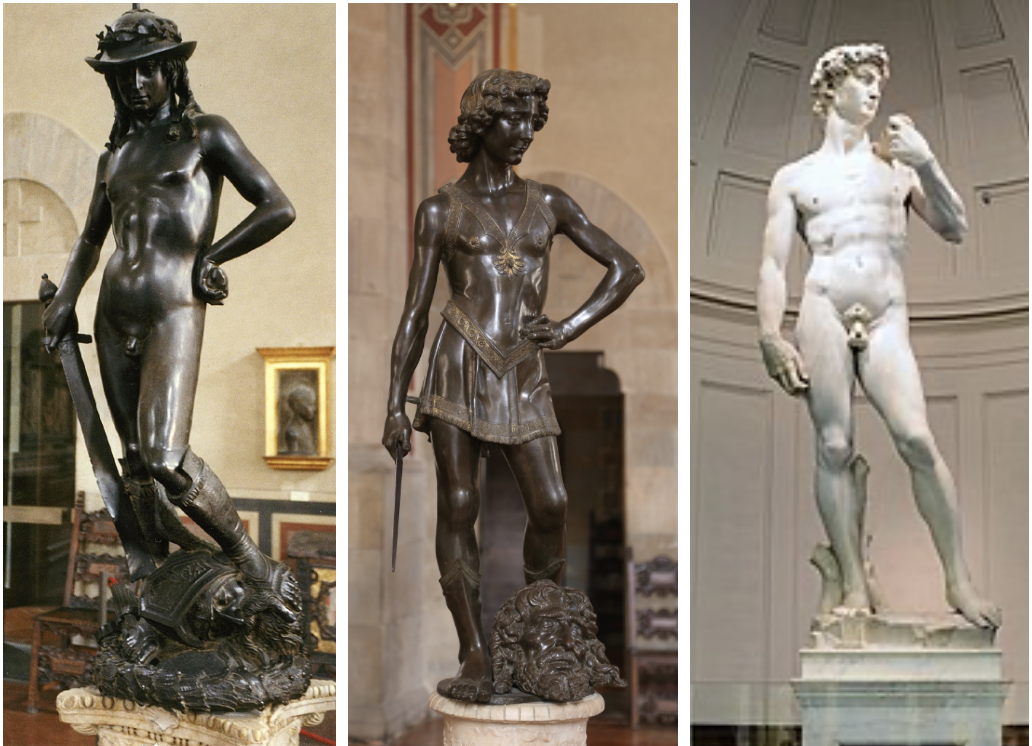

Verrocchio, David
Early Renaissance style, more detailed and refined compared to Donatello's David, showing strength and youth.
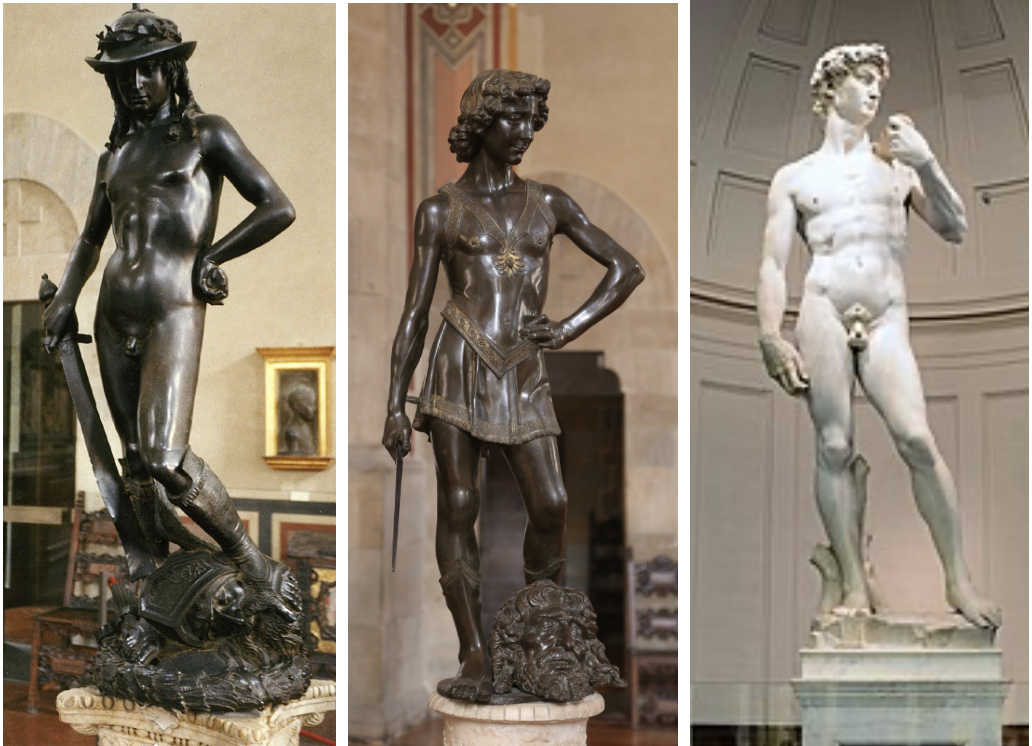

Michelangelo, David
High Renaissance style, idealized and muscular, representing the biblical hero as a symbol of human potential and strength.
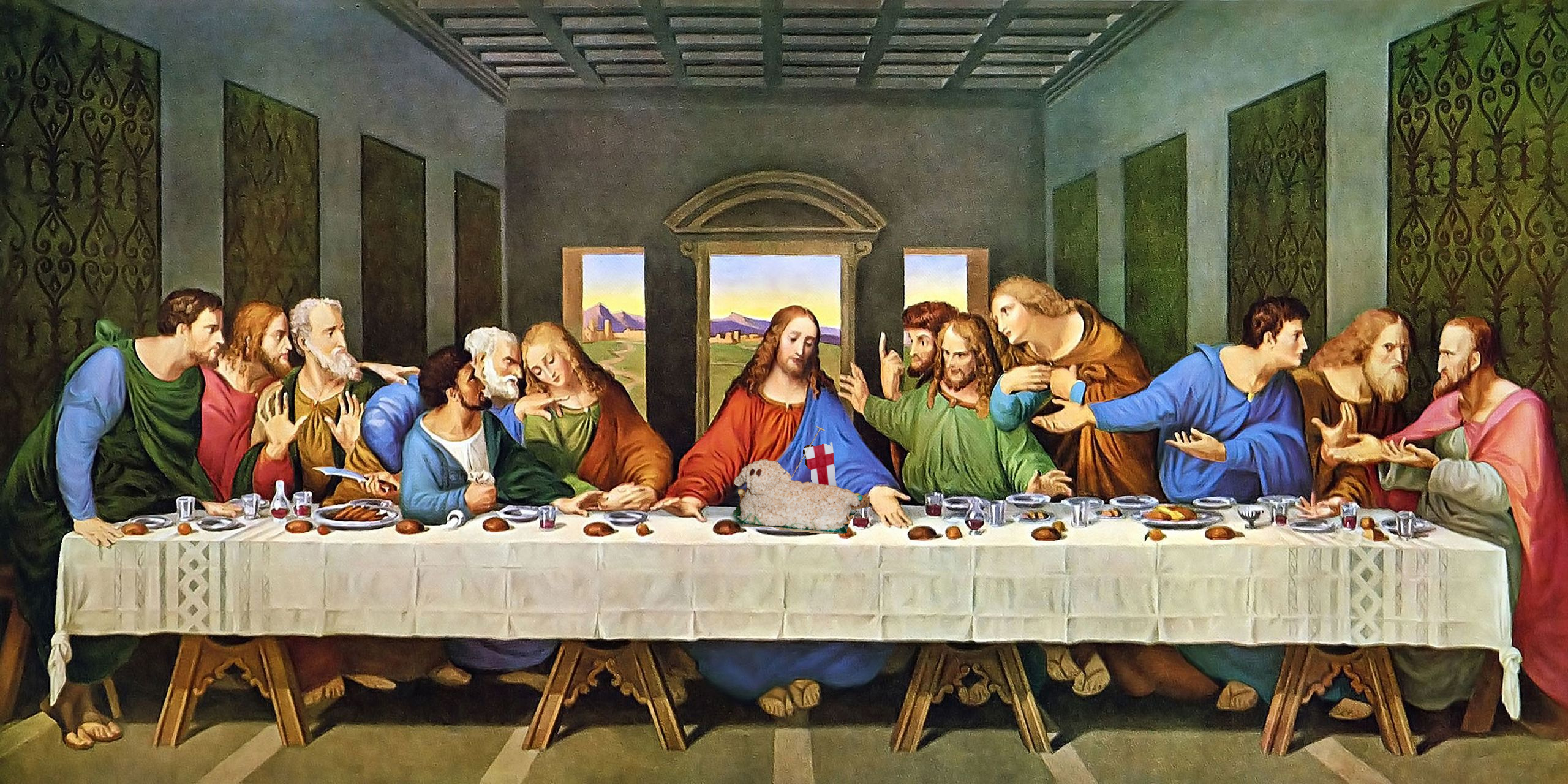

Leonardo da Vinci, Last Supper (Mentor)
Andrea del Verrocchio taught Leonardo, particularly in technique and composition.
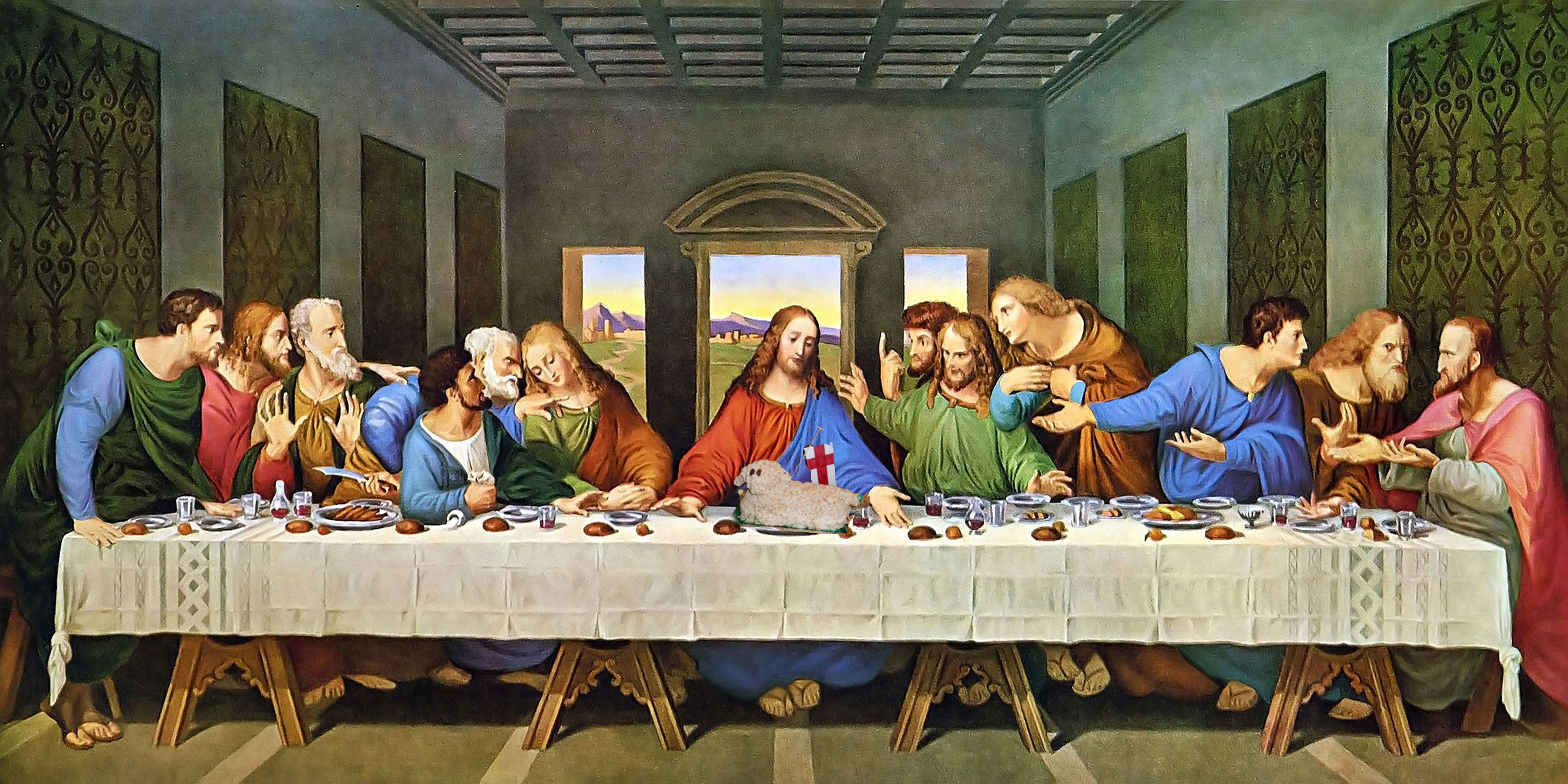

Leonardo da Vinci, Last Supper (Artistic Elements)
Use of perspective and emotional expression.
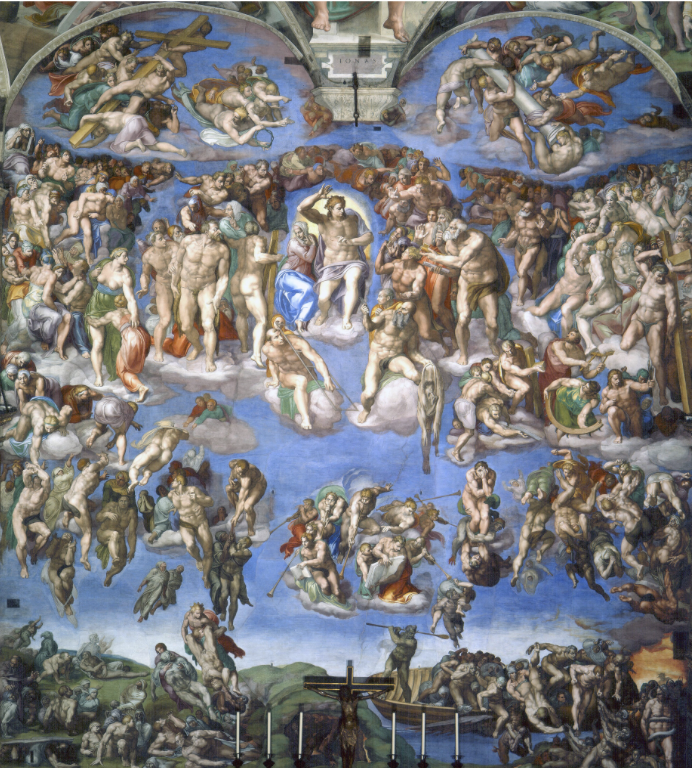

Michelangelo, Sistine Chapel Ceiling (Style)
High Renaissance, demonstrates human drama and anatomical precision.
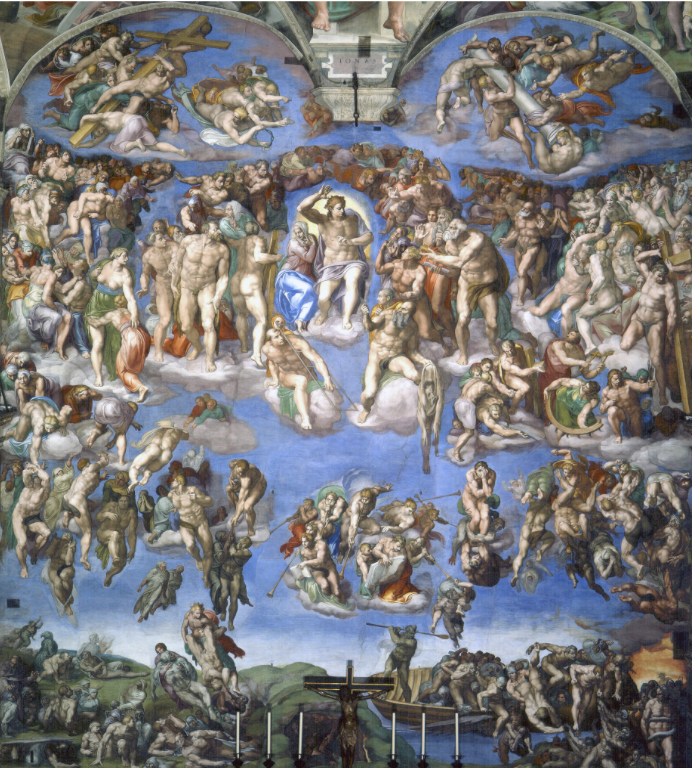

Michelangelo, Sistine Chapel Ceiling (Themes)
Biblical stories, from Genesis to the prophetic figures like Sybils.
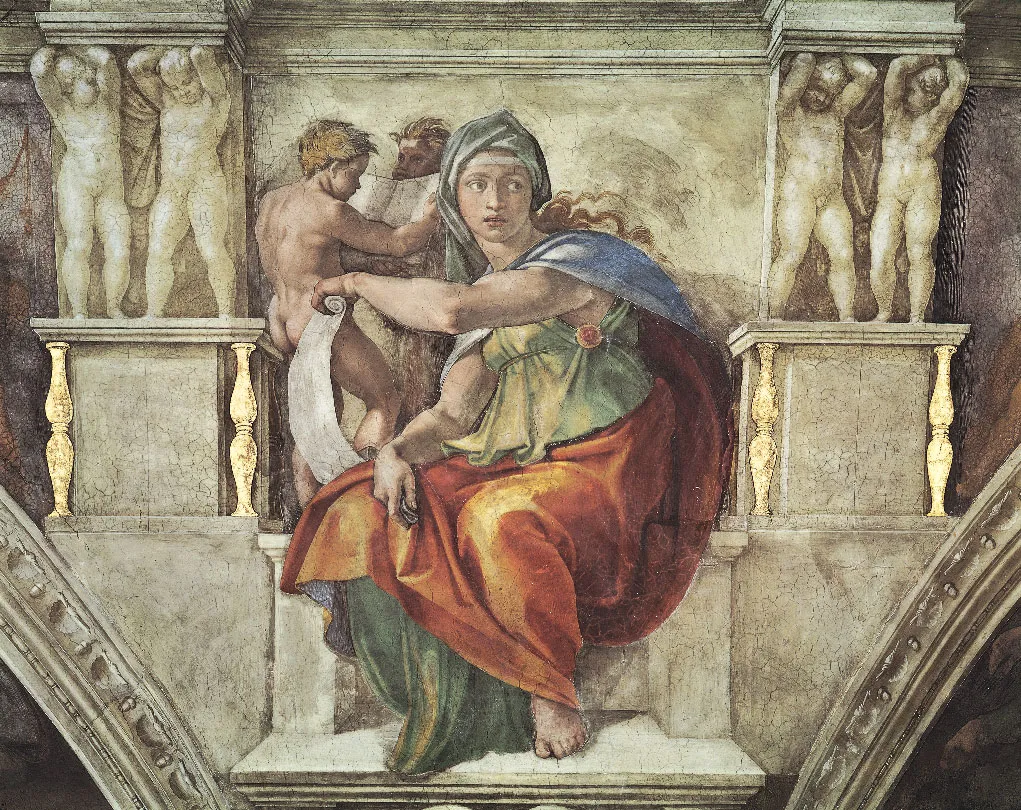

Michelangelo, Last Judgement
Mannerism style, characterized by exaggerated proportions and emotional intensity.
Raphael, School of Athens
High Renaissance style, focuses on classical philosophers and the synthesis of knowledge.

Titian, Venus of Urbino
Venetian Renaissance style, known for its sensuality and rich color palette.
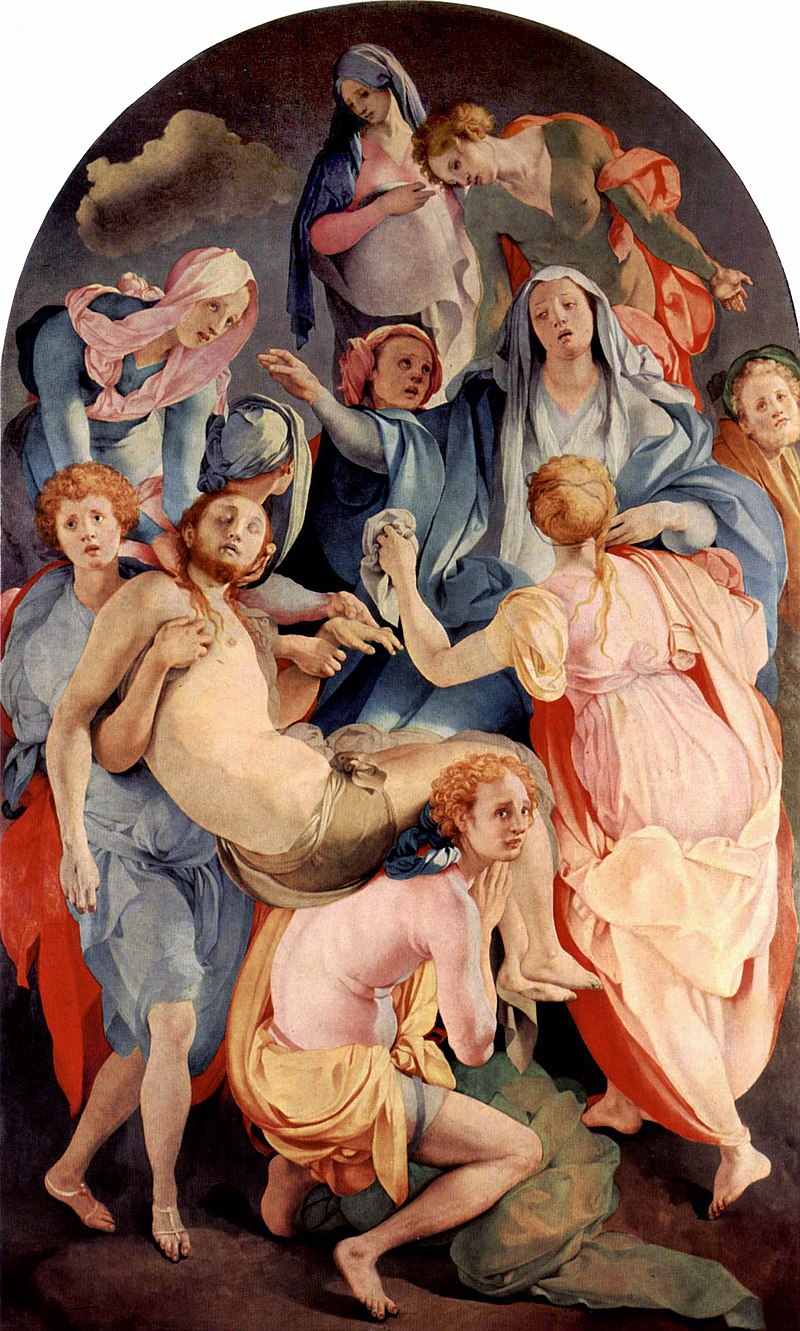

Jacopo da Pontormo, Entombment of Christ
Mannerism style, with elongated figures and a focus on emotional expressiveness.