BCEM 393 - Carbohydrates [UNFINISHED]
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Define: carbohydrates
Carbon-based molecules that are rich in hydroxyl (C-OH) groups (literally a carbon hydrate)
Fill in the blank: simple carbohydrates are called _______.
Monosaccharides
Fill in the blanks: complex carbohydrates - polymers of covalently linked _______ - are called _______.
Monosaccharides, polysaccharides
True or False: a polysaccharide can be as simple as two identical monosaccharides linked together or it can be quite complex, consisting of dozens of different monosaccharides.
True
True or False: the variety of monosaccharides and the multiplicity of linkages forming polysaccharides mean that carbohydrates provide cells with a vast array of three-dimensional structures that can be used for a variety of purposes as simple as energy storage or as complex as cell-cell recognition signals.
True
Fill in the blanks: monosaccharides are _______ or ________ that have two or more ________ groups.
Aldehydes, ketones, hydroxyl
Fill in the blanks: the D or L conformation of carbohydrates is determined by the position of the _______ group attached to the asymmetric carbon furthest from the ________ or ________.
-OH, aldehyde, ketone
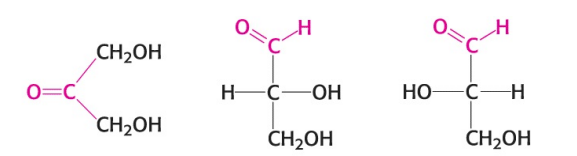
Name the monosaccharide in the image (left).
A ketose (dihydroxyacetone)
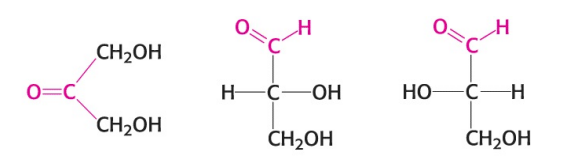
Name the monosaccharide in the image (middle).
An aldose (D-Glyceraldehyde)
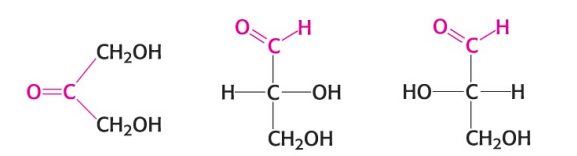
Name the monosaccharide in the image (right).
An aldose (L-Glyceraldehyde)
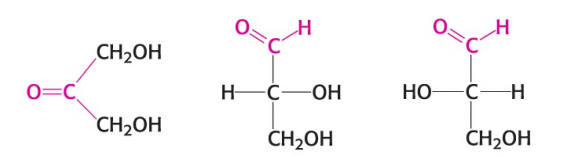
Fill in the blank: the simplest monosaccharides (depicted in the image) have three carbons, and are referred to as ________.
Trioses
True or False: carbohydrates exist in very few isomeric forms.
False; exist in many isomeric forms
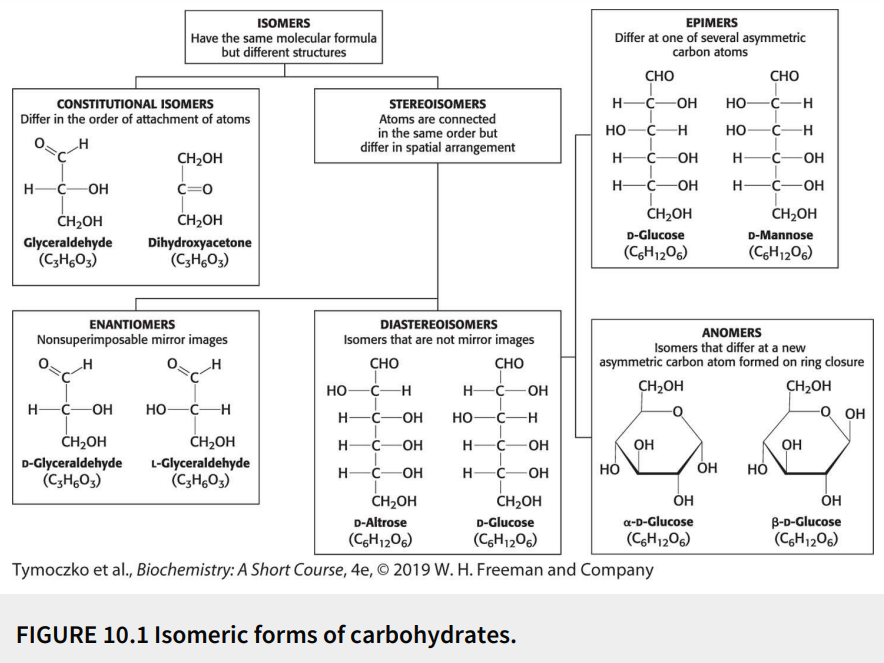
Fill in the blank: dihydroxyacetone and glyceraldehyde are _________ because they have identical molecular formulas but differ in how the atoms are ordered.
Constitutional isomers
Define: constitutional isomers
Have the same molecular formula (isomers) but differ in the order of attachment of atoms
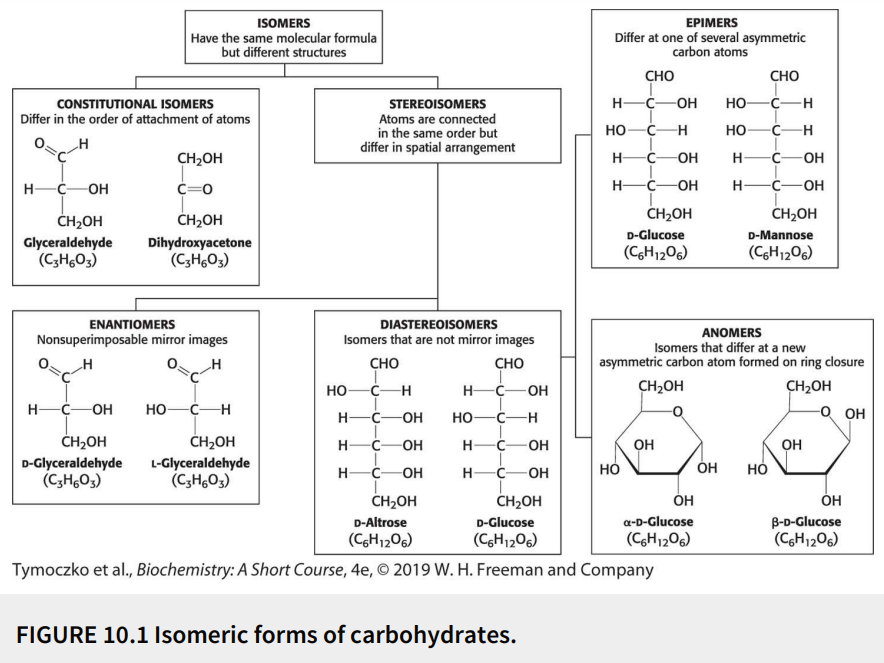
Define: stereoisomers
Have the same molecular formula (isomers) with the atoms connected in the same order but differ in spatial arrangement
Fill in the blank: glyceraldehyde has a single asymmetric carbon atom, and thus, there are two stereoisomers of this sugar - D-glyceraldehyde and L-glyceraldehyde. These molecules are a type of stereoisomer called ________.
Enantiomers
Define: enantiomers
Stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images
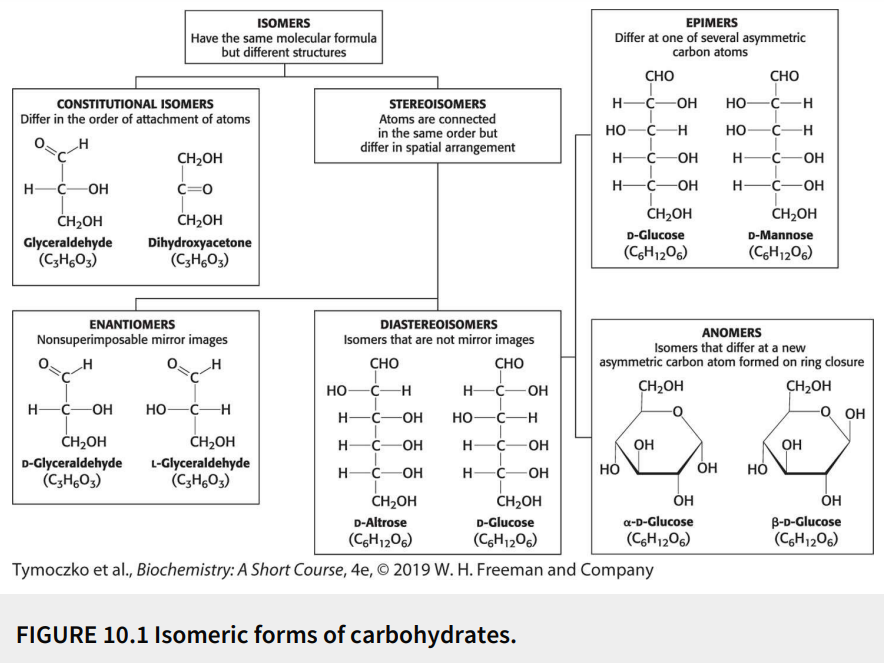
Fill in the blanks: monosaccharides made up of more than three carbon atoms have multiple asymmetric carbon atoms, and so they exist not only as _______ but also as ________.
Enantiomers, diastereoisomers
Define: diastereoisomers
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images
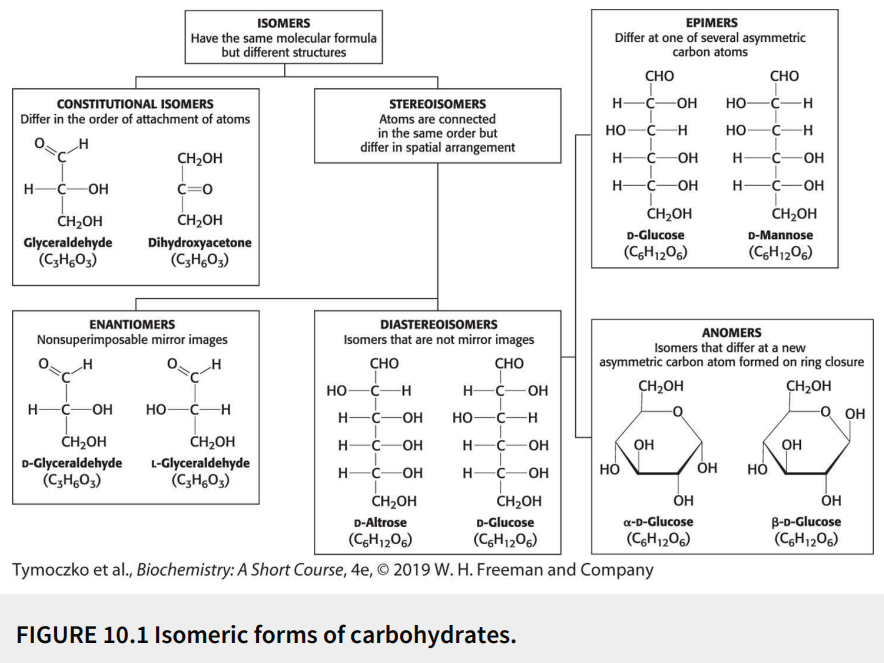
Define: epimers
Diastereoisomers that differ at one of several asymmetric carbon atoms
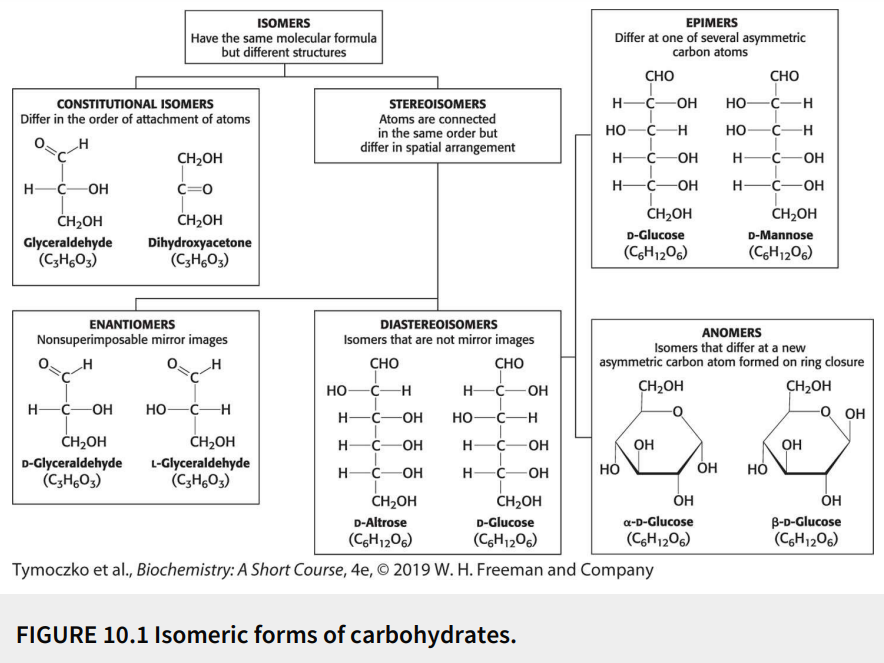
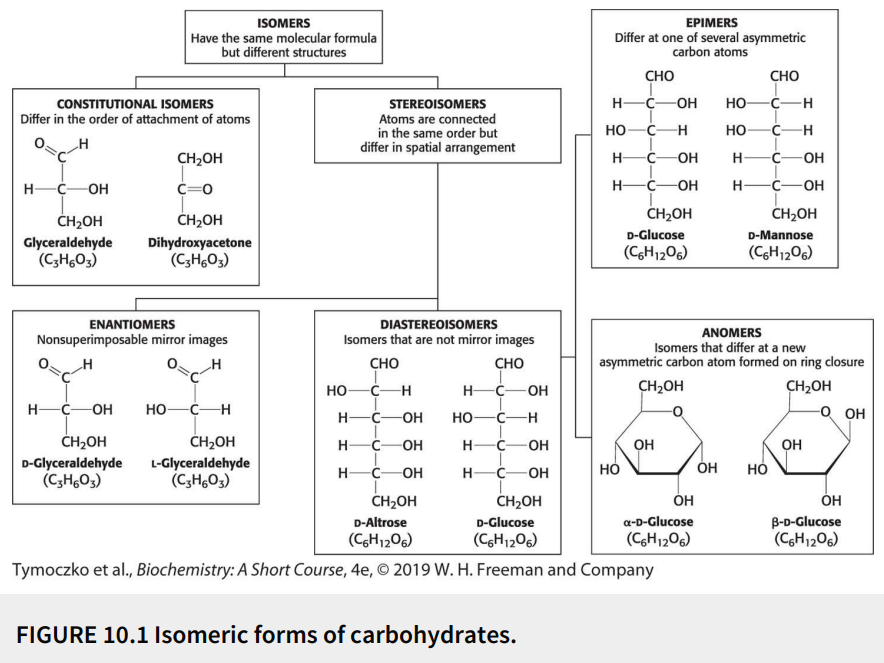
Define: anomers
Diastereoisomers that differ at a new asymmetric carbon atom formed on ring closure
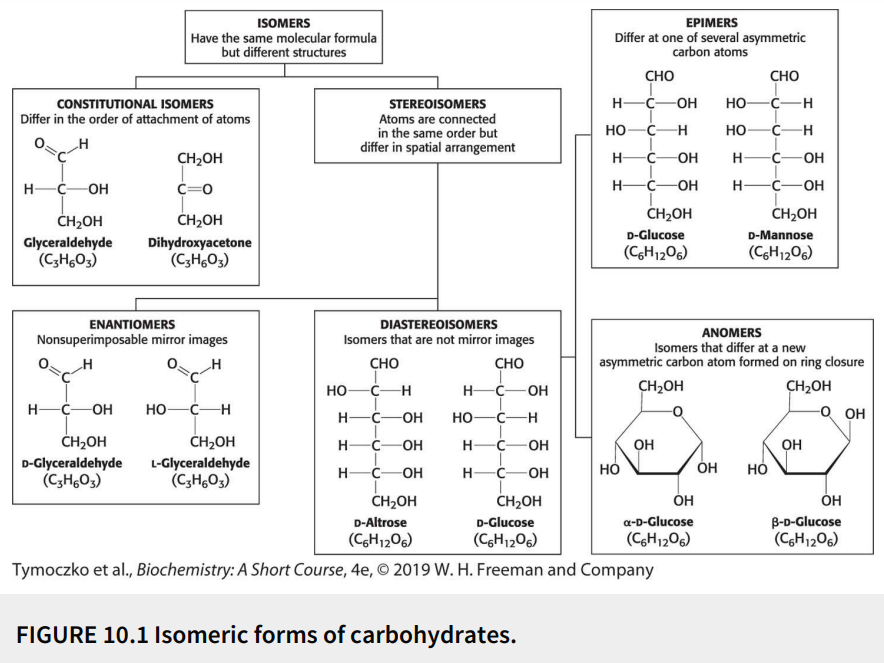
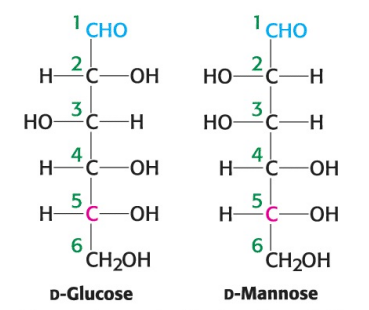
True or False: D-glucose and D-mannose are ketoses.
False; they are aldoses
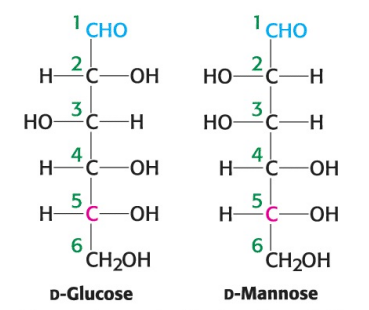
True or False: D-glucose and D-mannose are enantiomers.
False; they are not mirror images
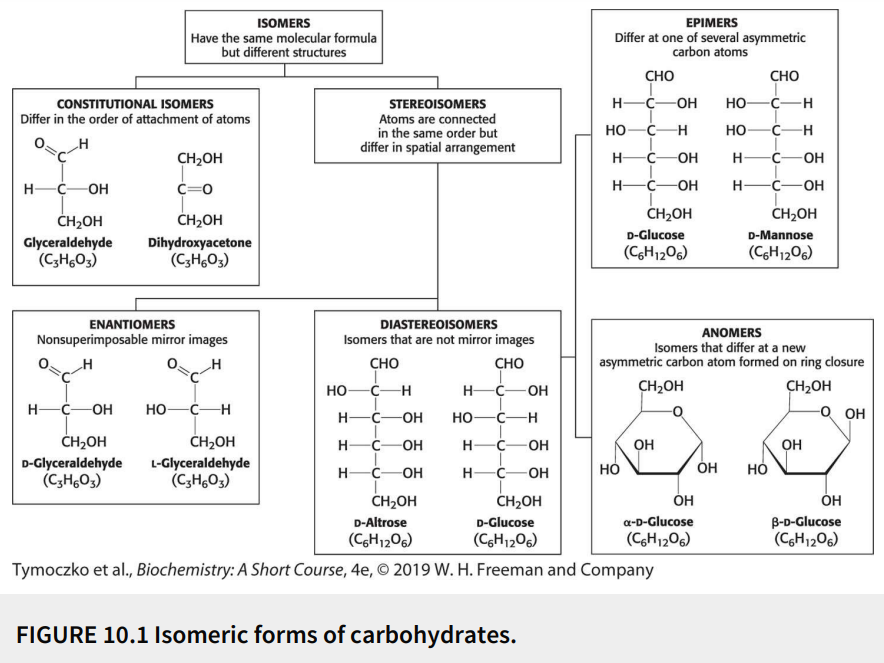
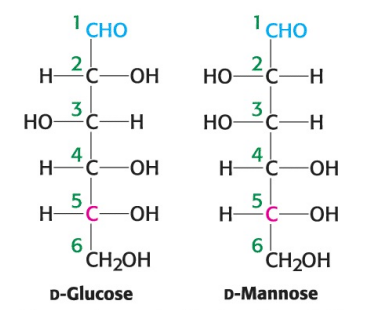
True or False: D-glucose and D-mannose are diastereomers.
True
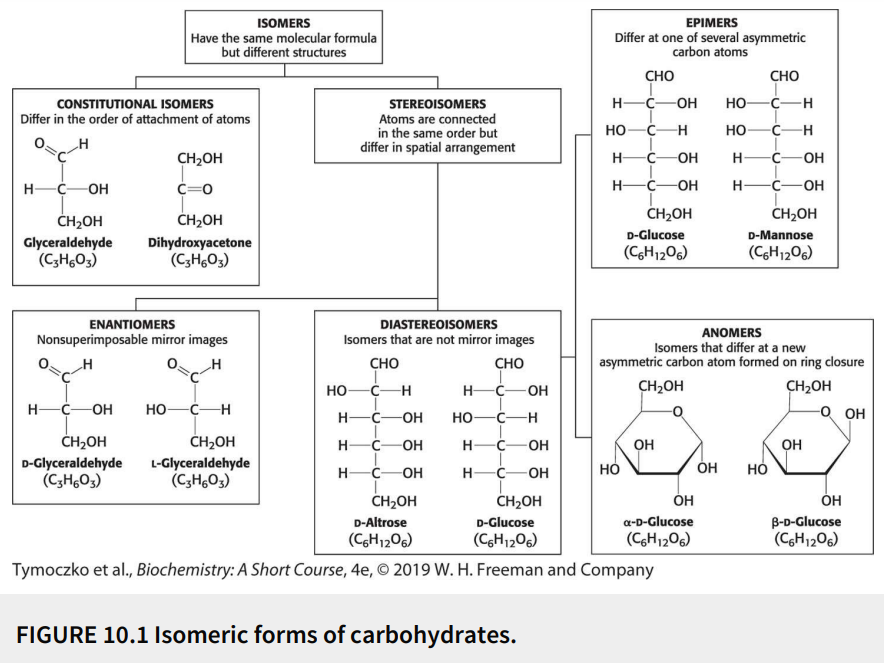
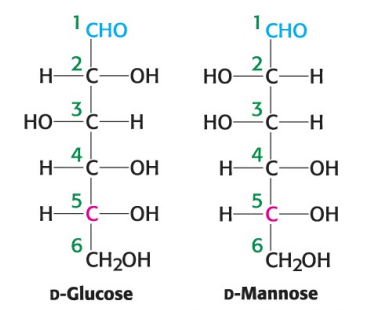
True or False: D-glucose and D-mannose are constitutional isomers.
False; they are stereoisomers (atoms are connected in same order but differ in spatial arrangement)
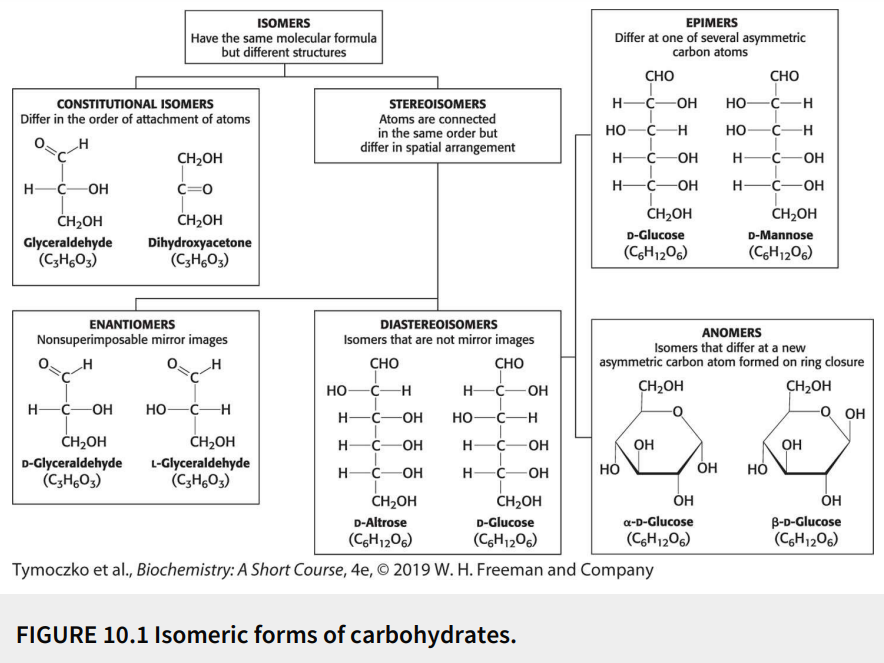
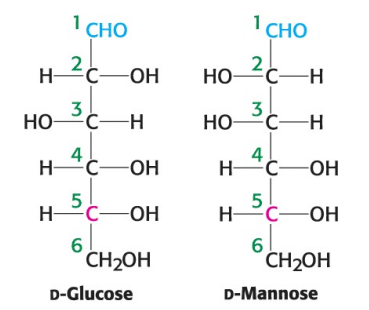
True or False: D-glucose and D-mannose are epimers.
True
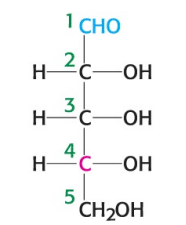
True or False: ketoses have one less asymmetric center than aldoses with the same number of carbons atoms.
True
What is the name of the sugar depicted in the image?
D-ribose
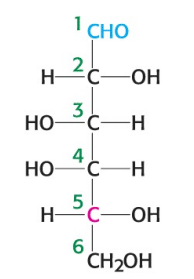
What is the name of the sugar depicted in the image?
D-deoxyribose
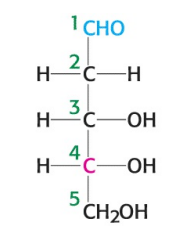
What is the name of the sugar depicted in the image?
D-glucose
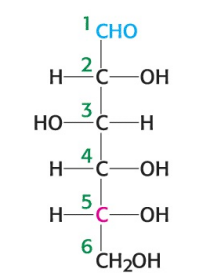
What is the name of the sugar depicted in the image?
D-mannose
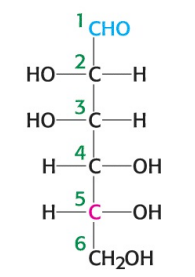
What is the name of the sugar depicted in the image?
D-galactose
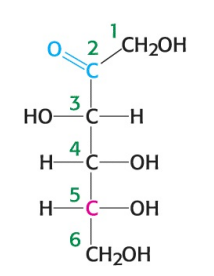
What is the name of the sugar depicted in the image?
D-fructose
True or False: the predominant forms of ribose, glucose, fructose, and many other sugars in solution are not open chains, but rings.
True
Fill in the blanks: the chemical basis for sugar ring formation is that an _________ can react with an ________ to form a ________.
Aldehyde, alcohol, hemiacetal
True or False: six- and five-membered sugar rings tend to be unstable.
False; they tend to be stable