Final 445 Study Guide
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Systems model including all parts of the systems as well as examples of each; system characteristic definitions
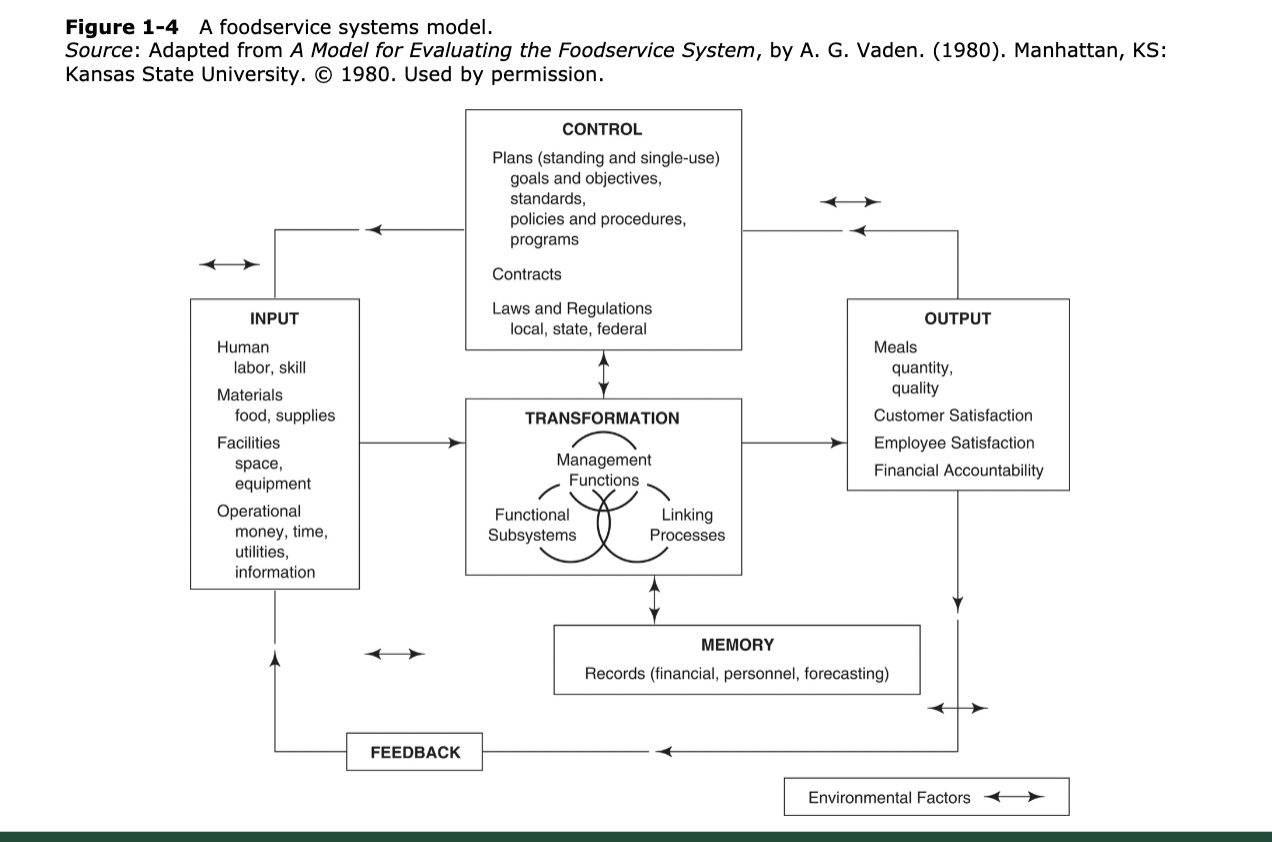
Characteristics of a system
Interdependency of Parts (Leads to integration and synergy) → Dynamic Equilibrium → Equifinality → Permeable Boundaries → Interface (Of systems and subsystems) → Hierarchy (Of the system)
Definitions of a system
1. Interdependency of Parts (Leads to Integration and Synergy):
- The components of a system or organization rely on each other for functionality and success. Integration and synergy occur when these parts work together harmoniously to achieve common goals, leveraging their combined strengths and resources.
2. Dynamic Equilibrium:
- Systems tend to maintain a state of balance or equilibrium despite internal and external changes. This dynamic equilibrium allows the system to adapt and adjust over time to maintain stability and functionality.
3. Equifinality:
- Refers to the principle that multiple paths or processes can lead to the same outcome or goal. It recognizes that different approaches or strategies may be equally effective in achieving desired results within a system.
4. Permeable Boundaries:
- Boundaries of a system that allow for the exchange of information, resources, and energy with the external environment. Permeable boundaries enable the system to interact with its surroundings, adapt to changes, and maintain flexibility.
5. Interface (Of Systems and Subsystems):
- The point of interaction or connection between different systems or subsystems within a larger system. Interfaces facilitate communication, coordination, and exchange of inputs and outputs between interconnected parts, ensuring seamless integration and functionality.
6. Hierarchy (Of the System):
- The organization of a system into levels or layers of subsystems, with each level having distinct functions and responsibilities. Hierarchy establishes a framework for organizing and managing complex systems, enabling efficient coordination and control of processes and activities.
Types of Business Ownership
Sole Proprietorship: Owned and operated by a single individual, who assumes full control and responsibility for the business.
Partnership: Involves two or more individuals or entities sharing ownership and management responsibilities.
Corporation: A legal entity separate from its owners (shareholders), providing limited liability protection.
Limited Liability Company (LLC): Offers limited liability protection to owners (members) with pass-through taxation and flexibility.
Franchise: Business arrangement where a franchisor grants a franchisee the right to operate under its brand.
Cooperative: Owned and operated by members who share ownership and decision-making.
Sustainability: three main aspects of sustainability
Ecologically sound
Economically Viable
Socially acceptable
Sustainability: Different areas of sustainability within foodservice
Energy Management
Types of appliances and equipment purchased (proper equipment)
Ex: proper use of equipment, turning the equipment off when it is not in use, automatic sensors, proper maintenance of equipment
Water/Waste water diversion
Amount of fresh water available, heating + cooling of water, water disposal waste water treatment
Ex: low flow fixtures, fixtures with sensors, tankless water heaters, sanitation equipment, warewashing
Waste management
Food
Sustainability issues involve the production of both food crops and animal products
Ex: Food shed, buy local, organic, biotechnology, animal welfare
Green foodservices
LEED certification
Green restaurant association
Education
Sustainable: Offenders of sustainability
Equipment involved in heat transfer (HVAC, refrigeration, cooking, hot holding)
Sustainability: Composting
Pre-consumer composting: This refers to organic waste generated before reaching the consumer, typically from agricultural, industrial, or food processing activities. Examples include fruit and vegetable trimmings from food production facilities, coffee grounds from cafes, or plant material from farms.
Post-consumer composting: This involves organic waste generated by consumers after use. It includes food scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials discarded by households, restaurants, or institutions after consumption or use.
Different Methods of Purchasing
Independent: One unit, purchasing for itself
Central: Personnel in one office do purchasing for all units
Group/Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs): Union of separate, unrelated units participate in joint purchasing
Warehouse Club Purchasing: Operation purchases directly from warehouse or
Just-in-Time (JIT) Purchasing: Ordering goods only when needed to minimize inventory costs and waste.
Bid buying: Daily Bid, Line Item Bidding, All-or-Nothing Bidding
Value and value analysis - Perceived value (powerpoint)
Value
Result of the relationship between the price paid for a particular item and its utility in the function it fulfills
is the perceived relationship between utility/function and price
Value analysis:
Methodical investigation of all components of an existing product or service with the goal of discovering and eliminating unnecessary costs without interfering with the effectiveness of the product or service
Method of improving a product’s value by relating elements of product worth to cost
Find alternate ways to meet required function at the least expense to the organization’s resources
(quality, quantity, price, likability)
Perceived value
depends on supply, demand, time, holidays/occasions, etc.
Value analysis- perceived value (Chat GPT)
Value:
Value in the food service industry refers to the perceived benefits or worth that customers derive from a product or service relative to its cost. It's about meeting or exceeding customer expectations in terms of quality, service, and price.
Value Analysis:
Value analysis involves systematically examining the components of a product or service to determine its value proposition and identify opportunities for improvement. It focuses on enhancing value by optimizing quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Perceived Value:
Perceived value is the customer's subjective assessment of the benefits received compared to the costs incurred. It encompasses factors such as food quality, taste, presentation, service quality, ambiance, convenience, and price fairness.
Sensory analysis: types of sensory tests, how to minimize bias, different sensory characteristics
Analytical
1. Difference Test:
- Determines if there is a perceptible difference between two samples of a product, such as formulations or processing methods.
2. Descriptive Analysis:
- Systematically evaluates and describes the sensory attributes of a food product using standardized terminology and scales.
3. Hedonic Test:
- Measures consumer preference or liking for different products or variations using a scale ranging from dislike to like.
4. Discrimination Tests:
- Evaluate panelists' ability to detect differences or similarities between samples based on specific sensory attributes.
Types of Affective Sensory Tests
Discrimination: Tests for detectable differences among food items
Descriptive: Evaluate the taste, aroma, texture, tenderness, consistency etc....
Acceptance and Preference: Determines whether or not people will like the menu item
How to minimize bias:
Randomization, blinded tests, QDA professionals
Analytical vs Affective tests
1. Analytical Sensory Tests:
- Analytical tests focus on objective evaluation of sensory attributes using trained panels and standardized methodologies, aiming to quantify specific characteristics such as flavor, texture, and appearance.
2. Affective Sensory Tests:
- Affective tests gauge consumer preferences, acceptance, and emotional responses to food products, often using untrained consumer panels or consumers in natural settings to measure overall liking or preference.
Onsite vs. commercial foodservice operations
Commercials (main goal to make money): limited-service, limited menu restaurants, full service restaurants, airport restaurants, cruise ship dining, zoos, museums, sports events, convenient stores
Onsite (main goal to provide care to those involved): hospitals, schools, colleges and universities, child care, senior care, military, correctional facilities
(feeding people who are already there, they need to feed people but are not trying to attract them)
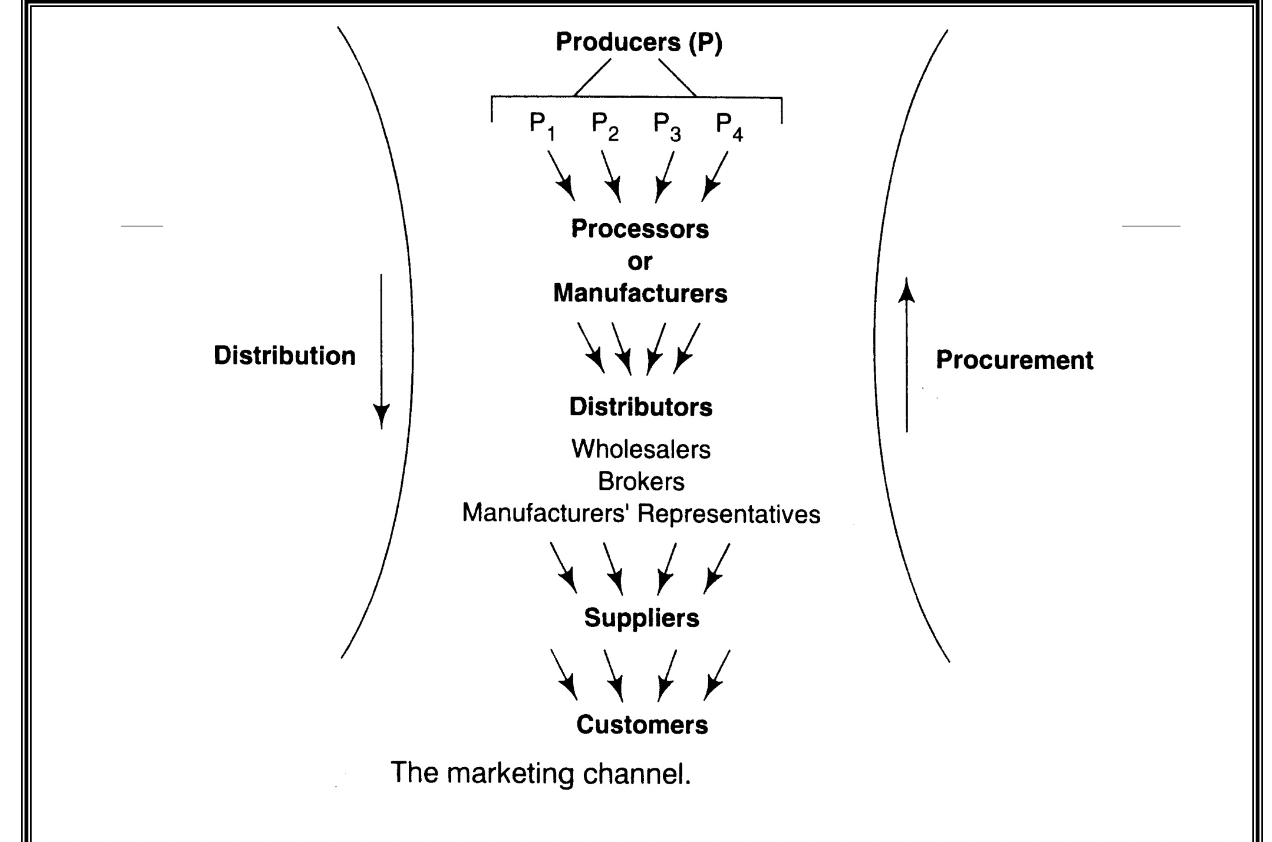
Distribution/marketing channel- different participants in the channel, effect of goods as they move through the channel
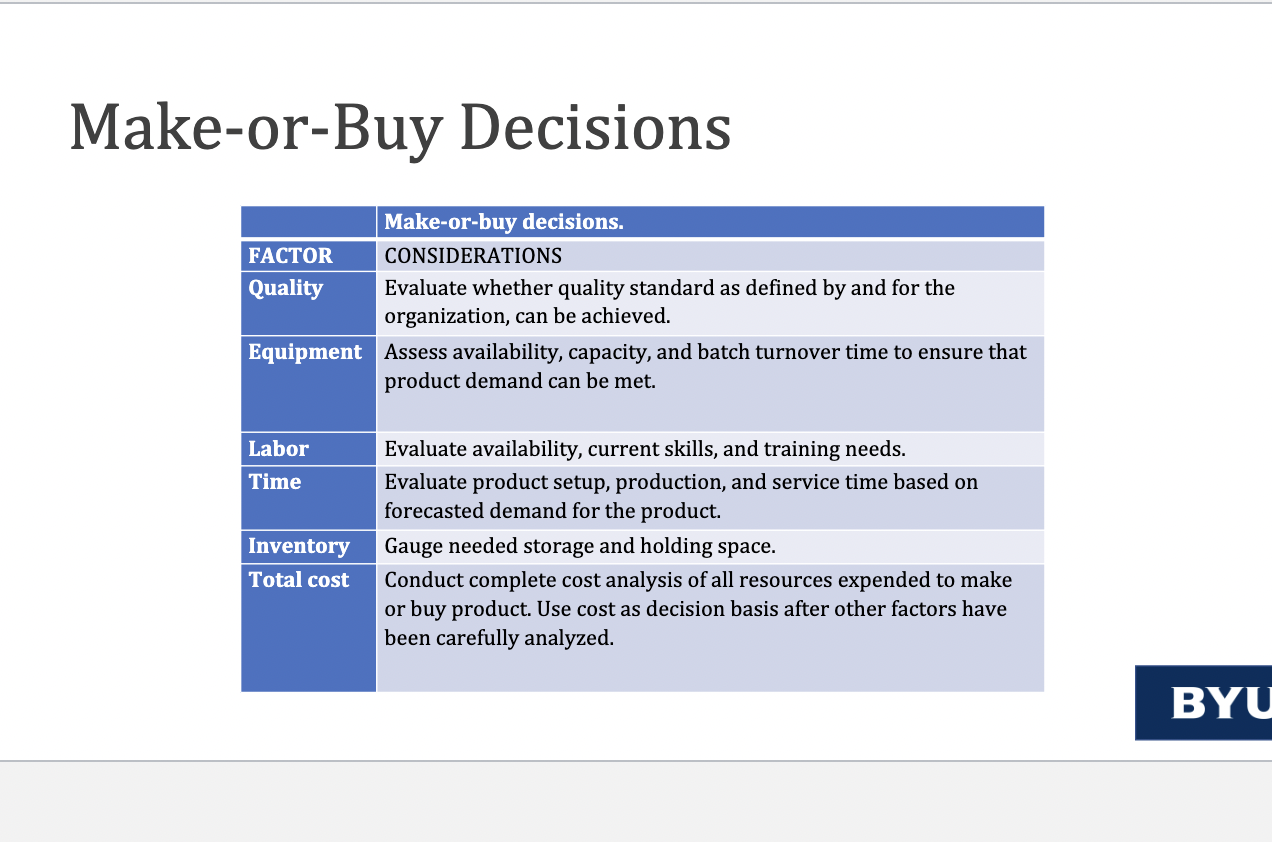
Make or buy analysis: purpose of
Types of vendors and the difference between each
1. Wholesalers:
Purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers and resell them to retailers and food service establishments, offering convenience and cost savings.
2. Broker:
Intermediaries who facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers, earning a commission for their services without taking ownership of the products.
3. Manufacturer's Representative:
Representatives of manufacturers who promote and sell products on their behalf, acting as a liaison between the manufacturer and the customer, providing product information and support.
Forecasting- definition, different types of forecasting, proper uses for different types of forecasting
- Definition: Forecasting is the process of making predictions or estimates about future events based on past and present data.
- Types of forecasting: Qualitative forecasting (subjective judgments), quantitative forecasting (statistical analysis), time-series analysis, causal models, and simulation.
- Proper uses: Qualitative forecasting is useful when historical data is scarce or unreliable, while quantitative methods are suitable when there is ample historical data available.
Inventory- Different methods of inventory management
Physical inventory: actual counting of all items in stock in all storage areas
Perpetual Inventory: Purchases and issues are continually recorded for each product in storage making the balance in stock available at all times
Inventory: calculate inventory turnover
Beginning inventory + Purchases - ending inventory = Usage or COGS
Average inventory calculation: Beginning inventory (ending inventory for previous month) + Ending inventory Divided by 2 = Average Inventory
Usage or COGS / Average inventory = Inventory Turnover
Three Q’s of recieving
Quality
Quantity
Quote (price)
Decentralized vs. Centralized service
Decentralized: Service is provided at multiple locations, often with decision-making authority dispersed among various units.
Centralized: Service is provided from a single location or a central authority, with standardized processes and decision-making.
Definitions and characteristics of the four types of foodservice system methods (conventional, ready prepared etc…)
Conventional: Food is prepared and served on-site.
Ready-prepared: Food is prepared in advance, chilled or frozen, then reheated for service.
Assembly/serve: Pre-prepared components are assembled upon order.
Batch cooking: Cooking food in smaller batches to ensure freshness and reduce waste.
Principles of time motion economy and work simplification
Time-motion economy aims to streamline work processes to minimize wasted time and effort.
Work simplification involves breaking down tasks into simple steps and eliminating unnecessary steps to increase efficiency.
Movement should be
Simultaneous
Symmetrical
Natural
Rhythmic
Habitual
Both hands, coordination of hands and eyes, and continuous motion- are aimed specifically at reducing the effort and energy required to do a job
Ingredient room
Usage: Storage and organization of ingredients.
Equipment: Shelving, refrigerators, freezers, bins, labeling tools, etc.
Best flow for kitchen design
Straight line flow minimizes backtracking and cross-over movement of food and people. Store at point of first use, allow for economy of motion, use space economically by providing for specific sizes, minimize handling and storage
Different types of service methods and their characteristics
Table service: Food served at the table.
Buffet service: Self-service from a variety of dishes.
Cafeteria service: Customers select pre-prepared items from a display.
Fast food service: Quick-service with limited menu options.
Different types of authenticity
Natural
exceptional
Influential
Original
Referential
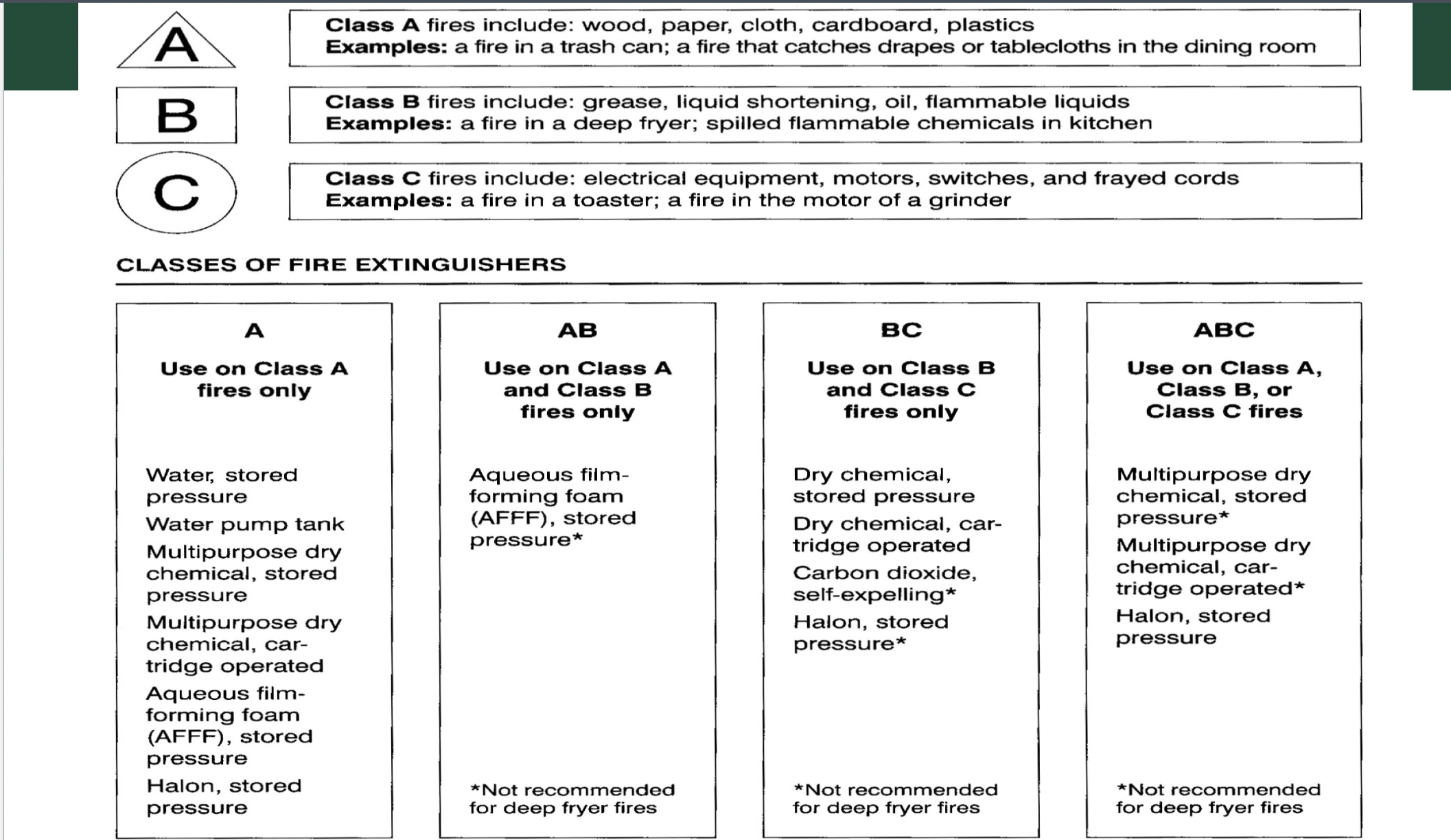
Classes of fires and how to properly extinguish
Class A Fires (Ordinary Combustibles):
Class A fires involve ordinary combustible materials such as wood, paper, cloth, and plastics. These fires typically leave ash when burned.
Extinguishing Method: Use water, foam, or multi-purpose dry chemical extinguishers to smother the fire and cool the burning material.
Class B Fires (Flammable Liquids and Gases):
Class B fires involve flammable liquids and gases such as gasoline, oil, grease, solvents, and cooking oils. These fires can spread rapidly and produce intense heat.
Extinguishing Method: Use a foam extinguisher, carbon dioxide (CO2) extinguisher, or dry chemical extinguisher to smother the flames and cut off the oxygen supply. Never use water to extinguish a Class B fire, as it can spread the flames or cause splattering.
Class K Fires (Kitchen Fires):
Class K fires specifically involve cooking oils and fats commonly found in commercial kitchens. These fires can be extremely dangerous due to their high temperatures and potential for grease splatter.
Extinguishing Method: Use a wet chemical fire extinguisher designed specifically for Class K fires. These extinguishers release a special agent that reacts with the cooking oil to create a blanket-like foam, smothering the fire and cooling the oil. In addition to using an extinguisher, you can also cover the flames with a metal lid or use a fire suppression system designed for commercial kitchens.
Employee safety
Programs
Workplace Violence
Occupational Safety & Health Act Fire Safety
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Supply appropriate PPE such as gloves and non-slip shoes to reduce the risk of injuries.
Kitchen design- planning process, elements of design, square footage requirements for kitchen design.
Planning process: Assessing needs, creating a layout, selecting equipment, considering workflow.
Elements: Workstations, storage areas, ventilation, safety features.
Square footage requirements: Based on the size of the operation and intended capacity. (General rule of thumb is 60% for dining space and 40% for kitchen space)
The seven steps to graciously solving service issues
Listen actively
repeat it back to them
Apologize sincerely
Acknowledges
Make it better
Explain how it is going to be resolved
Says “thank you”
Be able to calculate cost of goods sold, average inventory, and inventory turnover. (I will give you formulas)
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Opening inventory + Purchases - Closing inventory
Average Inventory: (Opening inventory + Closing inventory) / 2
Inventory Turnover: COGS / Average Inventory
SWOT/situation analysis
Strengths:
Strong brand reputation.
Prime location.
Talented staff.
Innovative menu.
Efficient operations.
Weaknesses:
Limited market reach.
Seasonal variability.
Operational challenges.
Cost structure.
Dependence on suppliers.
Opportunities:
Market expansion.
Technology integration.
Collaborations and partnerships.
Catering and events.
Sustainability initiatives.
Threats:
Intense competition.
Economic uncertainty.
Regulatory changes.
External factors.
Changing consumer preferences.
Marketing Environment - Marketing Concepts
Manufacturing/Production Concept
Customers favor products that are available and highly affordable
Product Concept
Customers prefer existing products and product forms
Selling Concept
Must undertake large selling and promotion efforts to get customers to buy sufficient amounts of product
Marketing Concept
Determine needs of target markets and deliver products to market more effectively than competitors
Societal Marketing Concept
Similar to marketing concept but also includes welfare of society
Marketing Environment
– Surrounds the buyer and the market
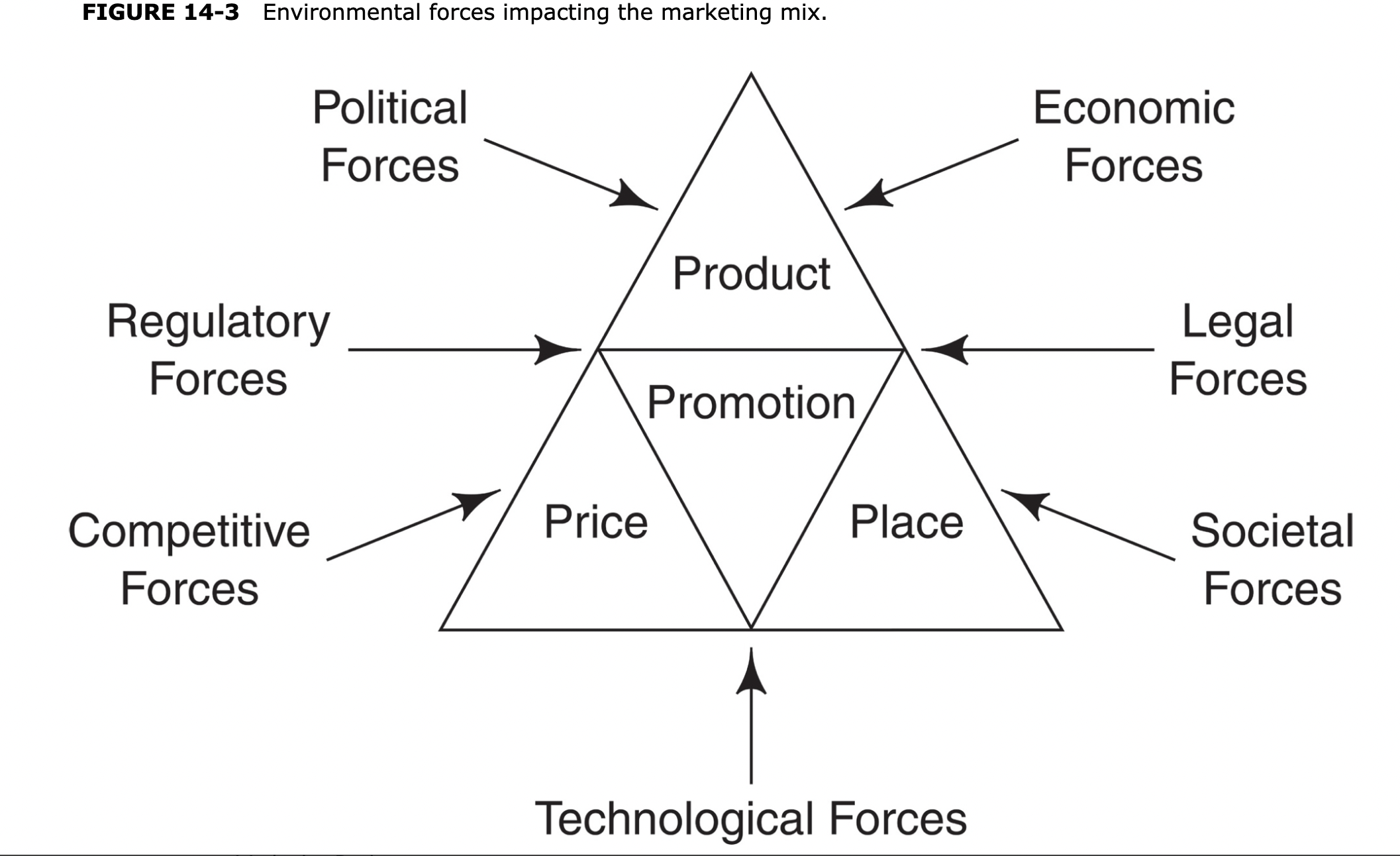
4 P’s of marketing
1. Product: Businesses develop goods or services with specific features, branding, and packaging to meet customer needs and desires.
2. Price: Determining the amount customers are willing to pay while considering costs, competition, and value proposition.
3. Place: Selecting distribution channels and logistics to ensure products reach customers efficiently and conveniently.
4. Promotion: Utilizing various marketing activities and communication strategies to raise awareness, generate interest, and drive sales of products or services.
Service vs. Product- Heterogeneity vs. Homogeneity; characteristics of service
1. Service vs. Product:
- Heterogeneity vs. Homogeneity: Services vary in quality (heterogeneous) due to their intangible nature, while products are standardized (homogeneous). In food service, each meal is unique, contributing to service heterogeneity.
2. Characteristics of Service in Food Service:
- Intangibility: Food service involves intangible experiences like dining ambiance and customer service.
- Inseparability: Production and consumption occur simultaneously, requiring real-time management.
- Perishability: Services are perishable and require immediate consumption.
- Variability: Experiences may vary due to factors like chef skills and customer preferences.
- Customer Involvement: Customers play an active role in service experiences, influencing quality and satisfaction.
Market Segmentation- examples of each of the different variable categories
1. Demographic Segmentation:
- Age, Gender, Income, Education
2. Psychographic Segmentation:
- Lifestyle, Personality, Values:
3. Behavioral Segmentation:
- Occasion, Usage Rate, Benefits Sought
4. Geographic Segmentation:
- Region, Urban vs. Rural, Climate
Market segment
– Mixture of individuals, groups, or organizations that share one or more characteristics
– Homogenous
• Similar product needs
– Heterogeneous
• Dissimilar product needs
Target Market vs. Market Segment
1. Target Market:
Customer(s) with common characteristics for which an organization creates products/services
2. Market Segment:
Division of total market into groups of customers who have similar needs, wants, values, and buying behavior
Brand Loyalty
Repeated customer purchase of a specific brand
• Often involves some kind of loyalty program
Four major subsystems
1. Procurement and Inventory Management:
- Handles sourcing, purchasing, storing, and managing inventory to meet demand efficiently while minimizing waste and costs.
2. Production and Operations Management:
- Plans, prepares, and executes food production processes to ensure consistency and efficiency in delivering menu items to customers.
3. Distribution and Service Delivery:
- Manages the distribution of prepared food items to customers through various channels, focusing on order fulfillment, presentation, and customer satisfaction.
4. Quality Assurance and Safety:
- Ensures compliance with food safety regulations, quality standards, and sanitation practices to safeguard the health of customers and maintain cleanliness and hygiene throughout the operation.