Porifera, Cnidarians, and Ctenophora (Invertebrates 1)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
metazoans
multicellular animals
synapomorphies of metazoans
-extracellular matrix w/ collagen (connective tissue)
signaling molecules
-blastula stage of development
Porifera
-sponges, the first visibly multicellular “animal”
-few cell types, no tissues, organs, no gut cavity
ostia
pores that allow water to come into the sponge
pinacoderm
outermost layer of cells; similar to epidermis
mesohyl
gelatinous matrix, acts as an endoskeleton in sponges
canal system
openings used for feeding an reproduction
spongocoel
large central cavity
osculum
large aperture were water is expelled

spicules
supporting and/or defensive skeletal structure
the three kinds of spicules
-spongin: collagen
-calcium carbonate: hard, calcium-rich
-silica: look like glass, often defensive
the three main sponge cell types
-choanocytes
-pinacocytes
-archaeocytes
choanocytes
-acts like a fan that creates a vortex to pull water through the sponge using flagella
-work w/ collenocytes to catch prey
-help to release gametes and absorb nutrients
pinacocytes
-”skin cells” of the sponge
-line exterior of sponge body wall
-thin, leathery, tightly packed together
archaeocytes
-totipotent: can change into all other cell types of sponges
-similar to stem cells
-ingest & digest food caught by the choanocytes and transport nutrients to other cells
-can develop into gametes
sponge reproduction
-asexual: external buds or gemmules
-sexual: gametes unite to form zygote, develops in parechymul or amphiblastula larva
-able to form into two separate sponges when cut in hald thanks to archeocytes
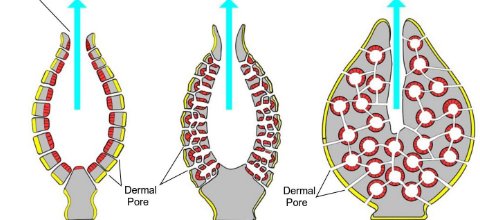
the three main sponge shapes
-asconoid: simplest sponges, usually tube shaped
-syconoid: more complex w/ branching channels that elad to the atrium
-leuconoid: most complex w/ branched canal system that leads to digestive chambers
classes in phylum porifera
-Homoscleromorpha
-Calcispongiae
-Demospongiae
-Hexactinellida
class Homoscleromorpha
a class of sponges that:
-lack spicules or have poorly developed spicules
-gelatinous/slimy
-live in deeper ocean
originally group w/ Demospongiae
class Calcispongiae
a class of sponges that:
-are usually small
-tubular or vase shaped
-can be any of the three shapes
-calcium-rich in spicules
-marine
class Demospongiae
a class of sponges that:
-95% of all sponges
-marine or freshwater (only freshwater sponge class)
-all leuconoid
-skeleton of silica, spongin, or both
class Hexactinellida
a class of sponges that are:
-”glass sponges”
-deep sea
-six-rayed highly siliceous spicules fused together
-very prickly, used for protection
-only leuconoid
bioindicator
an organism that can be used as an indicator for the health of an ecosystem (i.e. pollution, pH, etc.)
bioaccumulators
can remove pollutants from the water
Phylum Placozoa
-single species
-thought to be sponges until recently
-filter feed w/ flagellum
-don’t have main 3 cell types
Phylum Cnidarians
-coral, jellyfish, anemone, and hydroids (hydras)
-all have cnidocyts (stinging cells that contain nematocysts)
Cnidarian body plans
-Two main body types:
Polyps: tentacles facing upwards w/ stinging cells over entire body
Medusa: tentacles facing downwards w/ stinging cells only on tentacles
-blind guts (one opening for both feeding and excretion)
-radial symmetry
-both intra and extracellular digestion
-diploblastic w/ a “skin”
-no true muscle cells, only epitheliomuscular cells, controlled by nerve net of neurons
Class Anthozoa
a class of cnidarians that:
-are the largest class
-include sea anemones and stony corals
hard corals (Subclass Hexacorallia)
soft corals (Subclass Octatoria)
-form coral reefs
Class Hydrozoa
a class of cnidarians that:
-includes hydra and siphonophores (man o’ war)
hydra are only freshwater, no medusa
man o’ war are colonial w/ individual zooids
Class Scyphozoa
a class of cnidarians that:
-include “true jellies”
-have arms around the mouth
-tentacles can be long and short
Class Cubozoa
a class of cnidarians that include:
-box jellyfish
-have pedaliums, which are the base of the tentacle
-have eyes
have velarium, which is the sub-umbrella
Class Staurozoa
a class of cnidarians that:
-look like a star
Subphylum Myxozoa
a subphylum of cnidarians that:
-are now considered cnidarians
Phylum Ctenophora
-diploblastic
-no cnidocytes (stinging cells)
-8 comb rows, constantly pump water into body
-comb jellies