Aerobic Gram Positive Rods
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Listeria monocytogenes
- found in contaminated ?
-usually affects ?
-clin manif?
dairy, veg, meat, non-pasteurized cheeses → can grow in cold temp
neonates, pregnant women, immunocompromised (transplant pt)
flu-like symptoms, sepsis, meningitis, granulomatosis infantisepticum
L. monocytogenes can facultatively persist/multiply in __.
Other bacti?
monophages & macrophages (mono!)
Mycobacteria, Brucella, Legionella, Salmonella, Francisella, Yersinia
L. monocytogenes morphology
short GPR, non-spore
small, grey, translucent w/narrow zone of beta-hem (identical col morph to GBS)
L. monocytogenes
catalase ?
esculin hydrolysis?
CAMP test?
motility?
catalase + (r/o GBS, also GPR not cocci)
esculin hydrolysis, hippurate hydrolysis, CAMP test = positive
tumbling motility in broth
semisolid media → umbrella
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
found in (major resovoir?) → major exposures in?
causes __
cattle, horses, dogs, fish, poultry, rodents; pigs major resovoir → occupational ie farmers, fisherman, butchers
erysipeloid (form of cellulitis); may cause septicemia, endocarditis
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae ID
- morph
-biochemical?
short, slender, straight or curved GPR
2 col morph from same specimen!!: small, weakly alpha-hemo, OR larger spreading
bottle brush look in gelatin agar
catalase neg
TSI slant (or KIA agar) → prod H2S → black = +
TSI slant (H2S test)
diff Erysip. rhusiopathiae from other GPR
H2S (Erysip. rhusiopathiae prod) + ferrous ammonium sulfate → black +
inoculate tube w/needle stab/streak → incubate overnight 35C w/ cap loosened → add lead acetone paper to detect H2S gas
pos = black
neg = no black precipitate
Lactobacillus ssp
found where?
key role in?
normal flora of human vagina, GI tract, oropharynx
dairy, meats, grain products
fights against Candida vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis, UTI, STDs
Lactobacillus sp
morph
biochem
long, slender, or short coccobacilli, often chains, or spiral
col: pinpoint, a-hem, white, large
catalase = neg
Corynebacterium sp (aka __)
morph
found where?
pleomorphic, non-spore, GPR; may have club-shape or striations; V or L formations, palisading
widely found in soil, water
normal flora of human skin & mucous membranes
Corynebacterium diptheriae
-symptoms
-produces ___ that attacks ___.
-febrile illness, pseudomembrane forms on oropharynx
-exotoxin; heart, central/peripheral nervous system, liver, kidneys
**only exotoxin produced if strain carries beta-corynephage
infects the i-compromised
Corynebacterium diptheriae media
need agar w/ cystine & potassium tellurite
cystine-tellurite agar or modified Tinsdale medium) → black colony w/brown halo
Loeffler’s serum slant: methylene blue stain → stains metachromatic granules → all Corynebacterium sp + → not recc’d
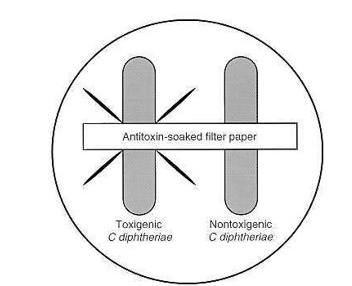
Corynebacterium diptheriae
biochem?
must be tested for ___ to conclusively call C. diptheriae
DM biochem!
ELEK immunoprecipitate test (immunodiffusion)
other important diptheroid is ___
like Staph. epidermidis, causes infns from ___
Abx
lipophilic → grows better w/___
Coryne. jeikeium
infn of indwelling medical devices, bacteremia
Tween 80
Arcanobacterium haemolyticum
clin manif?
assoc’d w/ acute pharyngitis in children & young adults → self-limiting infn → don’t need to treat w/Abx ; may also cause sepsis, endocarditis, cutaneous ulcers
Arcanobacterium haemolyticum
morph
biochem test
col: similar to beta-hem Strep
delicate, irregular GPR, some branching
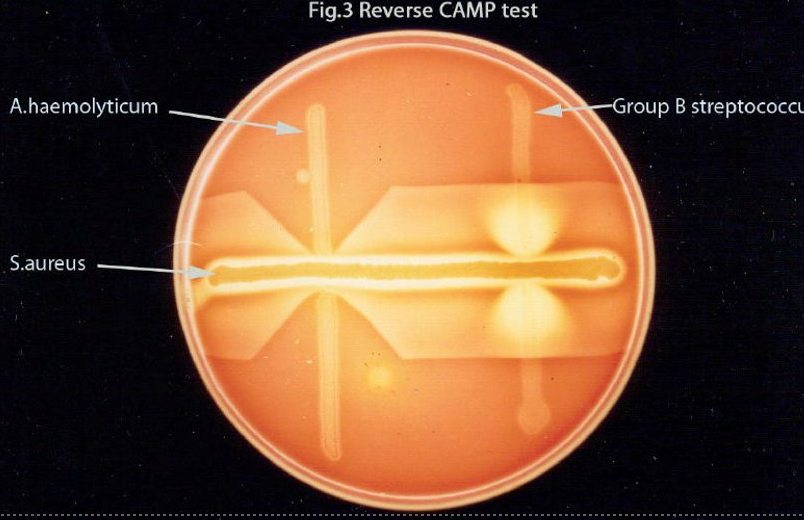
reverse CAMP test = pos (inhibits hemolysis of Staph aureus)
reverse CAMP test
requires CAMP S.aureus for beta-lysin
pos = red arrows (inhibition of hemolysis) towards Staph streak → Arcano. haemolyticum
Gardnerella vaginalis clinical significance
-what test can be done by the clinician to rapidly test for bact vaginosis?
bacterial vaginosis → no single organism responsible
-no WBC in GS
-malodorous vaginal discharge
-inc in G. vaginalis & anaerobes & dec in normal Lactobacilli
-clue cells seen
KOH sniff test - smell ammonium smell
G. vaginalis
morph
biochem tests
Gram variable rods
col: beta-hem on V agar (human blood) & non-hem on SBA
oxidase = neg
catalase = neg
hippurate hydrolysis = pos
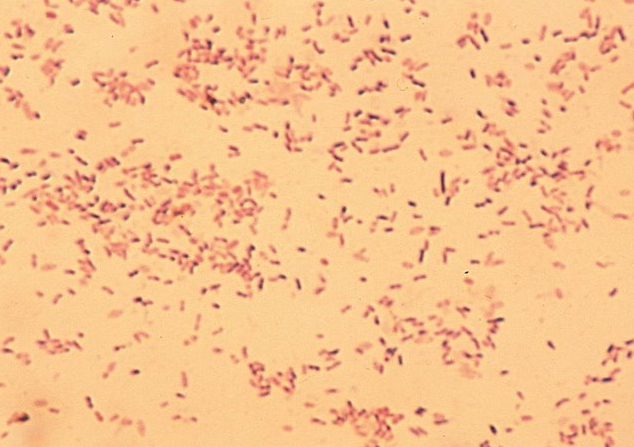
Bacillus sp. morph & biochem
col: large, spreading, gray-white, irregular margins; many beta-hemo
GPR (easily overdecolorized)
mostly catalase = pos
speciation is based on cell morph, size, spore shape/location, biochem test
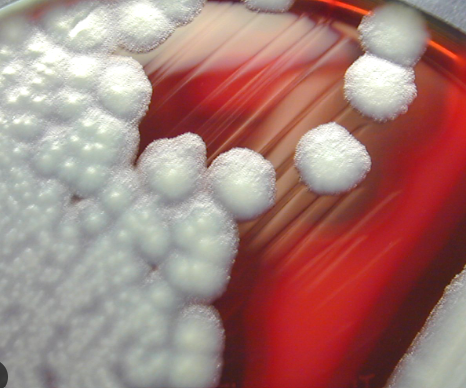
Bacillus anthracis importance
found in ___
agent of anthrax → bioterrorism → development of Laboratory Response Network
herbaceous animals
B. anthracis most common form: ___
cutaneous form
a slow healing painless ulcer w/black eschar & serosanguineous discharge
B. anthracis other high mortality forms (80-90% if untreated): ___ & ____
pulmonary (woolsorter’s disease)
caused by inhaling endospores
hemorrhagic mediastinal adenitis (chest infn)
gastrointestinal
contaminated meats
fever, bloody vomiting, bloody stool
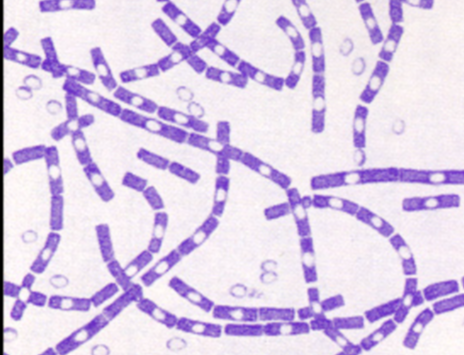
B. anthracis morph & how to r/o?
large GPR w/ovoid NON-swollen endospores, bamboo-like
col: flat, irregular, non-hem on SBA, “medusa-head”, ground-glass color
non-motile (not performed anymore)
if suspect → sent to PH lab
can treat with penicillin
Bacillus cereus: 2 enterotoxins (food poisoning)
short incubation (1-6 hr): vomiting, heat-stable, assoc’d w/fried rice!
long incubation (8-16hr): diarrhea, heat-labile, assoc’d w/meat, vet, cake, dairy (non-cooked)
B. cereus ID differs from B. anthracis in __ ?
motile, beta-hem, B-lactamase → penicillin-R
B. cereus clin manif
assoc’d w/operations, burns, IVDA
cause sepsis, endocarditis, meningitis, necrotizing pneumonia