Weather and Climate Unit Test Review
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Describe weather and climate. What is the difference between the two?
Weather is the Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place, Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period. Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions, while climate describes long-term patterns.
What do each of the following scientists study?
Climatologist:
Studies long-term weather patterns to understand climate change.
Hydrologist:
Studies water and its movement, distribution, and quality.
Meteorologist:
Studies the atmosphere to forecast weather.
Atmospheric Scientist:
Studies the physical and chemical properties of the atmosphere.
Describe how density is involved in the movement of both water in the ocean, and air in the atmosphere.
Density affects ocean and atmosphere movement. Cold/salty water sinks, warm water rises driving ocean currents. Warm air rises (convection), creating wind patterns.
What is the atmosphere composed of? Has this changed over time?
Earth’s atmosphere is mostly nitrogen and oxygen. Long ago, it had more carbon dioxide, but plants released oxygen, making it breathable. Humans add carbon dioxide, impacting climate.
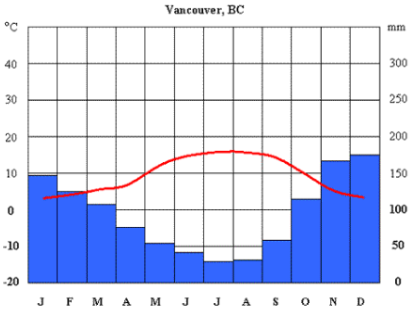
How would you describe the following climate based on the climate graph below?
Vancouver has a mild, rainy climate with cool, wet winters and warm, dry summers. It rarely gets very hot or very cold, and most of the rain falls in the winter months.
Mean
To calculate the mean (average), add up all the numbers in the data set, then divide by the number of values.
Median
The median is the middle number in a set of values when they are arranged in order. It shows the center of the data.
How does weather affect your daily life?
Weather affects clothing, comfort, and school activities. Rain means preparation, cold requires layers, and heat impacts daily routines. Severe weather may cause disruptions.
Name things that influence the climate of a region. Try to name at LEAST 3.
Three major factors that influence a region's climate are latitude, altitude, and proximity to water.
How is human activity related to the Earth’s changing climate?
Human activities, especially burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and gas) for energy, release large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Do you think the Earth’s climate would be different if the Earth was covered with more land than water? How would it change?
Earth would be hotter, drier, and more extreme. Less ocean means less rain, bigger temperature swings, and harsher winds. The planet’s climate would be way less stable.
What’s a causal relationship?
When one event directly causes another.
Define CORRELATION
Correlation is when two things change together, but one doesn’t cause the other.
Explain how ocean currents affect climates around the world. Talk about temperature and precipitation.
Ocean currents move warm and cold water, changing temperatures and rainfall. Warm currents make places warmer and wetter, while cold currents make them cooler and drier. They help balance climate around the world.
What is the Coriolis Effect? What causes it?
The Coriolis Effect makes winds and ocean currents curve because Earth spins. In the North, they turn right; in the South, they turn left. It helps shape weather and ocean currents
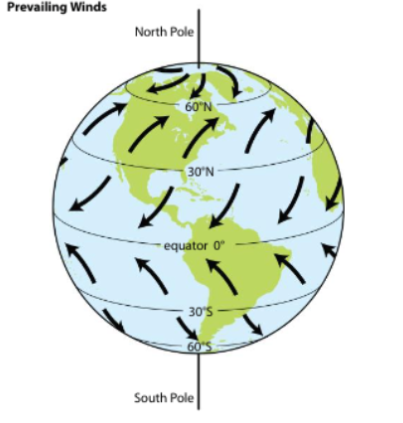
Name the prevailing winds
Polar Easterlies, Westerlies, Trade Winds
60°–90° (North & South)
Polar Easterlies. East ➡ West
30°–60° (North & South)
Westerlies. West ➡ East
0°–30° (North & South)
Trade Winds. East ➡ West