microbiology chapter 27 homework
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
The part of the antigen recognized by the antibody or TCR is called the
epitope.
T cell-target cell interactions induce specialized Tc cells to produce ________ that kill virus-infected target cells.
perforins
An individual has a child who is immunocompromised while undergoing medical treatment. As a result, the child's pediatrician recommends that no one in the family get a particular vaccine. Which of the following most likely describes the vaccine in question?
The vaccine contains an attenuated virus
Which of the following is an example of humoral immunity?
the production of antibodies by B cells
The most common circulating antibody, comprising about 80% of the serum immunoglobulin, is
IgG.
How are B cell receptors able to bind to so many different antigens?
The variable region binds to antigens through noncovalent interactions. Because of the variation in the variable regions, the receptors are able to bind to a wide variety of antigens.
Which of the following is involved in B cell selection and tolerance?
Clonal anergy and deletion
Some activated B cells differentiate into ________ cells that secrete antibodies, and others into ________ cells.
plasma / memory B
One of the foundations of vaccination is generating an antibody response against your virus. The antibody response is one part of the adaptive immune response. Which of the following are characteristics of an adaptive immune response?
The response is clonal. |
The response is inducible. |
The response has memory. |
The response is specific. |
In designing your vaccine, you will need to choose an antigen or antigens to stimulate the adaptive response. All antigens are not created equal--there are certain characteristics that make more effective antigens. Which of the following best describes why molecules such as glycoproteins are more effective antigens compared to molecules such as starch?
Glycoproteins contain a variety of shapes and subunits that contribute to the overall complexity of the molecule.
During the adaptive response, the MHC molecules are responsible for presenting an antigen to T cells. The two types of MHC (MHCI and MHCII) have specific roles during the response. Which of the following most accurately describes the characteristics of MHCII molecules in mounting the antibody response?
found on APC, present exogenous antigens, activate T helper cells
There are a variety of lymphocytes involved in the adaptive response, each with a specific function. One of the subsets of cells essential in the adaptive response is T helper cells. Choose the answer that most accurately describes the role of T helper cells in mounting the antibody response.
T helper cells aid the antibody response by binding to the B cell MHCII/protein complex and secreting cytokines like IL-4
Successful vaccination requires the generation of an antibody response and long-term memory. Mounting this response requires a coordinated series of events.
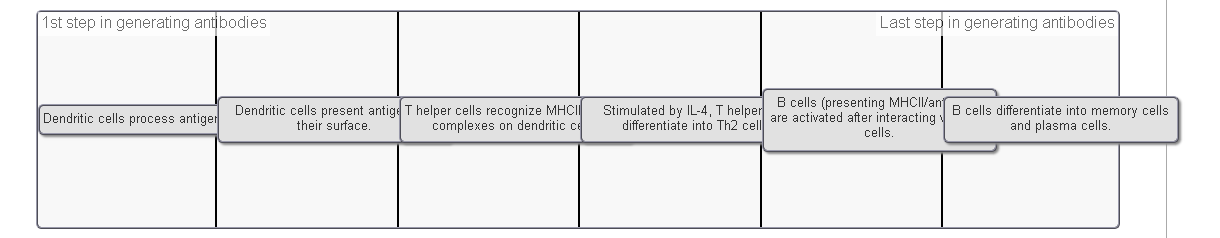
Which of the following presents processed antigens to T cells?
major histocompatibility complex proteins
What is the role of helper T cells in the adaptive immune response?
Helper T cells activate B cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes to kill infected host cells.
What is meant by the clonal expansion of a B cell?
An activated B cell divides into cells that give rise to memory B cells and plasma cells.
The student who caught the cold caused by this specific Rhinovirus was exposed to the exact same Rhinovirus 18 months later. What component of the immune system will protect her from getting the same cold again?
Memory B cells
Correctly order the steps involved cellular immunity:
The Tc recognizes the infected host cell
The Tc interacts with epitope presented by MHC-I on the dendritic cell
The Tc secretes perforin and granzyme, causing apoptosis
The helper T cell activates the Tc cell
2,4,1,3
Which of the following is NOT a step used by cytotoxic T cells to kill infected host cells?
Recognition of infected host cell using its CD4 glycoprotein
Place the following steps of phagocytosis in the order that they occur:
Endosome fuses with lysozome
Dendritic cell engulfs Rhinovirus
Epitopes are attached to MHC-II
Digestion of the Rhinovirus
MHC-II plus the attached epitope move to the outside of the dendritic cell
2,1,4,3,5
Which pair of molecules do NOT directly interact with one another?
BCR and TCR
Which of the following is NOT a step that ultimately leads to antibody production?
Activation of cytotoxic T cells by helper T cells
A person who has AIDS contracts rare and often life-threatening infections because their helper T cell count is so low. Which of the following components of the immune response still respond to antigen despite the low helper T cell count?
Clonal selection of B cells
Which of the following statements is true?
Adaptive defenses include both humoral and cellular immunity.
Immunoglobulin G consists of four polypeptides, ________ heavy chains, and ________ light chains.
two / two
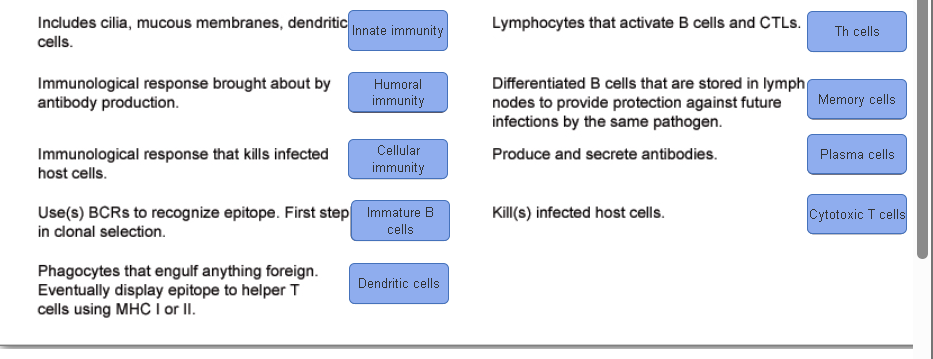
Match the key terms and concepts of the immune system with their descriptions.
Which of the following is an example of artificially acquired passive immunity?
Someone suspected of exposure to Clostridium tetani is given an injection of antibodies (antiserum).
What is apoptosis?
The process of programmed cell death.
What is the function of the CD8 receptor?
Bind to MHC molecules
What is the fate of activated cytotoxic T-cells?
They proliferate into a clone of cells specific to the same antigen; some of these cells then differentiate into long-lived memory T-cells, while others mature to attack infected cells.
Which molecule triggers apoptosis?
Granzyme
Which event happens first during cytotoxic T-cell activation?
CD8 binds to MHC molecules of infected cells