Questions from Test 1 and 2 for COSC
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
The contents of a queue can wrap around, while those in a stack cannot
Which of the following statements is true?
23
Suppose you push the values 12, 23, 45, 61, and 13 onto the stack in that order. Then you pop three items, and peek at the stack. What value do you see
False
True or False: A stack or a queue often serves as the underlying mechanism on which an array data type is based
A B / C D * -
What would A / B - C * D be when converted to postfix.
False
True or false: If there are N items, the bubble sort makes exactly NxN comparisons
a minimum key is repeatedly discovered
What happens in the selection sort?
Shift operations
Shifting a group of items left or right requires repeated _____
O(1)
Given the following segment of code what would the big O value be for running the segment?
Def avePos(a,b):
N = 0
total = 0
if(a > 0):
total += a
N += 1
if( b > 0):
total += B
N += 1
return N, total
24
What is the result of the following postfix: 2 4 + 8 2 / *
O(log (n))
Inserting an item into a priority queue takes what Big O time on average?
The lowest priority items are deleted first
The term priority in priority queue means that?
last in first out
What does LIFO mean?
Quicker to search
Ordered arrays, compared with unordered arrays are
O(N^4), O(N^2), O(N Log(N)), O(N), O(log(N)), O(1)
Slowest to fastest growth rates: O(N^2), O(N Log(N)), O(N), O(N^4), O(1), O(log(N))
9
What is the maximum number of items that must be examined to complete a binary search of an array of 300 elements?
False
True or false: Pushing and popping items for a stack and inserting and removing items from a queue all take O(N) time
O(N^2)
What is the big O for an algorithm who's running time is given by the function: T(N) = 35N + 4.5(N-1)+ 2N*N
True
True or False: When you delete an item from an unordered array, in most cases you shift other items to fill in the gap.
False
True or False: The bubble sort always ends up comparing every possible pair of items in the initial array
O(N^3)
Given the following segment of code what would the big O value be for running in the segment?
for i in range (N):
for j in range(N):
for k in range(N):
print(i + j + k)
constant
O(1) means that a process operates in _____________ time.
O(log(N))
Insertion and deletion in a binary search tree require what Big O time?
(3, 6, 12, 17)
Draw the binary search tree that is created from the sequence of keys:
10, 5, 15, 22, 3, 12, 17, 9, 6 for leaf notes
(10)
Draw the binary search tree that is created from the sequence of keys:
10, 5, 15, 22, 3, 12, 17, 9, 6 for root notes
(5, 9, 10, 15, 22, 5, 9, 15, 22)
Draw the binary search tree that is created from the sequence of keys:
10, 5, 15, 22, 3, 12, 17, 9, 6 for all internal nodes
not having to copy data when inserting or deleting items.
When compared with storing data in an array, the main benefit of storing it in a binary search tree is
defines the kinds of data that are represented and the operations that can be performed on them.
An abstract data type
first
Access to the links in a linked list is usually though the ___________ link.
Largest value - +
Smallest value - *
Blank #1 What node key has the largest value?
Blank #2 What node key has the smallest value?
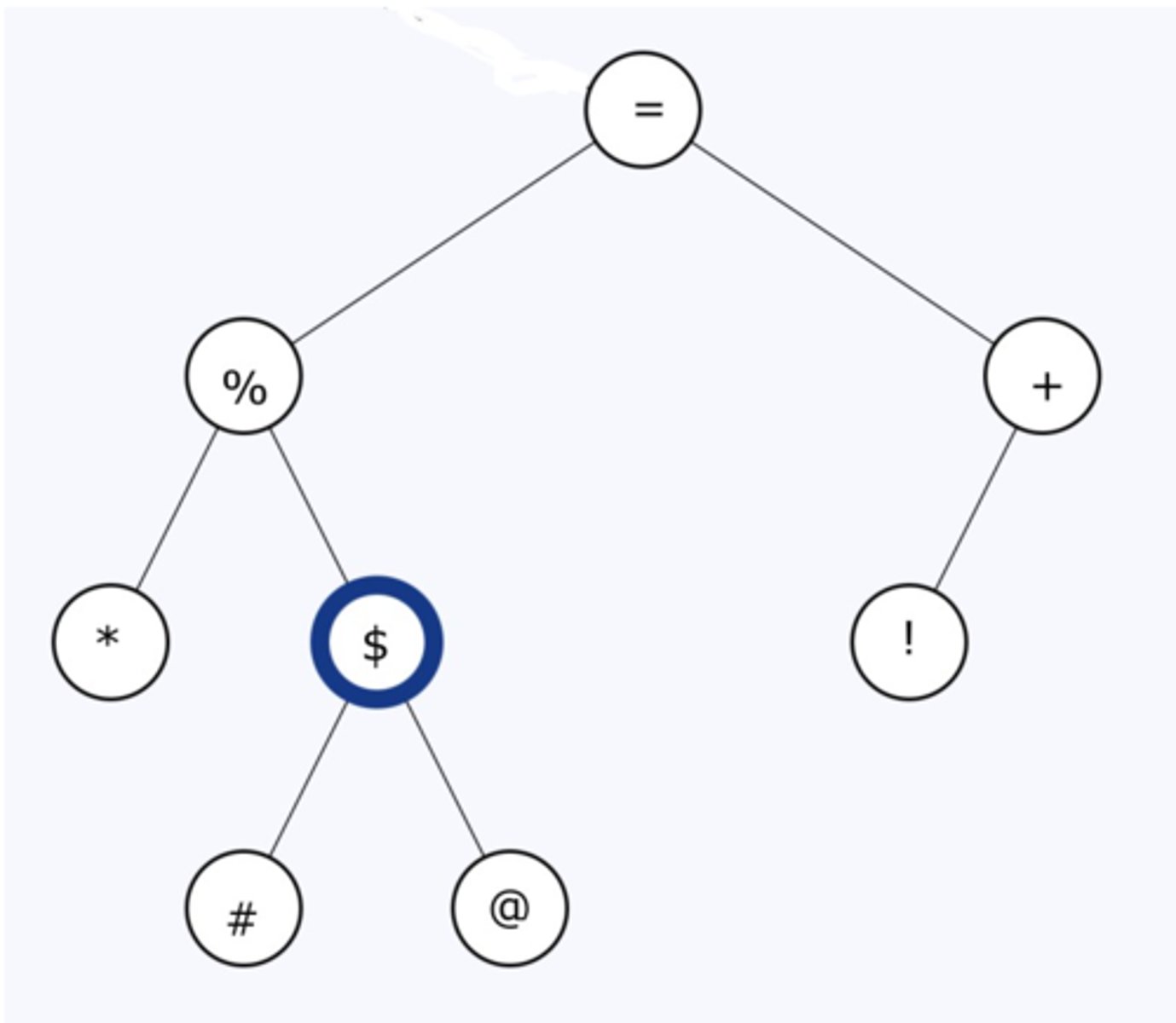
*%#$@=!+
What is the "in-order" traversal of this tree?
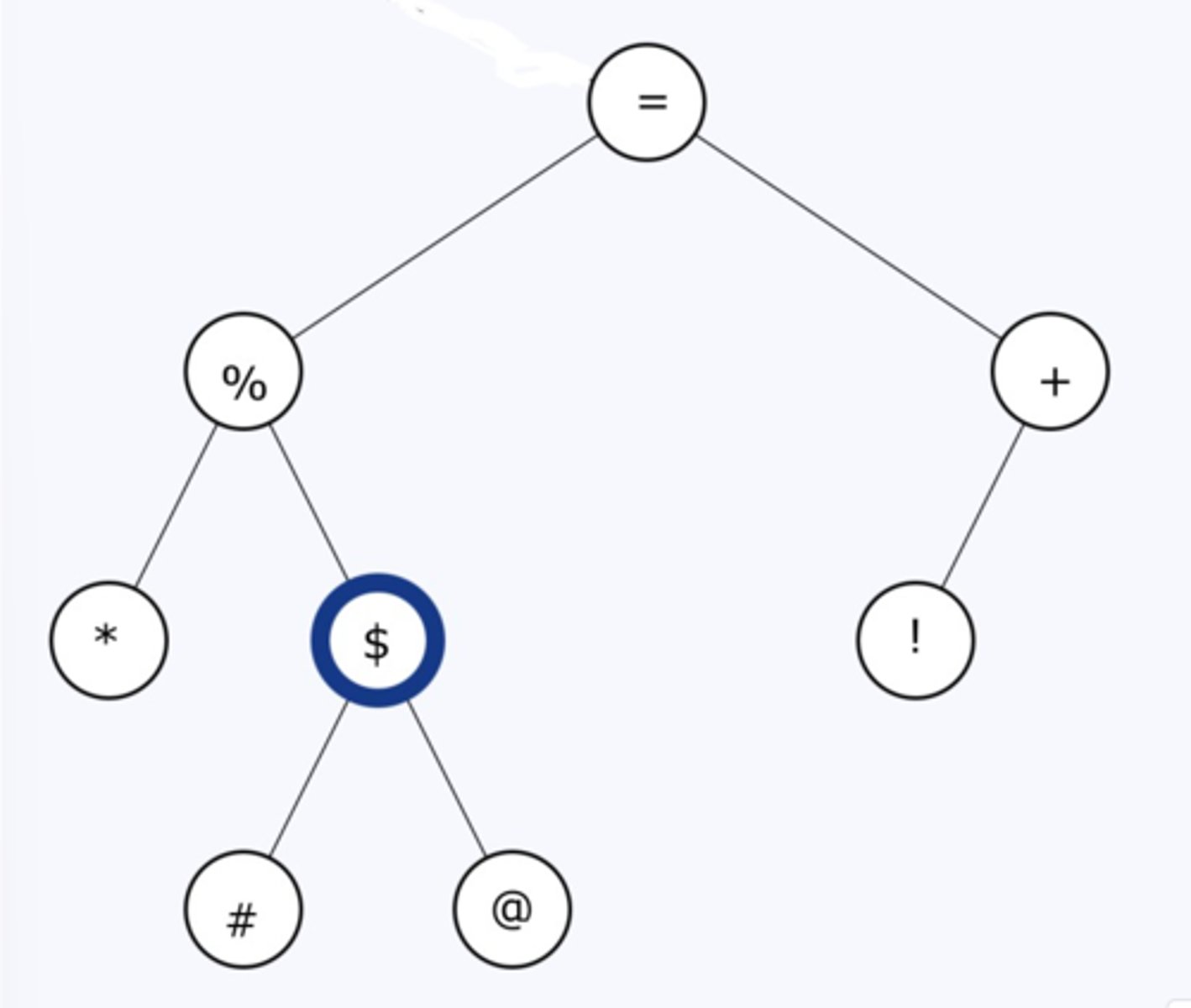
=%*$#@+!
What is the "pre-order" traversal of this tree?
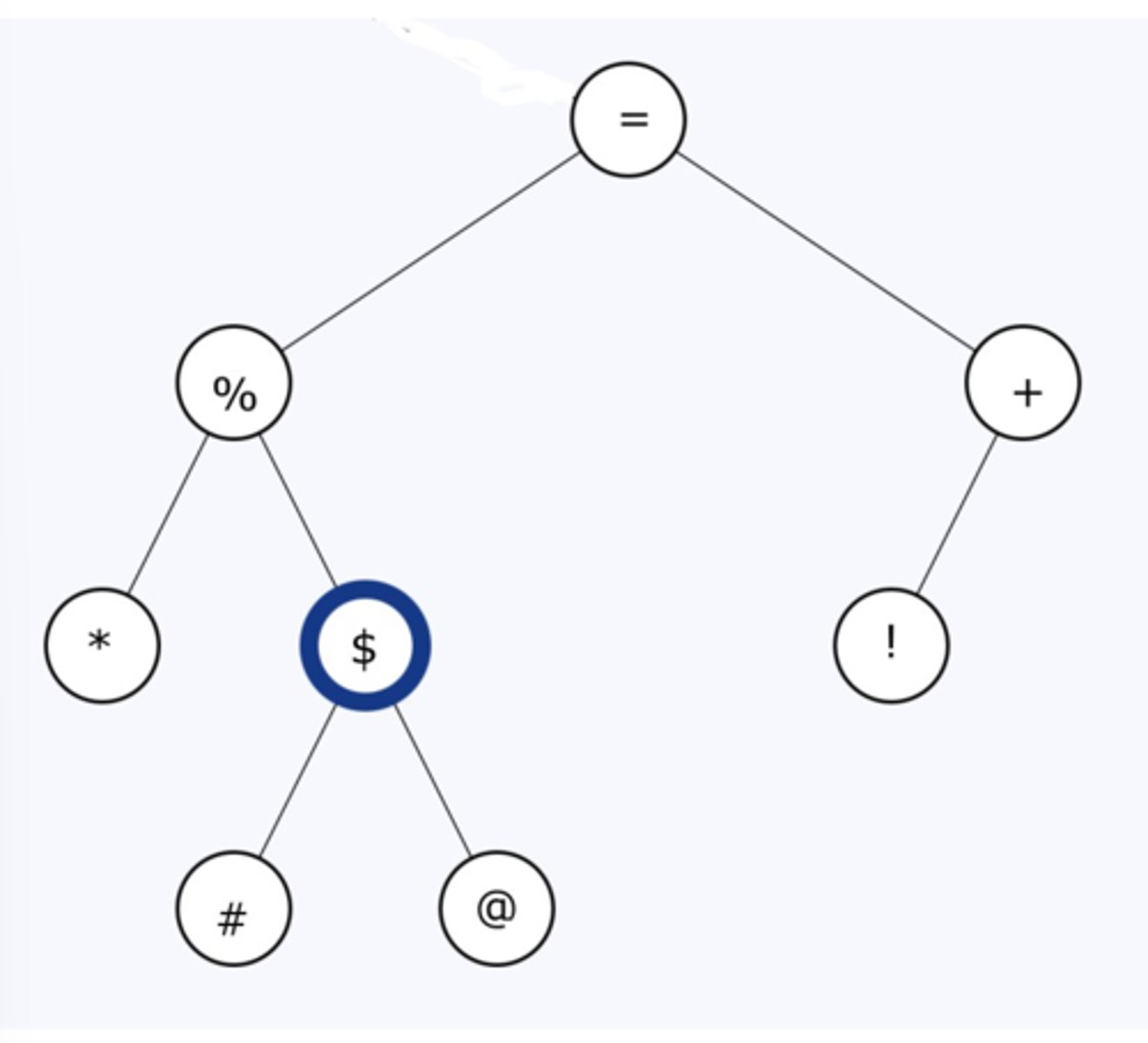
*#@$%!+=
What is the "post-order" traversal of this tree?
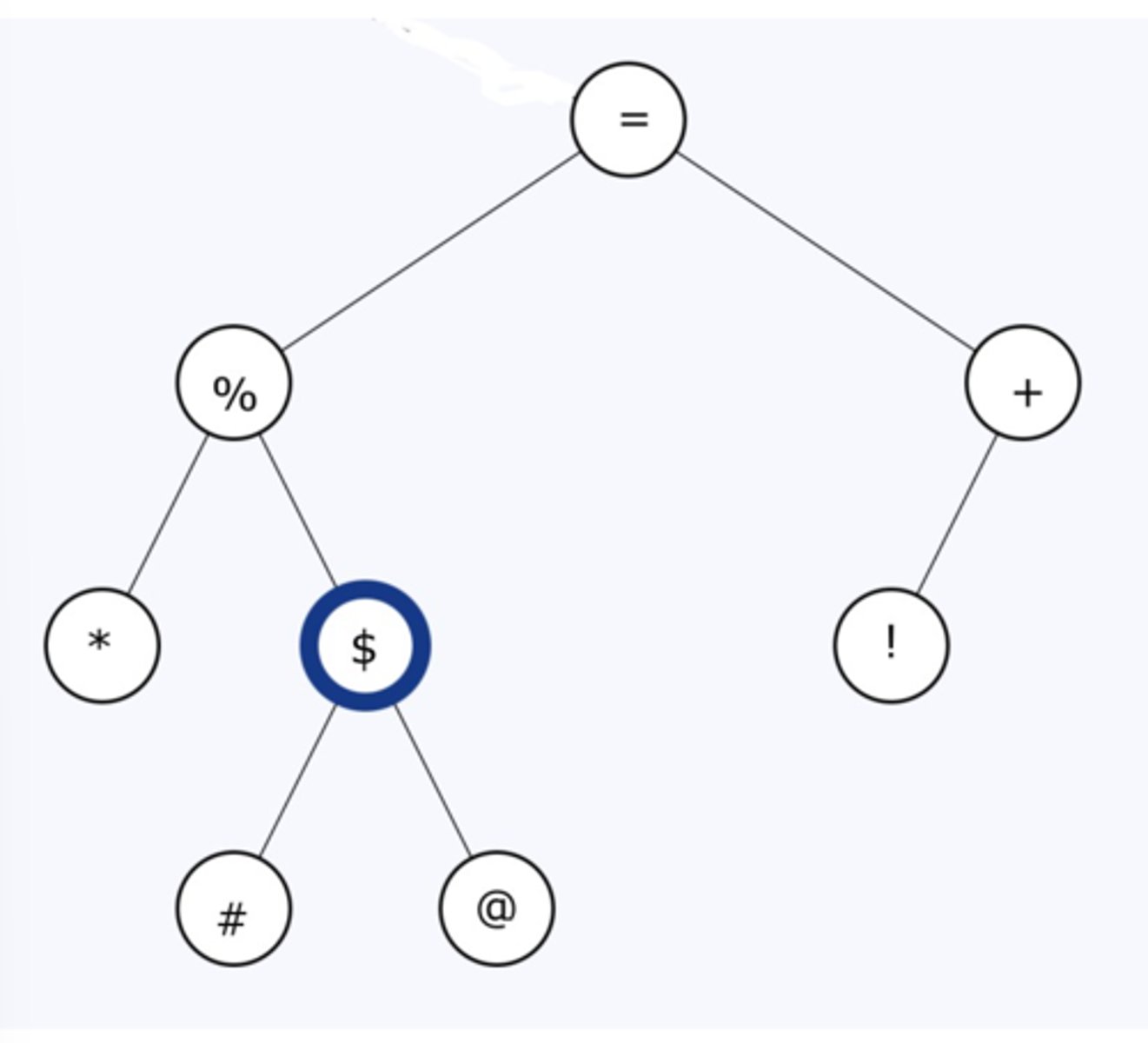
can be implemented using recursive functions or generators.
Traversing tree data structures
fewer nodes than the main tree.
A subtree of a binary tree always has
every left child has a key less than its parent and every right child has a key greater than or equal to its parent.
A binary tree is a search tree if
to get the Nth item in a list, a program must follow N links, whereas in an array, the program can compute the position of the item from N.
Lists differ from arrays in that:
2
How many references must be set or changed to insert a link in the middle of a singly linked list?