official bonding notecards
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
MX2 and MX2E3 (180° bond angle) |
Linear (formula and bond angle) |
MX3 (120° bond angle) |
Trigonal Planar (formula and bond angle) |
MX2E (118) and | MX2E2(104.5º) |
Bent (formula and bond angle)
MX4 (109.5)
Tetrahedral (formula and bond angle)
MX3E (107)
Trigonal Pyramidal (formula and bond angle)
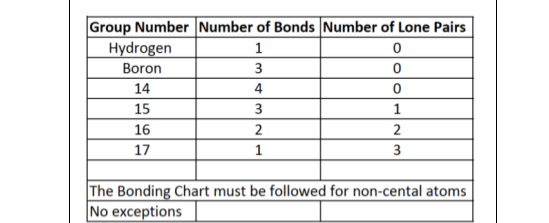
Bonding Rules of atoms that have no formal charge
Substitutional (similar size atoms)
Interstitial (different size atoms)
Types of Alloys
Substitution, interstitial
__ is on the right, _ is on the left.
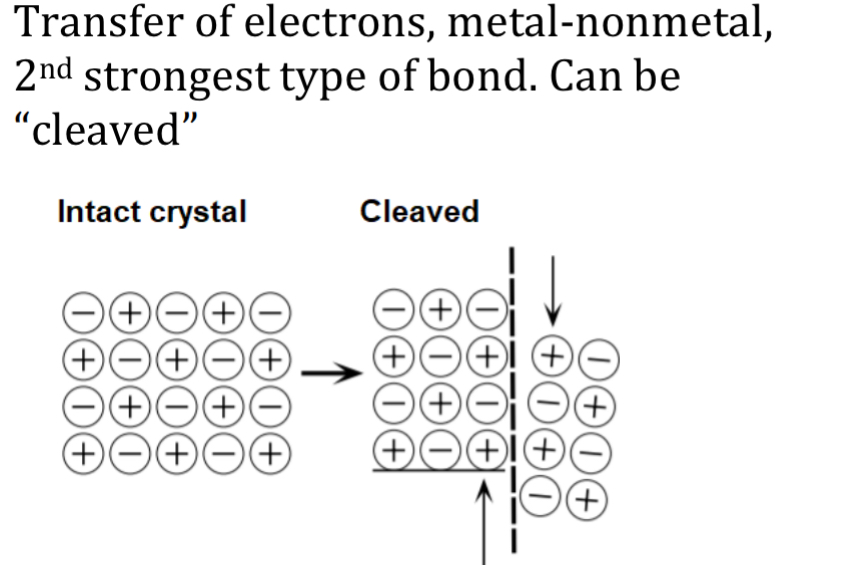
Ionic Bonds
Transfer of electrons, metal-nonmetal,
2nd strongest type of bond. Can be
“cleaved”
F 4.0, O 3.5, N 3.0
C 2.5, H 2.1
Electronegativities that
need to be memorized
Also good to know:
Cl 3.0, S 2.5
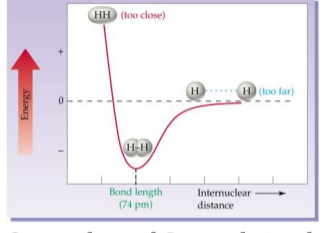
Internuclear distance
graph (Bond length
graph)
Strength and Length is always
the “low point in the curve”
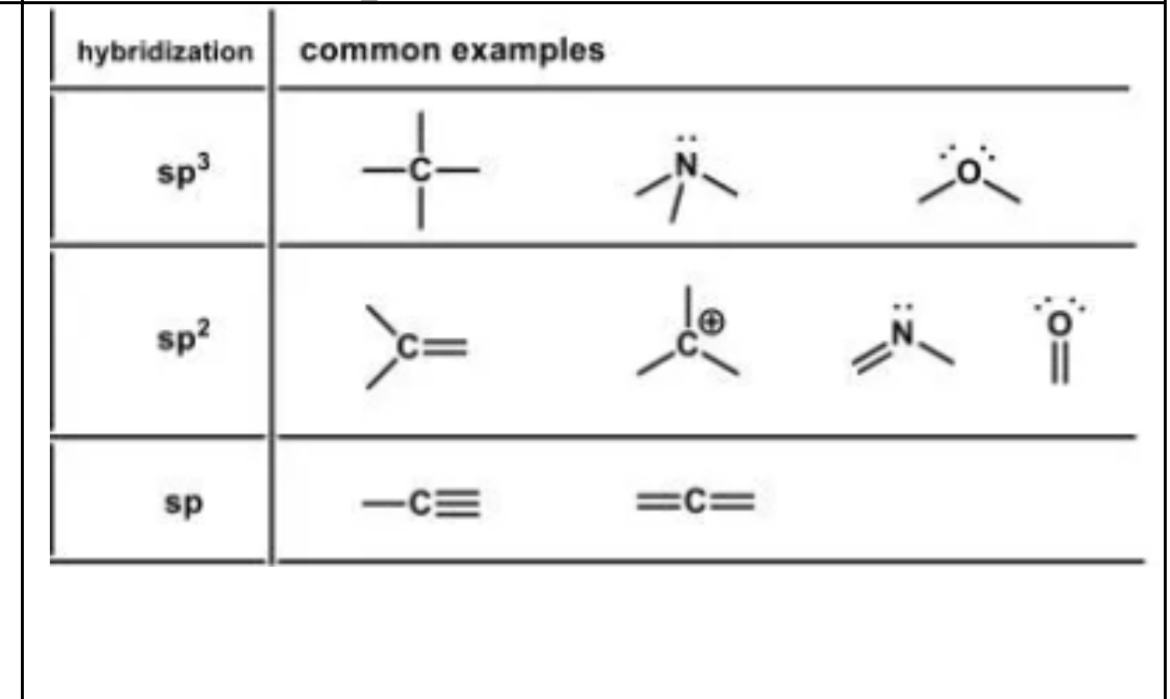
Hybridization examples
sp3
These are
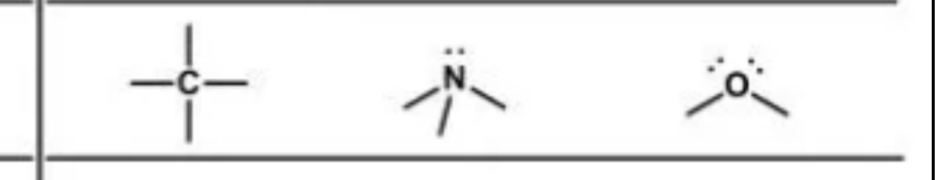
sp2
These are
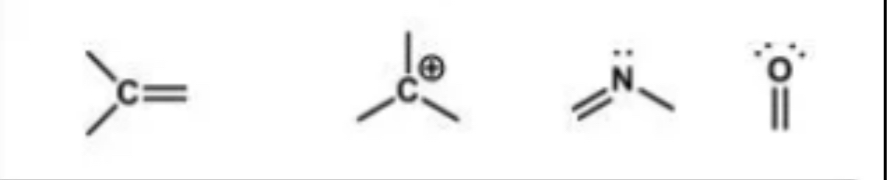
sp1
These are
= Valence electrons on the atom–
(number of bonds) – (number of
lone-pair electrons)
The more electronegative element
must have a negative formal if
there is formal charge created.
Less formal charge means a more
correct Lewis structure
Formal Charge formula
and rules
Double and triple bonds count
as single bond, lone pairs
count. Each letter means two
electrons around central.
s,p,p,p.
Hybridization
A single bond -
Sigma bonds (alpha level symbol) bonds
Pie bonds \pi
Double and triple
bonds.
Example: a triple
bond has one sigma
bond and two
pi bonds
= sum of the bond
energies for bonds broken
(absorbed energy) – sum of the
bond energies for bonds formed
(released energy)
Don’t use this one below!!
Finding bond energy
(DeltaH
rxn)
Formula must be
memorized for AP exam
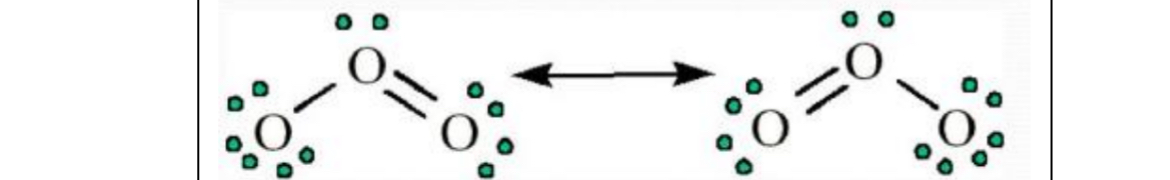
Resonance
Same atomic linkages, different bonding
Example:
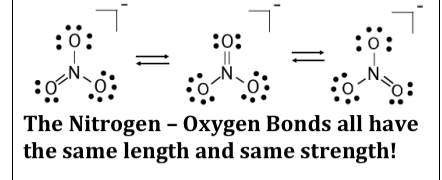
Nonpolar Covalent bonds
Electrons shared evenly.
Electronegativity
Diff. 0.0
Ex bonds/ Br-Br
Polar Covalent Compounds
Electrons shared unevenly
Electronegativity
Diff. of 0.1 and up
Enthalpy of fusion
The amount of heat
required in kJ/mol
to melt
Enthalpy of vaporization
The amount of heat
required in kJ/mol
to boil
low melting points, brittle,
nonconducting as a solid and in solution.
Molecular –
Variable melting points, Hard and
brittle, conducting
Metallic –
High to very high melting points, Hard
and brittle (can undergo clevage), nonconducting
solid, conducting liquid (molten), conducts when
dissolved (must be soluble)
Ionic –
Very high melting points,
Very hard, usually nonconducting solid, Diamond
(C) and Quartz (SiO2) are examples
Covalent Network –
Interstitial
If it has C or B in it, it’s
Force of attraction, Found in
nonpolar molecules esp.
More electrons = more
polarizing of the electron
cloud = stronger London
dispersion forces!
Example/ ALL molecules
have them!!!
Note: examples of molecules with London
only He, all noble gases, CH4 (non-polar
molecule therefore no dipole-dipole!)
Intermolecular Force:
London Dispersion
forces
Found in polar molecules.
Results from diff in E.N.
usually stronger than
London forces unless lots
of e- are present
Note: molecule must have overall dipole due
to geometry! Example CH3Cl or HCl
Intermolecular Force:
Dipole-Dipole force
Results from H bonded with
O,F,N. Strongest of three
forces usually. NOT
ACTUALLY A “BOND”.
Watch out for C-H tricks!
Intermolecular Force:
Hydrogen Bonding
Stronger forces, lower vapor
pressure at a given temp.
Example: H2O is less than
C8H18
Note: H2O - – London dispersion, dipole -dipole.
and hydrogen bonding
C8H18 – London dispersion only (non-polar
molecule)– high vapor pressure – becomes vapor
easily
Effect of intermolecular
forces on Vapor
Pressure
As molar mass increases in
hydrocarbons, B.P increases. --
Reason – Stronger London
Dispersion Forces due to more
atoms=more electrons, which
can be more polarized!
CH4 = -1640C, C8H18 = 1250C
***hydrocarbons are
nonpolar**
Effect of intermolecular
forces on Boiling Point
Covalent Network Solid
Strongest type of bond
Unique Covalent Bonding –
VERY HIGH M.P.
Examples/ Diamond, graphite,
SiO2
Molecular can contain polar bonds but be
nonpolar molecules: A General Rule: Molecules
with no lone pairs of electrons on central atom M,
as well as MX2E3 (linear) and MX4E2 (sq. planar):
Are nonpolar because bond polarities cancel out!
Examples – CO2 contains polar bonds but due to
linear geometry the polar bonds cancel out.
Polar Bonds but a
nonpolar molecule?
As the number of electrons around the
central atom increases the bond angles
decrease due to increased electron
repulsion. Lone pairs exhibit more
repulsion than bonding electrons.
Example: CH4 (no lone pairs) – 109.5,
NH3 – (1 lone pair) - 107, H2O (two lone
pairs) – 104.5
Effect of lone pairs on
bond angle
When a substance melts or boils
intermolecular forces are broken, NOT
intramolecular forces. Example: When
water boils, the hydrogen bonds (an
intermolecular force) are broken
between water molecules but the
covalent bonds (an intramolecular force)
within the water molecule between O
and H are NOT broken. Otherwise
heating water would result in H2 gas and
O2 instead of “steam/water vapor”
Understanding phase
changes! In terms of
intra and inter
molecular forces.
SUPER IMPORTANT!!!
A force within the
molecule. The bond
between H-H (in H2)
is one
Intramolecular force
A force between atoms and
molecules. The London
dispersion forces of one H2
molecule effecting another H2
molecule
Intermolecular force
As the number of electrons
around the central atom
increases the bond angles
decrease due to increased
electron repulsion and
because of decreased space!
Since electrons have the same
charge they repel as far away
from one another as possible.
Effect of bonding
electron pairs on bond
angle
Single Bond
Longest and weakest
Example: C-C SINGLE bond
length=154pm, bond energy = 348
kJ/mol
Triple Bond
Shortest and longest
C-C TRIPLE bond length=120pm,
bond energy = 839 kJ/mol
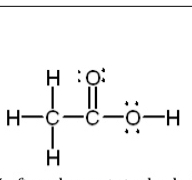
Left carbon – tetrahedral, 109.50 bond angles, sp3,
4 sigma bonds
Right carbon – trigonal planar, 120o, sp2 (double
bond counts as single for hybridization), 3 sigma
bonds, 1 pi bond.
Rightmost oxygen – Bent, 104.50, sp3 (lone pairs
count for hybridization), 2 sigma bonds
Determination of
geometry/bond
angles/hybridization/t
ypes of bonds with
respect to larger
molecules for
individual atoms.
When dry ice sublimes no
covalent C=O bonds are
broken (intramolecular forces)
but intermolecular forces are
broken (London dispersion
forces only since CO2 is
nonpolar due to geometry)
Sublimation of CO2 with
respect to intra and
inter molecular forces
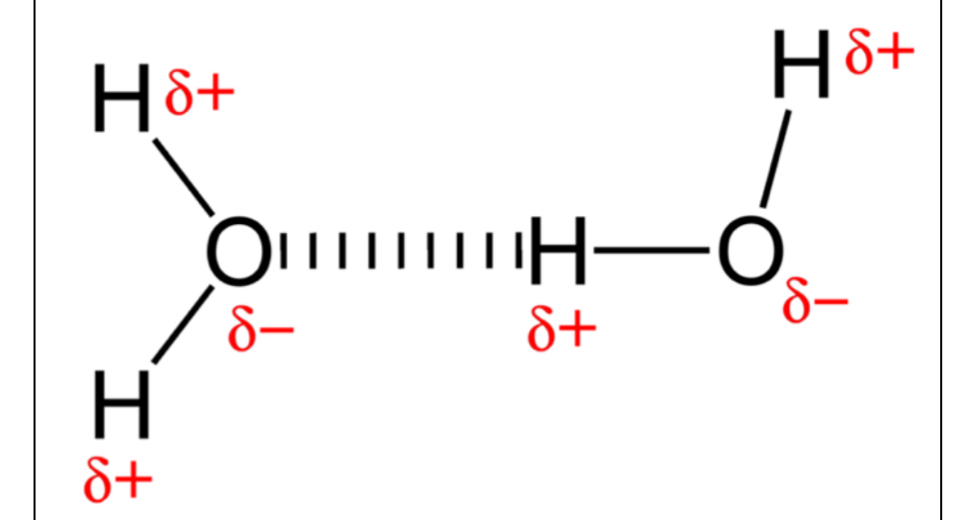
Hydrogen Bonding in
water. The dashed line
is the hydrogen bond
1
2
3
Bond orders are: Single bond =
Double bond =
Triple bond =
1.5
Nonwhole number bond orders are possible in
resonance.
All the O---O bonds have a bond order of ___ in
the resonance structures of O3