Year 11 physics mocks
1/356
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
357 Terms
static electricity
A buildup of charges on an object is usually caused by friction
Cause of static electricity
Rubbing two objects together causes electrons to be relocated from one object to another.
lightning
Abrupt electric discharge from cloud to cloud or from cloud to earth accompanied by the emission of light
electrical fields
fields around charged objects that exert a force (a push or pull) on other charged objects
opposite charges
attract each other
similar charges
repel
electrostatic force
The force between electrically charged objects (like charges repel and opposite charges attract each other).
field lines
How electrical fields are represented. they:
-Show the direction a positive charge would move
-They are closer together when the field is stronger
-Always point away from the positive charge and towards the negative charges
Isolated positive charges
field lines point outwards
Isolated negative charges
field lines point inward
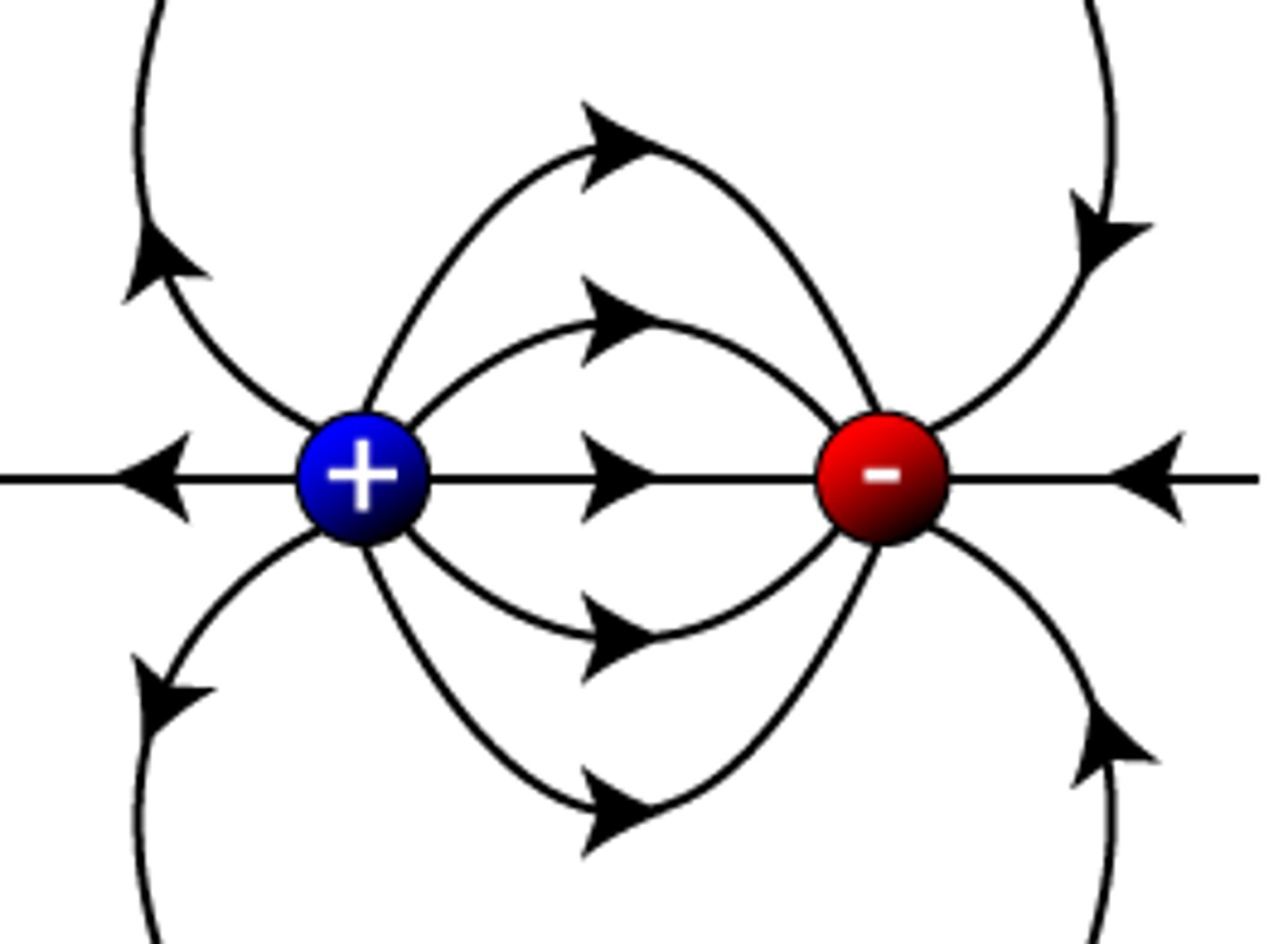
two opposite charges
field lines curve from positive to negative. showing attraction
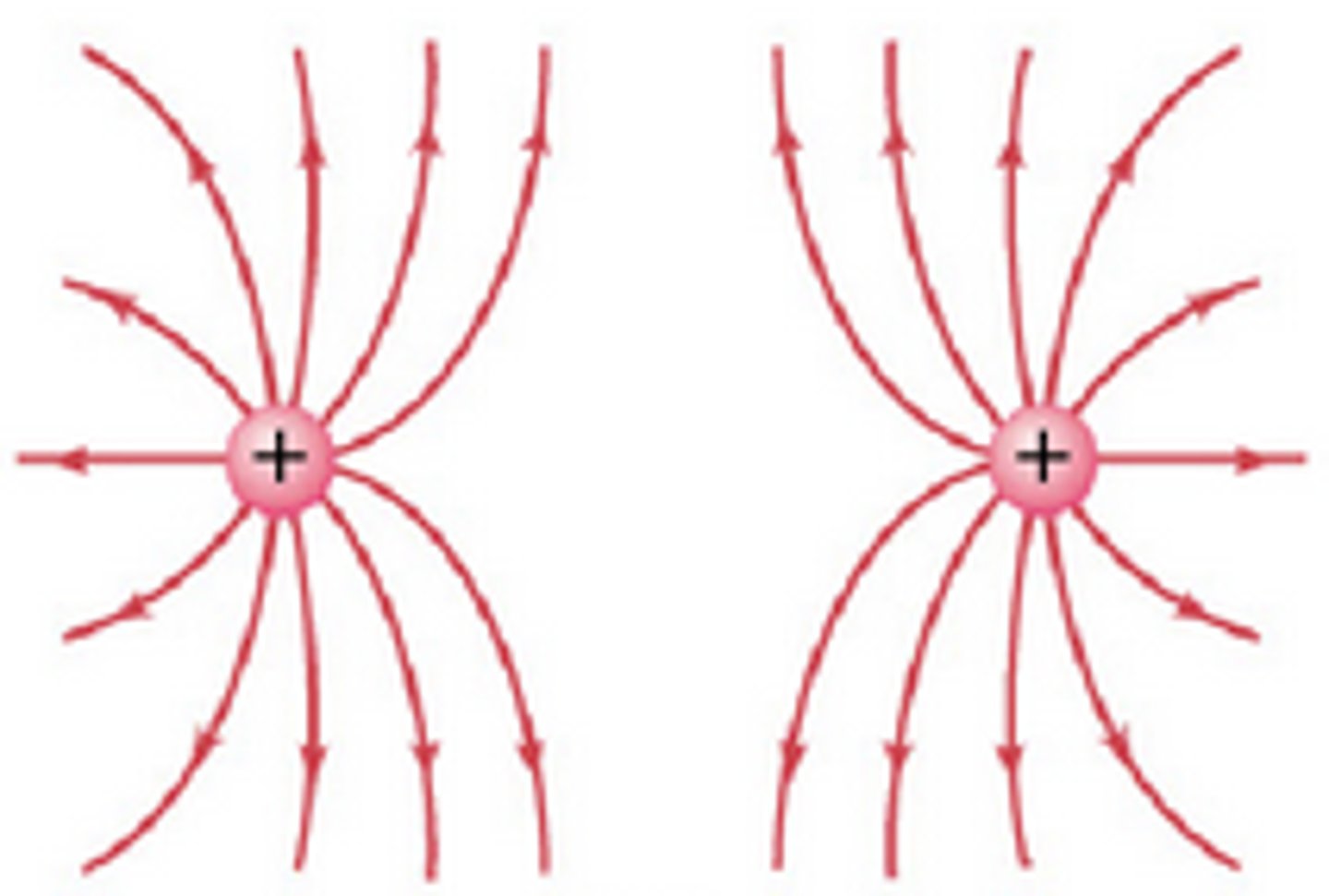
two like charges
field line move away from both. showing repulsion
sparks
if an electrical field is strong enough, it can pull electrons from the air, creating sparks
How many electrons are in a coulomb?
6.25x10^18
What is conventional current?
The direction that a positive charge would take in a circuit
What produces DC current?
batteries
What produces AC current?
Generators
What does a high voltage mean
The electric charges are strongly pushed, which can result in a higher current if the circuit allows it
What is potential difference?
- a measure of how much energy each charge is carrying
- The driving force that pushes the charge around
What is ohms law
V = IR
What does a current/voltage graph look like for a filament lamp?
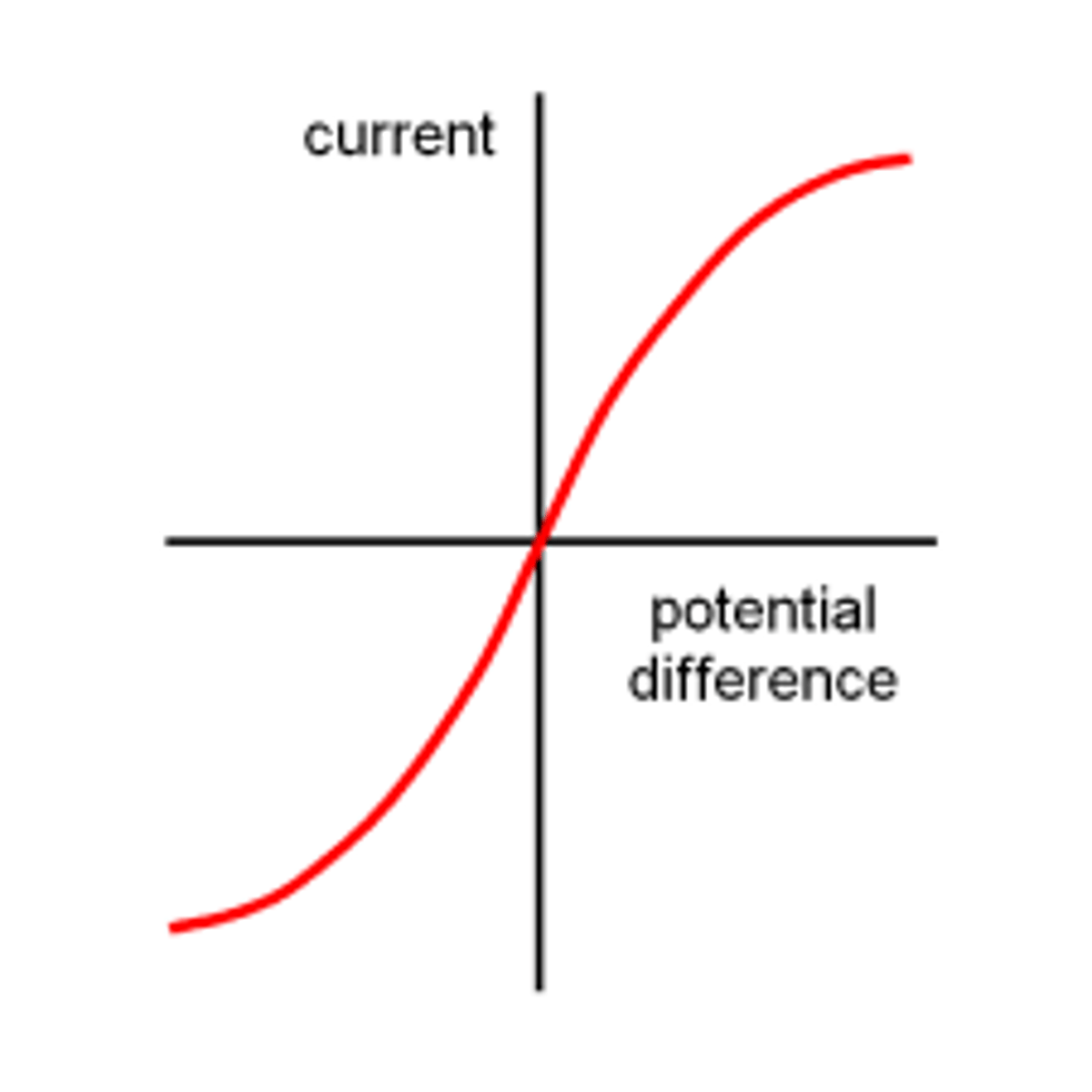
Why is a filament lamp graph S-shaped?
As the voltage increases, the filament heats up, which increases its resistance
What does a current/voltage graph look like for a diode?
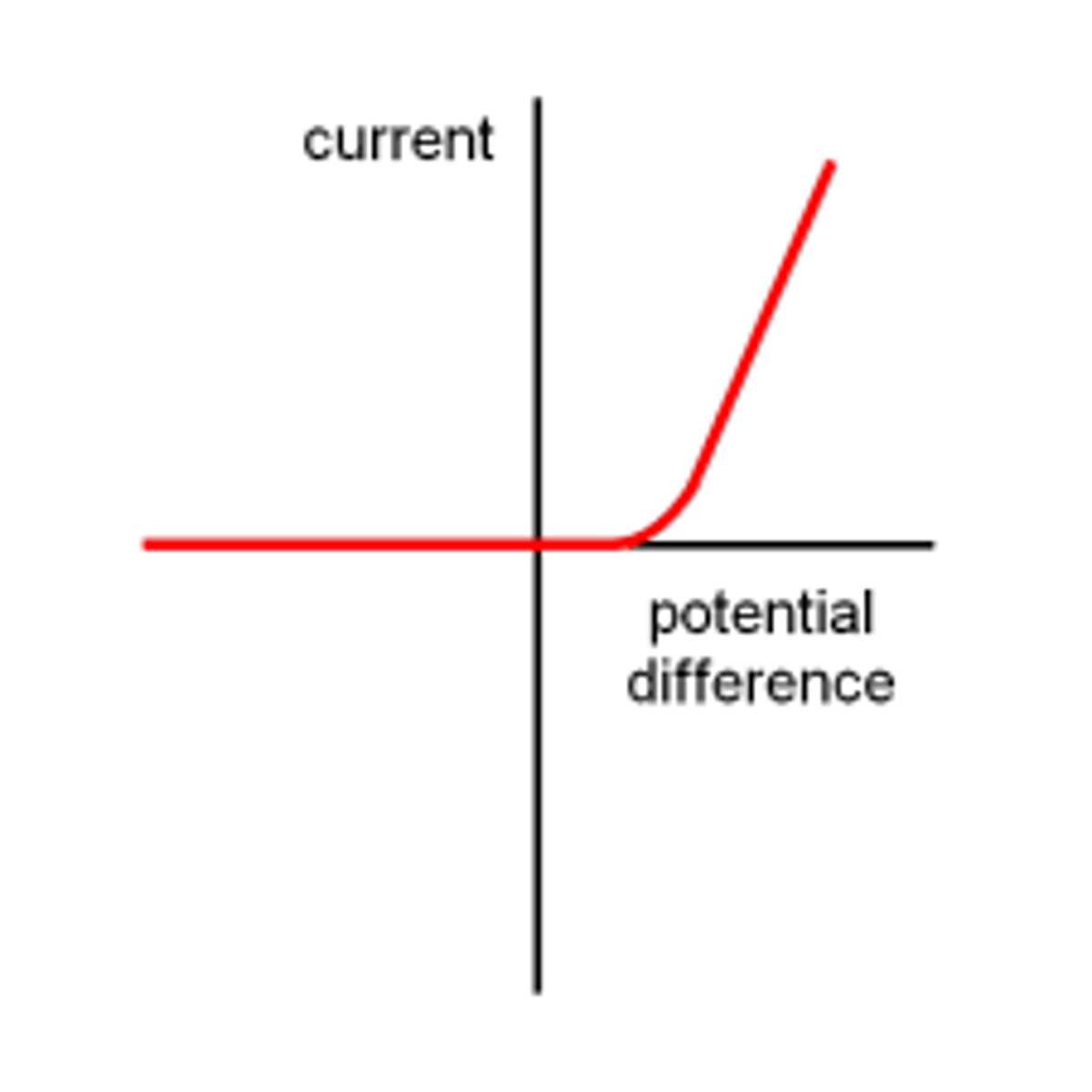
What does a current/voltage graph look like for a fixed resistor?
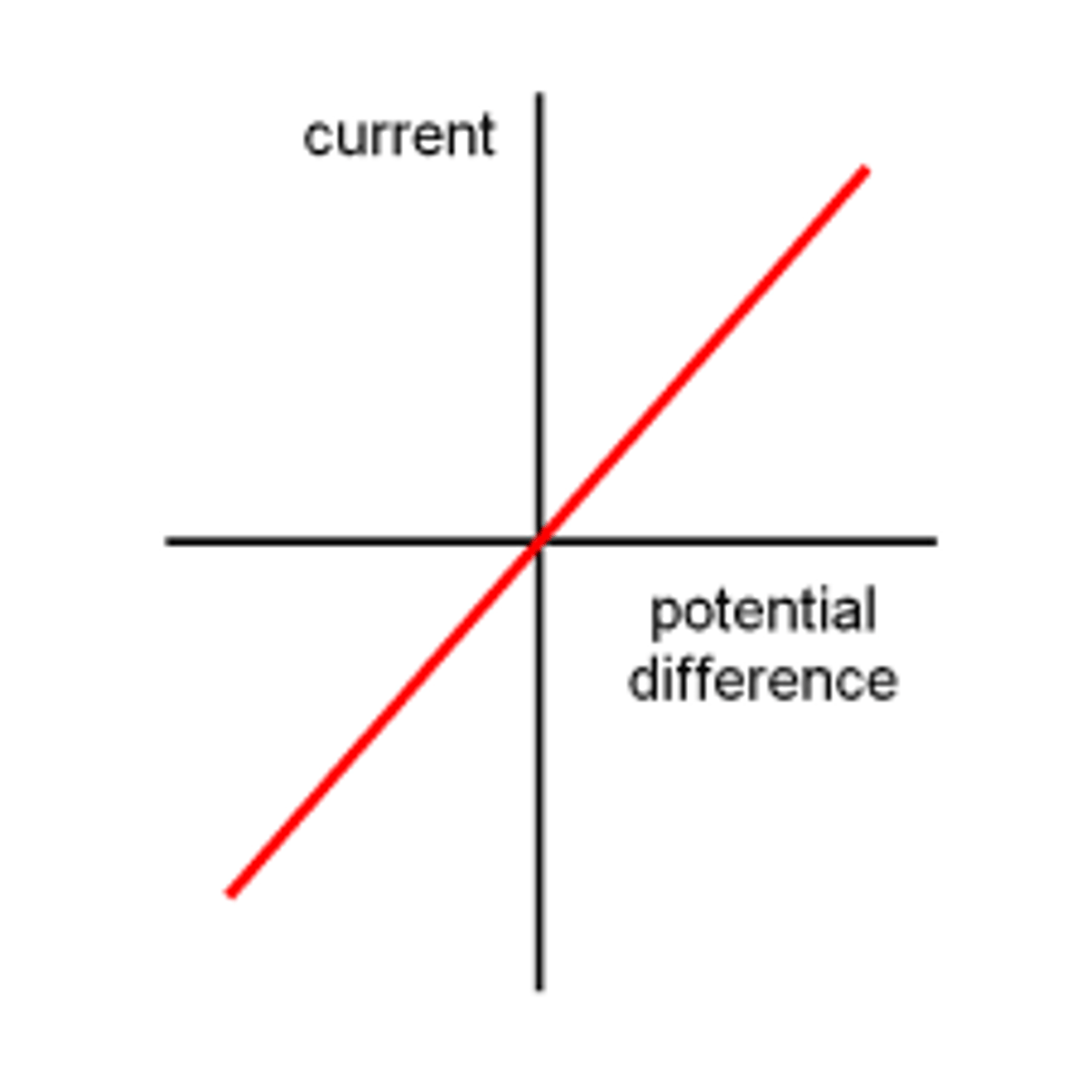
What does a steeper gradient mean in current/voltage graphs?
higher resistance
Why is a diode graph L-shaped
At positive voltages, the curve rises, indicating that current is free to flow through the device
Why is a fixed resistor graph straight?
because of Ohm's Law, which states that current is directly proportional to voltage when resistance is constant
How do you find the resistance of a current/voltage graphs?
For ohmic components, the resistance is constant and is equal to 1/gradient
What factors affect resistance?
- materials
- length of wire
- thickness
- temperature
How does the material of the wire affect resistance?
conductors (like copper) have a low resistance, whilst insulators (like rubber) have a low resistance
Why do conductors have a low resistance?
they have a high density of free electrons, which are weakly bound to atoms and can move easily throughout the material
Why do insulators have a high resistance?
their electrons are tightly bound to their atoms, making it very difficult for them to move and create an electric current
How does the length of the wire affect resistance?
The longer the wire, the greater the resistance
Why do longer wires have more resistance?
because the electros have a longer distance to travel
How does the thickness of the wire affect resistance?
A thinner wire has more resistance because there is less space for electrons to flow
How does the temperature of the wire affect resistance?
Higher temperatures increase the resistance because the atoms in the wire vibrate more when warm, making it harder for electrons to pass through
What is static electricity?
The buildup of electric charge on an object, usually caused by friction
Why does static electricity cause sparks?
the sudden, rapid movement of electrons to neutralize a large buildup of electric charge
How does static electricity work?
- When two insulating materials are rubbed together, electrons are transferred
- One material loses electrons and becomes positively charged, and the other gains electrons and becomes negatively charged.
- This static charge is a buildup of these imbalanced charges, which can then attract or repel other objects, or discharge in a spark.
How does lightning work?
occurs when oppositely charged particles within a storm cloud, between two clouds, or between a cloud and the ground become too strong for the air to insulate
What is static electricity used for?
photocopying, smoke precipitator, ink nozzle printer, spray paint
How can static build-up be prevented?
earthing. connecting objects to the ground with a wire allows excess charge to safely flow away
What are the dangers of static electricity?
- A build-up of charge can produce sparks, which may lead to explosions or fires if it happens near fuel which can be ignited.
- It's dangerous when you touch an object with a large electric charge, as it will discharge into you, causing an electric shock.
What are electric fields?
a region of space around a charged object where other charged particles will experience an electrostatic force
Positively charged electric field lines
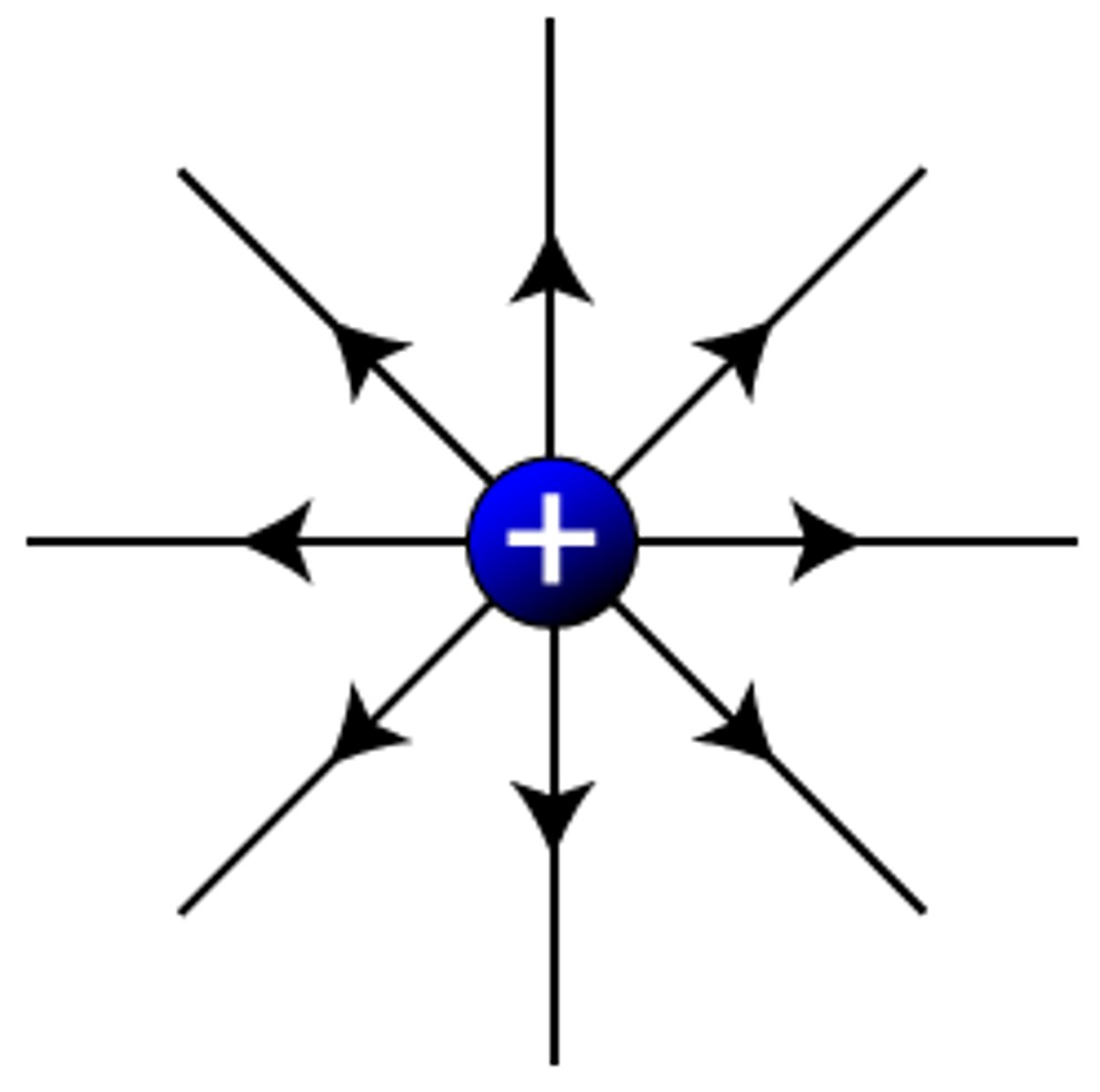
Negatively charged electric field lines
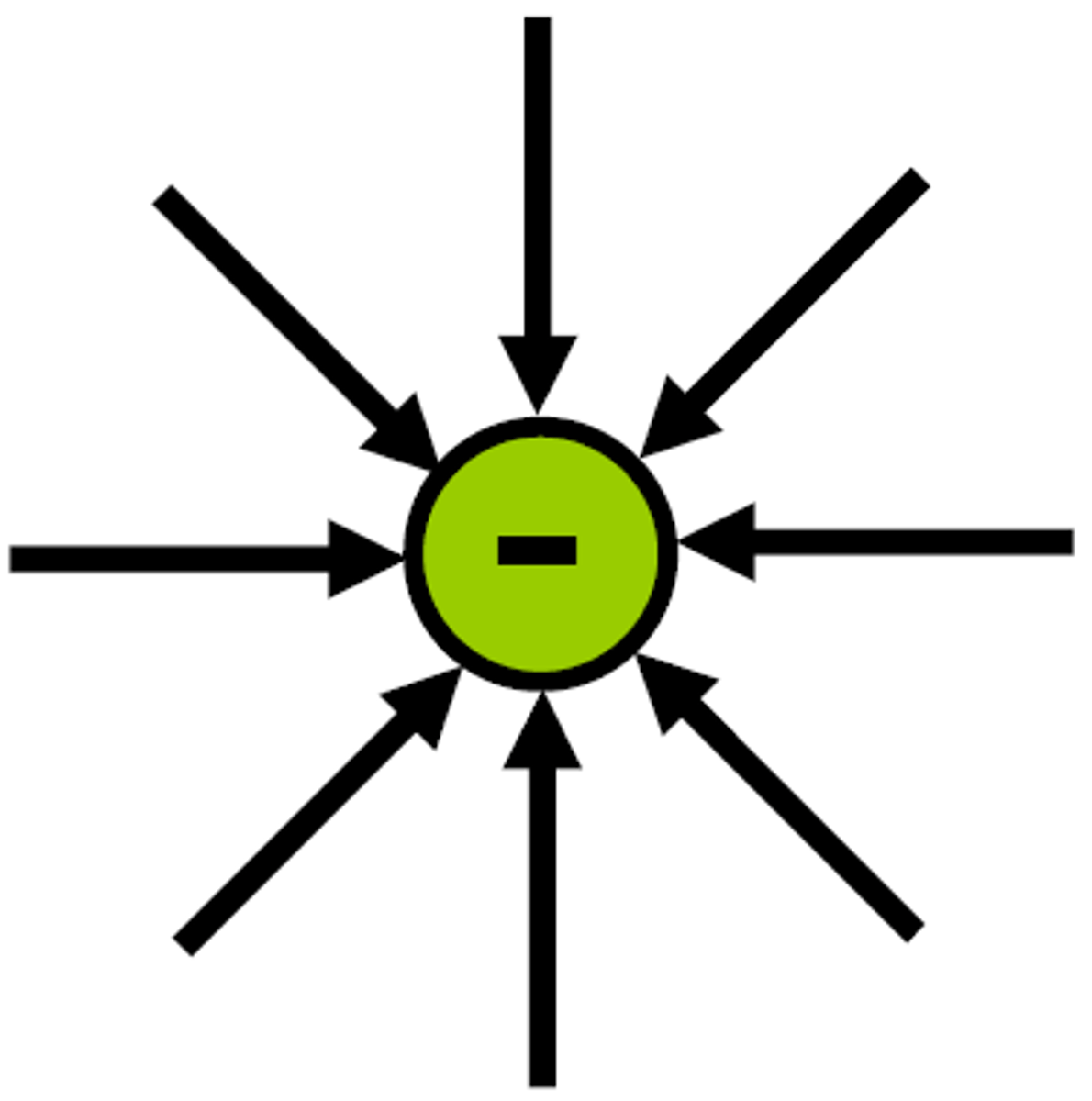
Oppositely charged electric field lines
Similarly charged electric field lines
How do sparks in electric fields work?
If an electric field is strong enough, it can pull electrons from the air, creating sparks
Energy Stores
1) Elastic potential
2) Gravitational potential
3) Thermal
4) Electrostatic
5) Nuclear
6) Chemical
7) Kinetic
8) Magnetic
9) Light
10) Sound
How is energy transferred?
1) Mechanically - force doing work
2) Electrically - work done by moving charges
3) Heating/Radiation - light, sound
How can work be done?
When a current flows or by a force moving an object
Kinetic energy formula
E=1/2mv²
Kinetic energy(J) = 0.5 x mass(kg) x speed²(m/s)
Gravitational potential energy formula
E=mgh
G.P.E(J) = mass(kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg) x height (m)
What happens when an object falls and there's no air resistance?
Energy lost from the g.p.e store = energy gained in the kinetic energy store
What does air resistance do when acting against falling objects?
It causes some energy to be transferred to other energy stores e.g. the thermal energy stores of the object and the surroundings
Elastic potential energy formula
E=1/2ke²
E.P.E(J) = 0.5 x spring constant(N/m) x extension²(m)
What is SHC?
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C
SHC formula
E=mcθ
Change in thermal energy(J) = mass(kg) x SHC(J/kg/°C) x temperature change(°C)
What is the conservation of energy principle?
Energy can be transferred usefully, or stored or dissipated (wasted energy), but can never be created or destroyed
What is power?
The rate of energy transfer, or the rate of doing work
What is 1W equal to?
1J of energy transferred per second
Power Equation 1
E=Pt
Energy transferred(J) = power(W) x time(s)
Power Equation 2
W=Pt
Work done(J) = power(W) x time(s)
What is conduction?
The process where vibrating particles transfer energy to neighbouring particles
Energy is transferred to thermal stores of the object - this energy is shared across the kinetic energy stores
What is thermal conductivity?
A measure of how quickly energy is transferred through a material via conduction
What is convection?
Where energetic particles move away from hotter to cooler regions
Energy is transferred to the thermal energy stores of the object and is shared across the kinetic stores
What do radiators create?
Convection currents
Convection currents - process
1) Energy is transferred from the radiator to the nearby air particles by conduction
2) The air by the radiator becomes warmer and less dense as the particles move quicker
3) The warm air rises and displaces the cooler air, which is then heated by the radiator
4) The previously heated air transfers energy to the surroundings - the air cools, becomes denser and sinks
What does lubrication do?
Reduce frictional forces
What does insulation do?
Reduce the rate of energy transfer by heating
Thermal insulation techniques
1) Cavity walls - made up of an inner and outer wall with an air gap in the middle - the air gap reduces the amount of energy transferred by conduction through the walls
2) Cavity wall insulators - the air gap is filled with foam also reduces energy transfer by convection in the wall cavity
3) Loft insulation - reduces convection currents being created in lofts
4) Double-glazed windows - air gap between two sheets of glass that prevent energy transfer by conduction through the windows
5) Draught excluders - reduce energy transfers by convection around doors and windows
How do you improve efficiency?
1) Lubrication
2) Insulation
3) Making objects more streamlined
Efficiency - energy transfer equation
Useful output energy transfer divided by total input energy transfer
Efficiency - power equation
Useful power output divided by total power input
Is any device 100% efficienct?
No
Where is wasted energy usually transferred?
Thermal energy stores
How do thick walls prevent energy losses through heating?
They're made from a material with a low thermal conductivity - the thicker the walls, the lower the thermal conductivity, the slower the rate of energy transfer
What objects are usually 100% efficient?
Electric heaters - all the energy in the electrostatic energy stores is transferred to useful thermal energy stores
Fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas)
Non-renewable
Cause acid rain
Cause global warming
Reliable currently - they are finite, so they will run out eventually
Coal mining ruins the landscape
Oil spillages cause serious environmental problems
Energy resources used for transport
Petrol and diesel from oil - non-renewable
Coal (steam trains) - non-renewable
Bio-fuels - renewable
Energy resources used for heating
Natural gas - non-renewable
Coal - non-renewable
Electric heaters - non-renewable
Geothermal - renewable
Solar water heaters - renewable
Bio-fuels - renewable
Wind Power
Renewable
Doesn't cause global warming
Doesn't cause acid rain
No pollution
No permanent damage to the landscape
Free - initial costs are high
Very noisy
Spoil the view
Not always reliable
Solar Power
Renewable
Doesn't cause acid rain
Doesn't cause global warming
No pollution
Free - solar panels are expensive though
Not always reliable
Geothermal Power
Renewable
Doesn't cause acid rain
Doesn't cause global warming
Free
Very little damage to the environment
Not very reliable - can only happen in certain places and there aren't very many of them
Hydroelectric Power
Renewable
Reliable
Doesn't cause acid rain
Doesn't cause global warming
No pollution
Provides an immediate response to high demand
Free - initial cost is high
Big impact on environment and possible loss of habitat
Wave Power
Renewable
Doesn't cause acid rain
Doesn't cause global warming
Free - initial costs are high
Not always reliable - waves die out when the wind drops
Disturbs the seabed and habitats of marine wildlife
Spoils the view
Hazard to boats
Tidal Power
Renewable
Reliable
Doesn't cause acid rain
Doesn't cause global warming
No pollution
Free - initial costs are moderately high
Spoils the view
Alters the habitats of wildlife
Bio-fuels
Renewable
Reliable
Doesn't cause acid rain
Carbon neutral
Free
Can cause global warming
Loss of natural habitat from destruction of forests
Cannot respond to immediate energy demands
Nuclear Power (Uranium or Plutonium)
Doesn't cause acid rain
Doesn't cause global warming
Reliable currently - finite
Non-renewable
High decommissioning costs
Produces radioactive waste - no other pollution
Nuclear waste is dangerous and hard to dispose of
Investigating Specific Heat Capacities - Method
1) Measure the mass of a block with two holes in it, then wrap it in an insulating layer (e.g. newspaper) to reduce the energy transferred from the block to the surroundings. Insert the thermometer into one hole and the heater into another
2) Measure the initial temperature of the block & set the potential difference of the power supply to be 10V. Turn on the power supply & start a stopwatch
3) When you turn on the power, the current in the circuit does work on the heater, transferring energy electrically from the power supply to the heater's thermal energy stores - this energy is then transferred to the material's thermal energy store by heating, causing its temperature to increase
4) As the block heats up, take readings of the temperature and current every minute for 10 minutes - the current shouldn't change
5) Turn off the power supply. Use the measurements of the current & the p.d. to calculate the power supplied to the heater, thus calculating how much energy has been transferred to the heater at the time of each temperature reading
6) If you assume all the energy supplied to the heater has been transferred to the block, you can plot a graph of energy transferred to the thermal energy store of the block against temperature
Investigating the Effectiveness of Materials as Thermal Insulators - Method
1) Boil water in a kettle. Pour some of the water into a sealable container to a safe level. Measure the mass of water in the container
2) Use a thermometer to measure the initial temperature of the water
3) Seal the container & leave it for 5 minutes. Measure this time using a stopwatch
4) Remove the lid & measure the final temperature of the water
5) Pour away the water & allow the container to cool to room temperature
6) Repeat this experiment, but wrap the container in a different material once it has been sealed. Ensure the mass of water is the same and so is the initial temperature each time
What is a closed system?
A system where neither matter nor energy can enter or leave
Why did electricity use in the 20th century increase?
1) The population grew
2) People began to use electricity for more & more things
Why did electricity use in the 21st century decrease?
1) Appliances are becoming more efficient
2) We're more careful with energy use in our homes
Why are we trying to increase our use of renewable energy resources?
1) Burning fossil fuels is damaging to the environment
2) Non-renewables will run out one day
3) Pressure from other countries & the public has led to targets being set e.g the UK aims to use renewable resources to provide 15% of the total yearly energy by 2020
What has pressure from the public & other countries led to?
Pressure being put on energy providers to build new power plants that use renewable resources to ensure that they don't lose business & money
What is the use of renewables limited by?
1) Reliability - since some energy resources aren't that reliable, a combination of different power plants would have to be used - expensive
2) Money - building new power plants costs money, the cost of switching to renewable power will have to be paid & some people don't want to or can't afford to pay
3) Politics - companies and governments can't force people to change their behaviour
What happens when a system changes?
Energy is transferred - it can be transferred into/away from the system, between different objects in the system or between different types of energy stores
Why are wind turbines unlikely to be able to power everything in the UK?
1) Large numbers of turbines would need to be built - takes up space & is expensive
2) Not always windy - the same amount of electrical power won't be produced every day