Reaction of Alkenes
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
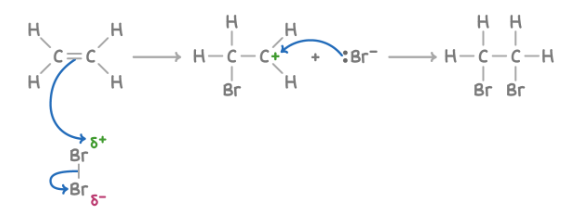
Reaction with halogens (Br2)
Reagent : Br2
Conditions : aqueous
What happens : C=C opens up; added onto the two C atoms of the C=C double bond: Br & Br
Overall equation : CH2=CH2 + Br2 ➔ CH2BrCH2Br
Mechanism : electrophilic addition
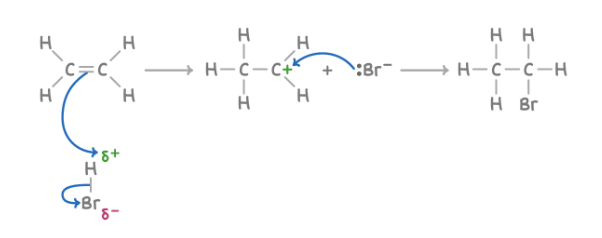
Addition of hydrogen halides (HBr)
Reagent : HBr
Conditions :
What happens : C=C opens up; and added onto the two C atoms of the C=C double bond: H & Br
Overall equation : CH3CH=CH2 + HBr ➔ CH3CH2CH2Br (1-bromopropane)
CH3CH=CH2 + HBr ➔ CH3CHBrCH3 (2-bromopropane) - major product because secondary carbocations are more stable
Mechanism : electrophilic addition
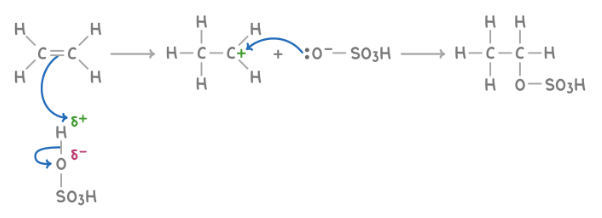
Addition of concentrated H2SO4
Reagent : H2SO4
Conditions : Cold, Concentrated H2SO4
What happens : C=C opens up; and added onto the two C atoms of the C=C double bond: H & O-SO2OH
Overall equation : CH3CH2OSO3H + H2O ➔ CH3CH2OH + H2SO4
Mechanism : electrophilic addition
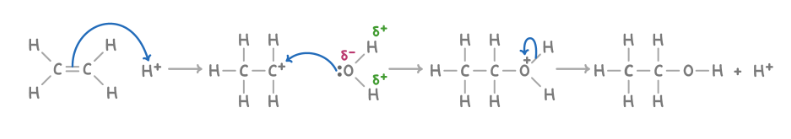
Hydration to form alcohols
Reagent : H2O with strong acid (e.g.H2SO4, H3PO4)
Conditions : Steam, 300° C, conc. phosphoric acid catalyst, 6.5 ×103 KPa
What happens : C=C opens up; and added onto the two C atoms of the C=C double bond: H & OH
Overall equation : CH2=CH2(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CH3CH2OH(g)
Mechanism : electrophilic addition
Dehydrating alcohols to form alkenes
Reagent : concentrated H2SO4
Conditions : heated acid catalyst such as concentrated H2SO4
What happens : protonation of the alcohol oxygen, formation of a carbocation intermediate via the loss of water, formation of an alkene via the loss of a proton.
Overall equation : CH3CH2OH ➔ CH2=CH2 + H2O
Mechanism : elimination
