DDT - Antibody based diagnostic techniques
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
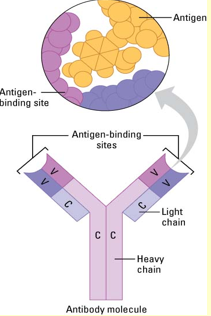
Structure of an antibody
Made from 4 polypeptides forming a Y shape, with the V region being able to alter any shape that fits the specific shape of the antigen. The C region will never change, and is always constant
Difference between monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies
Monoclonal only have one epitope (binding site of antigen) whilst polyclonal antibodies have multiple epitope for one antigen
Preparing polyclonal and monoclonal differences
Polyclonal preparation is generally easier, and cheaper but will yield a variety of antibodies, but monoclonal results in better antibodies but is more expensive and difficult
Different types of diagnostic based antibody technique
Immunohistochemistry would be used for tissue samples, ELISA for liquid samples and immunoprecipitation for complex mixture samples
Types of labelling antibodies
Using enzymes, fluorescent and radioisotopes are ways to label antibodies during immunoassays
Classifcation of natibody techinques
Choice of antibody label, method of signal detection and whether the immunoassay is competitive or non-competitive
Competitive vs non-competitive immunoassays, and when would competitive immunoassay be used
Non-competitive assays fix onto occupied sites and measure those while competitive assays measure unoccupied based on labelled analytes. Competitive ELISA would be used when small molecules are trying to be detected like testosterone, where a monoclonal antibody would be required
Advantages of immunohistochemistry
It is perfect for detecting particular cells and proteins, that no other techinques could give, as well as detecting certain cellular activites
Difference between primary and secondary antibodies
Primary antibodies bind directly to the primary antigen, while secondary antibodies bind to the primary antibodies
What is cardiovascular disease and what are the 3 layers of the heart?
Diseases that affect the cardiac system (Either the heart or the blood vessels) with the 3 heart layers being the pericardium (external layer), myocardium (muscles) and endocardium (inner layer)
Aetiology of ischemic heart disease
Gradual build-up of LDL due to hypertension, hyperlipidemia etc. which causes a build in blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis After causing stoppage of blood, myocardial infarction will be caused