chapter 23- aromatic compounds
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
3 characteristics of benzene
colourless
sweet smelling
highly flammable
what is each carbon bonded to in bezene
Each carbon in benzene is bonded to one hydrogen atom and two other carbon atoms,.
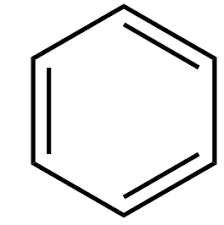
what did kekule suggest about benzene model
he thought it was a 6 membered carbon with alternating single and double bonds
what are the 3 reasons that kekules model for bezene was incorrect
had a lack of reactivity
the lengths of the carbon-carbon bonds
hydorgenation
how did the lack of reactivity disprove kekules model
if benzene contained the c=c it would be able to undergo electrophilic addition and decolourise in bromine water however this did not happen meaning that benzene cant have double bonds
how did the lengths of the carbon bonds disprove kekules model
Kathleen lonsdale found that single bonds were longer than double bonds, however benzene is a symmetrical molecule
how did hydrogenation enthalpies disprove kekules model
the enthalpy change for benzene following kekules model shouldve been 3x that of cyclohexene however its bond enthalpy was found to be much lower, indicating greater stability of benzene than predicted.
what is the enthalpy of hydrogenation in benzene
-208kjmol-1, therefore 152kjmol-1 than expected from kekules model
draw kekules model for benzene
why does carbon only bond 3 times in benzene
one electron is in the p-orbital at right angles to the plane of the bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms
describe the interaction of p-orbitals in benzene
adjacent p orbitals overlap sideways above and below the plan to form a ring of electron density. This overlapping creates a system of pi bonds
where are the deloclaised electrons in bezenes
the 6 electrons occupying the system of pi bonds
how to name a benzene with one alkyl group
the alkyl group is named first and then followed by the word "benzene."
how to name a benzene attached to an alkyl group with a functional group
you use phenyl benzene
which is the most common benzene reaction
electrophilic substitution
conditions for nitration of benzene
sulfuric acid and 50 degrees c
why is the nitration of benzene done at 50 c
to maintain a good rate of reaction (done with a water bath)
what happens if the nitration of benzene is carried out at a temp over 50c
further subsistution can occur resulting in the production of dinitrobenzene
use of nitrobenzene
dyes and pesticides
what is the electrophile in the nitration of benzene
NO2+
how is the electrophile in nitration of benzene made
a reaction between conc nitric acid and conc sulfuric acid
steps of electrophilic substitution
electrophile accepts an e- from benzene ring to form a dative covalent bond
The dative covalent bond then rearranges to restore the aromaticity of the benzene ring, resulting in substitution of a hydrogen atom with the electrophile.
equation for the creation of an electrophile in the nitration of benzene
HNO3 + H2SO4 —> NO2+ + HSO4- + H2O
final step of nitration of benzene
H+ + HSO4- —.> H2SO4
what is a halogen carrier
A halogen carrier is a substance that facilitates the generation of electrophiles by forming a complex with halogens
conditions for the bromination of benzene
room temperature and pressure and in the presence of a halogen carrier
what is the electrophile for the bromination of benzene
Br+
why is a Br+ needed for the bromination of benzene
benzene is too stable to react with a non polar bromine molecule and requires the electrophile Br+ to initiate the reaction.
halogen carriers for bromine
FeBr3 or AlBr3
steps for the bromination of benzene
the Br+ ion accepts a pair of electrons from the benzene ring and forms a dative covalent bond
the unstable organic intermediate breaks down to form the organic product and a H+ ion
step 1 in the bromination of benzene
Br2 + FeBr3 —> Br+ + FeBr4-
last step for bromination of benzene
FeBr4- + H+ —>FeBr3 + HBr
what alkylation of benzene
the substitition of hydrogen for a alkyl group
what is needed for alkylation
benzene + haloalkane and a halogen carrier (AlCl3)
what is the role of a halogen carrier
catalyst that generates an electrophile
why is alkylation useful
increases the length of the carbon chain
what is the non-organic product in alkylation
HCl
what is an acylation reaction
the reaction of benzene with an acyl chloride in teh present of AlCl3
what forms from acylation
an aromatic ketone
are arenes or alkenes more reactive
alkenes
why are alkenes more reactive than arenes
their pi bonds are localised making an area of high electron density in one spot which can easily attract electrophiles
why are arenes less reactive than alkenes
arenes have a stable deloclaised pi bond as electrons are spread evenly
why would a reaction with methyl benzene be faster than just benzene
methyl increases electron density on the benzene ring
this attracts an electrophile more
why would a reaction with propanone and propanal differ
the alkyl groups of propanone in a ketone would hinder the attack of an electrophile
what is a phenol
a benzene with an OH group
what is more soluble phenol or alcohol
alohols because phenol have a non-polar benzene ring
what type of acid is phenol
weak
how can you show a weak acid in an equation
double arrow
what forms when a phenol dissolves in water
it partially dissociates forming a phenoxide ion and a proton
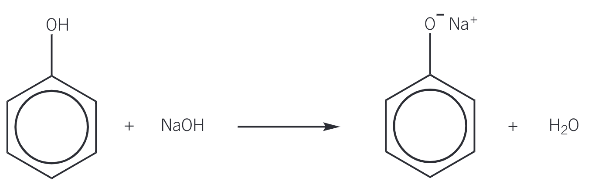
phenol + NaOH
sodium phenoxide + H2O
bromination of phenol
forms 2,4,6 tribromophenol and HBr
how can the bromination of phenol be used as a test for phenol
there will be deolouirstaion
the 2,4,6tribromophenol forms white ppt
what is the bromine test for phenol
react with bromine to form a white ppt
what is special about the bromination of phenol
needs no catalyst
nitration of phenol
the reaction of phenol and dilute nitric acid to form a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol
what is an example of comparing reactviity between benzene and phenol
the nitration of benzene requires concentrated nitric acid whereas the nitration of phenol only require dilute nitric acid
what is the main test for phenols
use a pH probe (low score for a weak acid)
will not react with carbonates
phenol + metal
forms a phenoxide salt and 1/2H2
why is phenol a better acid than a normal alcohol
it has a ring which stabilises the phenoxide ion
one example of evidence that could show that a molecule has kekules structure rather than the deloclaised structure
the bond lengths are different
what does NaOH hydrolyse
esters, phenols, an alcohol on a carboxylic acid
why is a phenylamine more reactive than benzene
a lone pair of electrons on the N is partially delocalised
this increases electron density (more than benzene)
making the molecule more susceptible to electrophillic attack
why are phenols more reactive than benzene
they have a lone pair of electrons on the oxygen which is partially delocalised
this increases electron density
making it more susceptible to electrophilic attack
where does the -NH2 direct
2 or 4
where does -NO2 direct
3
Explain the differences between Kekulé’s model and the delocalised model of benzene
P-orbitals overlap to form pi bonds
Pi bonds are delocalised in the delocalised model, the delocalised nature makes it more stable
In Kekulé’s model the pi bonds are localised between 2 carbons
phenol with a carboxylic acid + carbonate oragnic synthesis
only the carboxylci part reacts not the alcohol
phenol with a carboxylic acid + hydroxide oragnic synthesis
both the alcohol and the carboxylic acid react