AP Psych Semester 2 Final
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
172 Terms
stress
physiological and psychological reaction to challenges, conflicts, and demands that we face in our life
real stress
physical / tangible source of stress (Ex. paper due in English class)
imagined stress
an abstract source of stress (Ex. thinking your parents want you to get A’s, but they never said explicitly)
Richard Lazarus
_____ proposed the importance of how we assess and appraise situations regarding the reaction that will follow
micro stressors
small and annoying occurrences (Ex. running late); can be insignificant on their own but will pile up to have severe effects
eustress
when stress comes from good things / positive sources
approach-approach conflict
two possible options to choose from and both are equally desirable
avoidance-avoidance conflict
two possible options to choose from and both are equally undesirable
approach-avoidance conflict
only one option; has both desirable / undesirable qualities
double approach-avoidance conflict
more than one possible option, but each has desirable / undesirable qualities
vacillation
bouncing back and forth between available options in a conflict
ambivalence
having little choices but both qualities have mixed feelings
Hans Selye
one of the best known researchers in field of stress; developed general adaptation syndrome
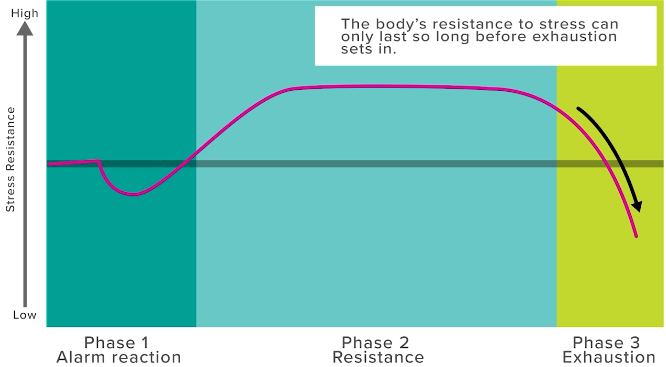
General Adaptation Syndrome
describes what the body is going through when confronting a stressor
alarm phase (1st stage)
occurs when the individual encounters the stressor; sympathetic nervous system reponds
heart rate + respiration increases
pupils dilate
digestion slows
body prepares fight/flight
resistance (2nd stage)
body functioning in state of sympathetic energy
remains ready to continue in fight/flight
remaining in this stage too long = vital source depletion
greater risk for illness and fatigue
exhaustion (3rd stage)
body returns to parasympathetic state either due to resolved stressor or depleted bodily resources
more susceptible to getting sick
feel mental / physical fatigue
psychoneuroimmunology
studies relationship between stress, immune system function, endocrine system function, and overall mental well-being
life inventory
a method to measure stress
Holmes and Rahe Social Readjustment Rating Scale
test designed to measure stress in life w/ life change units; looks at sources of eustress and distress
distress
negative sources of stress
Hans Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome
What is this graph showing?
positive psychology
branch of psychology based on study / promotion of positive aspects of human life
happiness
experiencing positive emotions and satisfaction with one’s life
eudaimonic happiness
positive emotional state achieved w/ experiences of MEANING and PURPOSE
hedonic happiness
positive emotional state achieved w/ experiences of PLEASURE and ENJOYMENT
flourish
fulfillment in life, accomplishing meaning and worthwhile tasks; connects with others at a deeper level
well-being
state of happiness and contentment; low levels of stress; overall good physical and mental health and outlook
character strengths
positive attributes in a person’s personality
values in action (VIA) character strengths
unique personality traits that lead to positive outcomes; 24 identifiable character strengths characterized into 6 categories
wisdom
category including:
curiosity
love of learning
crticial thinking
ingenuity / creativity
social / emotional intelligence and perspective
courage
category including:
bravery
perseverance
integrity
humanity & love
category including:
kindness and loving
allowing yourself to be loved
justice
category including:
citizenship / teamwork / loyalty
fairness and equity
leadership
temperance
category including:
self-control
discretion
humility / modesty
transcendence
category including:
appreciation of beauty and excellence
gratitude
hope and optimism
spirituality / sense of purpose
forgiveness
playfulness / humor
zest / passion / enthusiasm
gratitude
appreciation for what an individual receives, tangible or intangible
social well-being
positive correlation between gratitude and positive emotional states
social belonging
improving interpersonal relationships with others
prosocial behavior
acts a moral barometer; gratitude motivates and reinforces _____
mindfulness
relaxation and purposeful attention to your body’s senses and experiences in the present moment
growth mindset
belief that abilities can be developed through hard work, good strategies, and instruction from others
fixed mindset
belief that individual is born with certain amount of ability and it cannot be changed
resilience
process of adapting well in the face of adversity, trauma, tragedy, threats, or significant source of stress
grit
passion and persistence for long term goals
psychopathology
study of psychological disorders + description of psychological disorders
syndrome
clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior
reasons for diagnosis
subjective discomfort
statistically abnormal (Ex. washing hands x100 a day);
related to loss of control + is maladaptive
social non-conformity
maladaptive for individual
social norms
behavior normal to a culture or society a person lives in
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM)
published in 1952 by American Psychiatric Association to focus more on psychological disorders; used to guide diagnosis for disorder; lists symptoms, prevalence, and common occurrences in course of disorder
International Classification of Disease (ICD)
published by WHO in 1948; a series of books that listed medical illnesses, symptoms, possible causes, etc.
Hippocrates
____ believed in an imbalance of four humors
psychoanalytic perspective
includes Freudian view of the unconscious, and believes that psychological disorders are due to an imbalance of the id, ego, and superego; could stem from repressed childhood trauma
humanist perspective
believes that issue stems from how the person views themselves, self-esteem, or oversensitivity of judgement of others
cognitivists
believes that source are irrational thoughts that become automatic in the person’s mind; thoughts manifest in symptoms
behaviorists
believe that sources are a case of conditioning gone awry (Ex. classically conditioned to be anxious or operationally conditioned to be depressed)
biological perspective
medical model; believes psychological disorders are due to brain-based / neurotransmitter-based diseases
includes research of genetic transmission of the disorders
biopsychosocial approach
takes into account a person’s biological, psychological, and sociocultural influences
biological influences
genes, brain chemistry, hormones
psychological influences
thoughts, learned behaviors, emotions
sociocultural influences
family traditions, culture
David Rosenhand
performed experiment in 1973
went to diff. hospitals where people complaining that voices in their heads + empty thud
all admitted into hospital + diagnosed w/ mental illness
once admitted, no symptom complaint, but still labeled as mentally ill
normal patient behaviors seen as symptoms of a disorder, even if the researchers had those behaviors as well
result: importance of describing the disease rather than the person
personality disorders
a set of inflexible, unstable behavior patterns that impair a person’s ability to function normally with others
Cluster A personality disorders
disorders considered odd / eccentric
Cluster B personality disorders
disorders considered dramatic / emotional
Cluster C personality disorders
disorders considered anxious / fearful
paranoid personality disorder (Cluster A)
symptoms of excessive distrust in others
avoidance of close relationships
tendency to read into what people say for hidden meanings
shifts blame towards others
schizoid personality disorder (Cluster A)
avoids relationships
requires very little social contact or interaction
viewed as having weak social skills / humorless
schizotypal personality disorder (Cluster A)
symptoms of bizarre and eccentric patterns of thought, speech, and mannerisms
believes that own self has extra sensory movements (Ex. telekinesis)
antisocial personality disorder (Cluster B)
more prone to criminal behavior
lack of conscience
aggressive interactions / behaviors
impulsivity
sometimes categorized as psychopathic / socipathic
borderline personality disorder (Cluster B)
symptoms of mood instability
impulsivity
suicidal thoughts
self-mutilating behaviors
tendency to be involved in conflict-ridden relationships + intense symptoms near breakup
histrionic personality disorder (Cluster B)
described as attention seekers
strong desire to be in the center / focus of situations
engage in behaviors to shift focus back to them
exaggerated language, styles of dress, mannerisms
narcissisitic personality disorder (Cluster B)
symptoms of exaggerated self-esteem and self-love
exaggerate their achievements and feel they deserve admiration and praise
more self-centered
generally uninterested in the feelings of others
avoidant personality disorder (Cluster C)
symptoms of extreme social anxiety
fear of being in social situations
fear of being rejected
yearn for social interaction but do not feel capable of doing so
dependent personality disorder (Cluster C)
excessive neediness and clinginess to other people
oversensitivity to what people say
pervasive feeling of helplessness
obsessive compulsive personality disorder (Cluster C)
excessive focus on orderliness
perfect to the point where it interferes with task completion
avoidance of working with other people
anxiety disorders
disorders marked by excessive feelings of anxiety or uneasiness; maladaptive and out of proportion for the given situation
generalized anxiety disorder
defined by symptoms of excessive, unrealistic anxiety
does not appear to be related to any one thing
symptoms: restlessness, irritability, muscle tension, sleep disturbances, trouble concentrating
diagnosis: requires clinical distress + present symptoms for six months
“free-floating” source of anxiety
more than one source of anxiety that shifts from object / person to the next (Ex. school → familial relationships)
panic disorder
brief periods of intense and uncontrollable anxiety
severity of panic attack makes person worry that they will have more
builds up anxiety
symptoms: heart palpitations, sweating, dizziness, confusion, chest pain, difficulty breathing
phobias
intense and irrational fears of specific objects (Ex. spiders / clowns) or situations (Ex. closed spaces / heights)
diagnosis: must cause clinical distress + present for six months
obsessive-compulsive disorders
group of disorders characterized by unwanted anxiety, thoughts, and behaviors
obsessive-compulsive disorder
pattern of obsessions followed by compulsions; the latter occurs in an effort to reduce anxiety causing obsessions
compulsions
unwanted behaviors
obsessions
repeated and unwanted thoughts
trauma and stress disorders
group of disorders characterized by excessive amounts of anxiety and stress following a stressful event or traumatic experience
post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
has a cluster of symptoms including:
avoidance of event hearths of location
persistent intrusive thoughts, memories, or dreams of the event
distorted cognition and / or moods such as negativity
loss of joy and pleasure
feeling detached or estranged
arousal symptoms such as sleep disturbance, hypervigilance, and / or startle response
often accompanied by social isolation, depression, and sometimes substance abuse
diagnosis: must be present for one month
mood disorders
general category including depressive and bipolar disorders together
major depressive disorder
characterized by debilitation depression, symptoms including:
continuous depressive mood
diminished interest in previously enjoyable activities
significant weight fluctuation
significant sleep fluctuation
fatigue / loss of energy
feeling worthless / guilty
difficulty thinking / concentrating
recurrent thoughts of death or suicide
diagnosis: requires five or more symptoms present for nearly every day for two weeks
persistent depressive disorder
diagnosed when there are 2+ of the same symptoms for major depressive disorder for over 2 years
bipolar disorder
period of depression + mania or hypomania
hypomania
mild mania
Bipolar 1 disorder
manic episode followed by hypomania or depressive episode
Bipolar 2 disorder
mostly depression in one or more hypomanic episodes
manic episodes
episodes with symptoms of:
unrestrained euphoria
decreased need for sleep
feeling pressure to talk or maintain conversation
disconnected ideas
distractibility
reckless / hyperfocused behavior
schizophrenia
a severe psychological disorder with profound symptoms of delusions and / or hallucinations
diagnosis: requires exhibition of 2+ symptoms of…
delusions
hallucinations
disorganized speech
disorganized or catatonic behaviors
negative symptoms
delusions
___ are distorted thoughts
hallucinations
___ are distorted or imagined perceptions
disorganized speech
___ is a symptom of speaking gibberish or not making sense
disorganized or catatonic behaviors
___ are odd and eccentric behaviors, or lack of movement