Bio Midterm Study (UNIT 1B)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the functions of the cell membrane
It is responsible for homeostasis inside the cell and it controls how, when, and how much enters and leaves the cell.
What are the basic concepts of the cell membrane?
Cell membranes are fluid and flexible, cell membranes can self-repair, the organelles inside of the cell have their own membranes, cell membranes have many special types of proteins that give it certain properties, cell membranes can connect between two cells using gap junctions, and cell membranes go through a process called binary fission when the cell reproduces asexually.
What is the structure of the cell membrane?
It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer, where each phospholipid is made up of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails. The bilayer is created with the heads facing the outside and the tails lying inside.
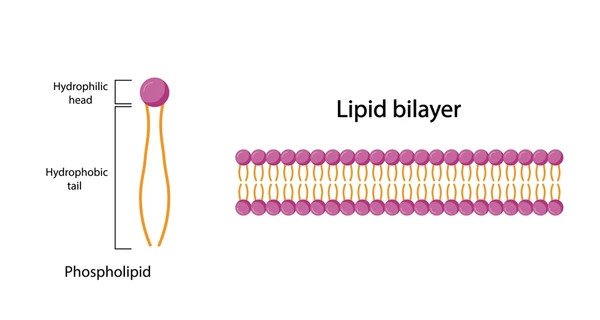
What is the Fluid Mosaic Model?
It is a representation of the cell membrane’s structure that describes the relationship between proteins and lipids in the phospholipid bilayer. It emphasizes the cell membrane’s fluidity and elasticity. Essentially, it “describes the cell membrane as a "mosaic" of various proteins and carbohydrates embedded in a "fluid" phospholipid bilayer.”
Intracellular fluid
Fluid inside of the cell
Extracellular fluid
Fluid outside of the cell
Diffusion
The net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, where no additional energy is required.
Dynamic Equilibrium
When molecules remain in motion, but all concentrations are equal.
Facilitated Diffusion
A type of diffusion that is preformed with the help of transport proteins to move substances across the cell membrane (No energy required).
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
Isotonic Solution
There is a balance of concentration of water and solutes inside and outside of the cell
Hypotonic Solution
There is a lower concentration of solutes outside of the cell than in the cytoplasm of the cell. This means that water has to move inside of the cell to balance the concentration.
Hypertonic Solution
There is a higher concentration of solutes outside of the cell than in the cytoplasm of the cell. This means that the water has to move outside of the cell to balance the concentration.
Active Transport
The movement of particles across the cell membrane, against the concentration gradient (low to high concentration), by using energy.
Passive Transport
The movement of particles across the cell membrane with the concentration gradient (high to low concentration), without using energy.
Homeostasis
The balance in an internal environment of a life form to help it grow.
Endocytosis
The process by which a cell surrounds an object in the outside environment in a portion of the plasma membrane, creating a vacuole.
Exocytosis
The process by which the cell undergoes the exertion of materials at the plasma membrane, using vesicles.
Tonicity
The capability of a solution to modify the volume of cells by altering their water content.
Lysis
The bursting of a cell
Crenation
The shrinking of a cell
Transport Proteins
Proteins that create tunnels through the cell membrane to move needed substances or waste materials.
Receptors
Proteins on the outer surface of a cell that send signals to the inside of the cell
Channel Protein
A type of transport protein that forms pores in the cell membrane to allow certain molecules to move down their concentration gradients quickly, without using energy.
Carrier Protein
A type of transport protein that binds to certain molecules, transporting them like a shuttle going through gates, and it can be either passive or active transport. (Both downhill and uphill)