Chapter 1 (Unit 1)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What percentage of living fishes are primarily marine?
About 60%
What percentage of living fishes are primarily freshwater?
39%
What percentage of living fishes move between salt and freshwater?
1%
Fishes make up how much of species of living vertebrates?
More than half of the over 60,000 species
Why yare fishes considered ecologically dominant?
They’ve dominates aquatic ecosystems for most of complex life’s history, inhabiting everything from frozen oceans and oxygen-poor swamps to deep seas and temporary desert ponds.
What is a fish?
An aquatic vertebrate with gills and limbs in the shape of fins. However, some fishes have lost their paired fins over time (eels) or nonvertebrate craniates (hagfishes).
Vertebrate Classes
Modern phylogenetics with an emphasis on utilizing DNA-based molecular appraisals of evolutionary lineages has yielded a more accurate view of the relationships amount the major groups of vertebrates.
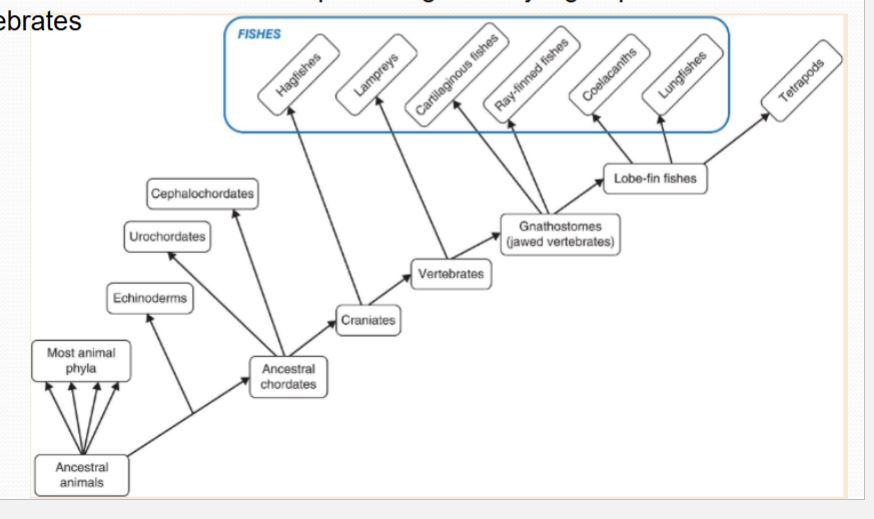
What has modern genetics done to help us significantly in fish genetics?
Has added to our understanding of evolution, ecology, and conservation of fishes.
What are some specialties that genetics contain?
Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes, ecological genetic can reveal breeding behavior, population genetics is used to define management units of (or stocks) for fisheries, evolutionary genetics demonstrates the basis of novel organismal traits, and molecular phylogenetic is th application of DNA data to resolve branches in the tree of life.
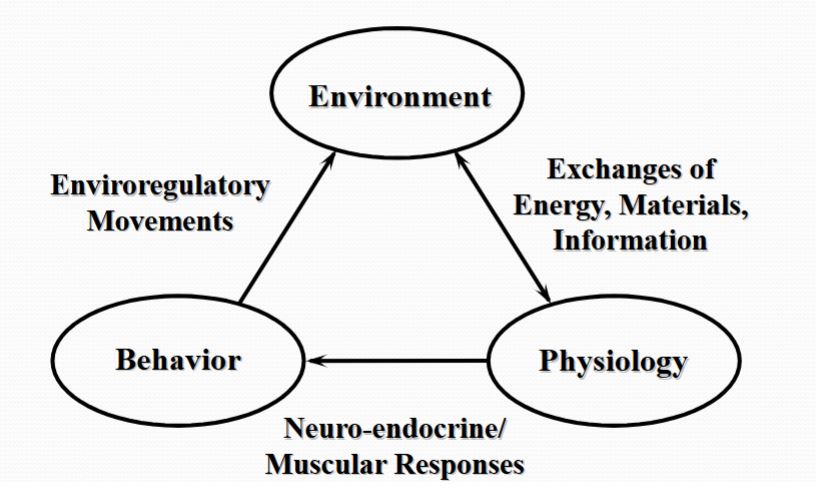
Fish Biology-in Symbols
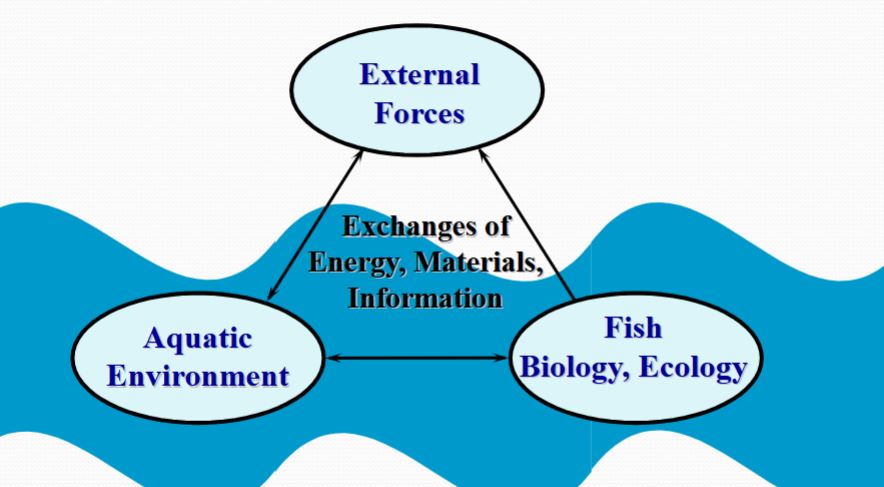
The Bigger Picture
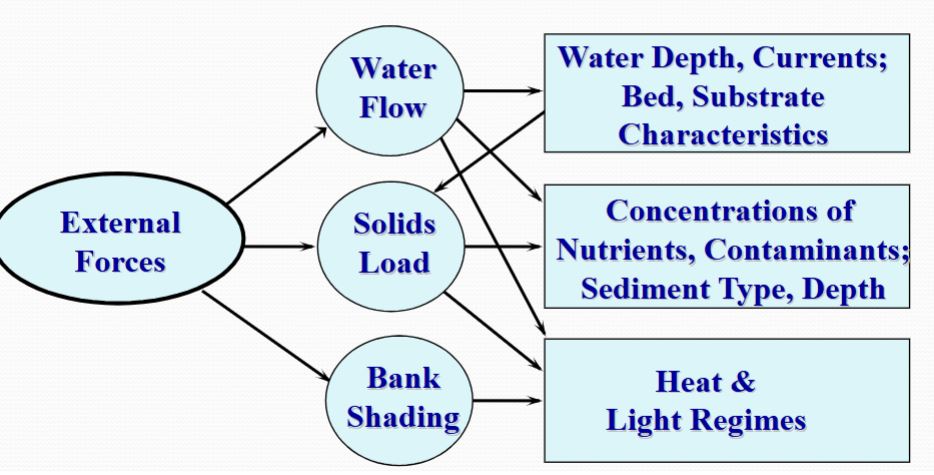
Aquatic Environment

WQ & Primary Production
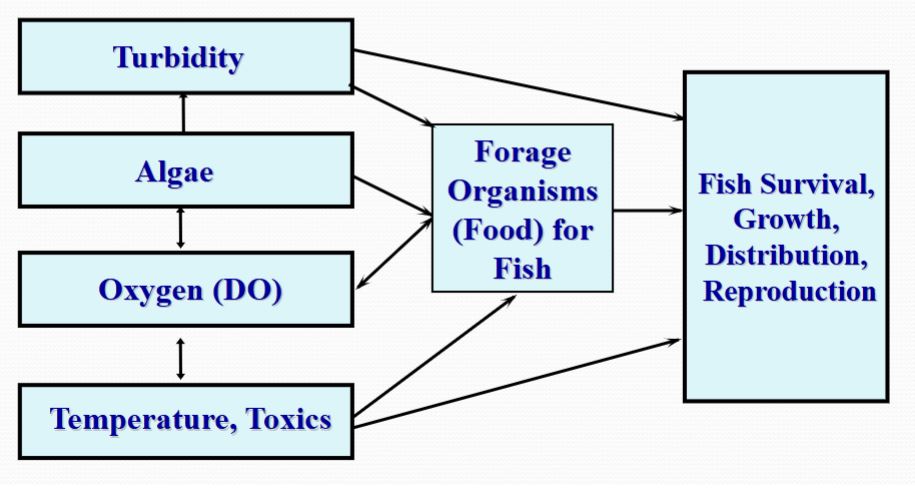
Secondary Production
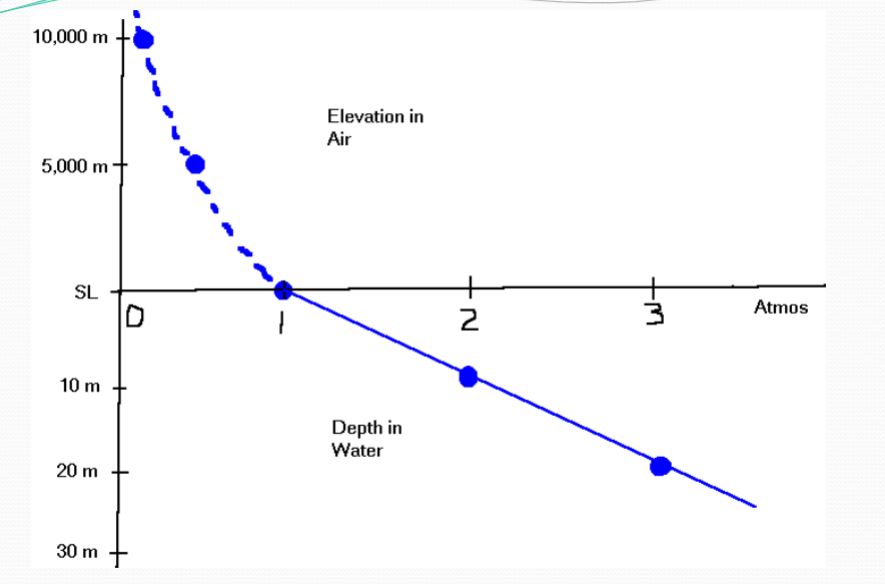
Atmosphere vs. Sea Level
Solids (Dissolved Substances)
-SW has about 200 x more DS than FW
-Salts similar between SW and blood sera
-Typical SW had 34-35 ppt (g/L), mostly ionized NaCl: 30.6% Na+, 55.3% Cl-; minor ions—So4^-2, Mg^+2, Ca^+2, K+
SW’s Minor Ions:
SO4^-2 7.7%
Mg^+2 3.8%
Ca^+2 (& Sr^+2) 1.2%
K^+1 1.1%
FW’s Major Ions:
HCO^-1 53%
SO4^-2 19%
Ca^+2 (& Sr^+2) 17%/89%
Solids (DS)
-Polar seas less salty (down to 30 ppt) than average SW, because precipitation: evaporation is relatively high
-Red Sea has 40 ppt; Laguna Madre, >50ppt Why?— High evaporation; low FW inflow, precipitation.
-Salinity gradient in Texas coastal bays, from low in N to high in S
Solids (DS) (cont’d)
-FWs have median TDS~ 170 ppm (mg/L); range, 70-400ppm
-Dominant inorganic ions are HCO3^-. SO4^-2, and Ca^+2
-”Hard” FWs have high Ca^+2 &/or Mg^+2
Gases-Oxygen
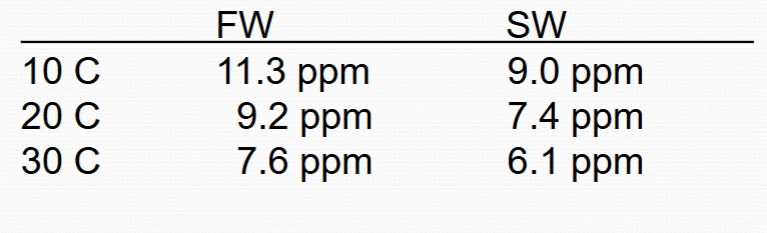
Dissolved Oxygen at air-sat and 1 atmos:
Gases-Oxygen (cont’d)
Low Dissolved Oxygen situations
-high BCOD: below sewage outfalls; at night or on cloudy days in algae-rich waters
-low DO resupply: stagnant water below euphotic zone; ground water; water covered with snow and ice
Gases_Oxygen (cont’d)
High-DO situations (supersaturation)
-on bright days in clear, stagnant, algae-rich waters
-power-plant outfall areas
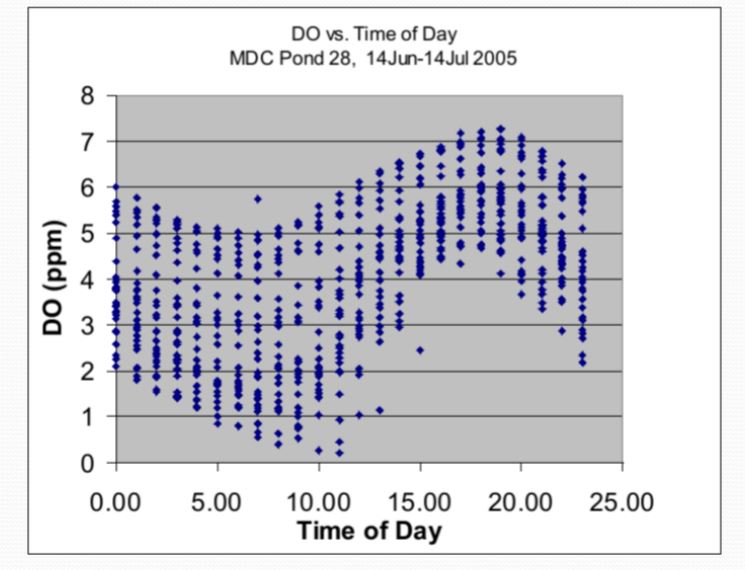
Diel cycles; Highest in afternoon, lowest in early morning
Diversity of Aquatic Environments
Thermal Pollution
-Heated effluents from steam-electric power plants; typical delta-T is 10 C
-Cold effluents (tailwaters) from hydroelectric power plants; delta-T can reach -20 C in Summer
-Run-off from defrosted land; delta-T is up to 5 C in summer
Currents and Water Movement
-Ranges from stagnant to 3m/sec (faster, if waterfalls are counted)
-Caused by tides, wind stress, density, differences, hydraulic-head differences
-Importance: Currents distribute the other stuff (DO, heat, forage, fish eggs & larvae, substrate), and they shape morphometry of habitat.
Diversity and Environment
The above environmental differenced have allowed for the many adaptations that are seen across various fish groups. We will be look at these various adaptations throughout the semesters and how they have allowed fishes to utilize and thrive in various environments.