ESS chap.5 Soil system and societies
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Composition of soil
minerals
organic matter
air
water
Primary functions of soil
medium for plant growth
water storage
habitats for one-quarter of all living species (bacteria, insects..)
modifies the atmosphere through respiration (organisms + plant roots)
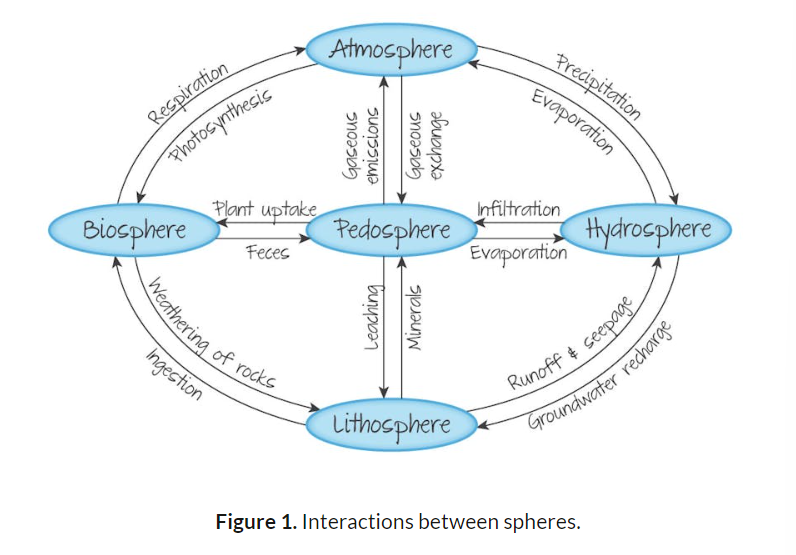
Spheres constituting the Earth
pedosphere (soil)
lithosphere (rocks)
hydrosphere (water)
atmosphere (air)
biosphere (living)
What factors affect soil characteristics?
climate: precipitation/evaporation balance (influence water movement)
organisms: role of decomposers
relief: elevation, aspect, and angle of the slope
parent material: original material that the soil develops from
time: amount of time the soil has had to develop
Translocation
movement of particles within the soil (up or down) through water
Salinization
when water and minerals flow up through evaporation (especially in deserts)
Leaching
when water flows down and transports/dissolves minerals (especially in places with heavy rainfall)
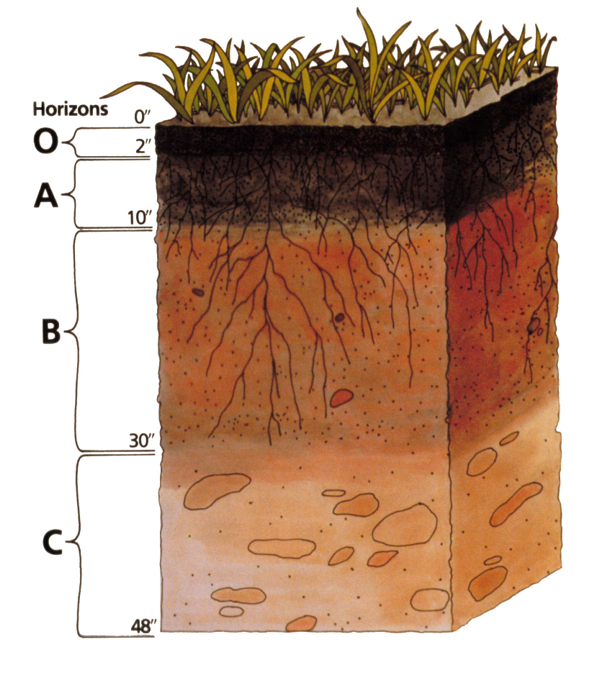
Cross-section of soil
O: leaf litter
where decomposition happens/most productive area
A: the organic material mixed with minerals (full of nutrients)
E: shows depletion of organic matter, clay, iron, aluminum
A + E = top-soil
B: sub-soil (rich in clay and iron)
C: where the bedrock starts breaking
R: hard bedrocks
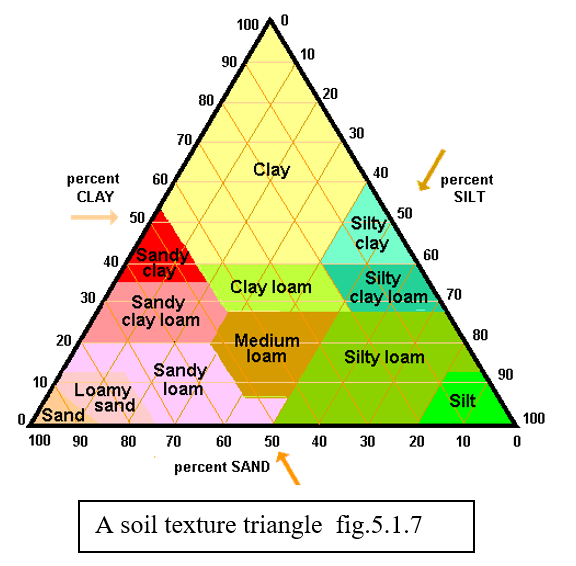
Soil texture
Sand (0.05-2mm)
Silt (0.002-0.05mm)
Clay (<0.002mm)
loam = equal amount of sand, silt, and clay
result of parent material + type of weathering
Porosity + Permeability
the amount of space between the particles of the soil
the ease at which gases and liquids can pass through the soil
the higher the porosity, the better the permeability
Acidification of soils
The high acidity in soils because of the evaporation, that soaks up the minerals out of the soil.
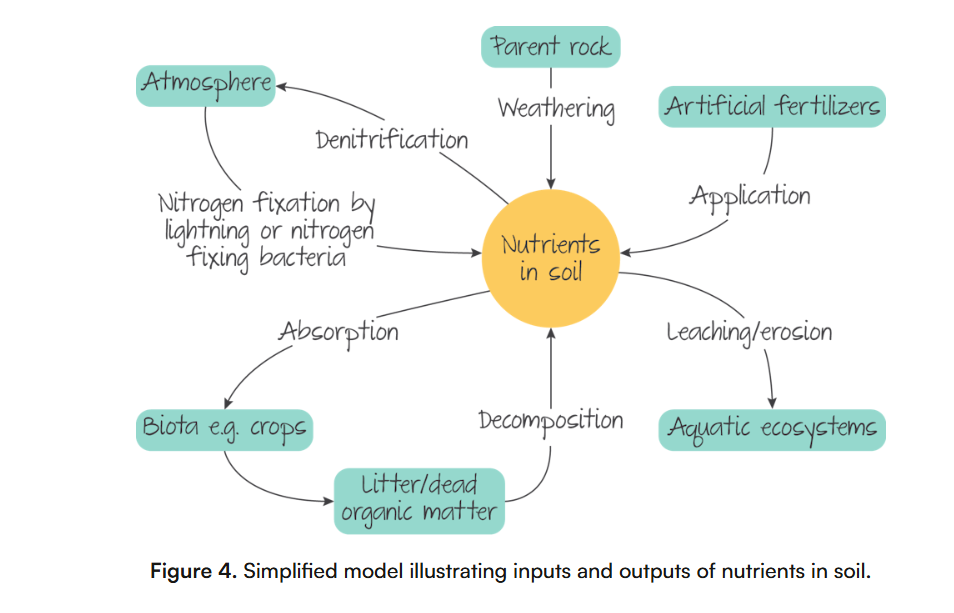
Inputs of soil
minerals: from the weathering (breakdown of material by physical, biological, and chemical processes)
organic matter: from living organisms on (ex: decomposition) and in the soil
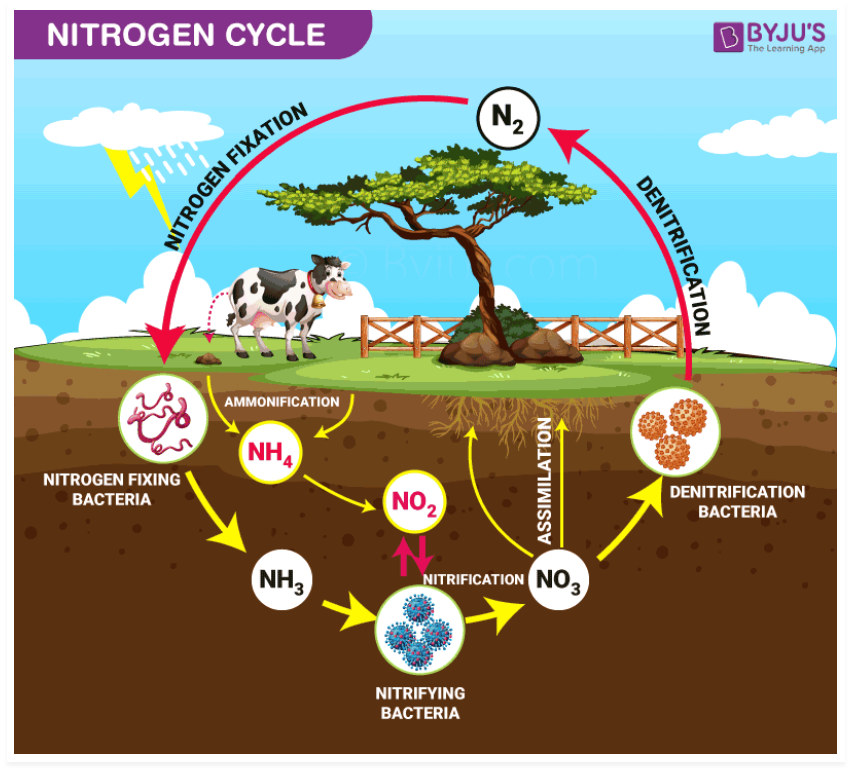
gases: by plants, nitrogen fixation (transforms nitrogen of the atmosphere in nitrates and ammonia) + c02 by living organisms
water: depends on the slope
Stores of soil
organic matter: dead organic matter (DOM) stores nutrients
minerals: forms the parent material
gases and water: depends on weather conditions + nbr of organisms and plant roots + soil texture
organisms: add nutrients through waste
nutrients: stored in the organic matter or free in the soil
Outputs of soil
lose of minerals, organic matter, water, and gases (inputs) through :
the action of the wind: blows loose soil away
water: leaches minerals and washes out the clay particles
plants: take away nutrients + CO2
animals: eat clay-based soil + herbivores
Soil properties
Sandy
big particles
large pores so high porosity and permeability
warm up quickly due to high air content + subject to drought
Silt
small particles
smooth feel
properties between sand and clay
Clay
smallest particles
small pores so low porosity and permeability
long dry time + warm up slowly due to high water content
rich in nutrients
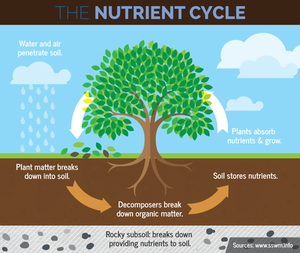
Nutrient cycle
Dust Bowl
1930s
USA - Texas, Colorado, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Kansas (Midwest)
Causes
Poor farming methods: overuse of the land, left fallow
Drought
Windy conditions: swept topsoil formed dust storms
Consequences
no harvest
destruction of the land + infrastructures
starvation
death (dust pneumonia)
migration of farmers
Soil inputs and outputs schema
Nitrogen cycle
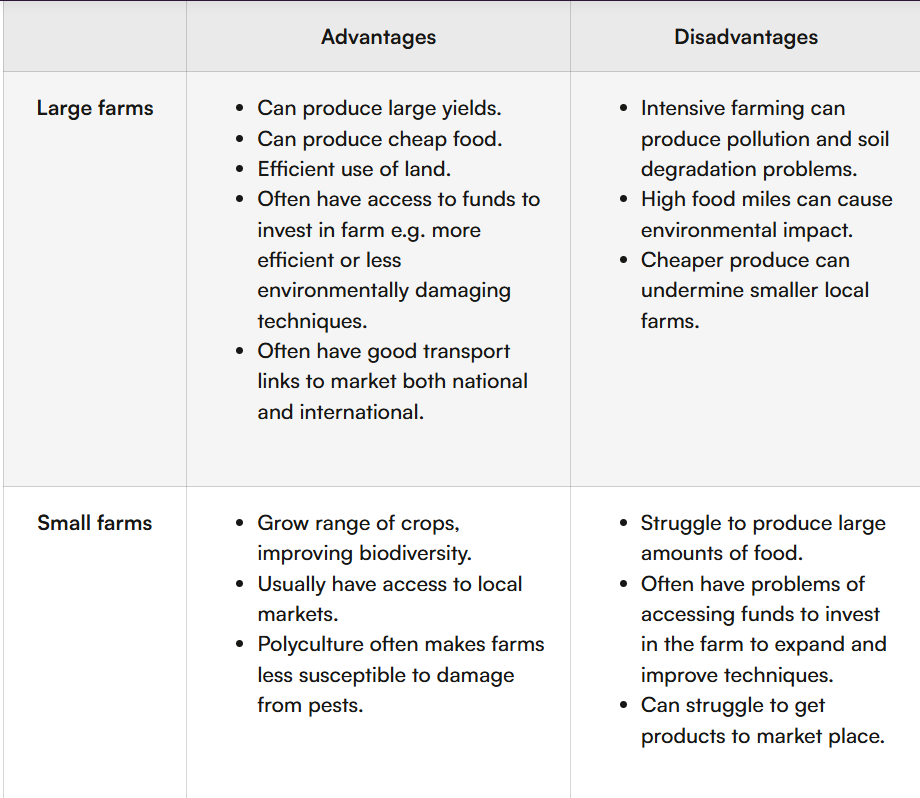
large vs small farms
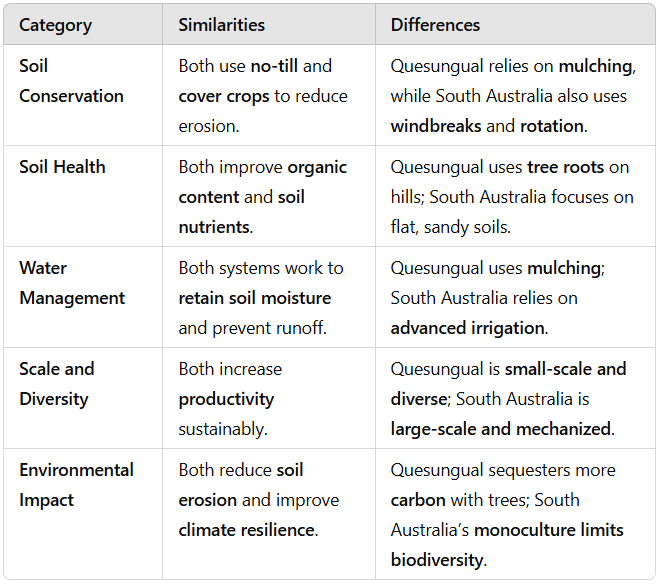
Case study : comparison Quesungual system in Honduras vs Large commercial farming in South Australia
SIMILARITIES
no-till (no plough) + use of cover crops (oats)
improved organic content and soil nutrients
retain soil moisture and control run-off
increase productivity
reduce soil erosion and improve climate resilience
DIFFERENCES
Quesungual covers the soil in mulch (compost) while South Australia also uses crop rotations, windbreaks (paravent) and advanced irrigation
Quesungual uses tree roots on hills while South Australia uses sandy and flat soils
Quesungual is a typre of subsistence farming so small-scale and diverse while South Australia is commercial farming so large-scale and mechanized
Quesungual can act as a carbon sink (especially after the stop of slash and burn) while South Australia is emptier