Apsc 451 next test
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
Tying Horses
What are the 2 ways to tie down a horse
To secure your horse with a trailer tie, follow these steps:
1. Close the divider before tying your horse in.
2. Attach the trailer tie to your horse’s breakaway halter.
3. Detach the lead rope.
• If you decide to use a lead rope to tie your horse in, follow
these steps:
1. Put the lead rope through the hook.
2. Lock the divider in place.
3. Tie the lead rope to the hook using a quick-release knot.
4. Leave two or three feet of slack.
What procedures take place before loading horses
certificate of veterinarian inspections
negative equine infectious anemia/coggins test
brand inspection test
other state specific requirements
what is the preparation for loading horse
• Find a trustworthy transport service
• Pick a transport option
• Check the trailer for damages
• Ensure service is prepared for mishaps
• Familiarize horse with the trailer
• Pack horse's needs
• Comfort horse before and after travel
when lading a hore you should use..
a ramp/step up t get horse inside
What are some behaviors and diseases horses might express when transported
anxiety, discomfort
colic (stress, dehydration, ulcers)
shipping fever
heat stroke
colitis
(stress/poor food + water intake/dietary changes/antibiotic
or anthelmintic treatment)
drivers operating livestock trailers must have a
cdl (commercial drivers license)
what are some vehicle requirements
gross vehicle weight rating
gross vehicle weight
electronic logging device (tracks route vehicle speed and more)
What are the types of vehicles / trailers used
bumper pull horse trailers
gooseneck
horse trailer with living quarters
What are some horse safety measures
adequate ventilation
temp control
secure and proper padding of the vehicle
be meticuluos when inspecting the trailer
what are spme meds horses are put on for transportation and what is the function
• Acepromazine: A rapid-acting tranquilizer used to
control fractious horses during examination,
treatment, trailer loading, and transportation. It
causes sedation, muscular relaxation, and reduced
activity.
• Detomidine: An α₂-adrenergic receptor agonist
providing sedation and analgesia. It’s commonly
used in horses and is available under various trade
names.
• Xylazine: A fast-acting sedative administered
intravenously or intramuscularly. It typically takes
effect within minutes and lasts approximately 20 to
30 minutes.
• Butorphanol: An opioid analgesic often combined
with sedatives like xylazine or detomidine to
enhance sedation and pain relief during
are horses typically medicated before they are transported
no, unless there is a specific need
What type of horses are the easiest to transport
Cold-blooded horses (draft horses)
are easier to transport than hot-
blooded horses (Thoroughbreds or
Arabians).
• The reason why is because cold-
blooded horses tend to have a
calmer, more docile temperament,
which would make them less likely to
become stressed or anxious during
loading and transportation
• Hot-bloods, however, are typically
more reactive and sensitive, which
makes it more challenging to load
and transport
Careers in the horse industry
How aree the horse careers categorized
• Primary industry
• Supplies/ Support industry
• Racehorse/ Show industry
describe the primary careers
Hands on: The primary
careers involve direct care,
health services, and
maintenance for horses.
Work environments: clinics,
stables, farms, and private
practices
Essential to all areas of the
horse industry: Health and
Maintenance
What careers are included in th primary industry
Veterinarian, farrier, equine trainer, equine therapist, horse breeder
describe the equine support and supplies industry
Essential Supplies and
Services: This sector supports
the performance and daily care
of horses through products.
Work Environments: tack
shops, equipment production
facilities, commercial feed
manufacturers.
Innovation and product
development: nutrition and gear
What careers are included in the equine support and supplies
commercial feed manufacturers, tack and equipment maker
what are some major feed manufacturers, and tack makers
purina mills, nutrena, triple crown nutrition, blue seal feeds
hermes (france)
stubben (germany)
Circle Y Saddles
what are some racehorse and show horse careers
jockey (horse riders)
equine racing chemist
Job search resources:
• Equilbase (www.equilbase.com) - Horse racing industry jobs and statistics
• The Jockey Club (www.jockeyclub.com) - Licensing and career info
• National Thoroughbred Racing Association (https://www.ntra.com/) - Industry Job postings
• Racing Officials Accreditation Program (http://www.horseracingofficials.com/) - Certification for
racing careers
• Equistaff (www.equistaff.com) – Equine professional job board
Networking and Professional Organizations:
• North American Jockeys Association (NAJA)
• American Quarter Horse Association (AQHA)
• American Farriers Association (AFA)
• Association of Racing Commissioners International (ARCI)
• American Association of Equine Practitioners (AAEP)
• Certified Horsemanship Association (CHA)
Biomechanics of movement
all movements require what
simultaneous contraction and relaxation of muscles
(many interactions between the nervous and muscular system)
how is action produced
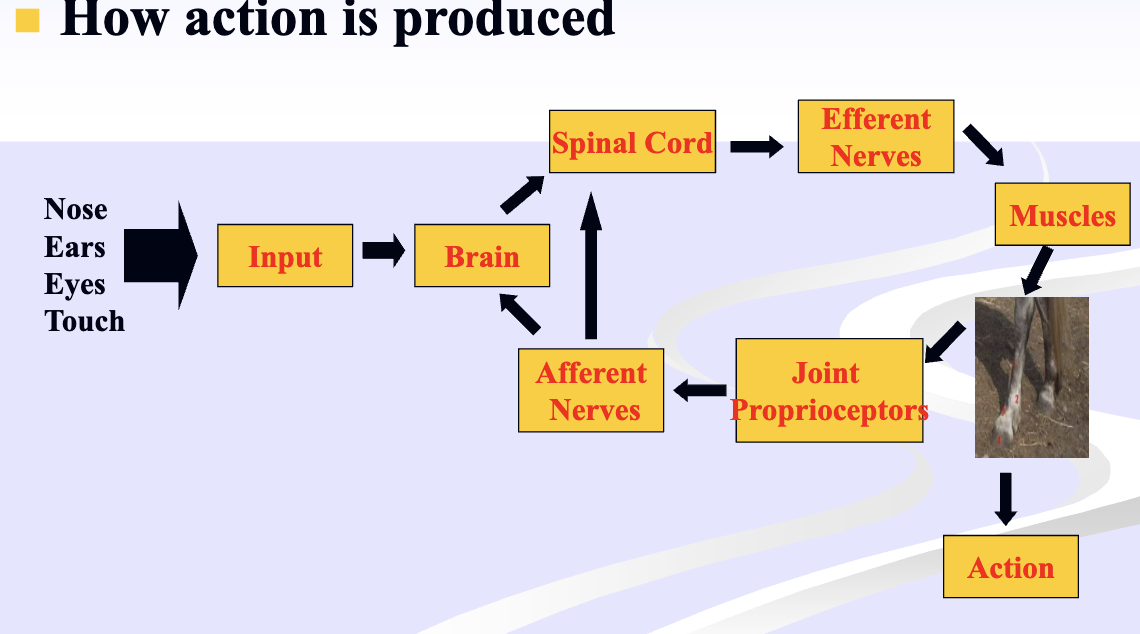
each muscle is made out of what
thousands of muscle filaments
muscle contractions or relaxation are controlled by
nervous impulses recieved by the muscle filaments
what is acetylcholine (ACH)
a neurotransmitter
when a muscle contracts what does acetylocholine do
this neurotransmitter excites the muscle
what is th process of a muscle contraction
When a muscle contracts, acetylcholine (ACH),
a (neurotransmitter), excites the muscle cells
Calcium ions are released and binds to troponin
Actin and myosin (muscle proteins) binds
together to form bridges
This causes the muscle to contract
When the calcium level drops and the muscle is
no longer excited by ACH, actin and myosin no
longer binds, and the muscle relaxes
What are the 3 factors contributing to the force a muscle generates
1. Short periods of stimulation causing contraction
Some force is taken up by overcoming elastic elements of the
tendons and other connective tissues
2. Length of muscle when stimulated to contract
Alters the relationship between actin and myosin. If the muscle
is stretched, number of bridges decrease resulting in less force
3. Number of actin and myosin filaments acting
The greater the number of filaments that are parallel, the
greater the force of contraction
ATP is derived from
nutrient metabolism
is carbon required for atp production
no, oxygen
When oxygen is available muscle contractionis called..
aerobic
when adequate oxygen is unavailable metabolic products are converted to lactic acid > ATP (which is called)
anaerobic
List and describe the 3 muscle fibers are associated with the athletic horses
Type 1 – slow-twitch fibers (aerobic):
Used during slow or light activity
Type 11a – fast-twitch fibers (aerobic):
Endurance fibers, used during aerobic work e.g. jogging or
long distance riding
Type 11b – fast-twitch fibers (anaerobic):
Speed or power fibers
Used during strenuous anaerobic work; sprinting, jumping
or cutting
What cause muscle fatigue
was build up in muscle cells
what is required to relieve muscle fatigue
the removal of waste by blood
What is a way you can physically relielve muscle fatigue
hand rubbing muscle to stimulate blod vessles and allow blood flow
what is another thing that helps with muscle fatigue
feeding easily digestable carbs
true or false untrained horses get fatigued mor easily than a trained one
true
can a horse be worked until exhaustion
no
what is a by product of muscle contraction
heat
heast must be… to avoid excessive increase in core body temp
dissipated
how is heast dissipated
through sweating and air movement across the body and blood transport
during exercise in hot environments what happens
blood flow to the skin increases
if there is more blood going to the skin what happens
less blood is going to the muscles less oxygen going to muscle0
fluid losses also decreases the plasma volume
increased electrolye loss in sweat
what are electrolytes needed for
acid-base balance, fluid balance, mucle contraction and nerve function
What are the muscles involved in gait
flexors
extensors
abducctors
adductors
Function of flexor
decreases angle of joint
extensor function
increase angle of joint
abductors function
move limb away from the center plane of the horse
adductor function
to pull limbs toward the center plane of the horse
what is a gait
a horses way of moving its legs during progression
why is understanding gait important
to be able to determine lameness, to train performance horses, or signal a specific gait
true or false most gaits are learned but some are natural
false, most are natural some are learned
what are the 6 types of gaits
Historically there were six gaits (walk, trot, pace,
canter, run, back)
define beat
the time when a foot or two feet strike the groung simultaneously. (may or may not be evenly spaced.
define step
distance between imprints of the to front or two hind legs
define stride
distance between succeessive imprints of the same foot
what are the two phases of a stride
stride stance- weight bearing phase
stride suspension- non weight bering phase
the speed of a orse is determined by
length of stride
frequency of stride
overlap time (time on ground vs time off the ground)
directness
line in which foot is carried forward during stride
power
to create the stride
height
radius of arc created from point of the foots take off to its contact with the ground
spring
maner in which the weight settles back on the supporting leg at the end of the stride
regularity
rhythmic precision of each stride
balance
ability of the horse to coordinate action, go composed and remain in form
what are te four natural gaits
walk, trot, canter, gallop
describe walk
slow, even, four-beat gait. Sequence of beats
are considered lateral because both feet on one side
strike the ground before the feet on the other side
describe trot
two-beat gait with the diagonal fore and hind
legs acting together. There is a period of suspension
when all four feet are off the ground between each
beat
describe canter (lope)
three beat gait, more weight on its hind qaurters
gallop
fast four beat gait
pace
two beat lateral gait
slow gait (stepping pace)
lateral four beat gait done under restraint in showy animated fashion
rack
even, fast, flashy, four beat gait.
it displays speed and knee action.
hard on horse easy on rider
wha are some cons of the rack gait
increase concussion an trauma in the legs
running walk
fast walk of the Tennessee walking horse four beat lateral gait
back
when a horse backs (trotting in reverse) two beat gait in which the diagonal pairs work together
common gait defects
Forging
Interfering
Paddling
Winding
Scalping
Speedy-cutting
Cross-firing
Pointing
Dwelling
Trappy
Pounding
Rolling
Center of gravity
*Nutrient needs of a horse
feeds and feedstuff contain and essintial for growth reproduction and health of horse
energy and nutrients
nutrient deficiencies or excesses can led to
reduced growth and or disease
what feed ingredients are needed
carbs
lipids
protein
minerals
vitamins
water
most sources of energy and protein are
grains and roughages including pastures
horses require nutrients for..
maintenance; support digestive and metaboic process
additional nutrients are needed for
growth, work, reproduction, and lactation
horses daily ration
roughages
concentrates
list some roughages
hay, silage, and or pasture
concentrates
grains, which may have protein supplements, minerals, vitamins.
can also include bran, cane molasses, or dehydrated alfalfa
what are horses main energy source
carbs
true or false most nonstructural carbs are digested and absorbed in the hindgut
false, foregut
where do structural carbs ferment
in the hindgut
fermentation in the hindgutresults in the
production of volatile fatty acids
give an example of some volatile fatty acids
acetate, propionic, butyric, isobutyric, isovaleric valeric
true or false vfa is then absorbed and converted into energy
true
true or false fats have 2.25 times more energy per unit weight than carbs and protein
true
during intense exercise fat is
mobilized and converted to energy
fat should be rancid
false