Final Exam
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Substantive Due Process:
based on the premise that the constitution protects the public from unwarranted government intrusion infringing upon their fundamental rights
can’t have laws that infringe on basic rights
rights of parents to send children to private school
rights to practice certain religions
ensuring content of laws
Procedural Due Process:
states government officials need to follow fair procedures
following the rules
did they search the property AFTER receiving a search warrant ordered and signed by a judge
When does a case go to Federal court?
if your civil rights were violated
violations of the U.S Constituition
if the violation is of a federal law
if the U.S government is a party to the dispute
State court:
most crimes and disputes
civil cases
criminal cases
offenses would go the Superior court
trial court
each state has different laws

Supreme Court:
highest court in the federal system
9 justices meeting in Washington D.C
appellate jurisdiction through certiorari process
limited original jurisdiction over some cases
Certiorari process:
a court process to seek judicial review of a decision of a lower court or administrative agency
What are 3 reasons a case might go to a state court?
violation of state law
civil case
criminal case
Frye Standards:
a legal test to determine whether scientific evidence is admissible
evidence must be sufficiently established to have gained general acceptance in the particular field to which it belongs
introduced in 1923 case concerning polygraphs
What is a disadvantage of the Frye test?
it is too restrictive of novel evidence that had excellent scientific verification
confused quality with consensus
Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals (1993):
two mothers sued Dow Chemicals because their children had birth defects
Claimed the birth defects were caused by taking Bendectin for morning sickness
Court didn't permit Plaintiffs' experts
failed the Frye standard → didn’t have general acceptance in scientific community
ruled that general acceptance by an expert witness is not absolute prerequisite to the admissibility of scientific evidence
Daubert Standard:
focuses on methodology and principles, not on the ultimate conclusions generated by the science community
judge has broad discretion to admit expert and acts as a gatekeeper for admissions of scientific evidence
applies to Federal and States that have adopted federal standards
What 4 questions are asked to determine if evidence passes the Daubert Standard?
are the ideas falsifiable?
methods + ideas been peer reviewed?
is there general acceptance of the methods?
is there a known or potential rate of error?
Double Jeopardy:
prohibition on the same sovereign trying defendants twice for the same crime or a similar crime
does not apply for a case that goes to criminal and civil court
Roe v. Wade (1973):
U.S. Supreme Court ruled that state governments could regulate but not prohibit abortion
followed the precedents of other cases that had developed the right to privacy in reproductive matters
What was James Gilligan’s hypothesis for the cause of violent behavior?
men seeking out justice
disrespect viewed as a form of injustice to them
hyper vigilant to signs of disrespect
no reserves of self esteem
According to Gilligan’s hypothesis, why do violent men struggle to cope with rejection/ humiliation?
traumatic childhoods leave them with less reserves and lack of self love
have withdrawn love from themselves and others to protect themselves emotionally
pro capital punishment
soul murder
Soul Murder:
the deliberate traumatization or deprivation by a caregiver to their child, robbing the victim of their identity and the ability to maintain authentic feelings
What percent of abused children grow up to abuse their own children?
about 30%
Widom Cycle of Violence study:
longitudinal study comparing long term outcomes for a group of children with validated maltreatment histories to a matched control group
11 years old and younger
matched control groups
age, race, SES, gender
compared rates of criminal and delinquent records
What were the results of the Widom’s Cycle of Violence study?
those who have been maltreated are more likely
arrested for delinquency, adult, and violent crimes
high number of earlier arrests
earlier start of crime
5 more arrests
those with physical abuse or neglected at higher risk
What theory for aggressive behavior was studied by Kenneth Dodge?
biased social information processing
What are the 5 steps of processing social information?
encoding relevant cues
interpret cues
access behavioral responses from LTM
evaluate consequence of possible behavior
select and enact behavior
According to Dodge, what sorts of attributions are aggressive people more likely to make about other people?
hostile intent
According to Dodge, what causes aggressive people to make attributions of hostile intent toward others?
enduring physical abuse as children
child physical harm → maladaptive social information processing → aggression
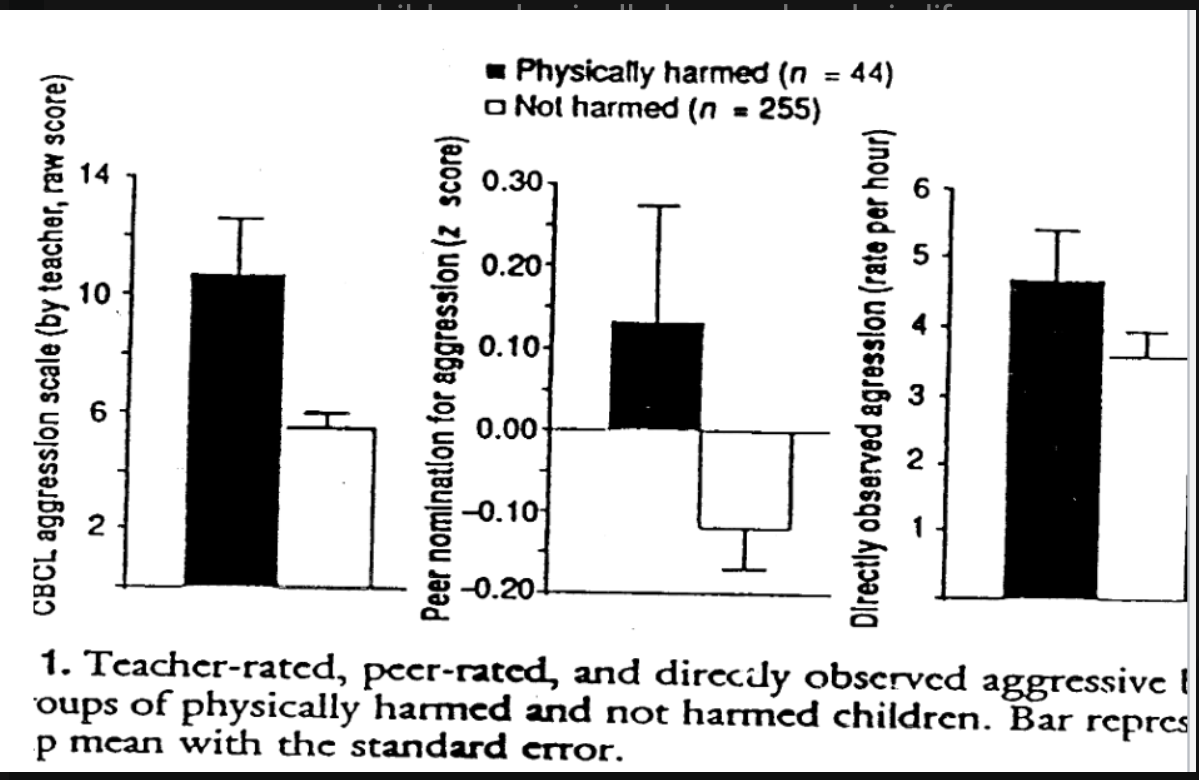
Kenneth Dodge’s study:
longitudinal study of 4 year olds that measured three things
mother reports of physical harm to child, early life experiences, and other factors
child social information processing at 5 years
child aggressive behavior 6 months later
What were the methods of Dodge’s social information processing study?
child presented with cartoon vignettes and told to imagine being the main character
peer in vignettes does something negative either with intention of being hostile, benign, or ambiguous
asked to recall vignettes and why peer did it
ask how they would respond
What were the results of Dodge’s social information processing research?
children physically harmed early in life were more aggressive
even when other family and factors considered
biased toward attributing hostile intent
SIP predicted later aggression
defensive processing
children who had been physically harmed early and did not show biased information processing were NOT aggressive
subgroup showed self blame (depressed)
Furman v. Georgia (1972):
the U.S. Supreme Court reviewed three death penalty cases and a deeply divided Court found that the death penalty had been “so wantonly and so freakishly imposed”
capital punishment as it was being administered in the states constituted cruel and unusual punishment in violation of the Eighth and Fourteenth Amendments
What were the impacts of the Furman v. Georgia (1972) decision?
decision resulted in a national suspension of the death penalty
State legislatures rewrote their death penalty statutes to meet the Supreme Court’s objections
new legislation specified which crimes should be subject to the death penalty
established guidelines for conditions that had to be met before imposing the death penalty
political developments attempted to reduce racial bias in capital sentencing
Gregg v. Georgia (1976):
the Supreme Court reviewed the death penalty statute that Georgia's legislature passed in response to Furman
new law specified the offenses subject to the death penalty
provided for a split, or bifurcated, two-phase trial in capital cases
What was the new procedure created due to the Supreme court case in Gregg v. Georgia (1976)?
phase 1 → the jury determines guilt or innocence of the capital offense
guilt phase
phase 2 → the jury determines whether to impose the death penalty on the defendant and the evidence is presented separately in each phase
mitigating vs aggravating evidence
penalty phase
Aggravating factors:
ten factors that juries in capital punishment cases must compare to the evidence presented to delegate death penalty
multiple murder
wantonly brutal killing
Mitigating factors:
evidence presented in a capital punishment case by the defense making the crime seem less severe or more understandable, or the defendant more sympathetic
True or False: If the jury finds one or more aggravating factors to be present in the crime, and, in their judgment believe these are not outweighed by the mitigating factors, jurors can impose the death penalty.
True
McCleskey v. Kemp (1978):
Warren McCleskey, an African American, was convicted in of killing a white policeman during a robbery and was sentenced to death
argued that had he killed a black person he would not have been given the death penalty
claimed that the sentence was influenced by racial factors based on a well-known statistical analysis of homicide convictions
What did the Court Rule in McCleskey v. Kemp (1978)?
in the Court's view, there was no direct evidence that McCleskey's death sentence resulted from racial discrimination
general statistics said nothing about McCleskey's particular case
Death Qualified Juries:
selected after jurors unwilling to impose the death penalty have been eliminated
might be more likely to convict
classified into five categories based on attitudes toward the death penalty
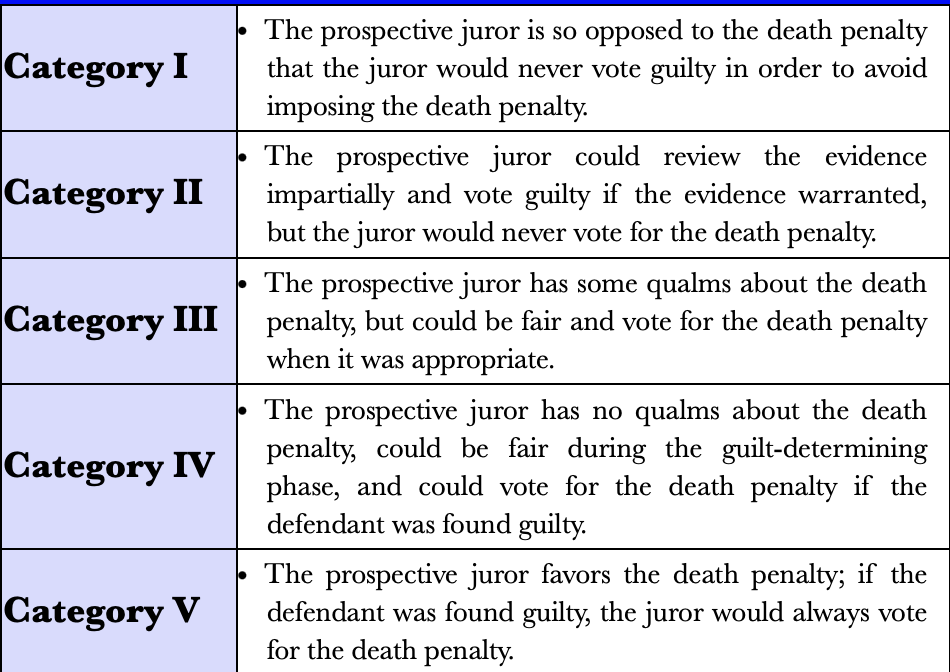
What awesome challenges during voir dire in capital punishment trials?
Prosecutors of capital cases can challenge prospective jurors for cause during the voir dire if their opposition to the death penalty would prevent them from reviewing evidence impartially or from voting for the death penalty
said there is bias when questioning/selecting jurors
Tarasoff v. Regents of the University of California (1976):
under civil law, obligated therapists to assess the dangerousness of their patients and to take appropriate action
duty of a mental health professional to take appropriate action including warning a third party when a patient or client threatens harm to an identifiable other
Jury Nullification:
when juries ignore law to acquit (free from charges) the defendant
juries have power, not right, to acquit for any reason whatsoever
applied in criminal trials
What are the purposes of jury trials?
fact-finding
attribute guilt, innocence, or liability
express community conscience or condemnation
protect from government interference
What is smallest jury allowed in criminal cases?
6 jurors
In civil cases, how many jurors must they have?
typically comprised of 12 but many states have them as small as 5 through agreement of both parties
some states allow verdict to be returned despite the dissent of 1-3 jurors
Why are juries 12% less likely to convict than judges?
juries are harder to persuade because they feel the need to see stronger evidence suggestive of guilt
When do judges instruct juries on the law?
jurors instructed verbally after the close of evidence
True or False: All courts provide juries with written instructions.
False, not all courts provide juries with written instructions
How do juries deliberate?
deliberate through a evidence-driven or verdict-driven approach
What do they mean by “story model” of jury decision?
referring to stories constructed to make sense of evidence at trial
useful in describing decision making in rape, murder, and sexual harassment trials
Peremptory challenge:
a defendant's or lawyer's objection to a proposed juror
made without needing to give a reason
Challenges for cause:
a preliminary challenge for which an attorney states the reason why a prospective juror should not be included on the jury
can’t deselect based on gender, race, religion
Hung jury:
jury cannot reach a unanimous decision, is usually considered a “failure,” a “waste” of its members’ efforts
Dynamite charge:
when a jury reports to a judge that they cannot reach an agreement, the judge may appeal to their sense of fairness to pressure for a verdict and “blast” the deliberations open again
critics believe this is does not serve justice
On average, how much of civil and criminal disputes are now resolved outside the courtoom?
around 90-95%
What are some different methods for resolving legal conflicts?
through negotiations such as mediation, arbitration, and trial
Mediation:
a process in which a neutral person (mediator) facilitates communication between the disputants to assist them in reaching a mutually acceptable agreement
Arbitration:
a private dispute resolution procedure where parties agree to submit their dispute to a neutral third party, called an arbitrator, to make a binding decision
What three things make a defendant competent to stand trial?
capable of understanding the nature and purpose of the criminal proceedings
comprehend their own status and condition in reference to these proceedings
able to assist their attorney in conducting a defense or be able to conduct their own defense in a rational manner
What happens after the defendant is found competent to stand trial?
prosecution must prove guilt beyond a reasonable doubt to 12 jurors
burden of proof
How does one get a verdict of NGI?
a jury must find the defendant guilty and then the defendant must prove they were more likely than not legally insane at the time of the crime
standard of proof
What two conditions must be met for someone to be considered legally insane?
at the time of the crime defendant had a mental disease or defect
the disease or defect rendered them incapable of knowing or understanding the nature and quality of their act
OR incapable of knowing or understanding their act was morally or legally wrong
Mens rea doctrine:
principle in criminal law that a crime requires not only a wrongful act but also a culpable state of mind at the time the act was committed
found guilty if they specific mental state when committing a crime
intent
The M’Naghten rule:
a legal standard used to determine whether a defendant can be excused from criminal liability by reason of insanity
critics argued that mental illness could affect volition as well as cognition meaning a person could know right from wrong but lack adequate self-control because of a mental illness
Malingering:
a concern for insanity cases where someone may try to fake a mental illness
especially in death penalty cases
no gold standard to test
but there are standardized instruments that can identify fakers at above-chance levels
rare occurence
Restorative justice:
emphasizes that wrongdoing has created a wound in the victim and in the social order
greater prominence to the victim
emphasize healing the breach
involve offender and community in the process
Retributive justice:
emphasizes punishment for an offense against the state
criminal act is interpreted as creating an “imbalance” in the social order that will be redressed by punishing the offender
victim has little role → except as a complaining witness
prosecutor represents the community
Kent v. United States (1966):
Supreme Court ruled that a case could not be transferred from juvenile to adult court without a hearing
judges are expected to look at the issues of individual dangerousness, maturity, responsibility, and potential for being rehabilitated
Social Framework Testimony:
a form of expert testimony that provides social science research conclusions to help jurors evaluate unfamiliar phenomena and other evidence in a case
doesn’t focus on evidence itself but rather social context
not always admitted
Fell Acres Day School Case (1987):
Cheryl Amirault LeFave was convicted in a jury trial of four counts of indecent assault and battery on a child under 14 and three counts of rape of a child under 16
Nine children testified against her
children who had been repeatedly interviewed by police, therapists, and parents gave main testimony
Why was Fell Acres Day School Case (1987) overturned?
Judge said prosecutors in original trial argued that children never lie or make up stories of sexual acts unless it happened
inconsistent with subsequent research
expert witnesses also testified in original trial that it was a pattern for children to deny abuse, then disclose, recant, and disclose again
after having served ten years in prison judge overturned conviction
expert testimony cast doubt on the veracity of children’s testimony obtained under the conditions described in the trial
experts testified that suggestive techniques could lead children to make inaccurate reports
*was later again overturned saying all this was already looked at in original conviction but defendant still let go*
What are some methods for recovering memory?
therapists who use these techniques have higher proportions of clients who report recovering memories than those who do not use such techniques
hypnosis
age regression
guided imagery
use of family photos as memory cues
interpreting physical symptoms as evidence of memories of abuse
Status Offenses:
refer to acts that are offenses only because of the juvenile’s age
acts would not be crimes if committed by an adult
run away from home
drink or smoke
truant from school
Status offenders are brought to the attention of the court when someone petitions the court for aid
Orders of Protection:
can direct the alleged abuser to stop abusive conduct, to leave or stay away from the family home, or to have no contact with the victim
Judges can customize the orders specifying what the alleged offender must do
easier for a victim to obtain an order of protection in a family court than to wait for a criminal arrest and court appearance