Oxidative phosphorylation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Where does oxidative phosphorylation take place?
Mitochondrial cristae
(inner mitochondrial membrane)
What is the 1st step?
The reduced NAD and FAD donate the electrons of the hydrogen atoms they are carrying to the first molecule in the electron transfer chain
(they’re oxidised by an electron carrier)
What happens as the electrons pass down the electron transfer chain?
The electrons pass along the electron transfer chain in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions
The energy they release causes the active transport of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane and into the inter-membranal space
What happens once the protons are in the inter-membranal space?
They diffuse back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase channels
What happens at the end of the electron transfer chain?
The electrons combine with the protons and oxygen to form water
What does oxygen act as?
The final electron acceptor
What does the diagram look like for the chemiosmotic theory?
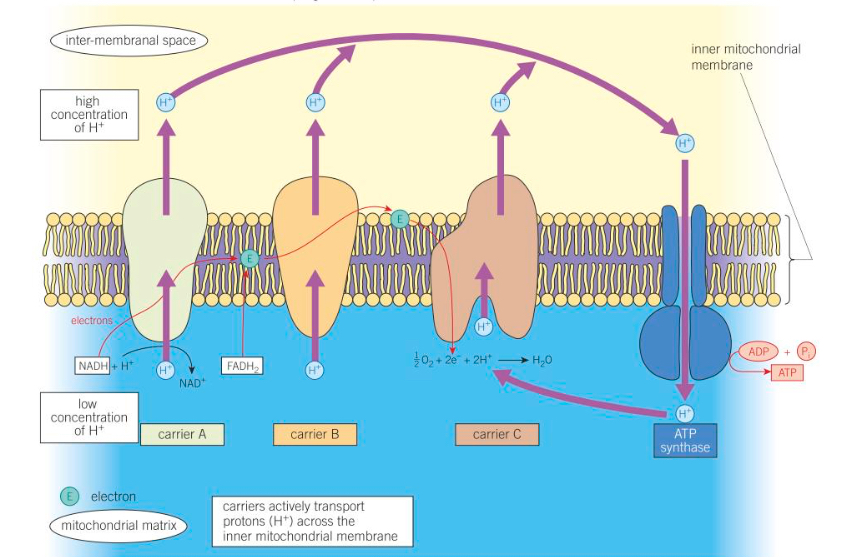
How do the electrons pass down the electron transfer chain?
They move down an energy gradient
This allows energy to be released gradually and more usefully
How are lipids used as respiratory substrates?
Lipids are first hydrolysed to glycerol and fatty acids
Glycerol is phosphorylated and converted to triose phosphate which enters the glycolysis pathway and then Krebs cycle
The fatty acid is broken down in to 2C fragments which are concerted to acetyl CoA which then enters the Krebs cycle
Why do lipids release more than double the energy of the same mass of carbohydrate?
The oxidation of lipids produced 2C fragments of carbohydrates and many hydrogen atoms
The hydrogen atoms are used to produce ATP during oxidative phosphorylation
How is protein used as a respiratory substance?
It is first hydrolysed to amino acids which have their amino groups removed (deamination)
3C compounds are converted to pyruvate
4C and 5C compounds are converted to intermediates in the Krebs cycle