Water Resources
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Phreatophytes
Deep-rooted plants that access groundwater
Potential Evapotranspiration (PET)
Max evapotranspiration under unlimited water
Lysimeter
Instrument to measure evapotranspiration
Interception
Rainfall caught by vegetation
Stemflow
Water flowing down stems/trunks
Vadose Zone
Unsaturated soil above water table
Phreatic Zone
Saturated zone below water table
Macropore
Large soil pore facilitating rapid water movement
Water Table
Top of the saturated zone
Saturation Overland Flow
Surface runoff from saturated ground
Horton Overland Flow
Surface runoff exceeding infiltration capacity
Fog Drip
Moisture from fog collected by vegetation
Overdraft
Excessive groundwater withdrawal beyond recharge
Baseflow
Sustained streamflow from groundwater discharge
DNAPL
Dense Non-Aqueous Phase Liquid; sinks in groundwater
Superfund
Program for cleaning hazardous waste sites
Primary Porosity
Original pore spaces in rocks
Secondary Porosity
Porosity from fractures, dissolution
Pump and Treat
Groundwater remediation technique
Point Source Pollution
Identifiable discharge location
Non-point Source Pollution
Diffuse pollution sources
John Snow
Mapped cholera outbreak; father of epidemiology
Joseph Bazalgette
Designed London sewer system
Colorado River Salinity Control Act
Reduces salinity in CO River
Colorado River Compact
1922 water allocation agreement
Dry-humid Boundary
Climatic dividing line (approx. 100th meridian)
John Wesley Powell
Explorer, early water management advocate
Jedidiah Smith
Explorer of western U.S. rivers
Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL)
Pollutant limit for waterbody
Progressive Price Structure
More usage = higher rates
Regressive Price Structure:
Lower cost/unit with higher use
Pump Storage Facility
Stores energy via water elevation (e.g., San Luis Reservoir)
Hoover Dam
Major dam on Colorado River
Glen Canyon Dam
CO River dam; Lake Powell reservoir
US Clean Water Act
1972 law for water pollution control
Cuyahoga River
Infamous for catching fire; inspired regulation
Flocculation
Clumping particles for removal
Desalination
Removing salts from water (e.g., reverse osmosis)
Potable Water
Safe for drinking
Consumptive Use
Water not returned to source
Fall Line
Geologic boundary with rapids/waterfalls
Mill Dam
Powers mills; modifies streamflow
Riparian Rights
Water rights for land adjacent to water
Prior Appropriation
"First in time, first in right" water law
‘State’ of Deseret
Mormon proposed state with water control
Freeboard
Distance between water surface and dam top
3 Gorges Dam
Major dam on the Yangtze River, China
St. Francis Dam
Failed dam in California (1928)
Teton Dam
Failed dam in Idaho (1976)
Columbia River and Grand Coulee Dam
Hydropower and irrigation in Pacific Northwest
Fish Ladder
Structure allowing fish to bypass dams
Channeled Scablands
Erosional features from Ice Age floods
Cadillac Desert (book)
Marc Reisner’s critique of western U.S. water policy
Water is for Fighting Over (book):
John Fleck's book on western U.S. water issues
Arch Dam
Curved dam transferring pressure to abutments
Gravity Dam
Uses weight to hold back water
State Changes of Water
Melting, freezing, condensation, evaporation, sublimation, deposition
Latent heat absorbed (melting, evaporation, sublimation)
Latent heat released (freezing, condensation, deposition)
Five Unique Properties of Water:
Latent heat transfer
Universal solvent
High specific heat
Solid state less dense than liquid state
Surface tension
Four Main Causes of Water Pollution:
Sewage and wastewater effluent
Garbage disposal
Agricultural runoff
Industrial discharges
Eight Factors Affecting Infiltration Rates:
Soil texture
Rainfall rate
Soil compaction
Vegetative cover
Impervious cover
Bioturbation (earthworms, etc.)
Macropores
Soil frost
Three Ways to Measure Stream Velocity:
Velocity Head Rod method
Wading method
Dye tracing
Five Physical Flood Control Measures:
Levees
Flood walls
Dams and reservoirs
Channelization
Channel diversion (spillways)
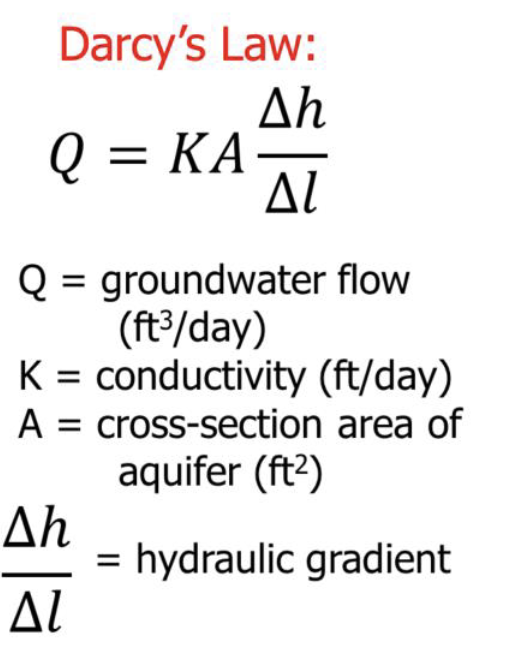
Darcy’s Law
Land Subsidence – Causes and Effects:
Causes: Groundwater over-pumping, mining, drainage of organic soils
Effects: Infrastructure damage, reduced aquifer capacity
Salt Water Intrusion – Causes and Effects:
Causes: Excessive groundwater withdrawal near coasts
Effects: Contamination of freshwater supplies
Dye tracing in karst systems
Used to determine flow pathways and travel times
Calcite Reaction in Limestone
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca²⁺ + 2HCO₃⁻
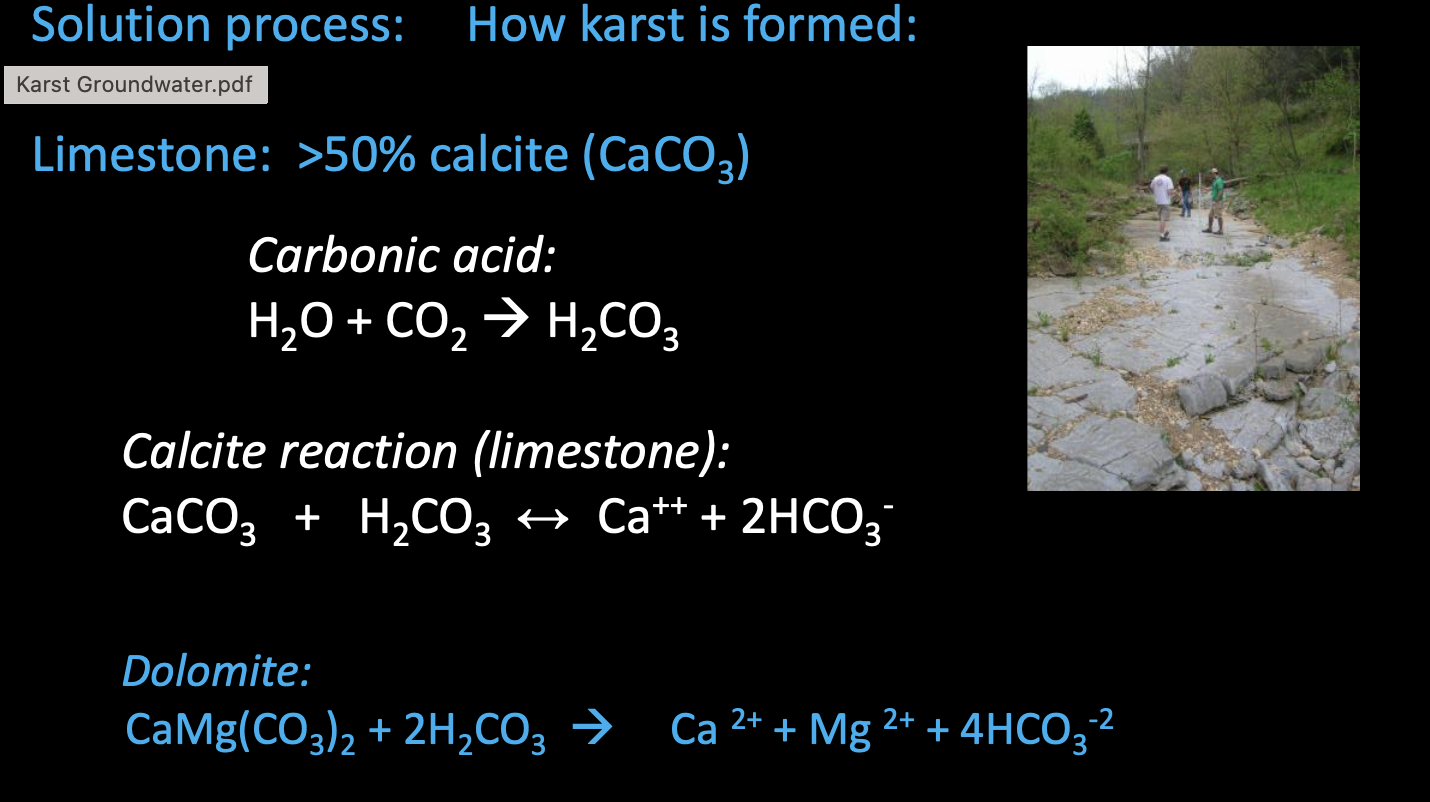
Karst watershed features
Flow in karst aquifers occurs mainly along solutionally enlarged fissures and conduits, rather than as diffuse intergranular flow
Fissure and conduit-flow systems are characterized by large diameter openings and high flow velocities where Darcy’s is not valid
Traditional concepts such as “drainage divides” and the “water table” are difficult to define for karst aquifers
Flow divergencies in karst aquifers are common and may vary depending on stage
Drinking water treatment steps
Pre screening at lake intakes, before pumping uphill to treatment facility
Flocculation
Sedimentation
Filtration
Disinfection
Storage and distribution
Wastewater treatment steps
Primary (screening and sedimentation)
Secondary (Biological treatment)
Tertiary (advanced filtration, disinfection)
Urban Stormwater Strategies
Green roofs, retention ponds, permeable pavement, and bioswales
Water Quality Parameters
Temperature: Affects DO, metabolism
Turbidity: Clarity
pH: Acidity/alkalinity
Hardness: Ca/Mg content
DO: Dissolved oxygen
VOCs: Volatile Organic Compounds
PCBs: Industrial pollutants
Cryptosporidium parvum & Giardia: Protozoan pathogens
Waterborne Infectious Disease Categories
Waterborne (e.g., cholera)
Water-washed (e.g., scabies)
Water-based (e.g., schistosomiasis)
Water-related (e.g., malaria)
Water Sources - Southern CA
Water brought in from Northern CA and CO river and delivered via aqueducts
Center Hill Dam problems
Leakage through limestone around dam
Grouting done to prevent this
Aswan High Dam Consequences
Increased crop yields
Reduced soil fertility
Disease outbreak
Delta erosion
Reduced fish harvest in the mediterranean