The Musculoskeletal System
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Describe bones.
Organs that make up the skeletal system, containing connective, epithelial and nervous tissue.
Name and describe the functions of the skeletal system.
Support - provides a rigid framework to support surrounding tissues.
Protection - create a physical barrier to internal organs
Assist in Movement - form joints that allow for joint movement of muscles
Mineral Regulation and Storage - mineral such as calcium and phosphorus regulate blood mineral concentrations
Blood Cell Production - production of blood cells in red bone marrow
Triglyceride Storage - yellow bone marrow stores triglycerides
Describe the 5 key cells of the skeletal system.
Osteoblasts - produce extracellular matrix of bones
Osetocytes - former osteoblasts that are trapped within extracellular matrix
Chondroblasts - produce extracellular matrix of cartilage
Fibroblasts - produce extracellular matrix for dense connective tissue
Osteoclasts - contain a ruffled exterior that breaks down bone tissue
Name and describe the 2 types of osseous (bone) tissue
Compact/cortical bone - hard dense external layer
Spongy/Trabecular - porous and honeycomb appearance internal layer
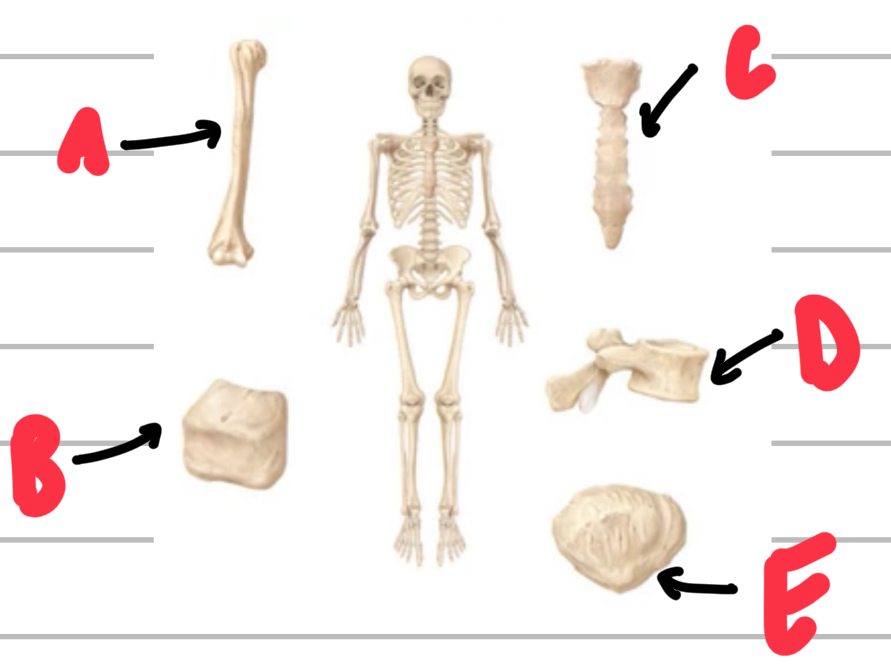
Name, describe and give examples of the types of bone shapes.
A - long bones, have greater length than width, eg. Humerus
B - short bones, roughly cuboidal, eg. Tarsals and carpals
C - flat bones, primarily flat, eg. Sternum and scapula
D - irregular bones, don’t fit into other categories, eg. Vertebrae
E - sesamoid, bones embedded within a tendon, eg. Patella
Describe the structure of compact bone.
Made up of a highly organised pattern of osteons that contain concentric lamellae surrounding a central canal of nerves, blood and lymph vessels.
Describe the structure of spongy bone.
Made up of a network of trabeculae containing lots of space for red and yellow bone marrow.
Describe ossification and name the 2 types.
Ossification is the formation of bones in early life.
Endochondral ossification
Intramembranous ossification
Explain endochondral ossification.
An initial cartilage model of hyaline cartilage is produced
During early growth, the cartilage model is slowly replaced by bone
After growth, a mature bone still contains remnants of cartilage (epiphyseal line)
Name and describe the 2 divisions of the skeletal system.
Axial skeleton - skull, spine, ribs and the sternum
Appendicular skeleton - girdles and limbs that attach to the axial skeleton
Describe bony landmarks
Distinct features on bone that act as attachment points.
Name and describe the types of bony landmarks.
Projections - bump that projects outwards
Depressions - divits that cave inwards
Openings - holes
Name and describe the 2 types of bones in the skull.
Cranial bones - bones that make up the wall that surrounds the brain
Facial bones - bones that don’t make the wall that surrounds the skull (make up the face)
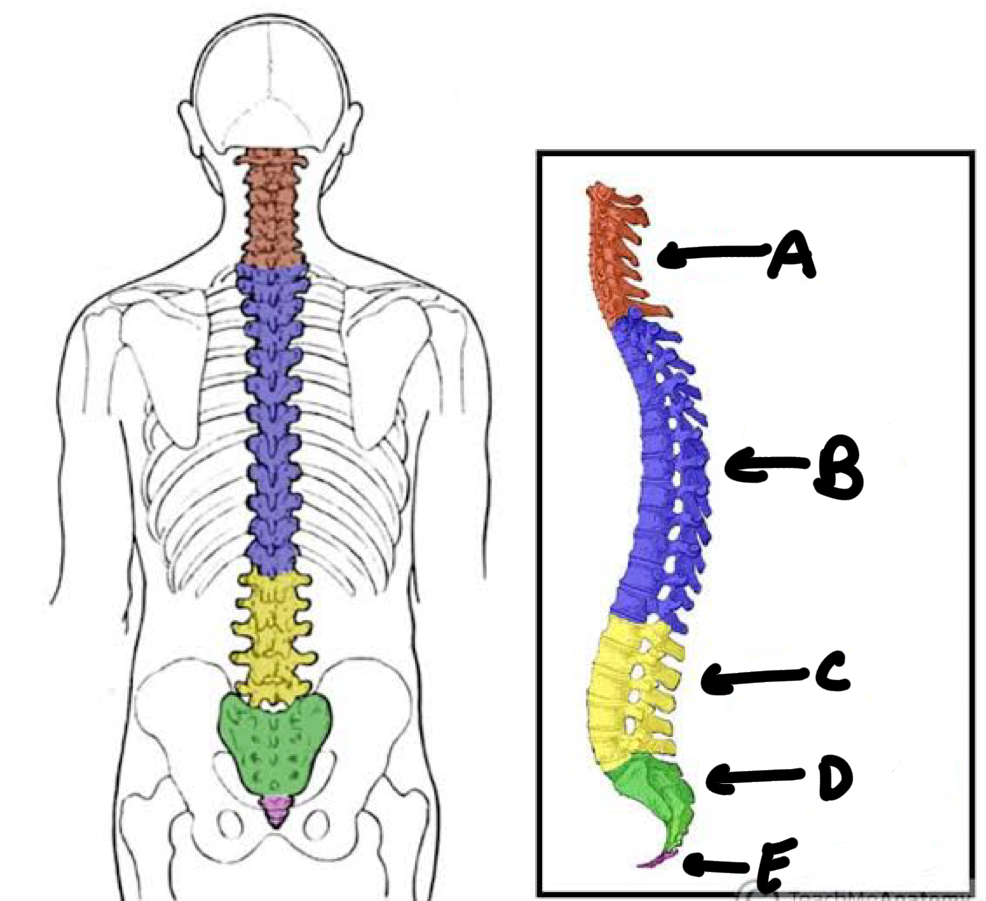
Name the types of vertebral columns and the number of vertebrae in each.
A - cervical (7 vertebrae)
B - thoracic (12 vertebrae)
C - lumbar (5 vertebrae)
D - sacral (5 fused)
E - coccyx (4 fused)
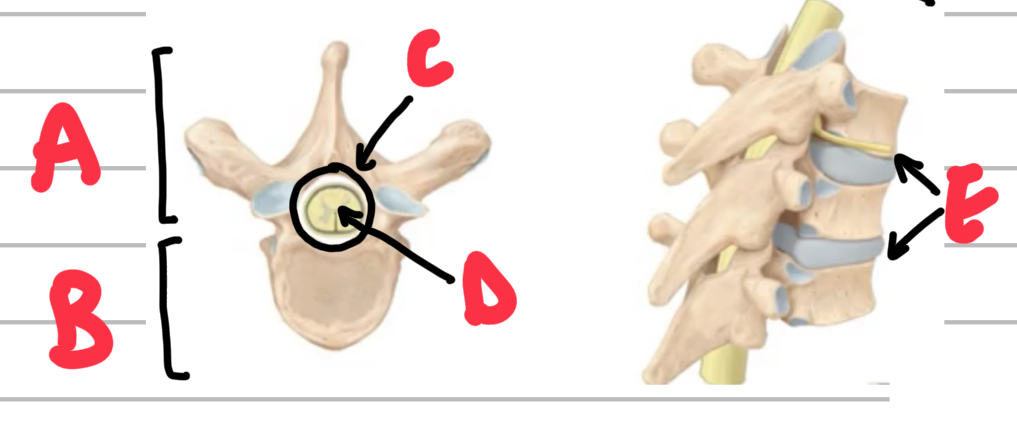
Name these parts of a vertebrae
A - arch
B - body
C - vertebral foramen
D - spinal chord
E - intervertebral discs
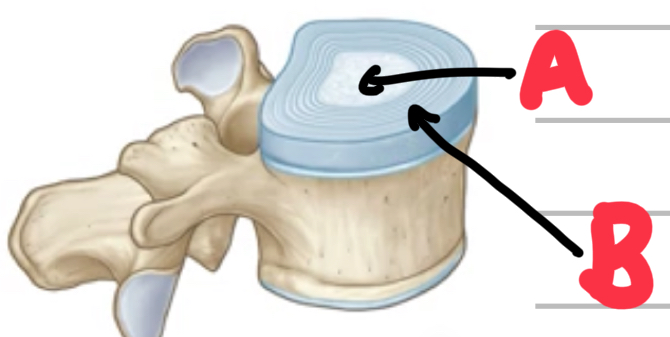
Name these parts of the intervertebral discs.
A - nucleus pulposus
B - annulus fibrosus (rings of cartilage)

Name these bony landmarks of the vertebrae.
A - transverse process
B - lamina
C - spinous process
D - pedicles
E - articular process
Name and describe the 2 girdles of the appendicular system.
Pectoral girdle - scapula and clavicle
Pelvic girdle - pelvis
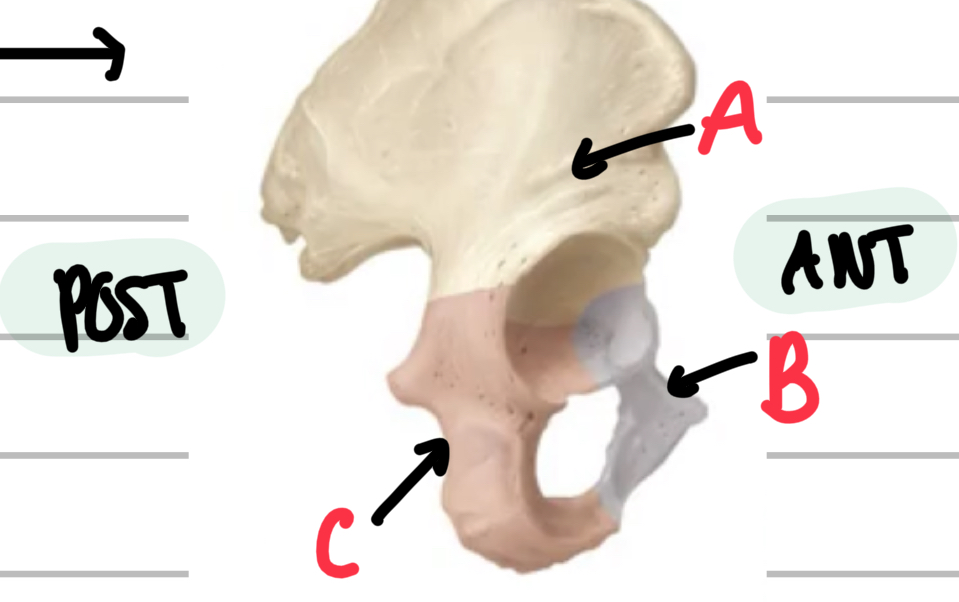
Describe the structure and name the bones of the pelvis.
3 fused bones:
A - ilium
B - pubis
C - ischium
Describe cartilage.
Strong and flexible connective tissue that protects bone, reduces friction and allows for flexibility.
Name and describe types of cartilage.
Hyaline Cartilage - smooth, white and glassy, most abundant
Fibrous Cartilage - very strong cartilage made up of thick collagen fibres
Elastic Cartilage - flexible cartilage made up of elastic fibres
Name and describe the types of joints.
Fibrous - no joint cavity and bones are attached by collagen fibre-rich connective tissue
Cartilaginous - no joint cavity in which bones are attached by a cartilage plate
Synovial - contains a joint cavity that allows for movement
Name and describe the types of fibrous joints and give examples.
Suture - in the cranium
Gomphosis - holds teeth in place
Syndesmosis - holds 2 bones together that are further away from each other, eg radius and ulna.
Name and describe the types of cartilaginous joints and give examples.
Primary/Synchondrosis - made up of hyaline cartilage, holding together 2 parts within 1 bone, eg. Epiphyseal cartilage growth plates in long bones.
Secondary/Symphysis - 2 bones lined with hyaline cartilage and attached by a plate of fibrous cartilage, eg. Intervertebral discs.
Name and describe the 6 types of synovial joints and give examples.
Plane/Gliding - 2 flat surfaces of bones sliding against one another, eg. Facet joint of the vertebrae
Hinge - allows for flexion and extension, eg. Knee and elbow
Pivot - allows for rotation, eg. Neck
Ball and Socket - wide range of motion, eg. Hip and shoulder
Condyloid - movement in 2 planes no rotation, eg. Wrist
Saddle - concave and convex surfaces that interlock, eg. Thumb
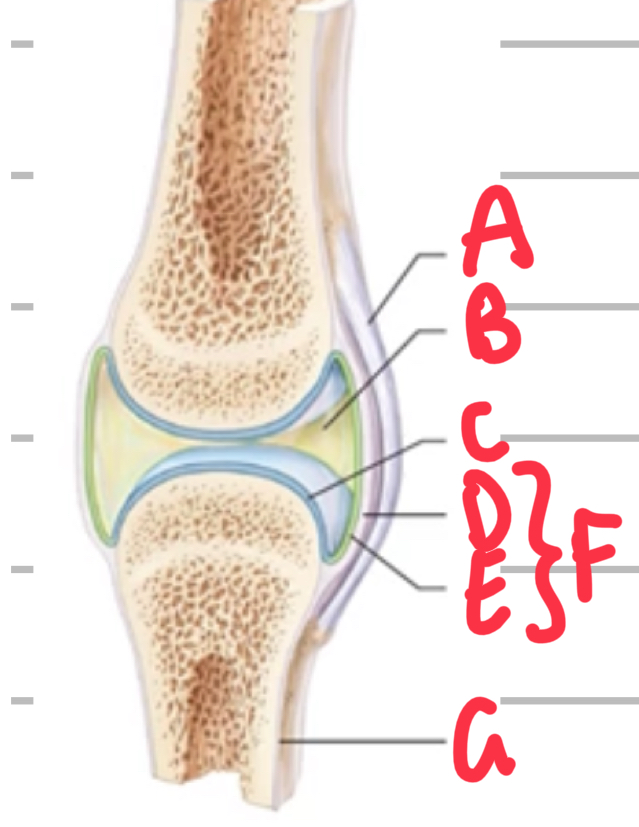
Name these features of synovial joints.
A - ligament
B - synovial fluid within joint cavity
C - articular cartilage
D - fibrous capsule
E - synovial membrane
F - joint capsule
G - bone
Describe articular cartilage.
Type of hyaline cartilage, smooth white and glossy that lines the ends of bones within a joint to reduce friction and damage as well as act as a shock absorber.
Describe the parts of a joint capsule
Synovial membrane is the innermost layer that produces synovial fluid
Fibrous capsule is the outermost layer that creates a fluid tight seal, is strong, preventing dislocation, however flexible, allowing for movement.
Describe synovial fluid.
Fluid within the joint capsule that acts as a lubricant and nourishes articular cartilage.
Explain the function of ligaments and name and describe the types.
Provide stability to the joint:
Capsular - an extension of the fibrous capsule
Intracapsular - independent of the fibrous capsule but inside the joint cavity
Extracapsular - independent of the fibrous capsule and outside the joint cavity.
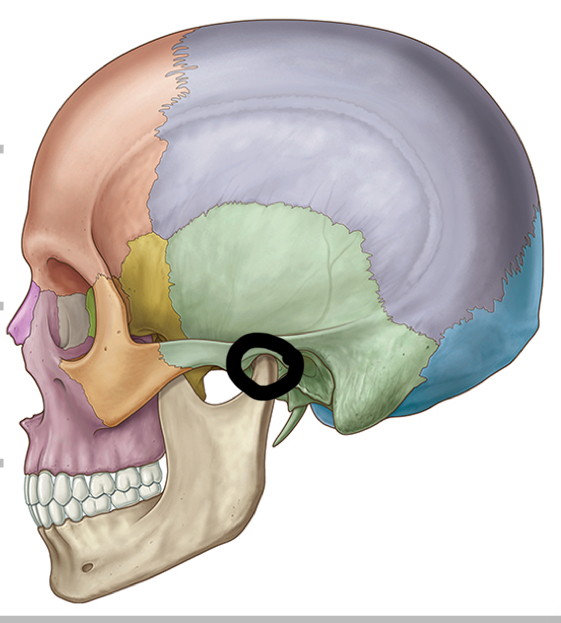
Name this joint.
Temporomandibular joint.
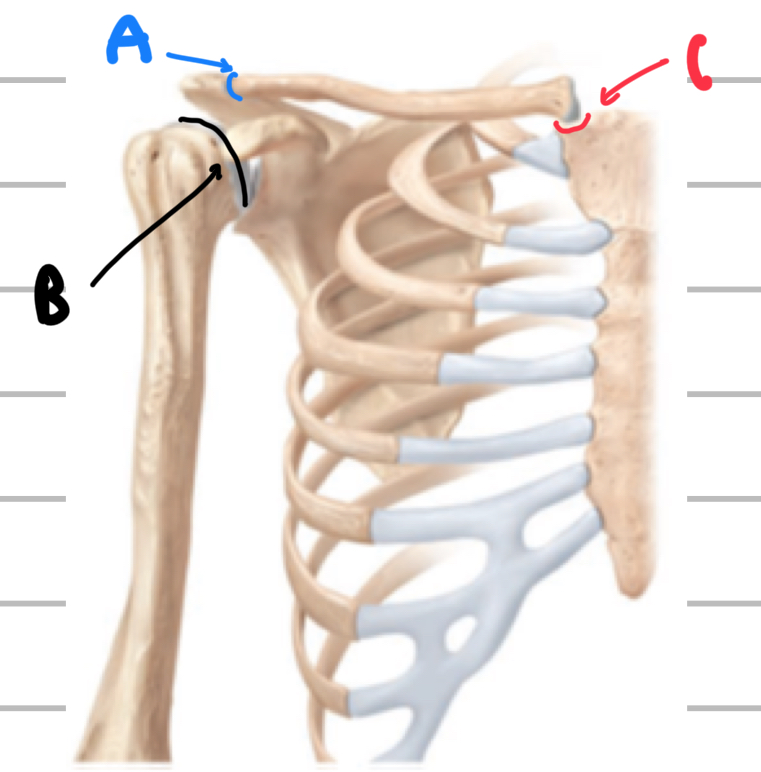
Name these joints of the pectoral girdle and upper limb
A - acromioclavicular joint
B - glenohumeral joint
C - sternoclavicular joint
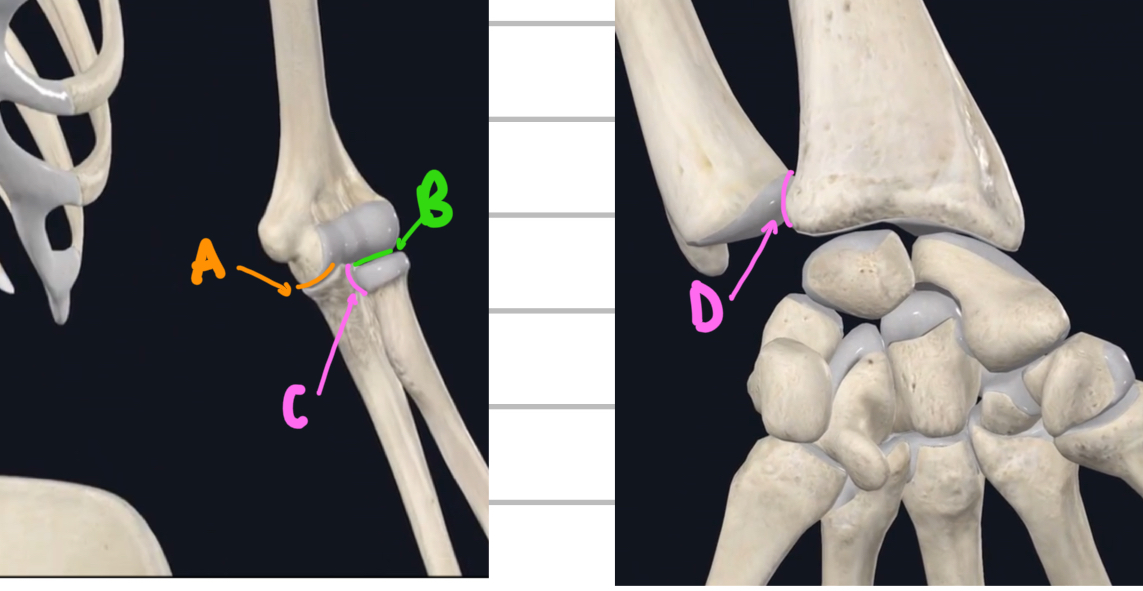
Name these joints of the lower arm.
A - humeroulna joint
B - radiohumeral joint
C - proximal/superior radioulna joint
D - distal/inferior radioulna joint

Name these joints of the pelvic girdle.
A - femoroacetabular joint
B - pubic symphysis joint
C - sacroiliac joint

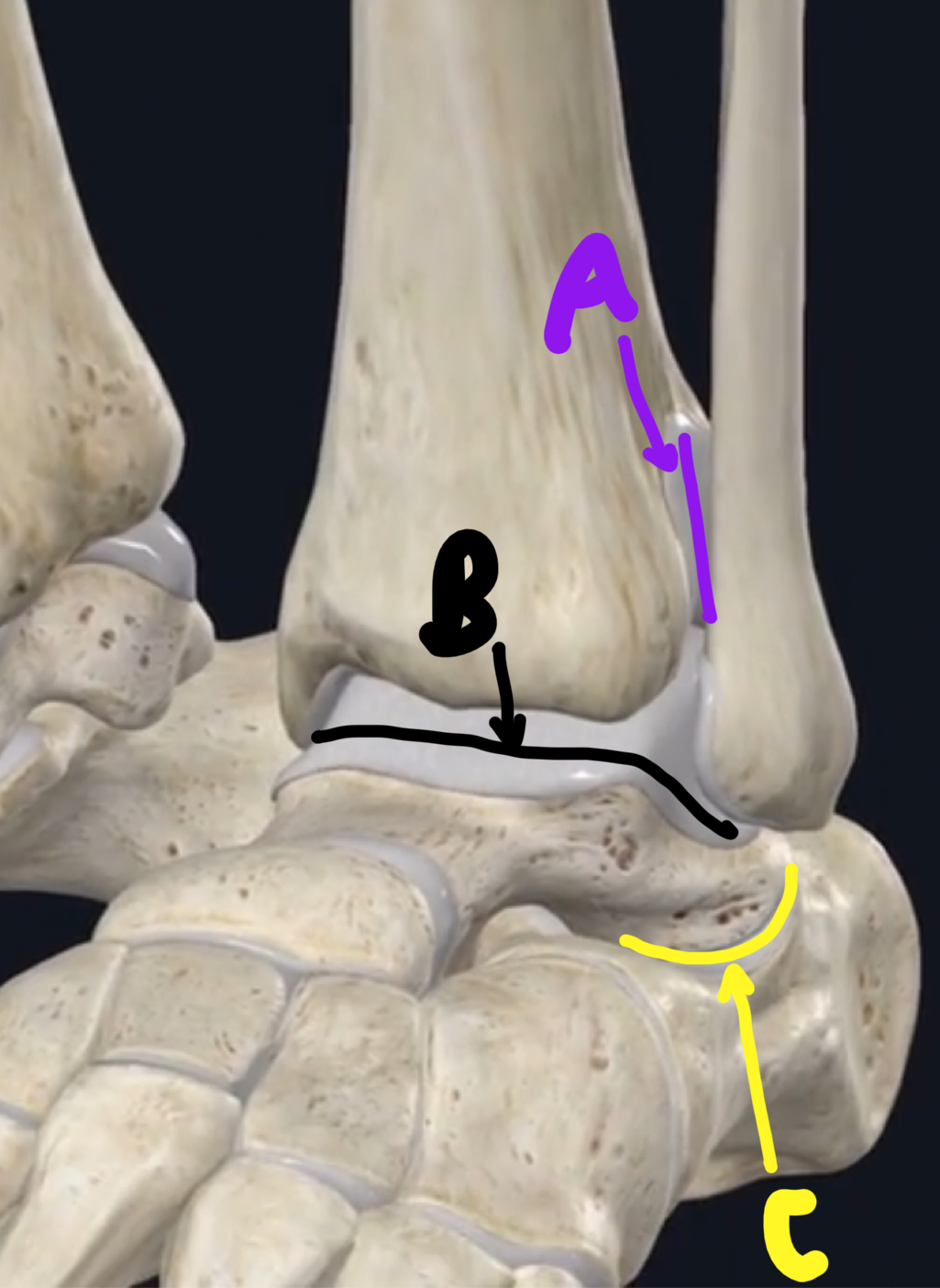
Name these joints of the knee.
A - patellofemoral joint
B - tibiofemoral joint
C - promixal/supeiror tibiofibular joint
Name these joint of the lower leg and feet.
A - distal/inferior tibiofibular joint
B - talocrural joint
C - subtalar
Describe protraction and retraction.
Protraction - jaw and shoulder movement horizontally in the anterior
Retraction - jaw and shoulder movement horizontally in the posterior
Describe lateral flexion and opposition.
Lateral flexion - trunk movement/bending to one side
Opposition - movement in which the pads of the thumb and another finger meet
Describe inversion and eversion.
Inversion - sole of the foot rotating towards the midline
Version - sole of the foot rotating away from the midline
Name and describe the 5 functions of the muscular system.
Producing Body Movement - skeletal muscles contract to generate force and movement of the joints
Stabilising Body Positions - skeletal muscle contraction stabilise joints
Storing Substances - Muscles store and release substances
Moving Substances - cardiac muscle contractions pump blood and substances throughout the body
Generate Heat - heat is a by-product of the chemical reactions during muscular contractions
Name and describe the 4 muscular tissue properties.
Electrically exciteable - actions potential cans be fired
Contractility - contract and generate force
Extensibility - can be stretched without damage, to an extent
Elasticity - tissue can stretch and recoil back to its original shape and size.
Name the 3 types of muscle tissue.
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
Describe skeletal muscle tissue.
Muscles attached to the skeleton that voluntarily contract. They contain cylindrically-shaped cells with multiple nuclei that have a striated appearance.
Describe cardiac muscle tissue.
Muscle tissue within the walls of the heart that involuntarily contract. They contain branched cells with a central nucleus that have a striated appearance.
Describe smooth muscle tissue.
Muscle tissue that lines the walls of organs, blood vessels and other structures that involuntarily contract. They contain spindle-shaped cells with a central nucleus that have a smooth appearance with no striations.
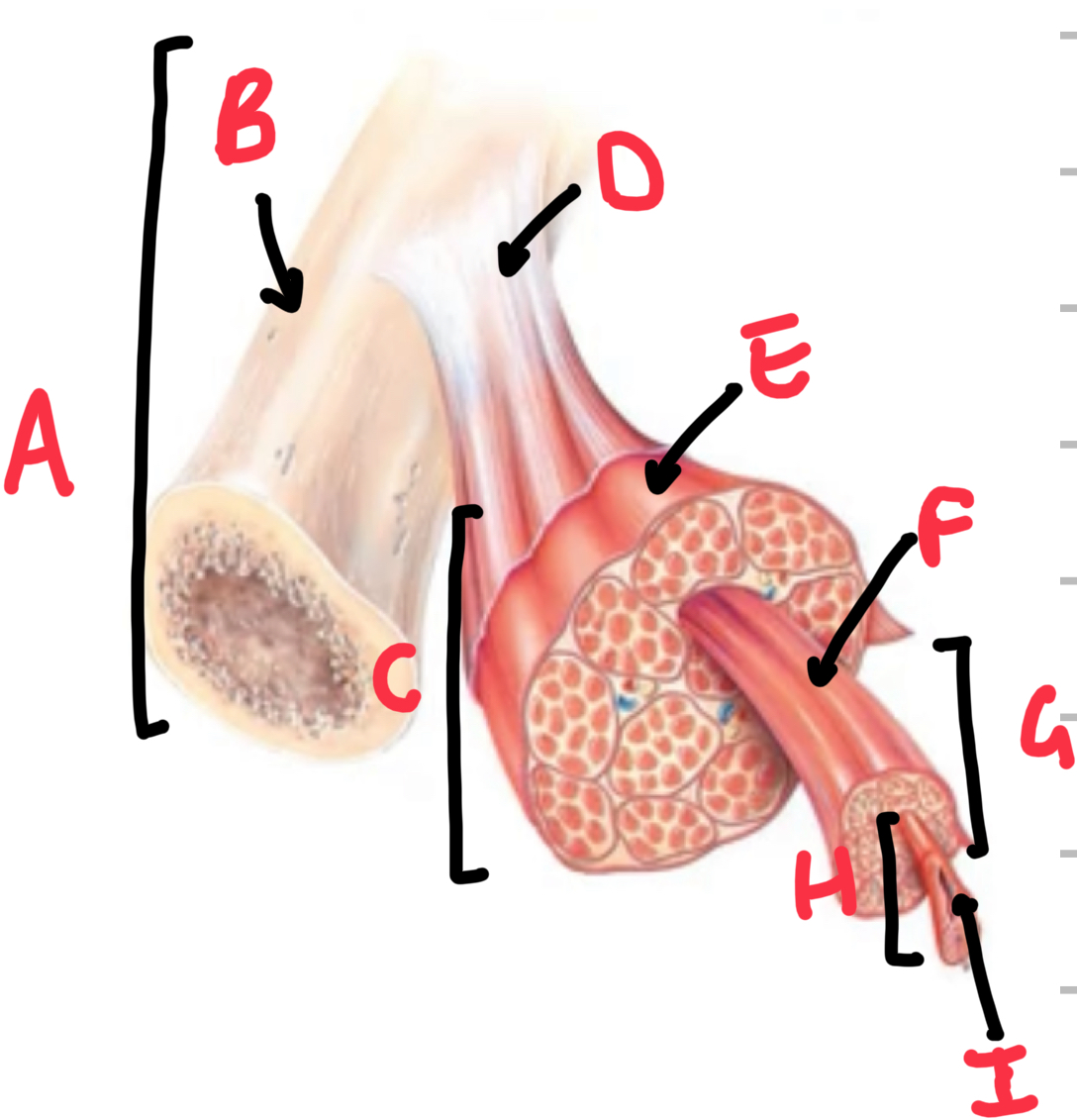
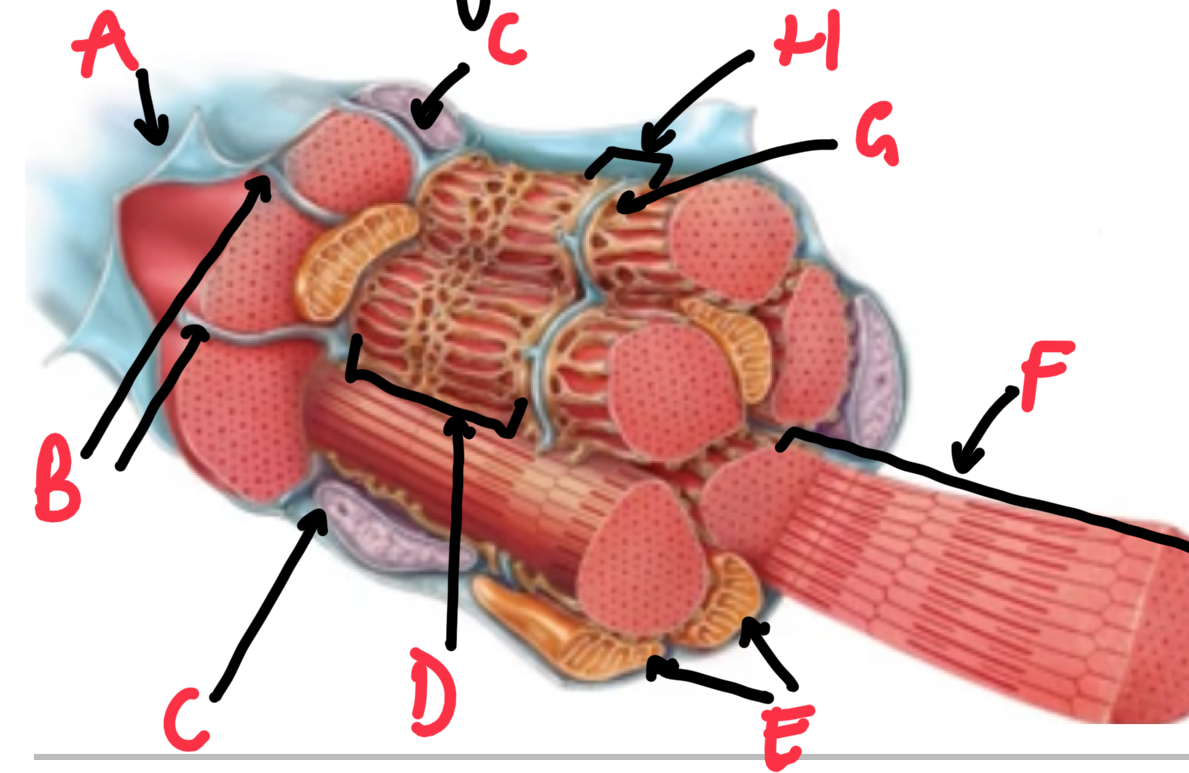
Name these structures that make up skeletal muscle.
A - bone
B - periosteum
C - muscle belly
D - tendon
E - epmysium
F - perimysium
G - fasicle
H - muscle cell/fibre
I - endomysium
Name and describe these structures of a skeletal muscle fibre/cell.
A - sarcolemma - plasma membrane
B - transverse tubules - extensions of the plasma membrane that that penetrate the fibre
C - nucleus
D - sarcoplasmic reticulum - network of fluid filled sacs that store calcium ions
E - mitochondria
F - myofibril - microfilament that contains protein filaments that move to contract the muscle fibre
G - terminal cistern - enlargement of the sarcoplasmic reticulum adjacent to a transverse tubule
H - triad - a transverse tubule that contains a terminal cistern on either side
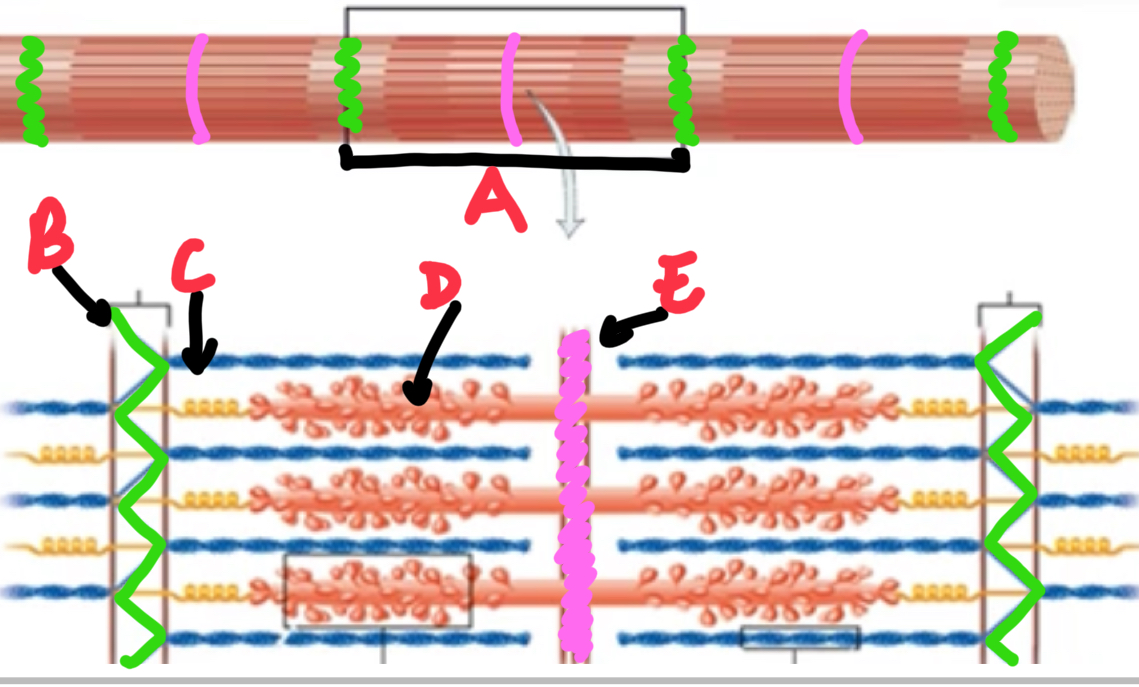
Name and describe these structures of a myofibril.
A - sarcomere - repeating unit of a myofibril
B - Z-disc - plate of protein that seperate sarcomeres
C - thin filament - made up of actin contractile proteins, attach to z-discs
D - thick filament - made up of myosin contractile proteins, attach to m-line
E - m-line - plate of protein in the centre of sarcomeres.
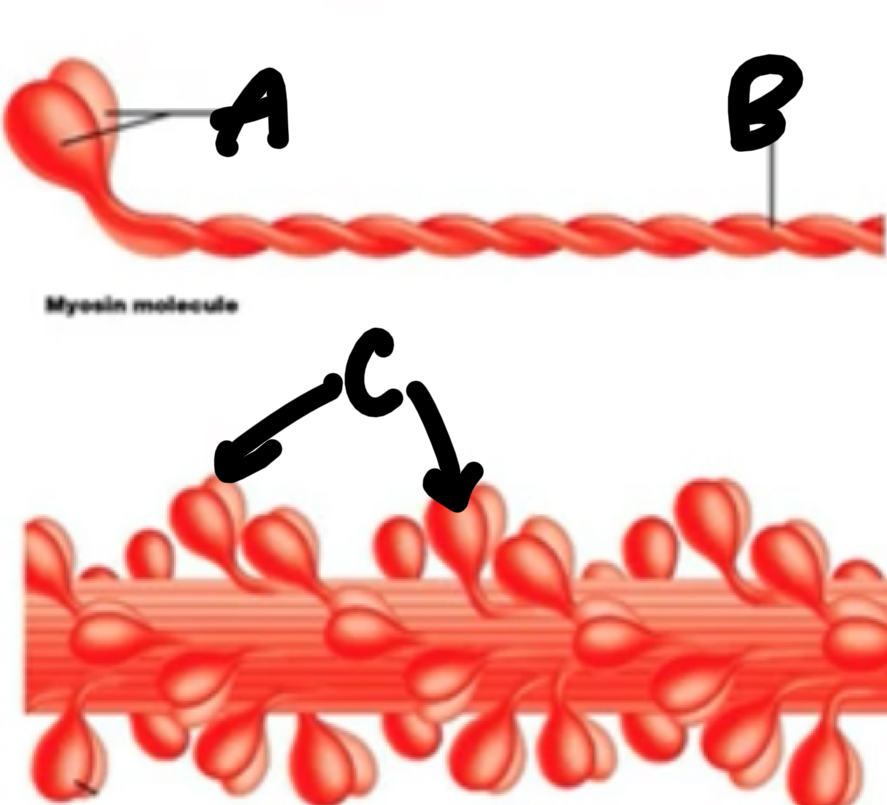
Name these structures of a thick filament.
A - 2 myosin heads
B - 2 intertwined tails
C - myosin
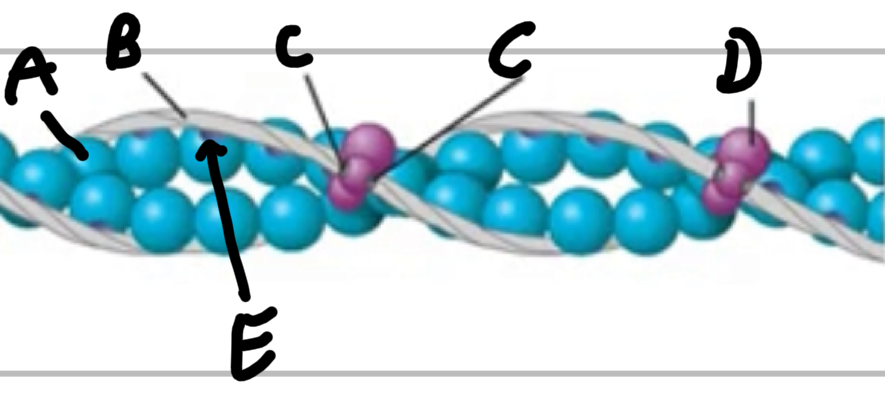
Name these structures of thin filaments.
A - actin
B - tropomyosin
C - calcium binding sites
D - troponin complex
E - myosin binding sites
Name, describe and give an example of the types of muscular contractions.
Isometric - muscle remains the same length, eg. Holding a plank
Isotonic Concentric - muscle shortens, eg. Upward phase of a bicep curl
Isotonic Eccentric - muscle lengthens, eg. Downwards phase of a bicep curl
Describe a neuromuscular junction.
The point where axon terminals of a motor neuron meet and transfer an action potential to the motor end plate of a muscle fibre
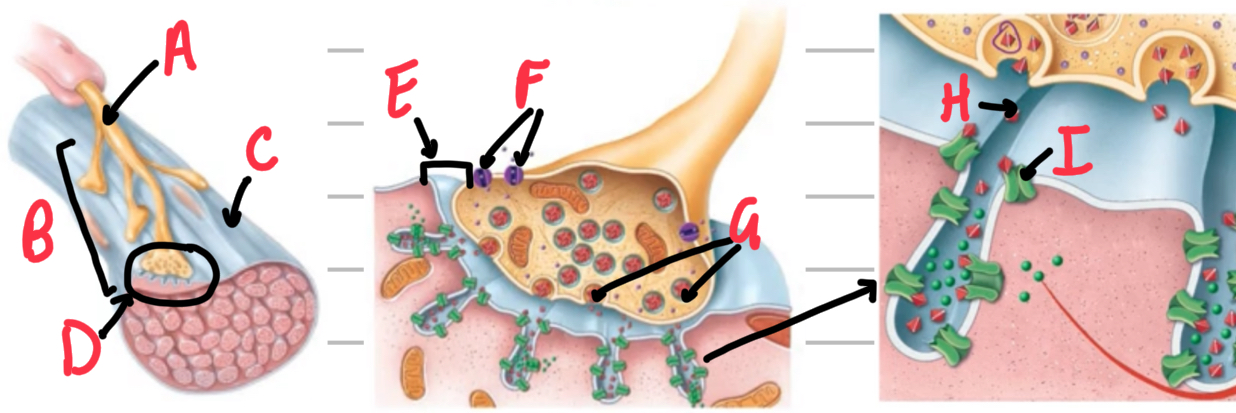
Name these structures of neuromuscular junction.
A - motor neuron
B - motor end plate
C - muscle fibre/cell
D - neuromuscular junction
E - synaptic cleft
F - voltage-gated calcium channel
G - acetylcholine vesicle
H - acetylcholine
I - ligand-gated cation/acetylcholine channel
Explain the process of an action potential exciting a muscle fibre/cell.
Action potential reaches the axon terminal of motor neuron
Voltage-gated calcium ion channels open and calcium ions are released into the axon terminal.
This triggers acetylcholine vesicles to dock and fuse with the neuronal membrane and release acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft.
Acetylcholine binds to ligand-gated cation/acetylcholine channels on the muscle fibre
Ligand-gated cation/acetylcholine receptors open when 2 acetylcholine molecules bind
More sodium ions rush into the cell than potassium ions leaving the cell, depolarising the membrane.
Once membrane potential reaches threshold, action potential propagates through the sarcolemma.
Explain the 2 processes in which acetylcholine is removed from the synaptic cleft.
Acetylcholine diffuses out of the synaptic cleft.
Enzyme acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine into acetic acid and choline which are diffused back into the axon terminals and resynthesized into acetylcholine.
Describe excitation-contraction coupling.
The process exciting a muscle fibre/cell that results in contraction.
Explain the process of excitation-contraction coupling.
The action potential travels through the sarcolemma and transverse tubules of the muscle fibre/cell
Once the action potential reaches a triad, voltage-sensitive proteins within change shape, causing calcium ion channel in the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions into the sarcoplasm.
Calcium ion release results in the contraction of the muscle fibre.
Explain the process of the sliding filament mechanism.
During isotonic concentric contractions:
Thin filaments slide along thick filaments
Myosin heads of thick filaments pull the thin filaments towards the m-line
during contraction the sarcomeres are shortened as the z-discs attached to the thin filaments are pulled towards the m-line.
Describe the cross bridge cycle.
The process of a myosin heads forming a cross bridge between thick and thin filaments.
Explain the process of the cross bridge cycle.
Calcium ions released in the sarcoplasm during excitation-contraction coupling, bind to the calcium binding sites on troponin complexes of thin filaments.
This causes troponin complexes to change shape, moving tropomyosin and exposing the myosin binding sites of actin
Myosin heads of thick filaments activate via ATP hydrolysis which releases energy, moving the myosin head into the cocked position
Cross-bridge formation occurs in which activated myosin heads bind to the myosin-binding site of actin and the inorganic phosphate from ATP hydrolysis on the myosin head is released, strengthening the bond.
Power stroke occurs in which the ADP from ATP hydrolysis is removed from the myosin heads which then pivots and pulls the thin filaments towards the m-line
Cross-bridge detachment occurs in which an ATP molecule binds to the myosin head, weakening its bond to the actin and therefore detaching.
This process repeats and the sarcomere shortens, contracting the muscle fibre until calcium ions are transported back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum, therefore troponin complexes return to their original shape, moving tropomyosin to cover the myosin-binding sites of actin.
Describe a motor unit.
The somatic motor neuron and all of the muscle cells it innervates.
Explain the ‘all or nothing’ principle
Describes how a motor neuron will stimulate all of the muscle fibres it innervates or none, will never only stimulate 1.
Describe the 3 mechanisms that change contractile strength.
The number of motor neurons stimulated, therefore changing the number of muscle fibres that contract
The frequency of motor unit stimulation
The type of muscle stimulated, larger muscles will have greater contractile strength than smaller muscles with fewer muscle fibres.
Explain why increasing frequency of motor unit stimulation increases contractile strength.
Increasing frequency of motor unit stimulation will result in stimulating the muscle fibre during its relaxation period in which the sarcomere isn’t fully relaxed, therefore causes summation of increasing force of contraction.
Name and describe the 2 types of attachment sites.
Origin - the attachment site that is more medial and stationary
Insertion - the attachment site that can move further away from the midline of the body.
Describe the muscle nerve supply.
The last nerve of a chain that innervates the muscle.
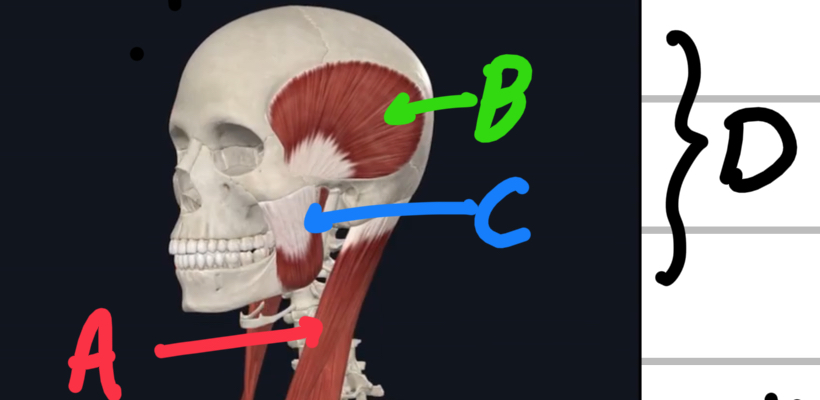
Name these head/neck muscles.
A - sternocleidomastoid muscle
B - temporal is
C - masseter
D - muscles of mastication
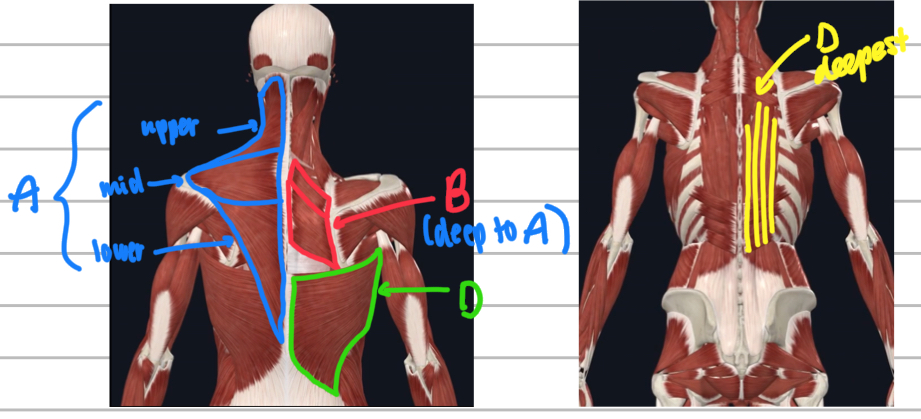
Name these posterior trunk muscles.
A - trapezius
B - rhomboids (deep to the trapezius)
C - latissimus dorsi
D - erector spinae muscles
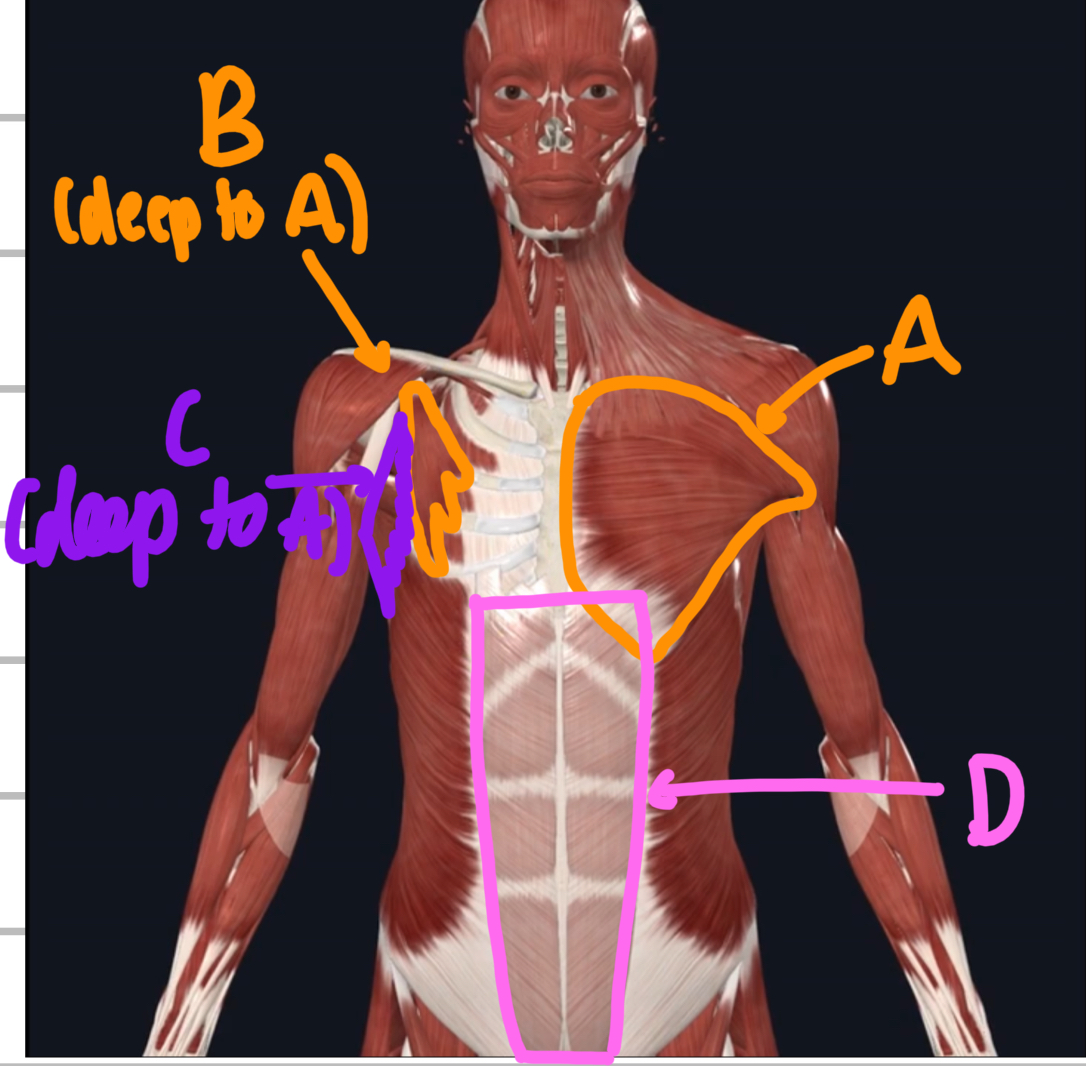
Name these anterior trunk muscles.
A - pectoralis major
B - pectoralis minor (deep to major)
C - serratus anterior (deep to major)
D - rectus abdominis
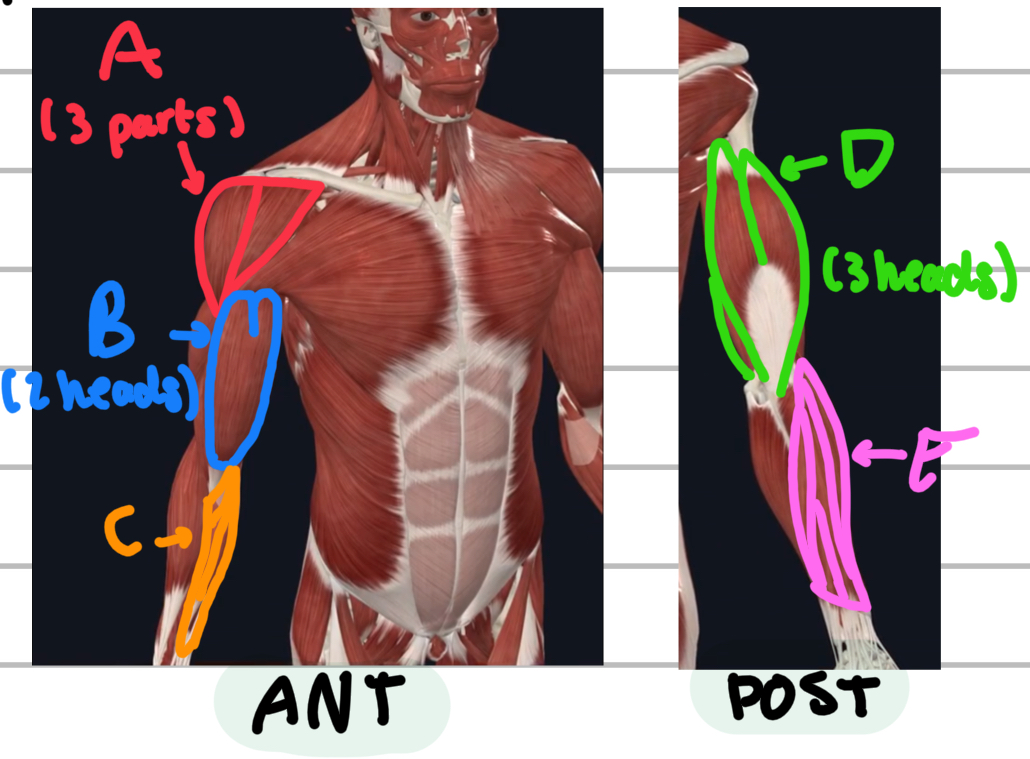
Name these superficial muscles of the upper limbs.
A - deltoid
B - biceps bracchi
C - forearm flexors
D - triceps tracchi
E - forearm extensor muscles
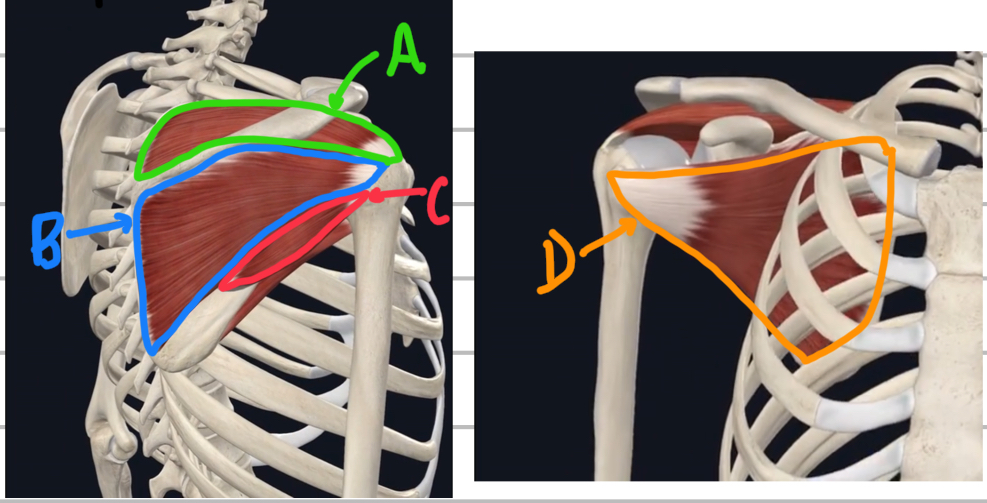
Name these deep rotator cuff muscles.
A - suprafinatus
B - infraspinatus
C - teres minor
D - subscapularis
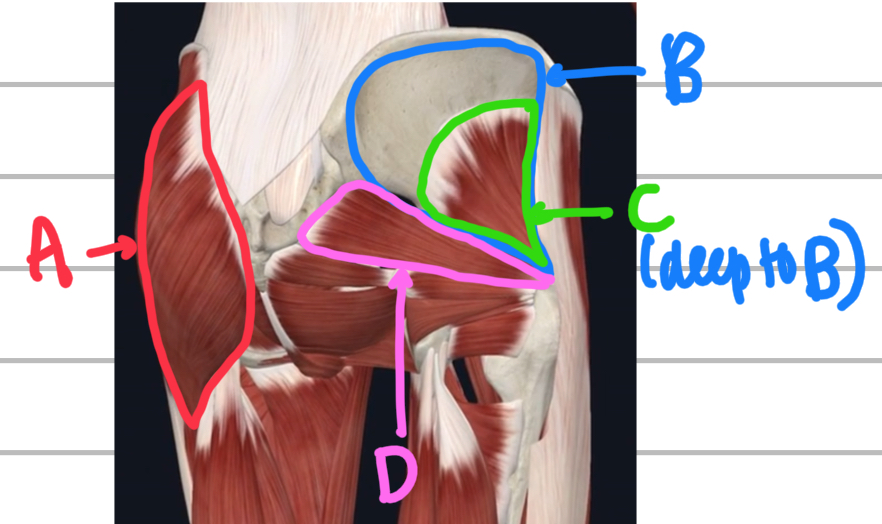
Name these glute muscles.
A - gluteus maximus
B - gluteus medius
C - gluteus minimus (deep to medius)
D - piriformis
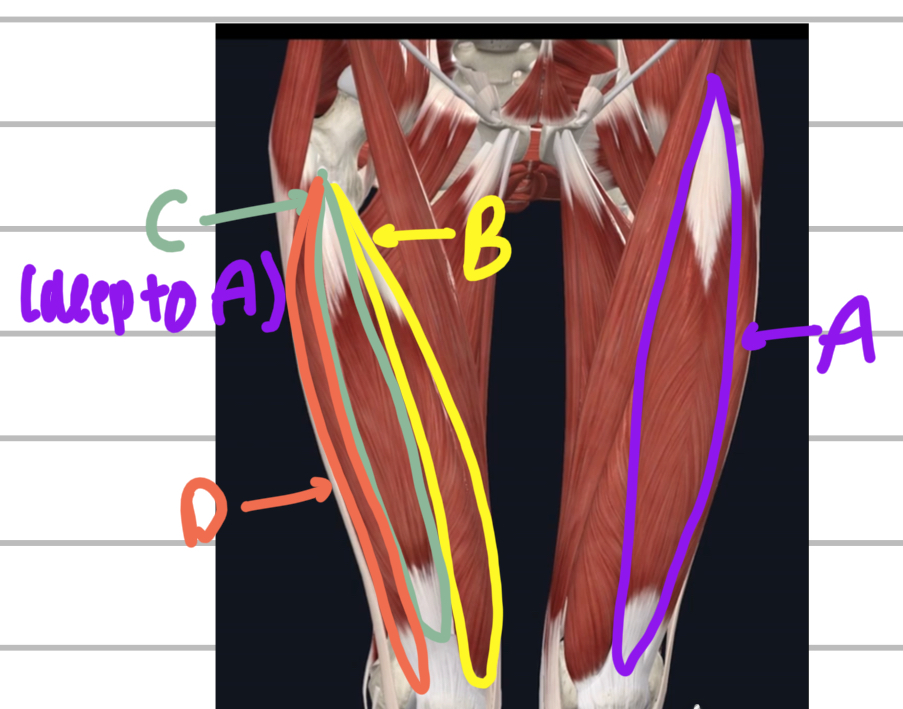
Name these anterior upper leg muscles.
A - rectus femoris
B - vastus medialis
C - vastus intermedius (deep to the rectus femoris)
D - vastus lateralis
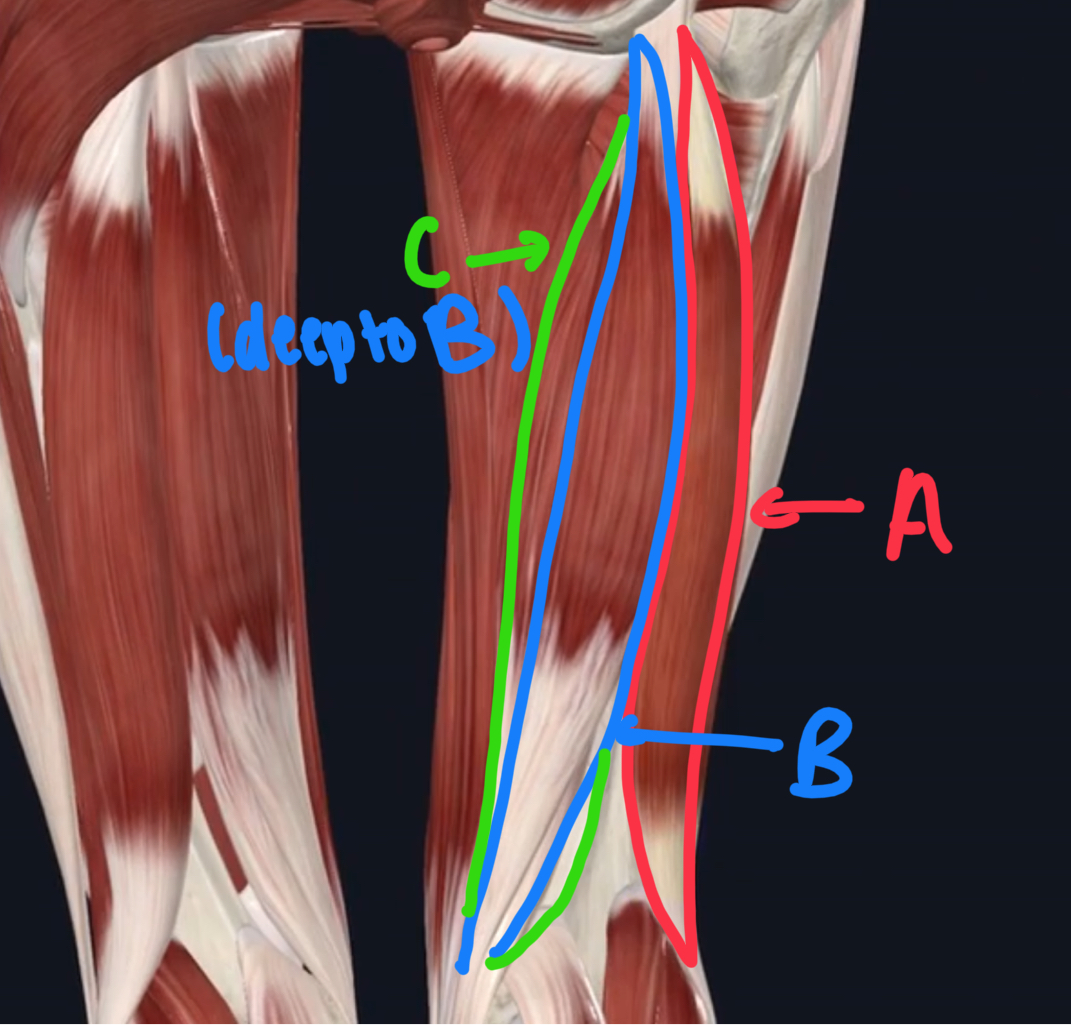
Name these posterior muscles of the upper leg.
A - biceps femoris
B - semitendinosus
C - semimembranosus (deep to the semitendinosus)
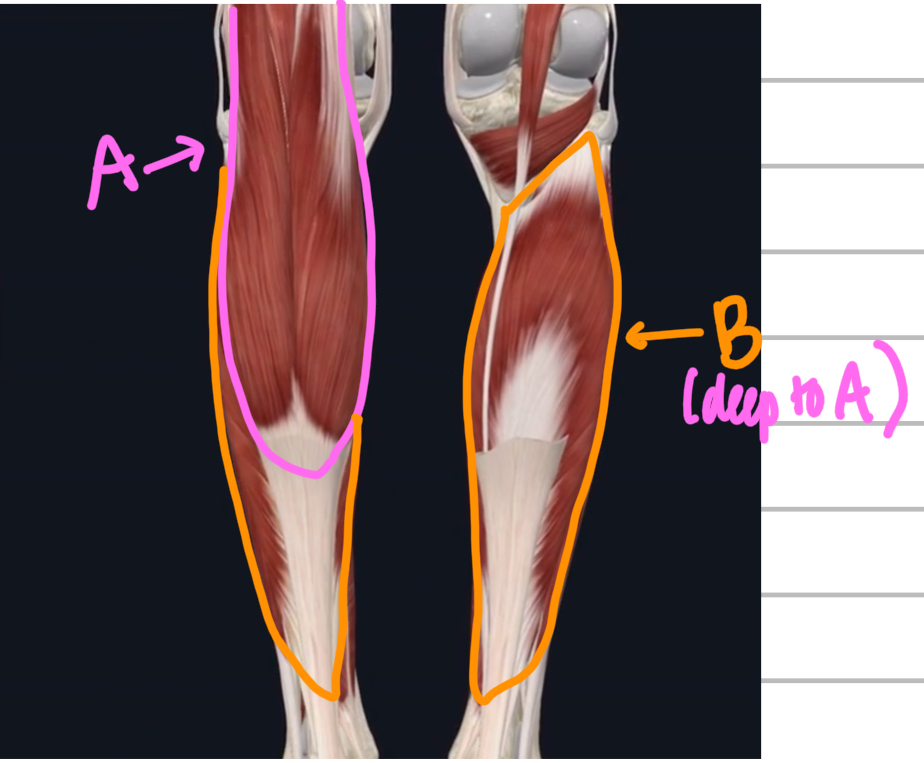
Name these posterior muscles of the lower leg.
A - gastrocnemius
B - soleus (deep to gastrocnemius)