Biomes, Ecosystems, and Biodiversity: Key Concepts and Processes
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What is a biome?
A large, relatively distinct terrestrial region with characteristic climate, soil, plants, and animals.
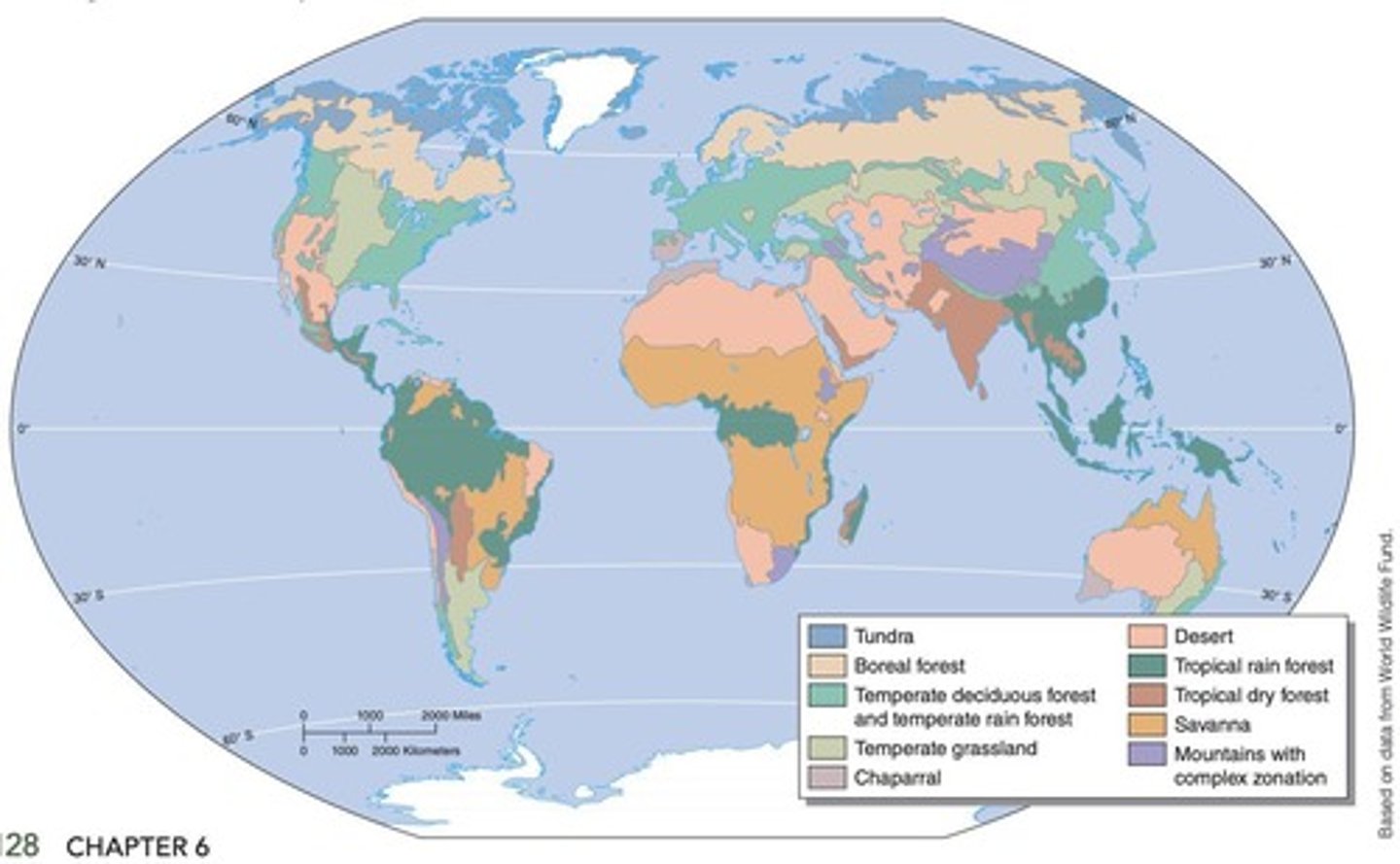
What factors determine biome distribution near the poles?
Temperature is generally the overriding climate factor.
What factors influence biome distribution in temperate and tropical regions?
Precipitation is more significant.
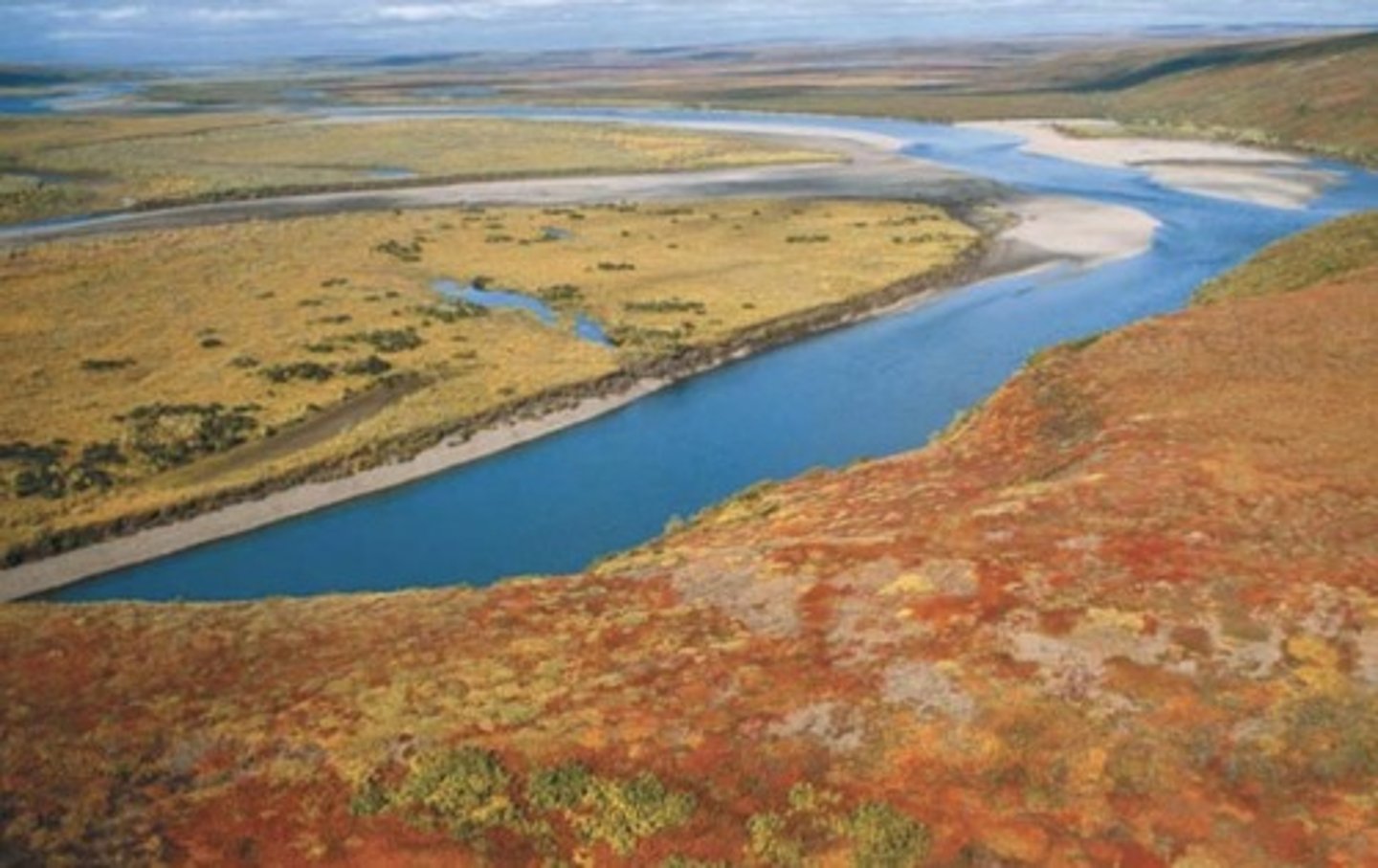
What characterizes the tundra biome?
A treeless biome in the far north with boggy plains, lichens, and small plants, experiencing harsh winters and short summers.

Where is the boreal forest located?
Just south of the tundra in the Northern Hemisphere.
What are the characteristics of a temperate rain forest?
A coniferous biome with cool weather, dense fog, and high precipitation.
What defines a temperate deciduous forest?
A forest biome occurring in temperate areas with a moderate amount of precipitation.
What is a temperate grassland?
A grassland with hot summers, cold winters, and less rainfall than temperate deciduous forests.
Describe the chaparral biome.
A biome with mild, moist winters and hot, dry summers, featuring small-leafed evergreen shrubs and small trees.
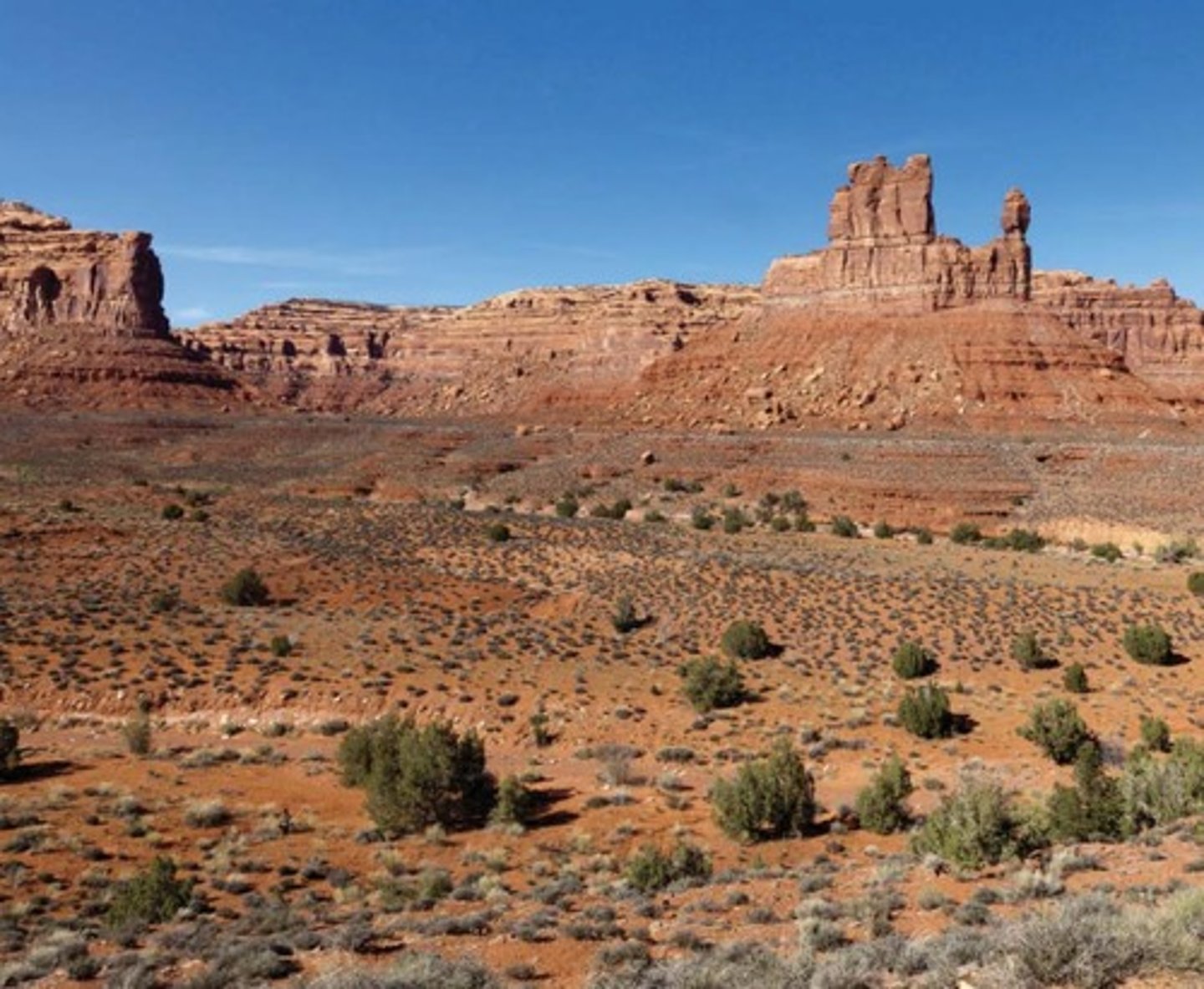
What limits plant growth in a desert biome?
The lack of precipitation.

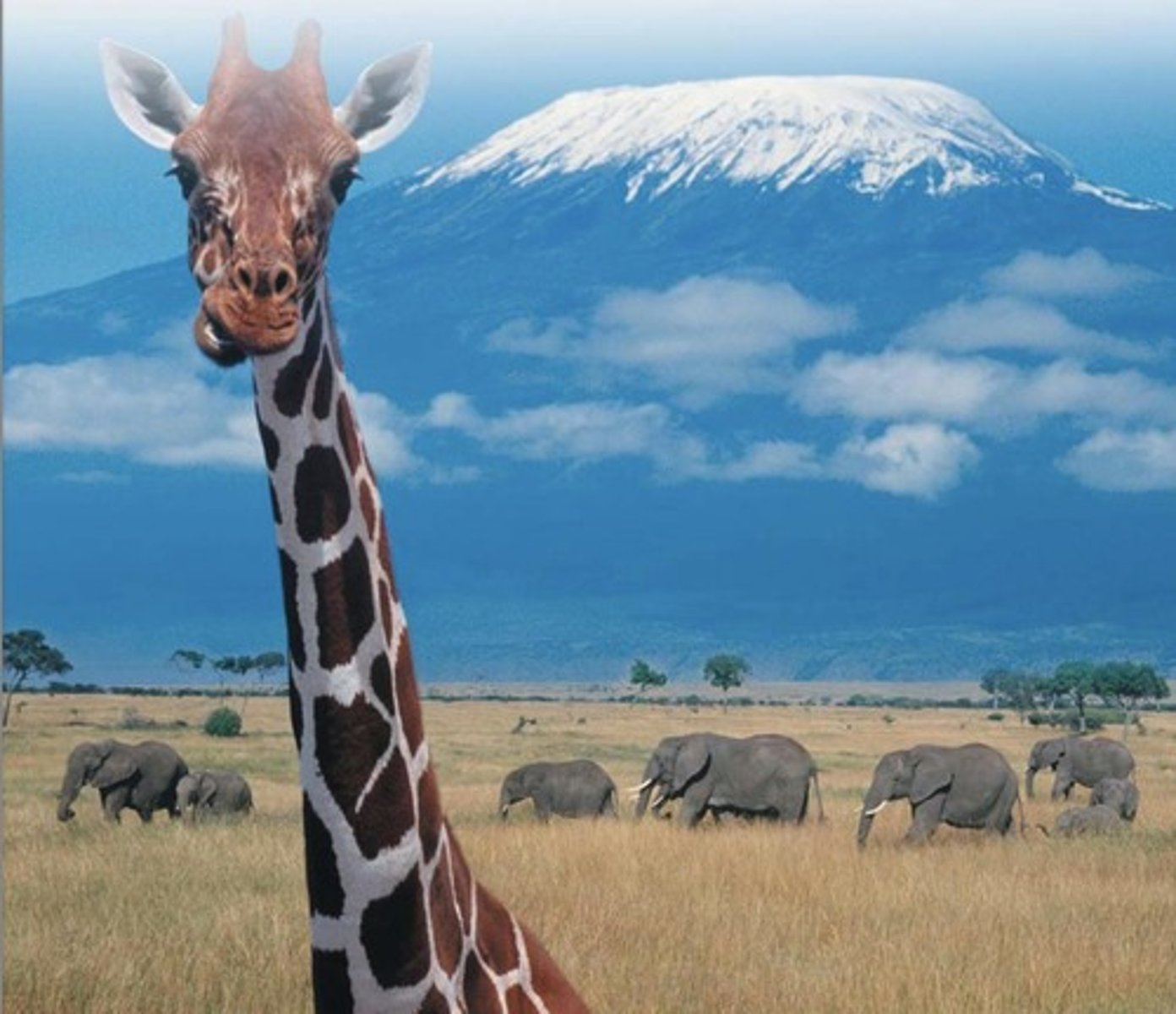
What is a savanna?
A tropical grassland with widely scattered trees or clumps of trees.

What characterizes a tropical rain forest?
A lush, species-rich forest biome that occurs in warm and moist climates throughout the year.

What are important environmental factors in aquatic ecosystems?
Salinity, amount of dissolved oxygen, and availability of light for photosynthesis.
What defines a standing-water ecosystem?
A body of fresh water surrounded by land with non-flowing water, such as a lake or pond.

What is a flowing-water ecosystem?
A freshwater ecosystem such as a river or stream where water flows in a current.
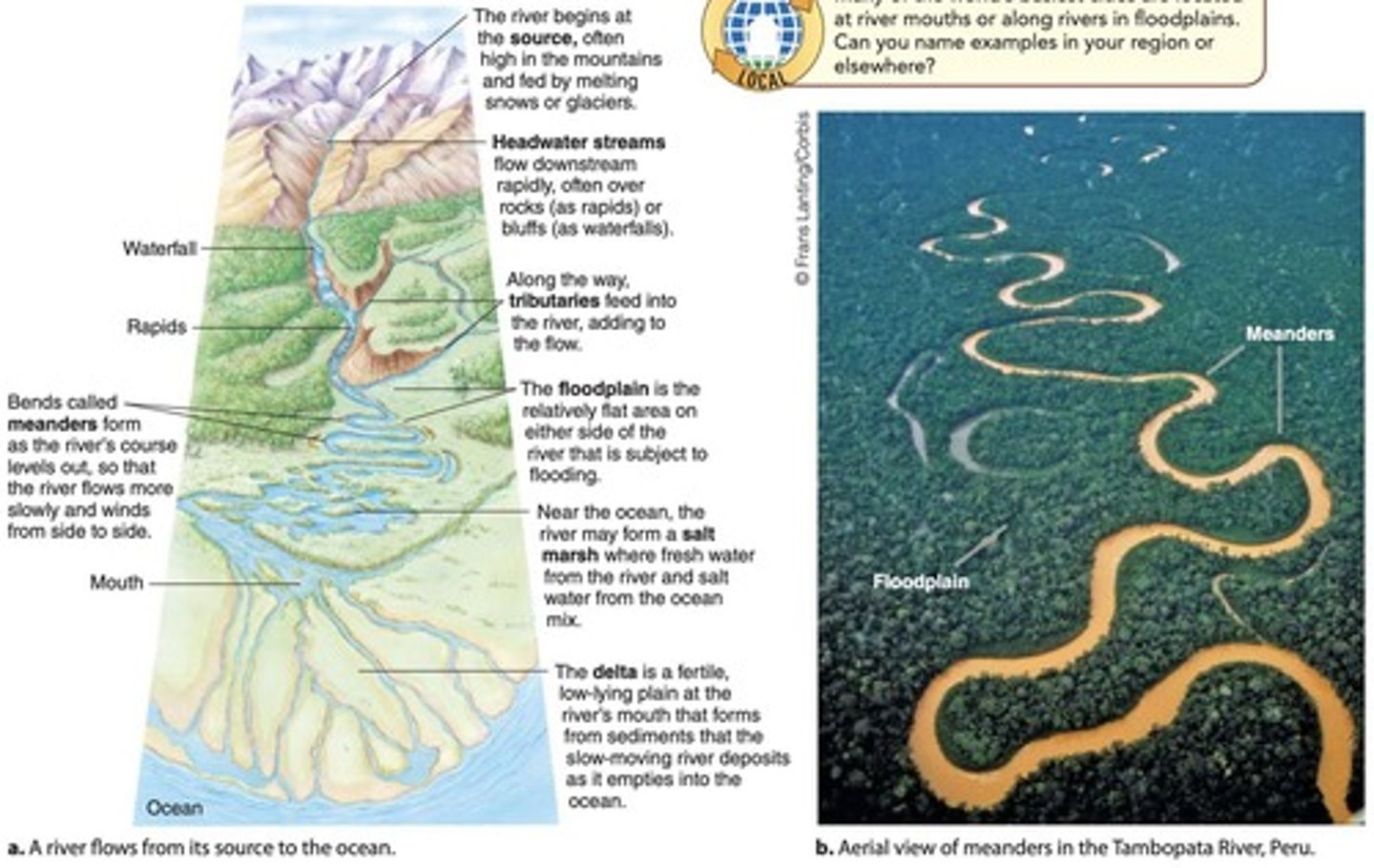
What are freshwater wetlands?
Marshes and swamps covered by shallow fresh water at least part of the year.
What is an estuary?
A coastal body of water partly surrounded by land, with access to the open ocean and a large supply of fresh water from a river.
What is the definition of evolution?
The cumulative genetic changes in populations that occur during successive generations.
What is natural selection?
The tendency of better-adapted individuals to survive and reproduce, increasing their proportion in the population.
What are the four observations of natural selection established by Charles Darwin?
1. Each species produces more offspring than will survive. 2. Organisms compete for resources. 3. Individuals exhibit heritable variation. 4. Individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
What is ecological succession?
The process of community development over time, involving species replacement.
What is primary succession?
The change in species composition in an environment that was not previously inhabited, such as bare rock.
What is secondary succession?
The change in species composition after a disturbance that destroys existing vegetation, where soil is already present.
What climate factor primarily determines biome distribution near the poles?
Temperature.
What climate factor is more significant in temperate and tropical regions for biome distribution?
Precipitation.
What defines a temperate deciduous forest biome?
A forest biome that occurs in temperate areas with a moderate amount of precipitation.
What are the conditions of a temperate grassland?
Hot summers, cold winters, and less rainfall than the temperate deciduous forest.
What is the chaparral biome characterized by?
Mild, moist winters and hot, dry summers, with small-leafed evergreen shrubs and small trees.
What defines a tropical rain forest?
A lush, species-rich forest biome that occurs where the climate is warm and moist throughout the year.
What are the important environmental factors in aquatic ecosystems?
Salinity, amount of dissolved oxygen, and availability of light for photosynthesis.
What is a standing-water ecosystem?
A body of fresh water surrounded by land and whose water does not flow, such as a lake or pond.
Describe the tundra biome.
A treeless biome in the far north, consisting of boggy plains covered by lichens and small plants, with harsh, very cold winters and extremely short summers.
What characterizes the temperate rain forest biome?
It is a coniferous biome with cool weather, dense fog, and high precipitation.
What type of forest occurs in temperate areas with moderate precipitation?
Temperate deciduous forest.
Describe the temperate grassland biome.
A grassland with hot summers, cold winters, and less rainfall than the temperate deciduous forest.
What are the characteristics of the chaparral biome?
Mild, moist winters and hot, dry summers, with vegetation typically consisting of small-leafed evergreen shrubs and small trees.
Describe the tropical rain forest biome.
A lush, species-rich forest biome that occurs where the climate is warm and moist throughout the year.
What defines a flowing-water ecosystem?
A freshwater ecosystem, such as a river or stream, in which the water flows in a current.
What is evolution?
The cumulative genetic changes in populations that occur during successive generations.
List the four observations that form the basis of natural selection according to Charles Darwin.
1) Each species produces more offspring than will survive. 2) Organisms compete for resources. 3) Individuals exhibit heritable variation in traits. 4) Individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
What factors primarily determine biome distribution near the poles?
Temperature is the overriding climate factor.
What factors primarily determine biome distribution in temperate and tropical regions?
Precipitation is more significant.
What characterizes the boreal forest biome?
A region of coniferous forest located just south of the tundra in the Northern Hemisphere.
What are the key features of the temperate rain forest biome?
A coniferous biome with cool weather, dense fog, and high precipitation.
What defines the temperate deciduous forest biome?
A forest biome occurring in temperate areas with a moderate amount of precipitation.
What is the climate like in a temperate grassland biome?
Hot summers, cold winters, and less rainfall than in temperate deciduous forests.
What characterizes a tropical rain forest biome?
A lush, species-rich forest that occurs where the climate is warm and moist throughout the year.
In temperate and tropical regions, what is the significant climate factor for biome distribution?
Precipitation is more significant.
What are the characteristics of a temperate grassland?
Grassland with hot summers, cold winters, and less rainfall than temperate deciduous forests.
What is a tropical rain forest?
A lush, species-rich forest biome that occurs where the climate is warm and moist throughout the year.
What is brackish water?
Water in an estuary that is a mixture of fresh and salt water.
How does temperature affect biome distribution near the poles?
Temperature is the overriding climate factor in determining biome distribution.
What are the main features of a temperate rain forest?
A coniferous biome with cool weather, dense fog, and high precipitation.
What is the desert biome characterized by?
A lack of precipitation that limits plant growth, found in both temperate and tropical regions.
What environmental factors are important in aquatic ecosystems?
Salinity, amount of dissolved oxygen, and availability of light for photosynthesis.
What is biological diversity also known as?
Biodiversity.
What does biodiversity include?
Diversity in genes, populations, species, communities, and ecosystems.
What is species diversity?
The number or variety of species found in a particular region.
What defines species richness?
The number of species inhabiting an area.
What does evenness or relative abundance refer to in species diversity?
The extent to which species in a given area differ in numbers of individuals.
What are subspecies?
Populations of a species that occur in different geographic areas and differ from one another in slight ways.
What is genetic diversity?
The differences in DNA composition among individuals, providing raw material for adaptation.
Why are populations with more genetic diversity more likely to persist?
They are better equipped to adapt to environmental changes.
What is ecosystem diversity?
The number and variety of ecosystems, including the diversity of communities or habitats.
What does functional diversity refer to?
The variety of processes such as energy flow and matter cycling within ecosystems.
How is biodiversity distributed across different groups of organisms?
Some groups have more species than others, and biodiversity is unevenly distributed.
What pattern is observed in species richness as one approaches the equator?
Species richness generally increases.
What is the latitudinal gradient in species richness?
It is one of the most obvious patterns in ecology, showing that species richness varies with latitude.
How many species have been described so far?
More than 1.8 million species.
What ecological role does each species play?
Each species plays a specific ecological role called its niche.
What are the four important roles a species may play in an ecosystem?
Native, nonnative, indicator, or keystone.
What is a generalist species?
A species that has a broad niche.
What is a specialist species?
A species that occupies a narrow niche.
What is an example of specialized feeding niches?
Various bird species in a coastal wetland.
What are native species?
Species that normally live and thrive in a particular ecosystem.
What are nonnative species?
Species that migrate into or are deliberately or accidentally introduced into a new ecosystem.
What are invasive species?
Nonnative species that compete with and reduce an ecosystem's native species.
What are indicator species?
Species that provide early warnings of environmental change in a community or ecosystem.
What is a keystone species?
A species that plays several critical roles in helping to sustain ecosystems.
What are foundation species?
Species that create and define particular ecosystems and control the distribution and abundance of associated flora and fauna.
What is speciation?
The process by which one species splits into two or more species.
What is geographic isolation?
The physical isolation of populations for a long period, which can lead to reproductive isolation.
What is reproductive isolation?
The inability to produce viable offspring when members of two different populations mate, often due to mutations and natural selection.
What are the benefits of biodiversity?
Enhances food security, provides drugs and medicines, offers ecosystem services, helps maintain functioning ecosystems, and fosters connections with nature.
What is local extinction?
The disappearance of a particular population from a given area, but not the entire species globally.
What is extinction?
The event when the last member of a species dies and the entire species ceases to exist.
What is the current extinction rate compared to the natural background rate?
Today's extinction rate is far higher than the natural background rate.
What are some major causes of biodiversity loss?
Habitat loss, pollution, overharvesting, invasive species, and climate change.
How many mass extinction events has Earth experienced in the past 440 million years?
Five mass extinction events.
What is the significance of the sixth mass extinction?
Human impact is now initiating a sixth mass extinction.
What has happened to populations of vertebrate animals in the last 50 years?
They average less than half the size they were just half a century ago.
What happens when a population declines to a very low level?
Extinction becomes a possibility.
What is extirpation?
The local extinction of a species from a specific area.
What is the role of foundation species in ecosystems?
They create and define ecosystems and modulate core ecosystem processes.
What can geographic isolation lead to?
Reproductive isolation, divergence of gene pools, and speciation.
What is the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem services?
Biodiversity provides essential ecosystem services that help maintain ecosystem functioning.