Psych exam 1
1/240
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
241 Terms
Psychodynamic perspective
Focuses on the role of the unconscious and childhood experiences in affecting conscious behavior. Sigmund Freud, Erik Erikson
Behavioral perspective
Focuses on observing and controlling behavior through what is observable. Puts an emphasis on learning and conditioning.Ivan Pavlov, John B. Watson, B. F. Skinner
Humanistic perspective
Emphasizes the potential for good that is innate to all humans and rejects that psychology should focus on problems and disorders. Abraham Maslow, The Blackfoot Nation, Carl Rogers
Cognitive perspective
Focuses not just on behavior, but on mental processes and internal mental states. Ulric Neisser, Noam Chomsky, Jean Piaget, Lev Vygotsky
behaviorism
the psychological focus on observing and controlling behavior. Behaviorism as a theory holds that behaviors are learned or conditioned through environmental experiences.
biological perspective
a psychological approach that examines physiological causes for behavior
biopsychology
study of how biology influences behavior
biopsychosocial model
perspective that asserts that biology, psychology, and social factors interact to determine an individual’s health
clinical psychology
area of psychology that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of psychological disorders and other problematic patterns of behavior
cognitive psychology
area of psychology that focuses on studying thoughts and their relationship to our experiences and actions
cognitive revolution
a period of change in psychology during the 1950s and 1960s, characterized by a shift back to studying mental processes and the emergence of cognitive psychology as a prominent perspective
counseling psychology
discipline that focuses on emotional, social, vocational, and health-related outcomes in individuals who are considered psychologically healthy
cross-cultural psychologists
compare populations across countries
developmental psychology
the scientific study of development across a lifespan
dissertation
long research paper about research that was conducted as a part of the candidate’s doctoral training
eclectic approach
an approach in psychology where psychologists draw from multiple ideas and theories, integrating different perspectives to understand and study human behavior
empirical method
method for acquiring knowledge based on observation, including experimentation, rather than a method based only on forms of logical argument or previous authorities
evolutionary perspective
A psychological approach that posits behaviors have an evolutionary cause and grew from functionalist views
evolutionary psychology
seeks to understand human behavior as the result of psychological adaptation and natural selection
forensic psychology
area of psychology that applies the science and practice of psychology to issues within and related to the justice system
functionalism
focused on how mental activities helped an organism adapt to its environment
health psychology
the study of how psychological factors, including thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and social interactions, influence health and well-being
humanism
perspective within psychology that emphasizes the potential for good that is innate to all humans
multicultural psychologists
develop theories and conduct research with diverse populations, typically within one country
natural selection
a process by which heritable traits conferring survival and reproductive advantage to individuals tend to be passed on to succeeding generations and become more frequent in a population
personality psychology
study of patterns of thoughts and behaviors that make each individual unique
personality trait
consistent pattern of thought and behavior
cause-and-effect relationship
changes in one variable cause the changes in the other variable; can be determined only through an experimental research design
clinical or case study
observational research study focusing on one or a few people
confirmation bias
tendency to ignore evidence that disproves ideas or beliefs
confounding variable
an unanticipated outside factor that affects both variables of interest, often giving the false impression that changes in one variable causes changes in the other variable, when, in actuality, the outside factor causes changes in both variables
control group
serves as a basis for comparison and controls for chance factors that might influence the results of the study—by holding such factors constant across groups so that the experimental manipulation is the only difference between groups
correlation
relationship between two or more variables; when two variables are correlated, one variable changes as the other does
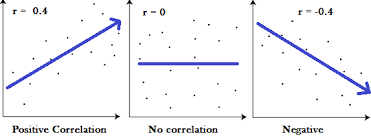
correlation coefficient
number from -1 to +1, indicating the strength and direction of the relationship between variables, and usually represented by r
correlational research
tests whether a relationship exists between two or more variables
cross-sectional research
compares multiple segments of a population at a single time
debriefing
when an experiment involved deception, participants are told complete and truthful information about the experiment at its conclusion
deception
purposely misleading experiment participants in order to maintain the integrity of the experiment
deductive reasoning
results are predicted based on a general premise
dependent variable
variable that the researcher measures to see how much effect the independent variable had
descriptive research
research studies that do not test specific relationships between variables; they are used to describe general or specific behaviors and attributes that are observed and measured
distribution
the pattern of variation in a set of data
double-blind study
experiment in which both the researchers and the participants are blind to group assignments
experimental group
group designed to answer the research question; experimental manipulation is the only difference between the experimental and control groups, so any differences between the two are due to experimental manipulation rather than chance
experimental research
tests a hypothesis to determine cause and effect relationships
experimenter bias
researcher expectations skew the results of the study
hypothesis
tentative and testable statement about the relationship between two or more variables
independent variable
variable that is influenced or controlled by the experimenter; in a sound experimental study, the independent variable is the only important difference between the experimental and control group
inductive reasoning
conclusions are drawn from observations
longitudinal research
studies in which the same group of individuals is surveyed or measured repeatedly over an extended period of time
naturalistic observation
observation of behavior in its natural setting
negative correlation
two variables change in different directions, with one becoming larger as the other becomes smaller; a negative correlation is not the same thing as no correlation
observer bias
when observations may be skewed to align with observer expectations
operational definition
description of what actions and operations will be used to measure the dependent variables and manipulate the independent variables
placebo effect
people’s expectations or beliefs influencing or determining their experience in a given situation
positive correlation
two variables change in the same direction, both becoming either larger or smaller
random assignment
method of experimental group assignment in which all participants have an equal chance of being assigned to either group
random sample
subset of a larger population in which every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected
single-blind study
experiment in which the researcher knows which participants are in the experimental group and which are in the control group
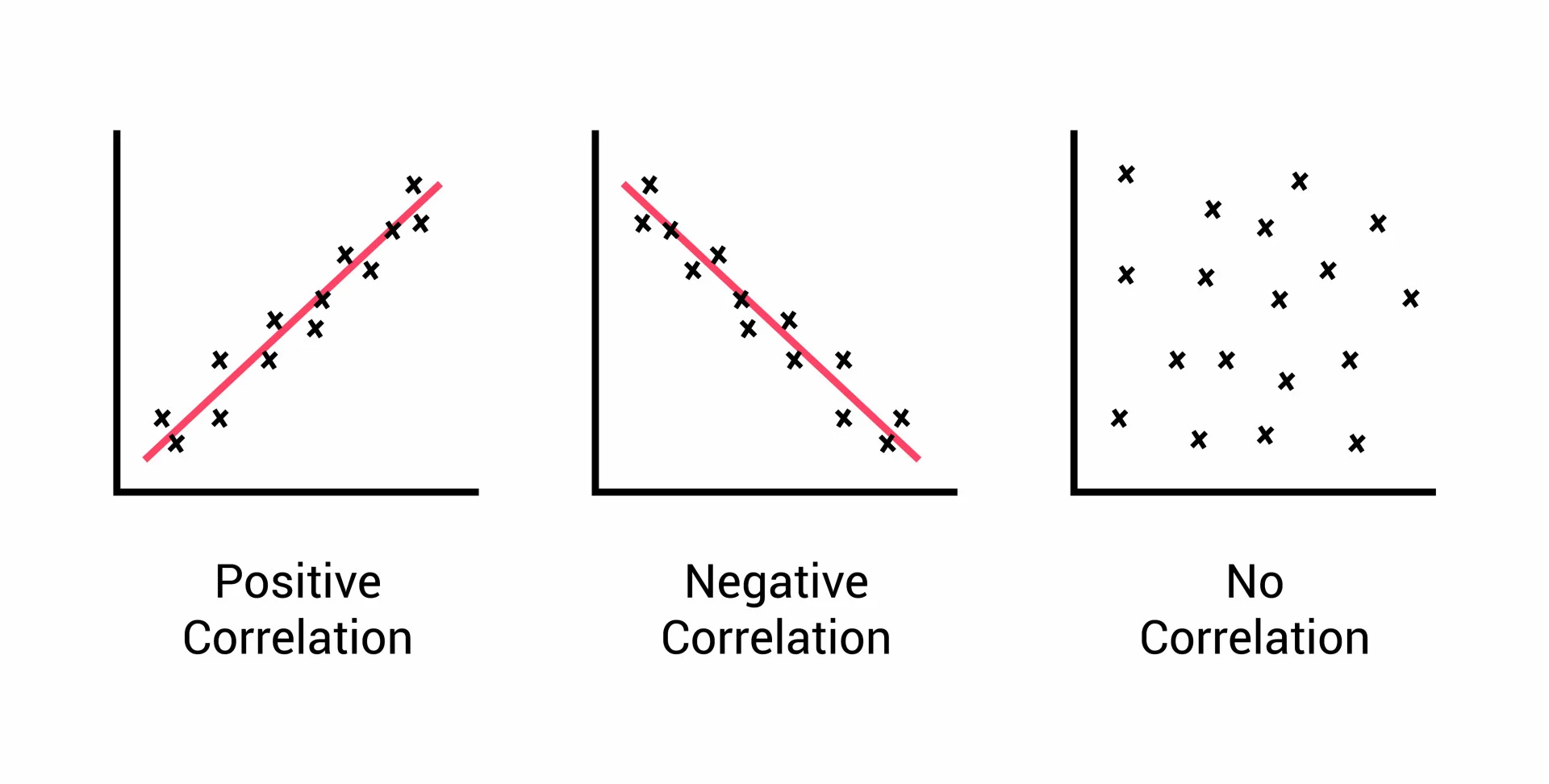
standard deviation
a measure of how much the data varies from the mean score
statistical analysis
determines how likely any difference between experimental groups is due to chance
survey
list of questions to be answered by research participants—given as paper-and-pencil questionnaires, administered electronically, or conducted verbally—allowing researchers to collect data from a large number of people
test-retest reliability
the degree to which the outcomes of a particular measure remain consistent over multiple administrations
theory
well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena
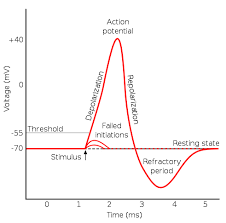
action potential
an electrical signal that moves down the neuron’s axon
adrenal gland
sits atop our kidneys and secretes hormones involved in the stress response
agonist
a drug that mimics or strengthens the effects of a neurotransmitter
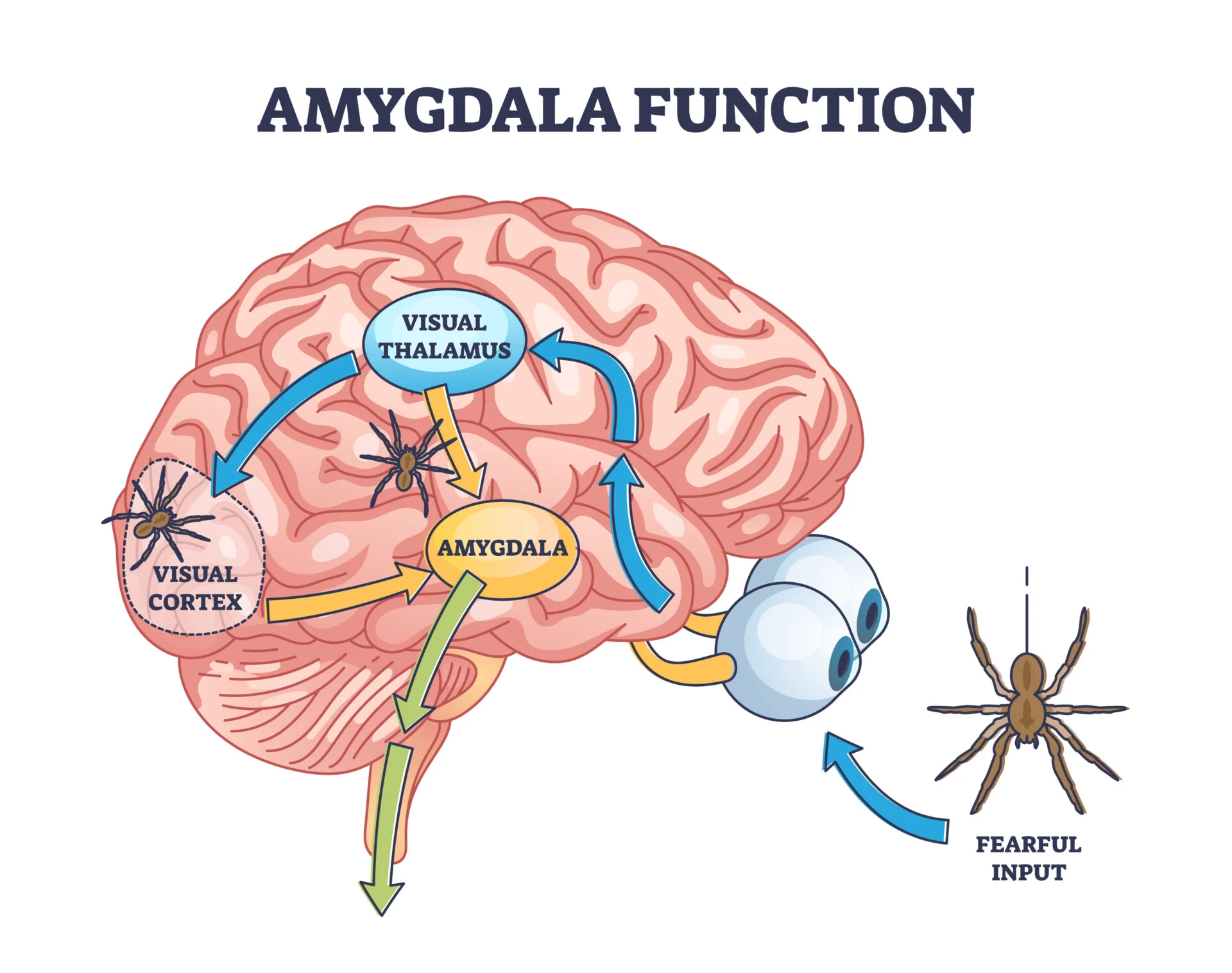
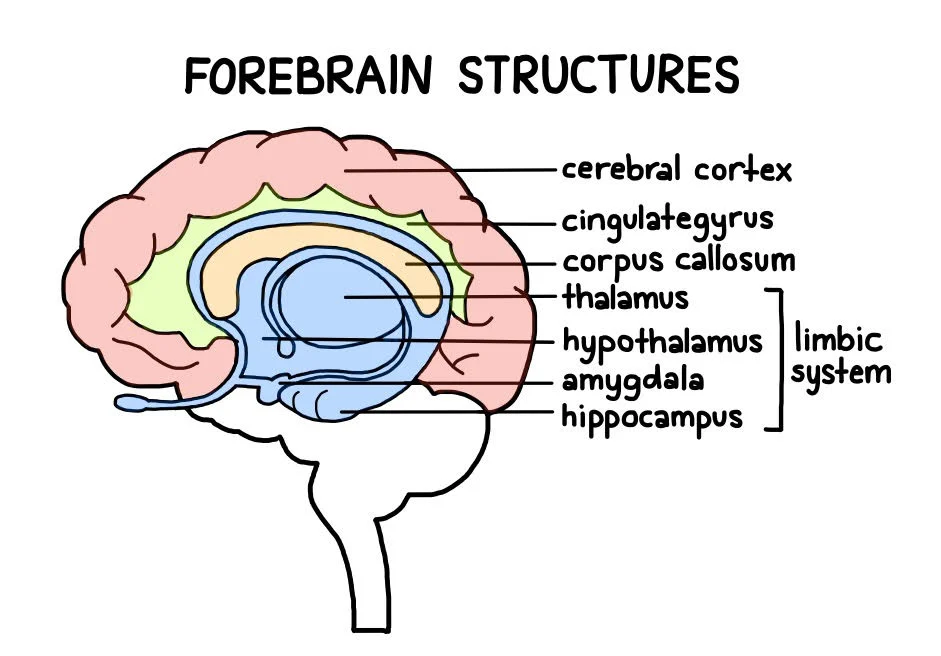
amygdala
structure in the limbic system involved in our experience of emotion and tying emotional meaning to our memories
antagonist
a drug that blocks or impedes the normal activity of a given neurotransmitter
auditory cortex
a strip of cortex in the temporal lobe that is responsible for processing auditory information
autonomic nervous system
controls our internal organs and glands
axon
a major extension from the neuron’s soma, which allows electrical signals to be passed from one neuron to another
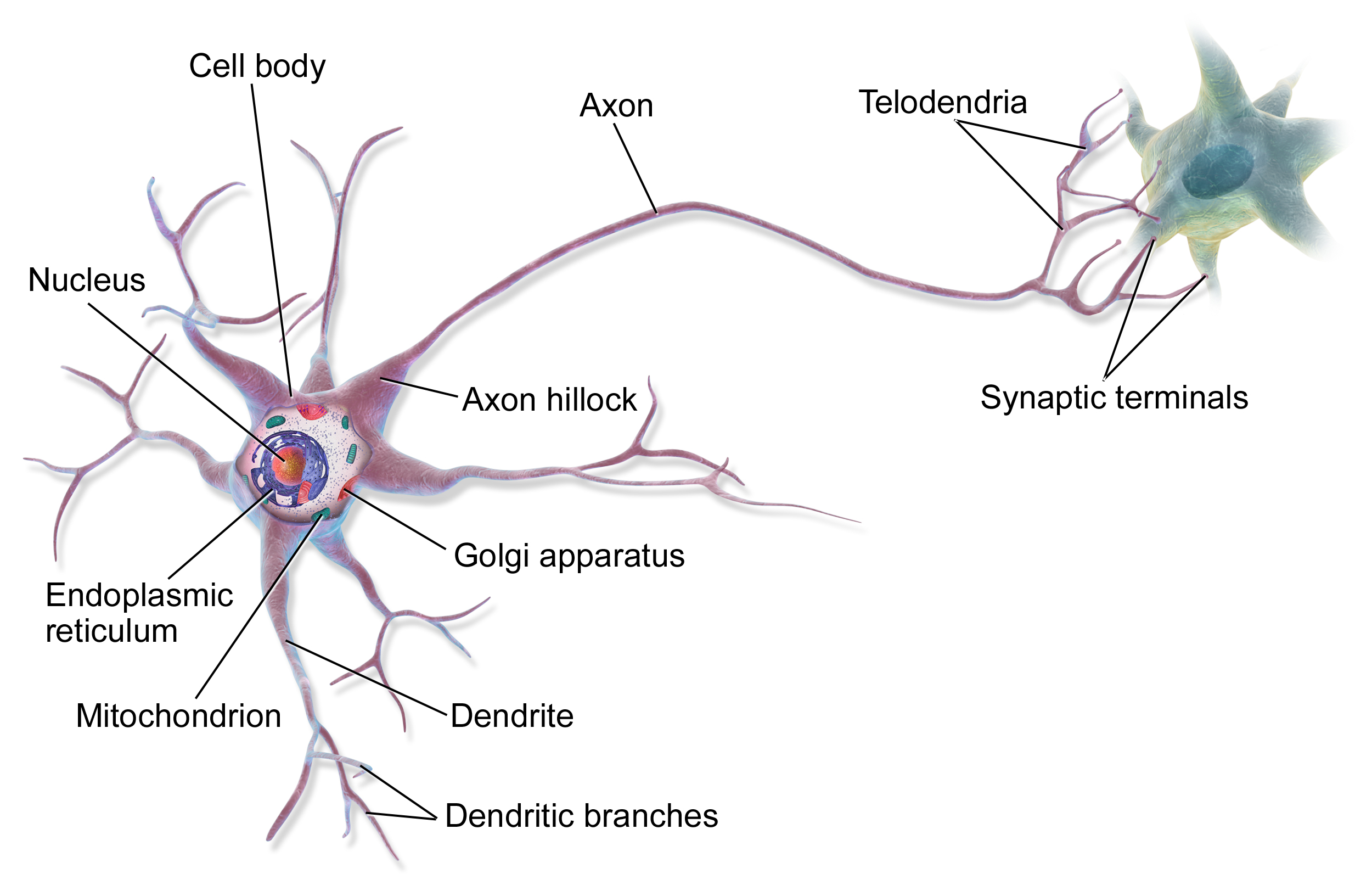
axon terminals (terminal buttons)
the ends of a neuron’s axon where synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters send chemical messages to the next neuron
behavioral endocrinology
the study of psychology and the endocrine system; the scientific study of the interaction between hormones and behavior
behavioral genetics
the empirical science of how genes and environments combine to generate behavior
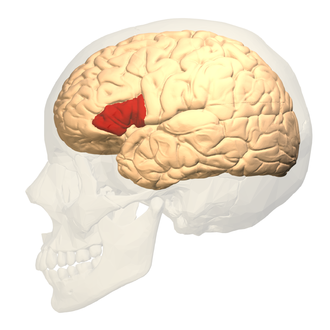
Broca’s area
a region in the left hemisphere that is essential for language production
central nervous system (CNS)
the brain and spinal cord
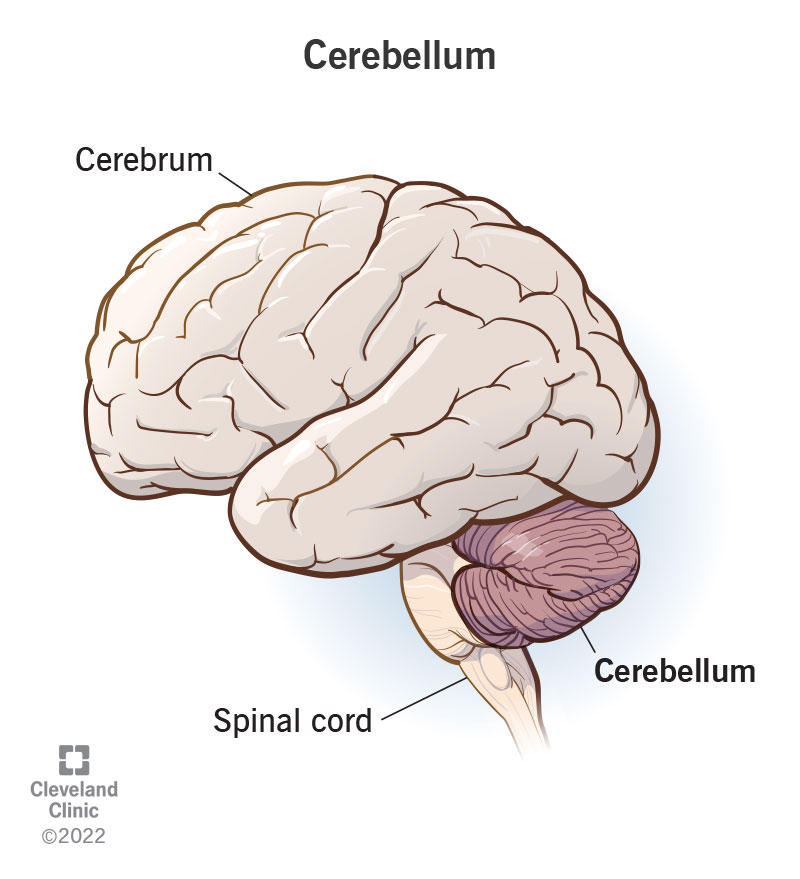
cerebellum
hindbrain structure that controls our balance, coordination, movement, and motor skills, and it is thought to be important in processing some types of memory
cerebral cortex
the surface of the brain that is associated with our highest mental capabilities
chromosome
a long strand of genetic information
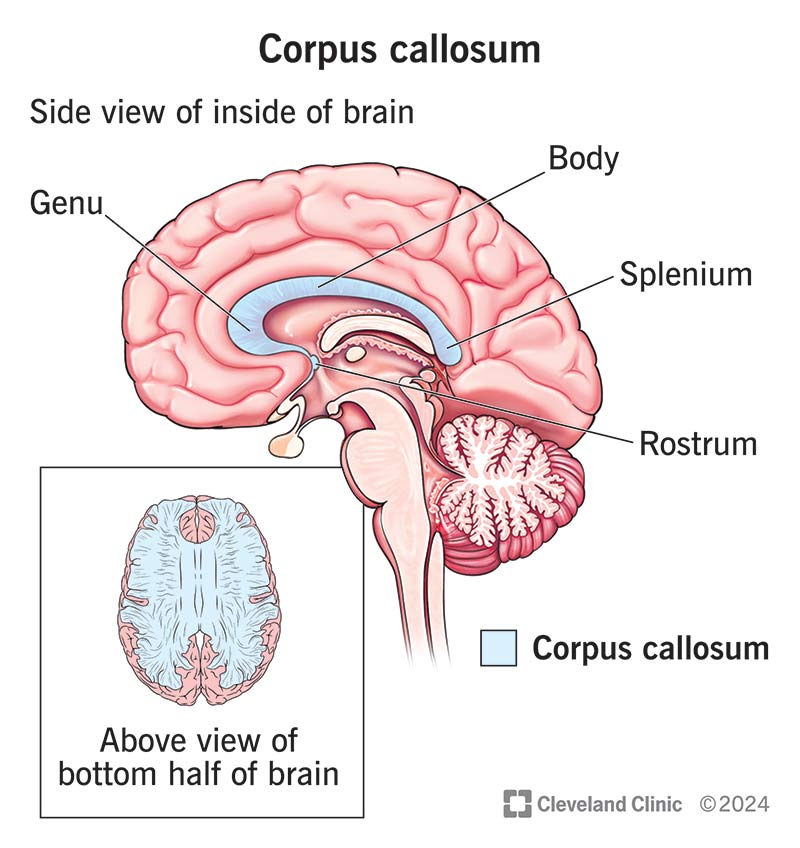
corpus callosum
a thick band of neural fibers connecting the brain’s two hemispheres
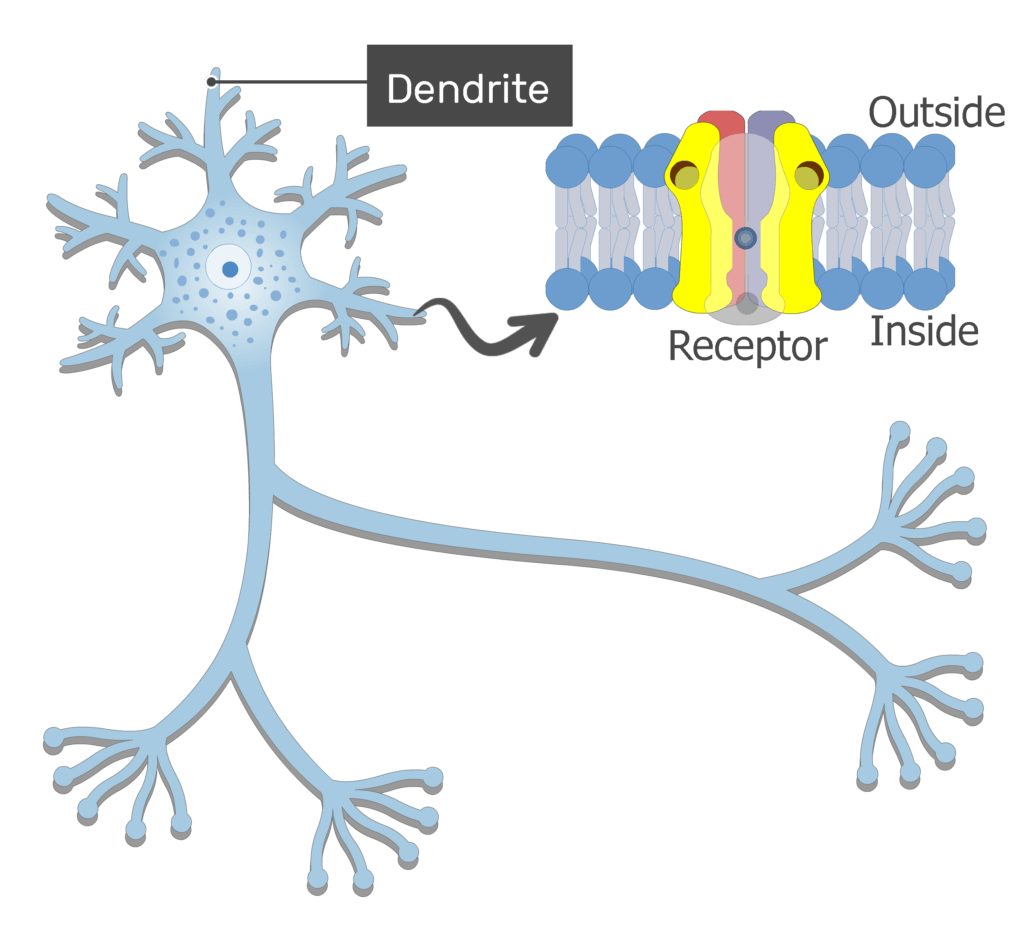
dendrites
branch-like extension of the soma that receives incoming signals from other neurons
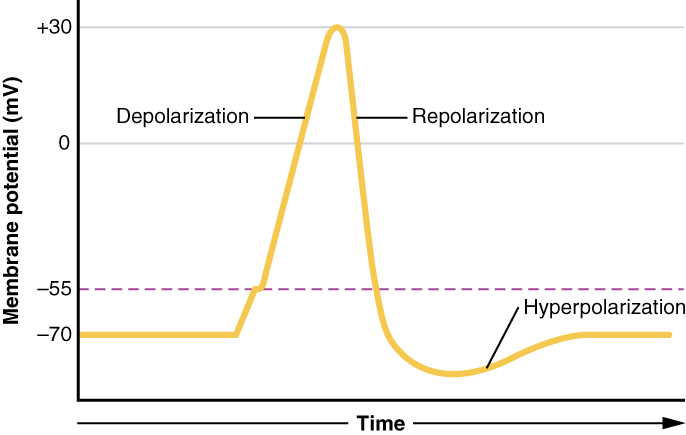
depolarization
when a cell’s charge becomes positive, or less negative
endocrine system
series of glands that produce chemical substances known as hormones
fight or flight response
activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, allowing access to energy reserves and heightened sensory capacity so that we might fight off a given threat or run away to safety
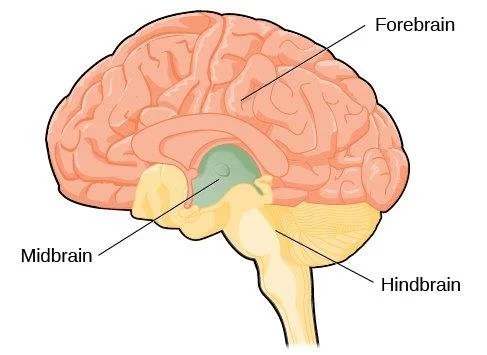
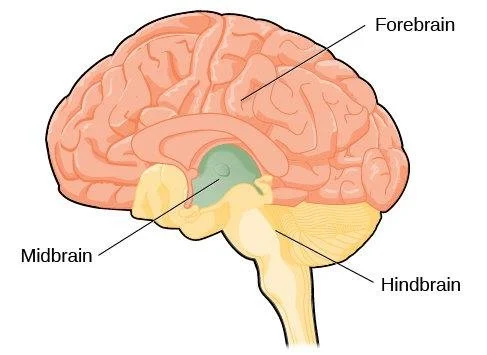
forebrain
the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex, the thalamus, and the limbic system, among other structures
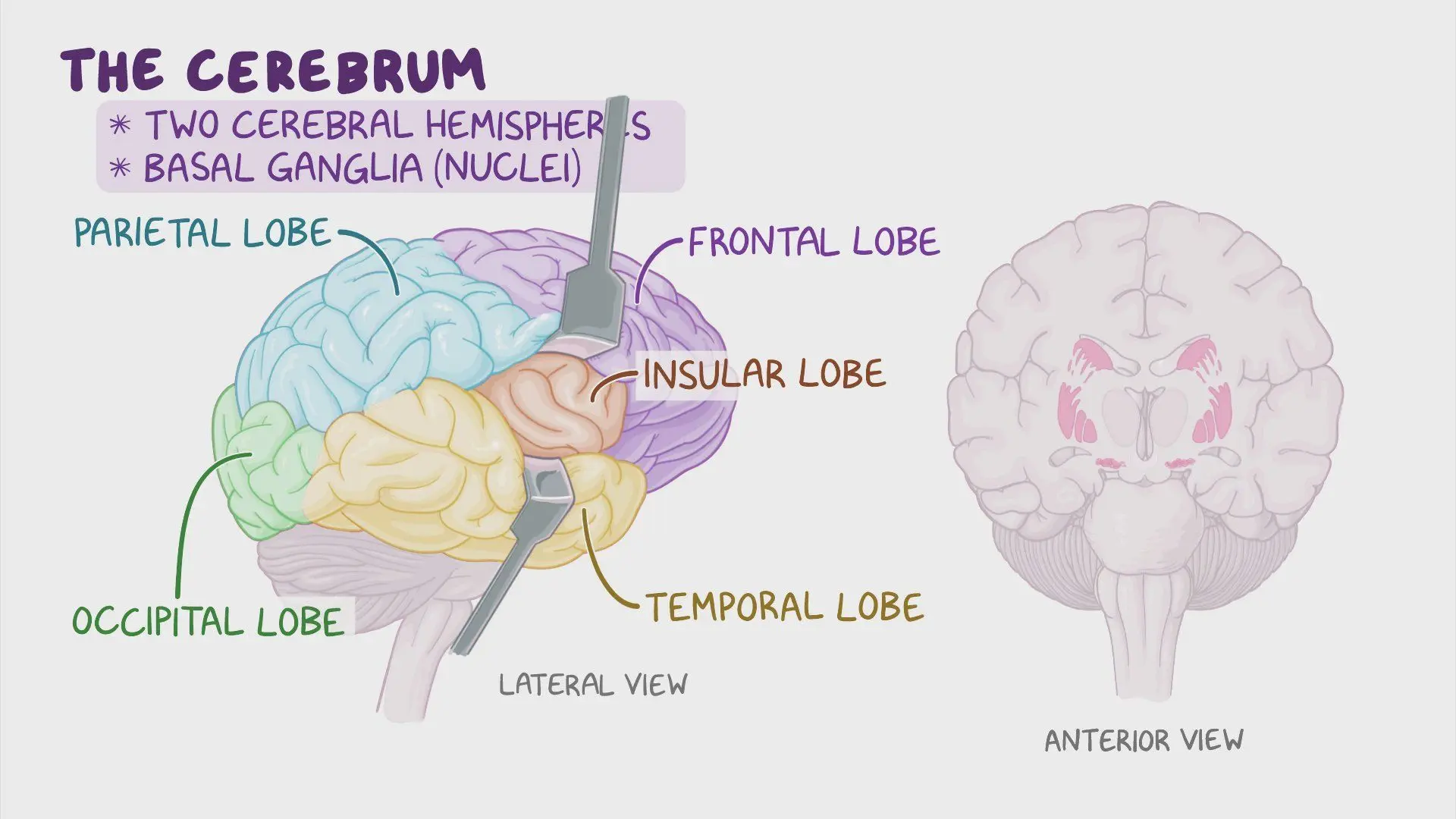
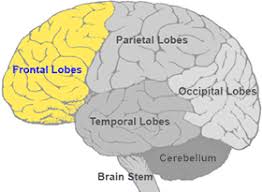
frontal lobe
the part of the cerebral cortex involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language; contains motor cortex
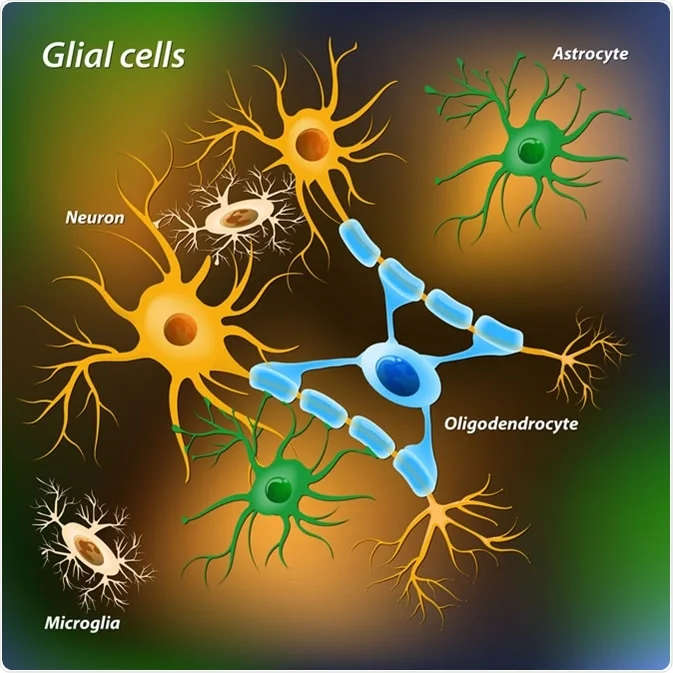
glial cell
a nervous system cell that provides physical and metabolic support to neurons, including neuronal insulation and communication, and nutrient and waste transport
hindbrain
division of the brain containing the medulla, pons, and cerebellum
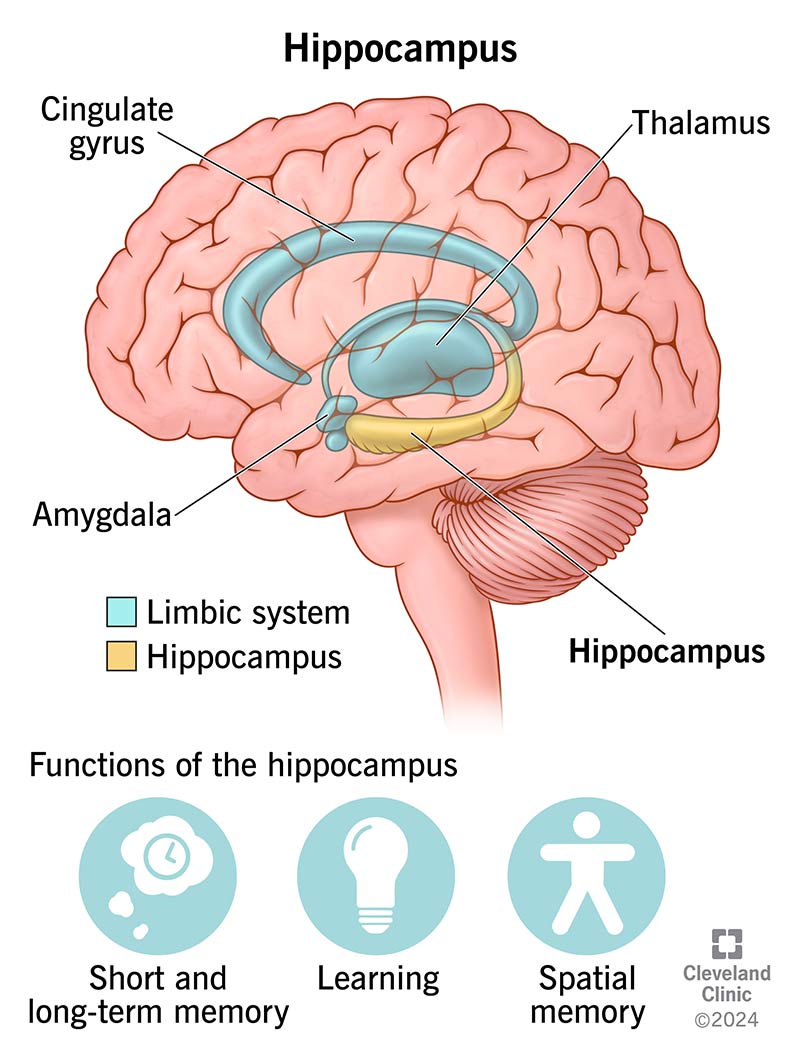
hippocampus
structure in the temporal lobe associated with learning and memory
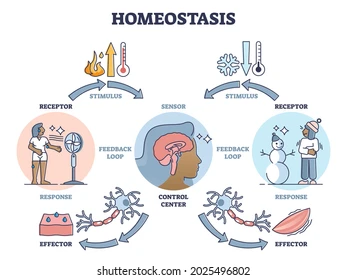
homeostasis
state of equilibrium—biological conditions, such as body temperature, are maintained at optimal levels
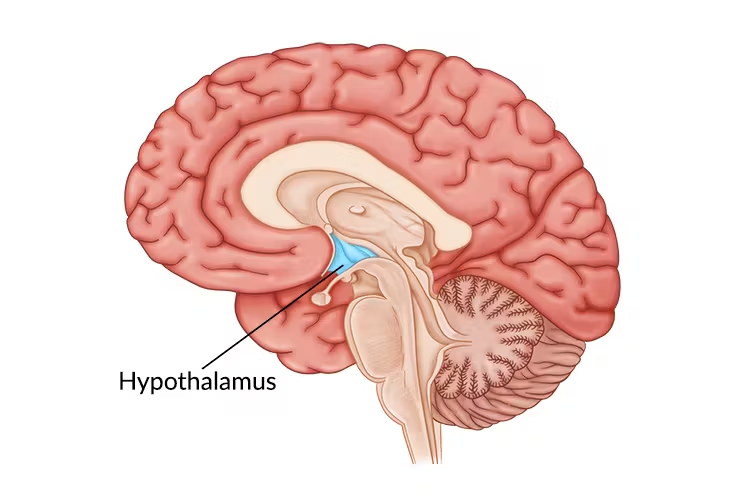
hypothalamus
forebrain structure that regulates sexual motivation and behavior and a number of homeostatic processes; serves as an interface between the nervous system and the endocrine system
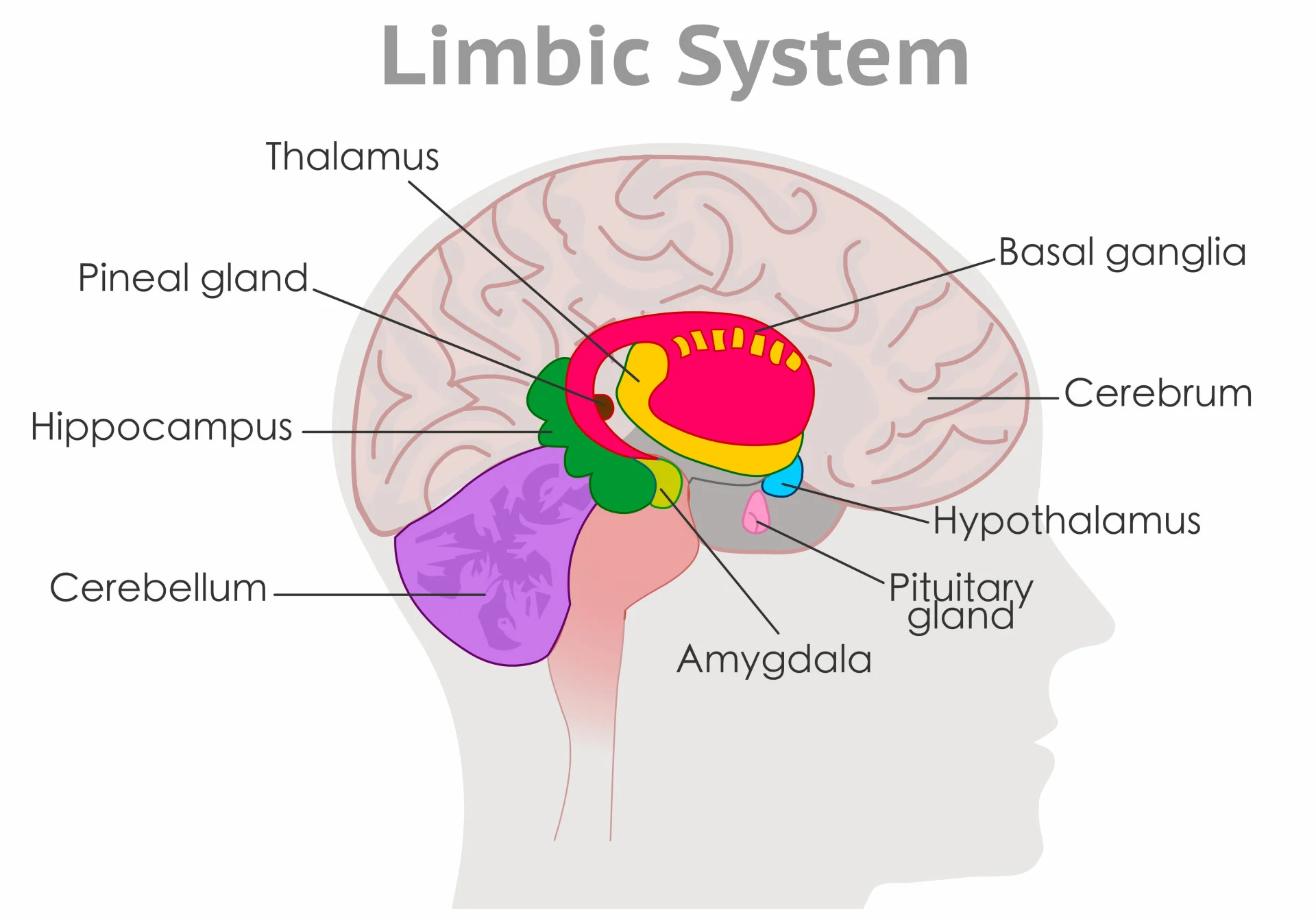
limbic system
the collection of structures involved in processing emotion and memory
longitudinal fissure
a deep groove in the brain’s cortex
medulla
hindbrain structure that controls automated processes like breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate
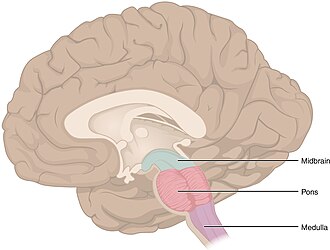
midbrain
division of the brain located between the forebrain and the hindbrain; contains the reticular formation
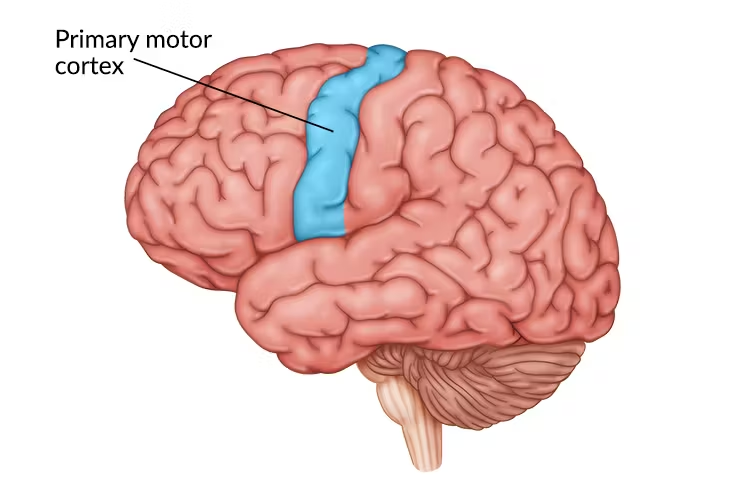
motor cortex
a strip of the cortex involved in planning and coordinating movement
myelin sheath
a fatty substance that insulates axons which increases the speed at which the signal travels

neuron
cells in the nervous system that act as interconnected information processors, which are essential for all of the tasks of the nervous system; the central building blocks of the nervous system
neuroplasticity
the ability of the nervous system to change and adapt