Unit 1: Intro and Brain Gross Anatomy Objectives
1/40
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Sagittal plane
Separates the body into left and right sides.
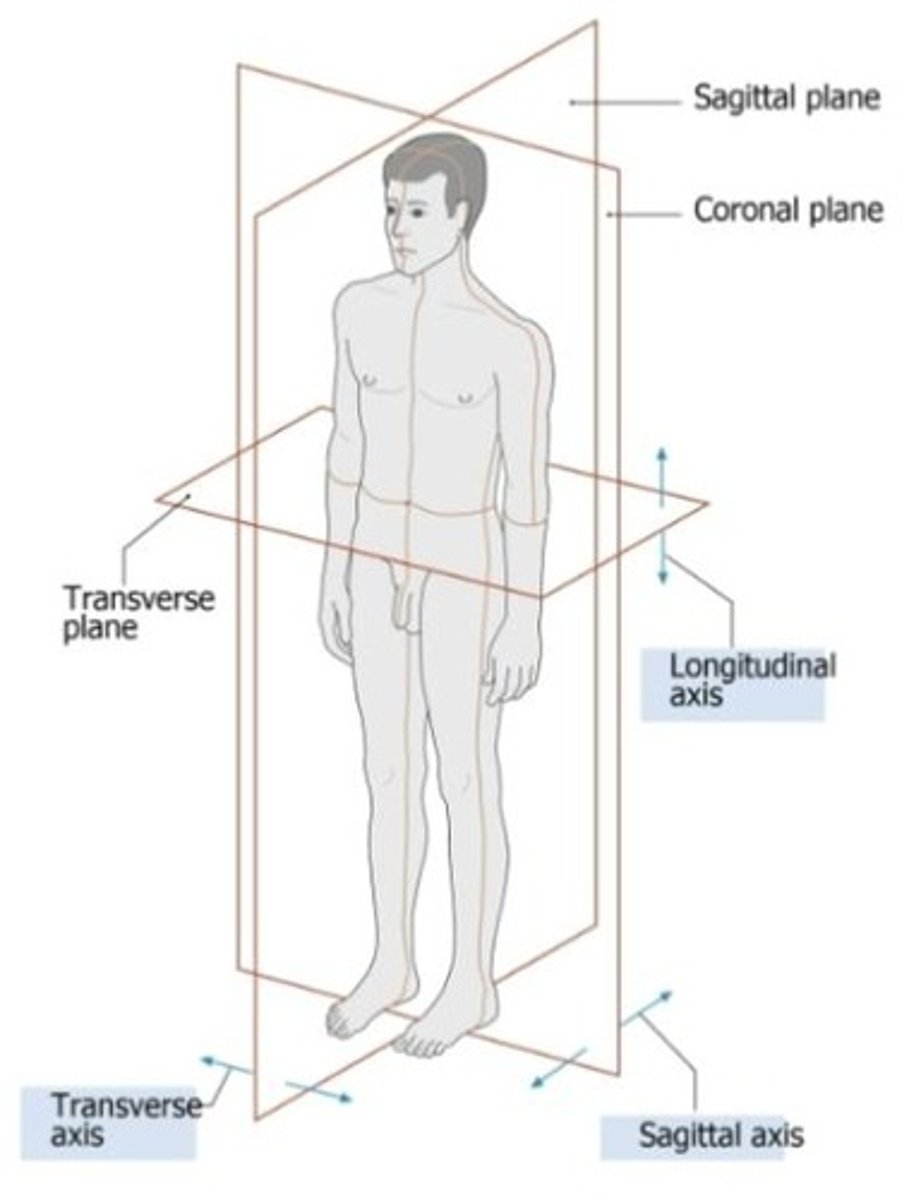
Transverse plane
Separates the body into superior and inferior halves.
Coronal (frontal) plane
Separates the body into anterior and posterior halves.
Which axis moves the sagittal plane
transverse axis
Which axis moves the transverse plane
longitudinal axis
Which axis moves the frontal plane
sagittal axis
Functions of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) function
Protect the brain and spinal cord from trauma
Supply nutrients to the CNS
Support the brain
Methods of protection for the brain
Bones of the skull
Cranial meninges
CSF
Blood brain barrier
Dura mater
Outermost layer, thick connective tissue made of collagen.
Arachnoid mater
Middle 'web-like' layer.
Pia mater
Surface of the CNS.
Blood brain barrier
Helps regulate chemical environment; anything fat soluble can cross.
Longitudinal fissure
Separates the left and right hemispheres.
Transverse fissure
Separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum.
Central sulcus
Separates the frontal and parietal lobes.
Lateral sulcus
Separates the temporal and frontal lobe.
Precentral gyrus
Primary motor area, anterior to the central sulcus.
Postcentral gyrus
Primary somatosensory area; posterior to the central sulcus.
Primary motor area
anterior to the central sulcus, initiates voluntary movements by sending signals to the muscles
Primary somatosensory area
posterior to the central sulcus, detects and processes sensory information from the body, such as touch, temperature, pain, and body position
Premotor area
anterior to the primary motor area and contains motor programs, sends information to the motor area
Motor programs
"muscle memory", complex muscle actions you do not need to think about (running, walking upstairs)
Primary somatosensory association area
Interpretation of sensory stimuli
Broca's area
Location in the lower anterior area of the premotor area; functions in planning speech
Temporal lobe
hearing and smell
Occipital lobe
vision association cortex
Frontal lobe
planning, decision making, problem-solving, judgement, attention
Parietal lobe
sensory processing
Basal nuclei
controls starting, stopping, and intensity of motor movements, inhibits antagonistic muscles during movements
Huntington's disease and basal nuclei
Degeneration of the basal nuclei causes people to lose the neurons responsible for regulating movements so they may drop things or lose the ability to properly aim their movements
Function of thalamus
relays information
Function of hypothalamus
coordinates the nervous system and endocrine systems; regulates body temperature, thirst, hunger, sex drive, basic emotions, endocrine system, autonomic nervous system
Parts of the brain stem
contains midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
Function of midbrain
Contains centers for startle reflexes
contains the Substantia Nigra
Pathway for communication between lower and upper brain function
What is the corpora quadrigemina
Four bumps called colliculi on the dorsal surface of the midbrain
Function of superior colliculi
visual startle reflex
Function of inferior colliculi
auditory startle reflex
Location and function of the pons
the large bulb looking structure on the anterior portion of the brainstem; helps regulate respiration, helps coordinate involuntary skeletal muscle movements and muscle tone, relays information to and from the brain/spinal cord
Location and function of the cerebellum
posterior and inferior to the cerebrum; adjusts the postural muscles of the body to maintain balance, programs and fine-tunes (smooths) voluntary and involuntary movements
Location and function of medulla oblongata
Physically connects the brain with spinal cord
It is a relay station, a house for cranial nerve nuclei, and controls viscera
Blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate
Location of medullary pyramids
Ridge like structures running the length of the medulla oblongata on the ventral side