13.0 Fiscal and Supply Side Policies (All in 1)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What does fiscal policy involve
The manipulation of government spending, taxation, and the budget balance to influence the economy
What are the two main fiscal policy instruments
Government spending and taxation
What is the macroeconomic function of fiscal policy
To stimulate economic growth and stabilise the economy
What is the microeconomic function of fiscal policy
Targeted spending/taxation to influence specific sectors or address market failures
What is expansionary fiscal policy
Policy to increase AD by raising government spending or reducing taxes
Draw expansionary fiscal policy
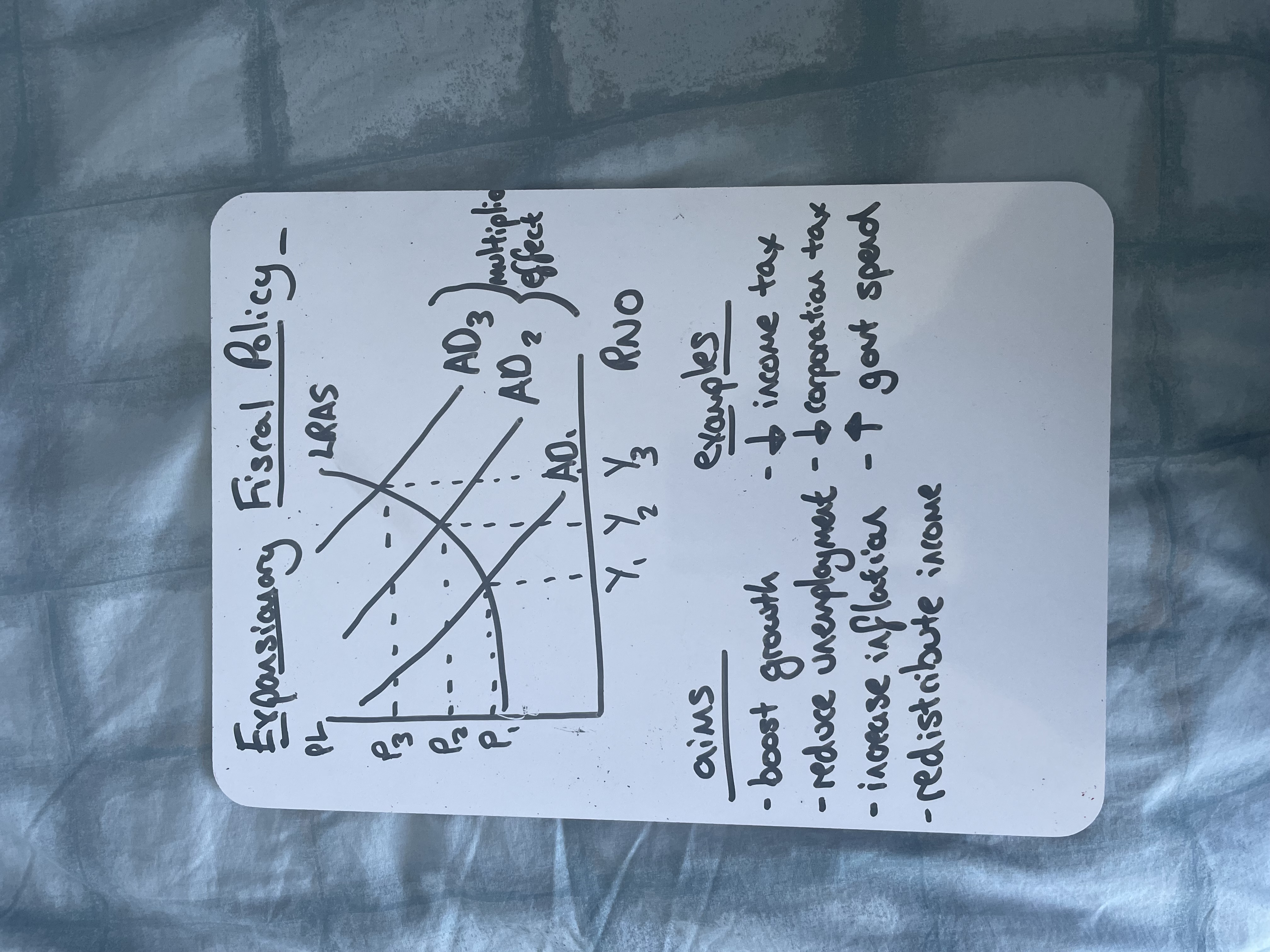
What is contractionary fiscal policy
Policy to reduce AD by cutting spending and increasing taxes
Draw contractionary fiscal policy
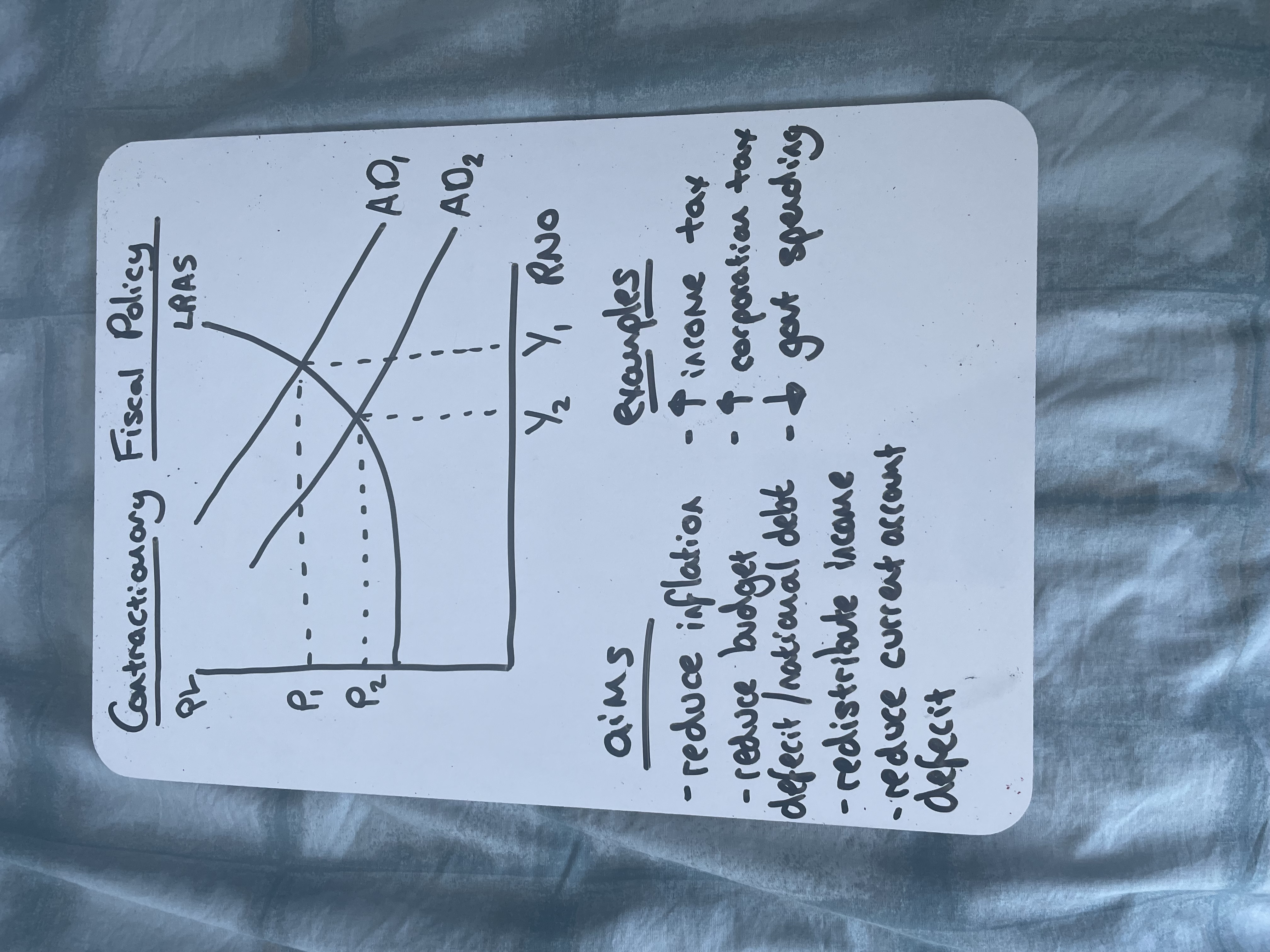
Disadvantages of expansionary fiscal policy
Worsen budget deficit - increases national debt
Higher interest rates
Can lead to high inflation
Time lag
Disadvantages of contractionary fiscal policy
Can reduce economic growth - leads to unemployment
Worsen inequality
Could lead to a recession
Time lag
Harms business and consumer confidence
How can fiscal policy improve AS
By reducing taxes, subsidising training, increasing education, healthcare and infrastructure spending
How do subsidies for training affect AS
They lower firm costs and increase labour productivity
How can government spending influence the circular flow of icome
By injecting demand into sectors needing stimulation
Which areas receive most UK government spending
Pensions, welfare, health and education
What is capital expenditure
Spending on long-term assets like roads and schools
What is current expenditure
Recurring spending on short-lived goods/services like NHS drugs
What are transfer payments
Welfare payments with no exchange of goods/services (e.g. state pensions)
Why do government engage in public expenditure
To ensure minimum living standards, promote equality and simulate growth
What are the main reasons for taxation
To raise revenue, redistribute income, influence behaviour, correct markets failures
What are direct taxes
Taxes on income or profits paid directly by the individual or firm
What are indirect taxes
Taxes on expenditure (e.g. VAT), usually included in the price of goods
What is progressive tax
A tax where the average rate increases as income increases
What is proportional tax
A tax with a constant rate regardless of income
What is a regressive tax
A tax where lower-income individuals pay a higher proportion of their income (e.g. VAT)
What are Adam Smith’s four canons of taxation
Low collection cost, certainty, convenience, equity
What is the UK’s main source of tax revenue
Income Tax
What is the difference between the budget defecit and national debt
The deficit is the annual gap between spending and revenue; debt is the accumulation of past deficits
What is a cyclical deficit
A temporary deficit caused by economic downturns
What is structural deficit
A persistent imbalance not related to the economic cycle
What is crowding out
Government borrowing reduces private sector investment due to higher interest rates
Why might high national debt be problematic
It can raise borrowing costs and lead to higher taxes or spending cuts
How can national debt affect investor confidence
Excessive debt may require higher interest rates to attract investment
What does the Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) do
Analyses UK public finances, provide economic forecasts, assesses govt targets
What fiscal targets does the OBR monitor
Balancing the budget in 5 years and reducing net public sector debt
What are supply-side policies
Government measures designed to increase long-run productive potential of the economy by improving efficiency and productivity of markets
What are supply-side improvements
Increases in productive potential arising from the private sector without government intervention
Draw effects of a supply-side policy on a diagram
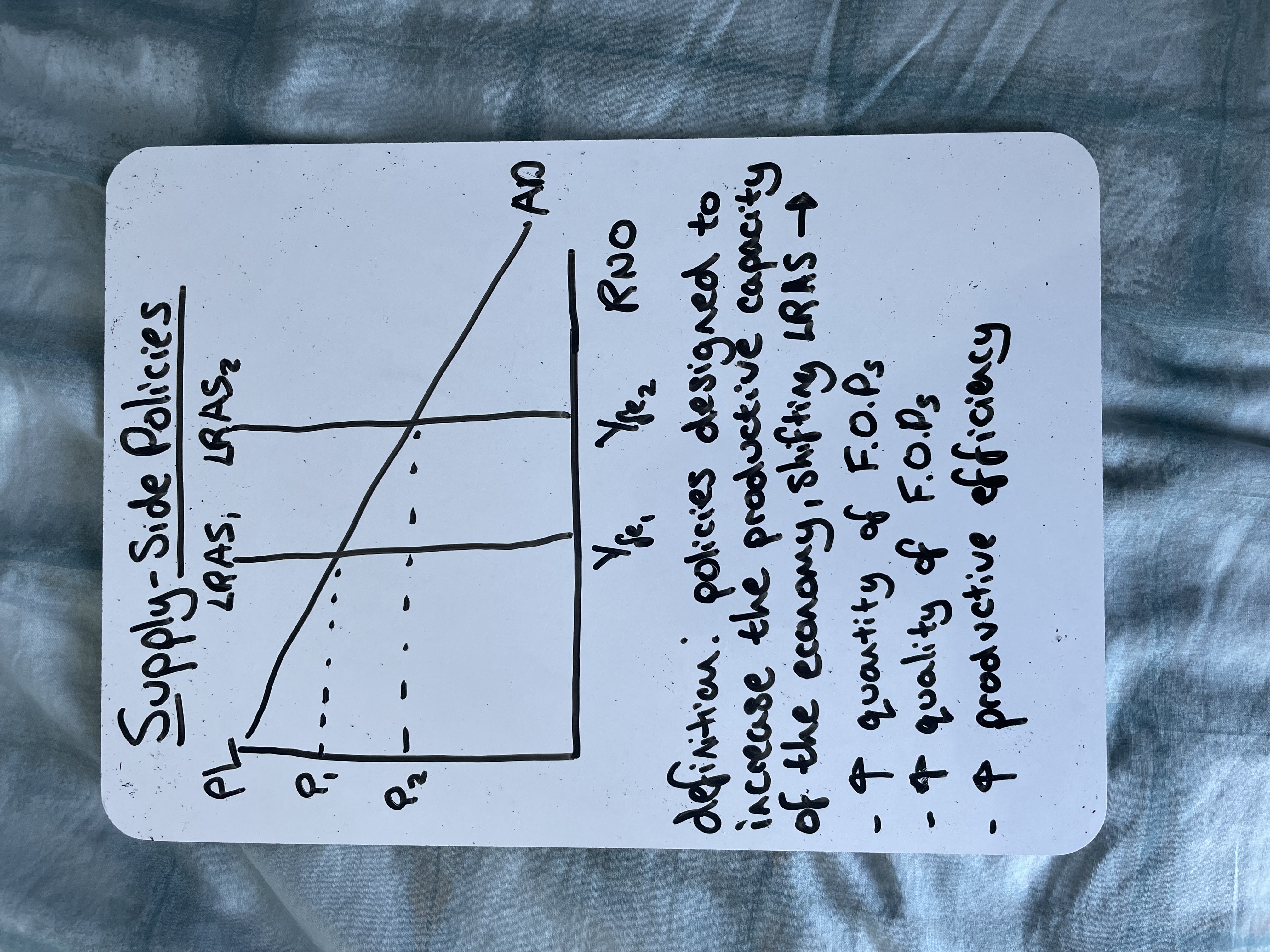
How can tax cuts act as a supply-side policy
They increase incentives for work and investment, boosting productivity and potential output
How does deregulation promote supply-side improvements
It reduces barriers to entry, encouraging competition and innovation, which improves efficiency and productivity
How do education and training policies help achieve supply-side improvements
By improving worker skills and productivity, leading to higher output and economic growth
How does infrastructure spending contribute to supply-side improvements
Improved infrastructure enhances efficiency and connectivity, supporting higher economic output
How do income tax cuts increase potential output
By increasing incentives to work, they may raise labour supply and productivity
How do corporation tax cuts promote economic growth
They encourage investment in capital and innovation, enhancing productive capacity
How do supply-side policies reduce structural unemployment
By improving education, training, and labour market flexibility
How can supply-side policies reduce inflationary pressure
By increasing productive capacity, they shift the LRAS curve right, reducing cost-push inflation and demand-pull inflation
How do supply-side policies affect the current account of the balance of payments
By improving productivity and competitiveness, they can increase exports and reduce the trade deficit
How can education and training reduce the natural rate of unemployment
By increasing employability and reducing skill mismatches in the labour market
What are free market supply side policies
Policies that reduce govt intervention and allow market forces to operate freely (e.g. deregulation and privatisation)
How do tax cuts promote free market supply-side outcomes
By incentivising work, investment and innovation, which boosts productivity
How does deregulation improve economic efficiency
It increases competition and removes unnecessary restrictions on business
What is the role of privatisation in free market supply-side policy
It transfers ownership to the private sector, which may operate more efficiently due to profit motives
How do labour market reforms (e.g., reducing NMW) promote efficiency
The allow wages to be set by supply and demand, potentially increasing employments and flexibility
What are interventionist supply-side policies
Policies where the government actively intervenes to improve economic performance
Why is spending on healthcare considered a supply-side policy?
Healthier workers are more productive, reducing absence and increasing output
How can infrastructure spending improve long-run economic performance
It lowers transport and communication costs, increasing business efficiency and ouptut
How does industrial policy (e.g. subsidies for R&D) support supply-side improvements
It encourages innovation and technological advancement, raising productivity
What are some macroeconomic effects of supply-side policies
Higher potential output, lower unemployment, improved competitiveness and reduce inflationary pressure
What are some microeconomic effects of supply-side policies
Increased efficiency, improved productivity, enhanced competition and better resource allocation