5- Price Discrimination
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What are the conditions necessary for price discrimination
Price maker
Prevent re sale
Information to separate the market
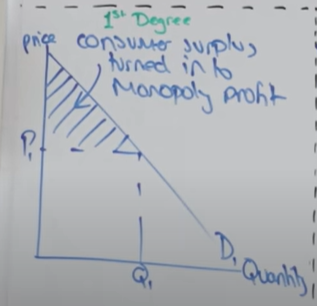
What is 1st degree price discrimination
When consumers are charged the exact highest price they are willing to pay
What occurs in 1st degree price discrimination
All consumer surplus is converted into monopoly profit
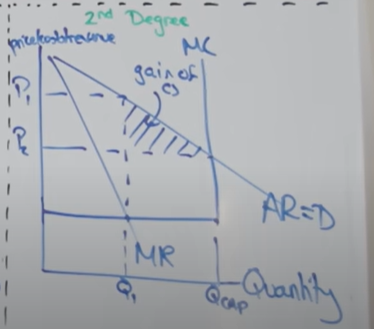
What is 2nd price discrimination
Bulk buying - changing different prices based on the quantity purchased - crate of coke is cheaper than 6 individual cokes
Draw diagram for 1st degree price discrimination
Draw diagram for 2nd degree price discrimination
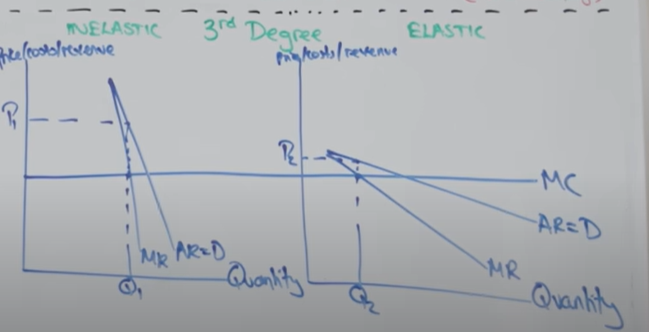
What is 3rd price discrimination
Where the firm is able to split a market into different groups of elasticity (Elastic and Inelastic groups) Firms can do this by looking at factors such as time, age of these areas
Example: Firms can separate two towns that have different amounts of income. In the richer town they can charge a higher price and lower price in the poorer town to maximise profits
Draw the 3rd degree price discrimination diagram
Cons of using price discrimination
Exploiting consumers results in allocative inefficiency
Inequalities - If in 1st price discrimination lower income groups are targeted then inequality will rise
Anti- competitive pricing - In 3rd degree discrimination the low prices could cause a drop in competitiveness
Pros of price discrimination
Increase in dynamic efficiency - As firms gather a bigger profit from consumers when using price discrimination
As 3rd degree and 2nd degree discrimination can cause an increase in units sold we can experience economies of scale
In 3rd and 2nd degree some consumers could benefit from this discrimination
Profits from using price discrimination could allow firms to cross subsidise other sectors to keep them afloat