forensics impression evidence
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
patent impression
2D
an impression visible to the unaided eye
latent impression
•2D
•an impression requiring special treatment (chemicals) to be visible to the unaided eye
plastic impression
•3D
•an impression in soft materials such as soil, snow, or congealing blood, and mud
What questions can shoe, and foot impressions answer to provide clues about the crime scene?
how many people were at the crime scene?
were people moving?
what direction were they moving in?
what entrance and exit routes?
is there evidence of anyone sustaining injuries at the crime scene?
what information about an individual can be revealed from impressions?
•shoe size
•height of person
•weight
•gait
What info does the databases contain and what can they tell investigators?
• contains names of specific manufacturers and tread pattern used to identify different types of shoes
• crime scene investigators can search to find: manufacturer and company that produced the sole and bought sole for shoe
what factors can help personalize shoe wear patterns?
• shape of foot
• body weight
• activity types
• what surface they walk
• if toes point out/in
• pressure outside/inside heel
• holes, cuts, debris on shoe
What is the difference between gait and tracks?
gait: a persons pattern of moving
track: if persons running, walking, injured, older/disabled: movement of feet going toward direction
step 1: photographing
take photograph with and without ruler
fill cameras viewfinder with impression
take photograph with lens perpendicular to print/evidence
step 2: lifting latent
several different methods used
luminol (blood)
dusting (make visible footprint/print)
electrostatic lifting and gel lifting
step 3: casting plastic
• if impression in sand or soil, plaster of paris impression is made
• if impression in snow, casting material is called dental stone
What is the difference between luminol, dusting, and electrostatic/ gel-lifting?
• luminol: chemical spray, apply on surface uses uv light
• dusting: powder use to reveal impressions
• electrostatic: uses charge to hold dust particles of latent print in place
• gel: gel sandwiched between paper/plastic cover sheet
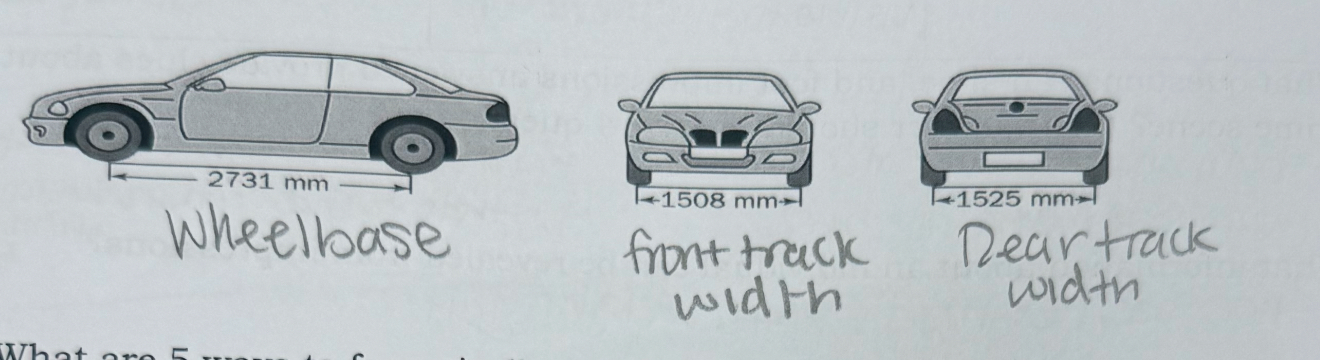
What 2 characteristics do forensic scientists examine tire tread and impressions for?
tread pattern
wear characteristics
(track width wheel base)
What situations cause the following type of tire impressions?
PATENT
• after vehicle has driven through a fluid like oil, tar, or blood after abruptly accelerating or stopping
What situations cause the following type of tire impressions?
LATENT
• on asphalt or concrete roads by manufacturers oils used to keep tires soft and pliable
What situations cause the following type of tire impressions?
PLASTIC
• off-road surfaces, mud, grass, sand, and snow
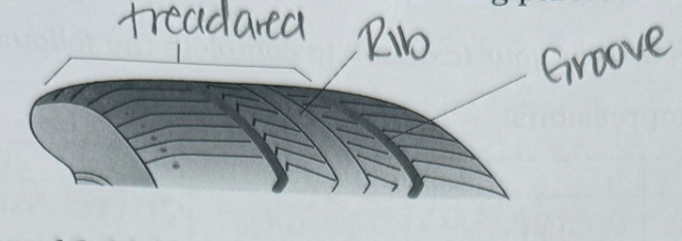
The anatomy of a tire is made up of ribs and grooves. What is the difference between ribs and grooves? What is the purpose of ribs and grooves on a tire?
ribs: ridges running around circumference of tire
grooves: indentations
purpose: to channel water away and provide traction as surface makes contact with road/ground
Refer to Figure 16-10 and label the following parts of a tire tread:
Refer to Figure 16-11 in your textbook Label the diagram below:
What are 5 ways to forensically establish car movements?
Skid marks
Yaw marks
Tire scrubs
Indentation Marks
Abrasion Marks
Cutting Marks