Musculoskeletal System
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/182
Earn XP
Description and Tags
axial and appendicular skeleton, blue highlight/underline = important, yellow highlight and underline = import and MAYBE ON THE TEST
Last updated 11:36 PM on 9/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
1
New cards
Bones are dominated by what type of tissue?
Bone CT dominates what specific organ?
2
New cards
Other bone tissues
nervous and blood CT
3
New cards
What are the __5 main functions of bones__?
__Support, protection, movement, mineral storage, and energy metabolism__ are the functions of what organ?
4
New cards
What cell do osteoprogenitor stem cells turn into?
Where are osteoblasts derived from?
5
New cards
What do ^^osteoblasts^^ do?
What cell actively produces and secretes bone matrix?
6
New cards
What cell breakdown and reabsorbs bone?
What do ^^osteoclasts^^ do?
7
New cards
Extra info about osteoclasts
derived from WBC, secrete hydrochloric acid and lysosomal enzymes
8
New cards
What type of bone is longer than it is wide?
What are long bones?
9
New cards
What are short bones?
What are cube shaped bones classified as?
10
New cards
What are bones that don’t fit into the long/short bone category called?
What are irregular (weirdo) bones?
11
New cards
What is compact bone?
What is the dense outer layer of bone called?
12
New cards
What is the inside/”internal network” of bone called?
What is spongy bone?
13
New cards
What is the __function of trabeculae__?
What are the “little beams” that __help dissipate force__ called?
14
New cards
What part of the bone is the diaphysis?
What is the middle/long (shaft) part of a bone called?
15
New cards
extra stuff about long bones
well vascularized, filled with red marrow!
16
New cards
What is the ^^deep, hollow part of a bone^^ called?
Where is the ^^medullary cavity^^ located?
17
New cards
What is the most __important function of trabeculae__?
What structure __dissipates forces/stress of the body__?
18
New cards
What provides information about the functions of bone muscle?
What is the purpose of bone markings/landmarks?
19
New cards
What does the osteon of a compact bone make passage for?
Where are the blood/lymph vessels and nerves located in the bone?
20
New cards
What bone is too small to contain osteons, but has trabeculae instead?
^^What are some characteristics of spongy bone?^^
21
New cards
What is the term for bone tissue formation?
What happens in ^^ossification^^?
22
New cards
__What growth does the epiphyseal plate allow__?
Why does the __diaphysis__ grow?
23
New cards
__**What separates/pushes the diaphysis and epiphysis away from each other?**__
The __epiphyseal plate__ separates was two structure?
24
New cards
__**bone growth**__
* cartilage cells stack on top of each other (length)
* chondroblasts (cartilage cells) at the top of the stack divide fast
* older chondroblasts enlarge and signal surrounding matrix to calcify and then they die/disintegrate
* trabeculae partially eroded by osteoclasts
* osteoblasts then cover trabeculae with bone tissue! - new bone formation aka ossification
* trabeculae eaten away from tips by osteoclasts
* chondroblasts (cartilage cells) at the top of the stack divide fast
* older chondroblasts enlarge and signal surrounding matrix to calcify and then they die/disintegrate
* trabeculae partially eroded by osteoclasts
* osteoblasts then cover trabeculae with bone tissue! - new bone formation aka ossification
* trabeculae eaten away from tips by osteoclasts
25
New cards
growth of endochondral bones during childhood and adolescence
* bones lengthen by growth on epiphyseal plate
* cartilage replaced w/ bone CT at same rate as growth = bone lengthening
* cartilage replaced w/ bone CT at same rate as growth = bone lengthening
26
New cards
Growth of endochondral bones as adolescence ends
* epiphyseal plate thins and stops growing
* replaced by bone tissue
* bone stops growing when diaphysis and epiphysis fuse
* replaced by bone tissue
* bone stops growing when diaphysis and epiphysis fuse
27
New cards
What is being added in appositional growth?
What is it called when bone tissue gets added to the surface of bone?
28
New cards
__**what does growth hormone do for bone growth?**__
What hormone from the pituitary gland tells bones to __“keep growing?__”
29
New cards
__**What hormone ensures that skeleton retains proper proportions?**__
What does __thyroid hormone__ do for bone growth?
30
New cards
^^How does growth hormone make bones grow^^?
What hormone ^^stimulates the epiphyseal plate^^?
31
New cards
__**What do sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone) do for bone growth?**__
Which hormone promotes bone growth and __induces the closure of the epiphyseal plate__?
32
New cards
cartilage facts
very flexible. found throughout body
33
New cards
What are the three types of cartilage?
hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic
34
New cards
What are the characteristics of ^^hyaline cartilage^^?
What cartilage ^^provides flexibility, resilience^^, and stays in one area but doesn’t move?
35
New cards
What cartilage ^^tolerates bending due to its elastic fibers?^^
What are some characteristics of ^^elastic cartilage^^?
36
New cards
What cartilage ^^resists strong compression and tension of the body^^?
What does ^^fibrocartilage^^ (intermediate/hybrid) do?
37
New cards
hyaline cartilage locations
rings of trachea, ribs, sternum
38
New cards
fibrocartilage locations
pubis symphysis, menisci
39
New cards
elastic cartilage locations
epiglottis, outer ear
40
New cards
What is the axial skeleton consist of?
What skeleton does the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage make up?
41
New cards
Number of bones
* 206 names bones
* 80 axial
* 126 appendicular
* 80 axial
* 126 appendicular
42
New cards
^^What is the most complex structure of the axial skeleton?^^
the ^^skull^^
43
New cards
__**What function do the cranium bones have?**__
Which bones __enclose/protect the brain and provide attachment sites__ for some muscles?
44
New cards
__**What bones provide the framework of the face and anchor facial muscles?**__
Why are __facials bones__ so important?
45
New cards
__**skull bones (8)**__
* __paired: parietal and temporal__
* __unpaired: frontal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid__
* __unpaired: frontal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid__
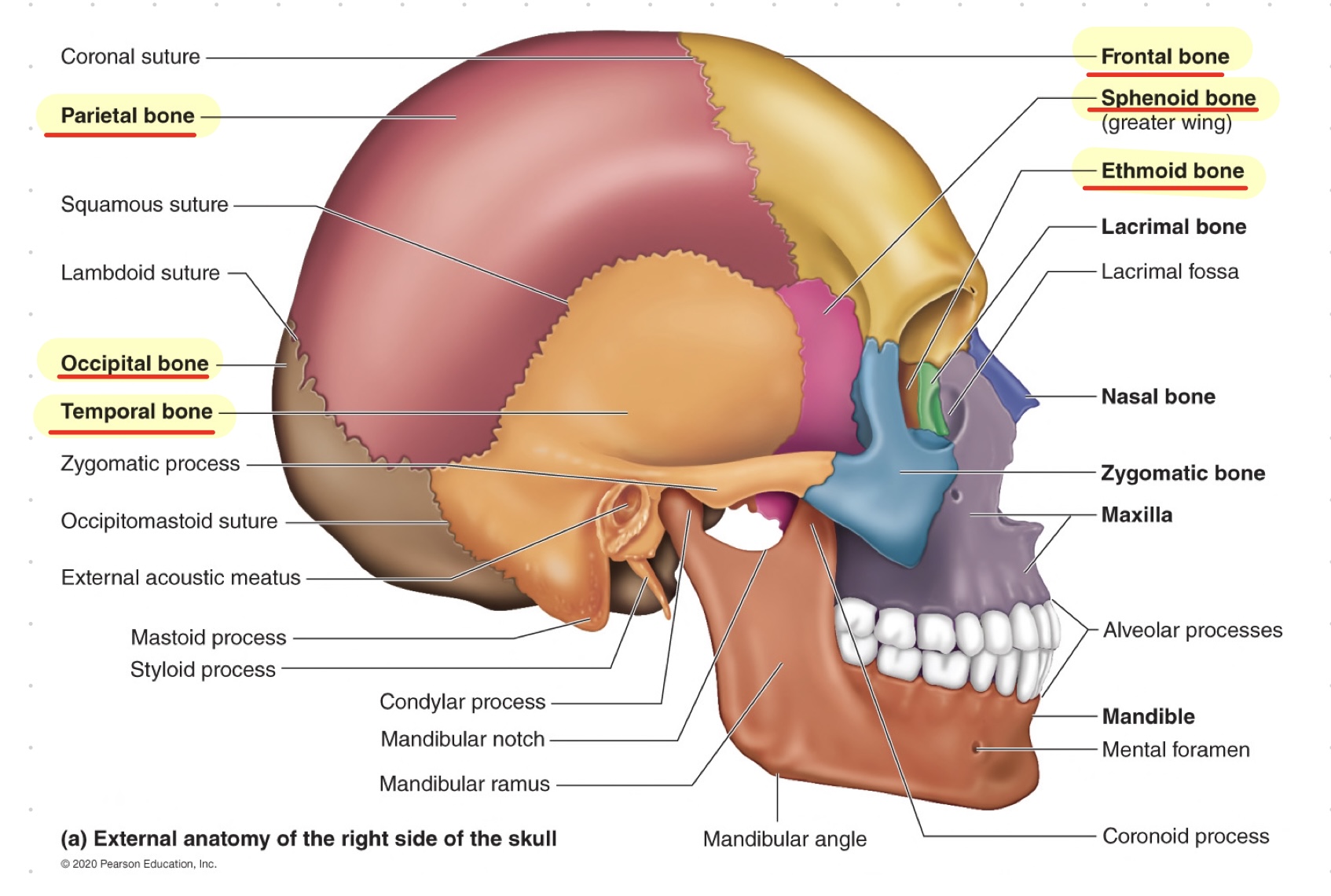
46
New cards
__**What are the four immovable sutures?**__
__coronal, squamous, sagittal, lambdoid__
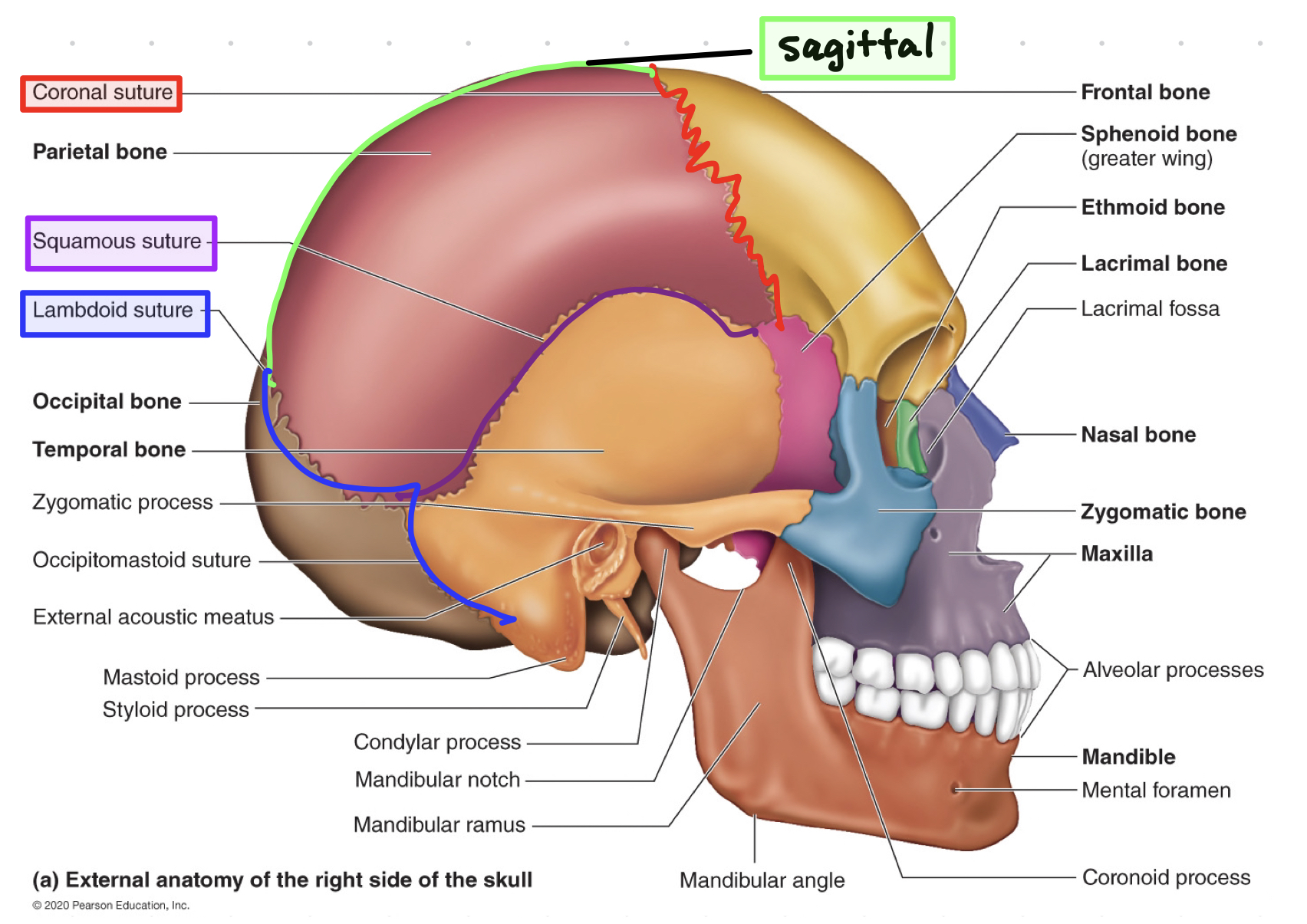
47
New cards
^^Where is the coronal suture located?^^
What suture do the parietal and frontal bone form?
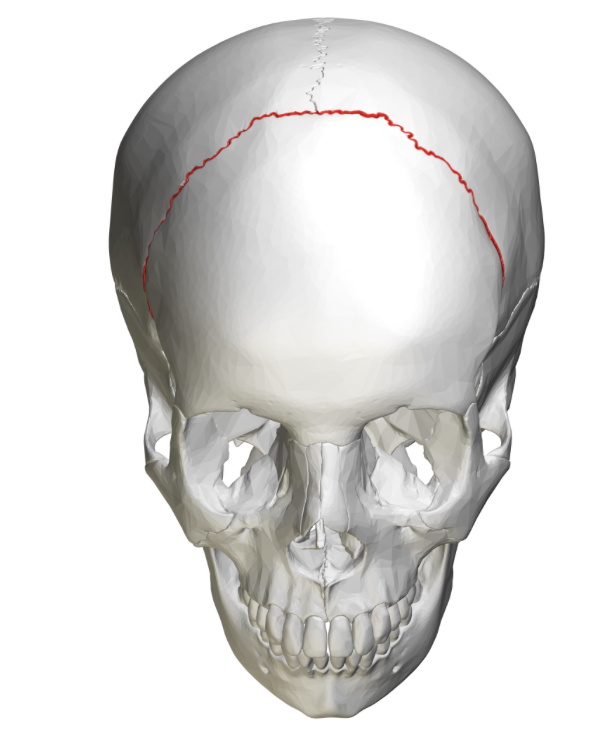
48
New cards
^^Where is the squamous suture located?^^
What suture do the partial and temporal bone form INFERIORLY?
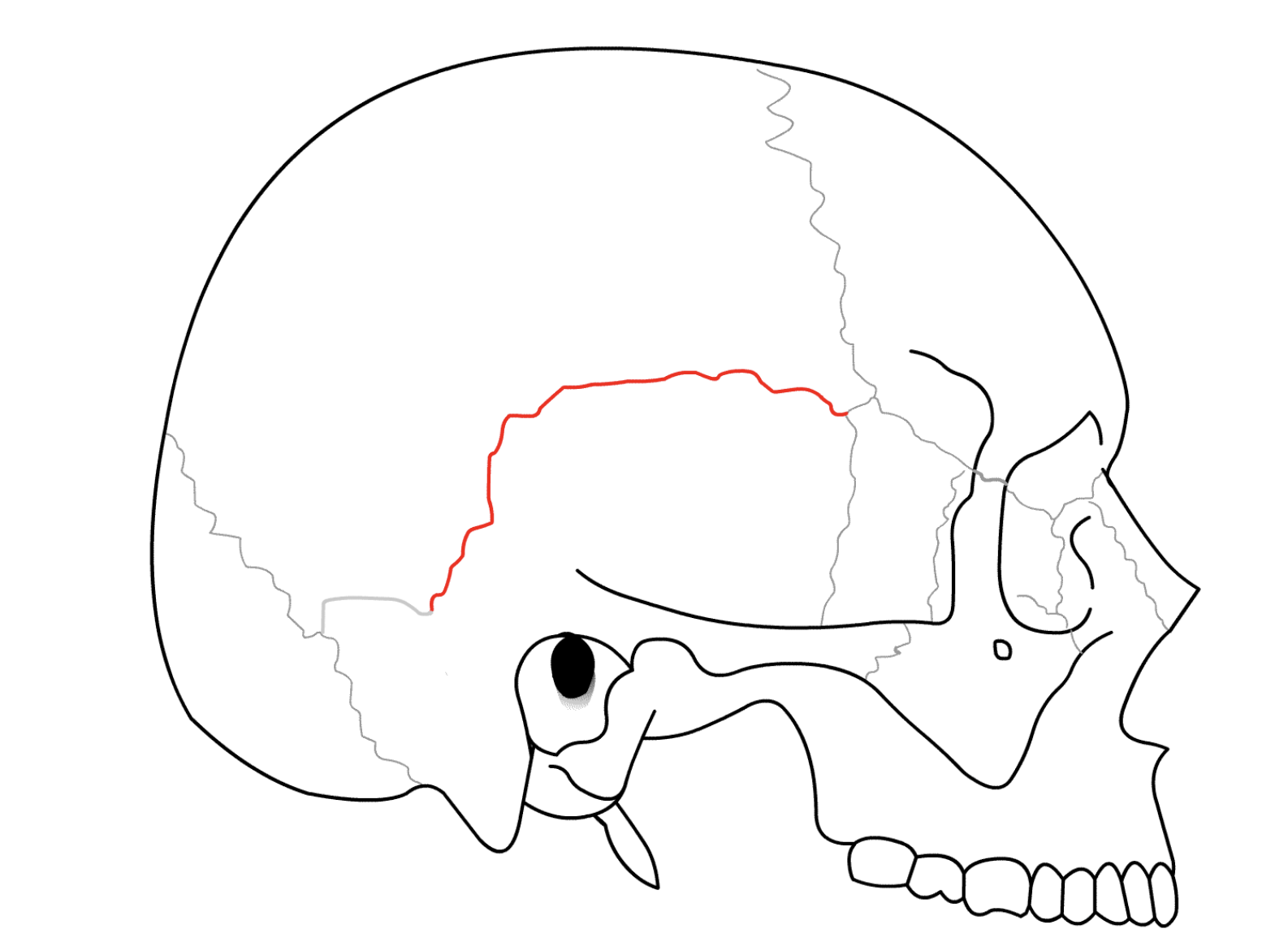
49
New cards
^^Where is the sagittal suture located?^^
What suture do the left and right parietal bone form SUPERIORLY?
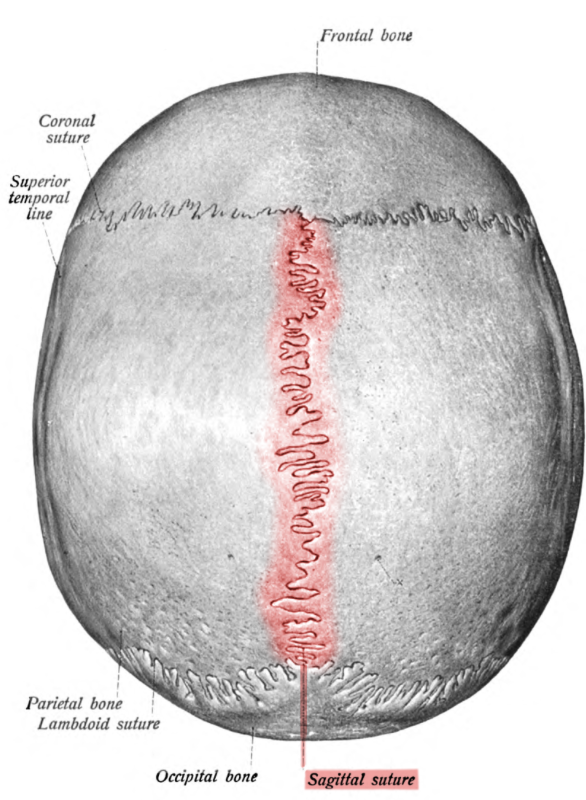
50
New cards
^^Where is the lambdoid suture located?^^
What suture do the parietal and occipital bone form POSTERIORLY?
51
New cards
__**Which bone is the largest, strongest, and ONLY movable facial bone?**__
What are some characteristics of the __mandible__(lower jawbone)?
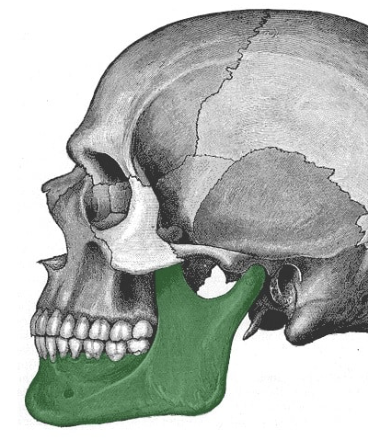
52
New cards
Which facial bone provides ^^facial structure^^ and doesn’t articulate with the mandible?
What are some characteristics of the ^^maxillary bone^^?
53
New cards
What are the prime movers(agonists) in mastication(chewing)?
^^What do the masseter and temporalis do?^^
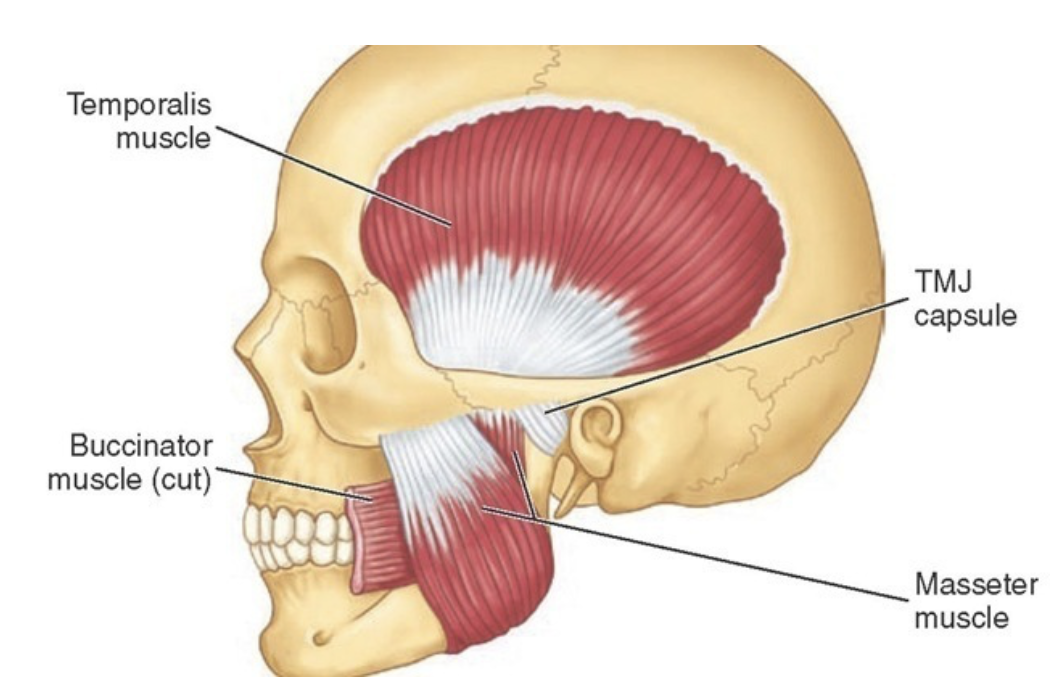
54
New cards
What muscles allow the mandible to go side to side and front and back?
^^What do the medial and lateral pterygoid do^^ for the mandible?
55
New cards
What separates the maxillary and mandible bone?
What two bones are separated by the teeth?
56
New cards
hyoid bone facts
* inferior to the mandible
* ^^only bone w/ no direct articulations^^
* movable base for the tongue
* ^^only bone w/ no direct articulations^^
* movable base for the tongue
57
New cards
__**What are the functions of the vertebral column?**__
What 33 bones __surround and protect the spinal chord__ and help us stand erect?
58
New cards
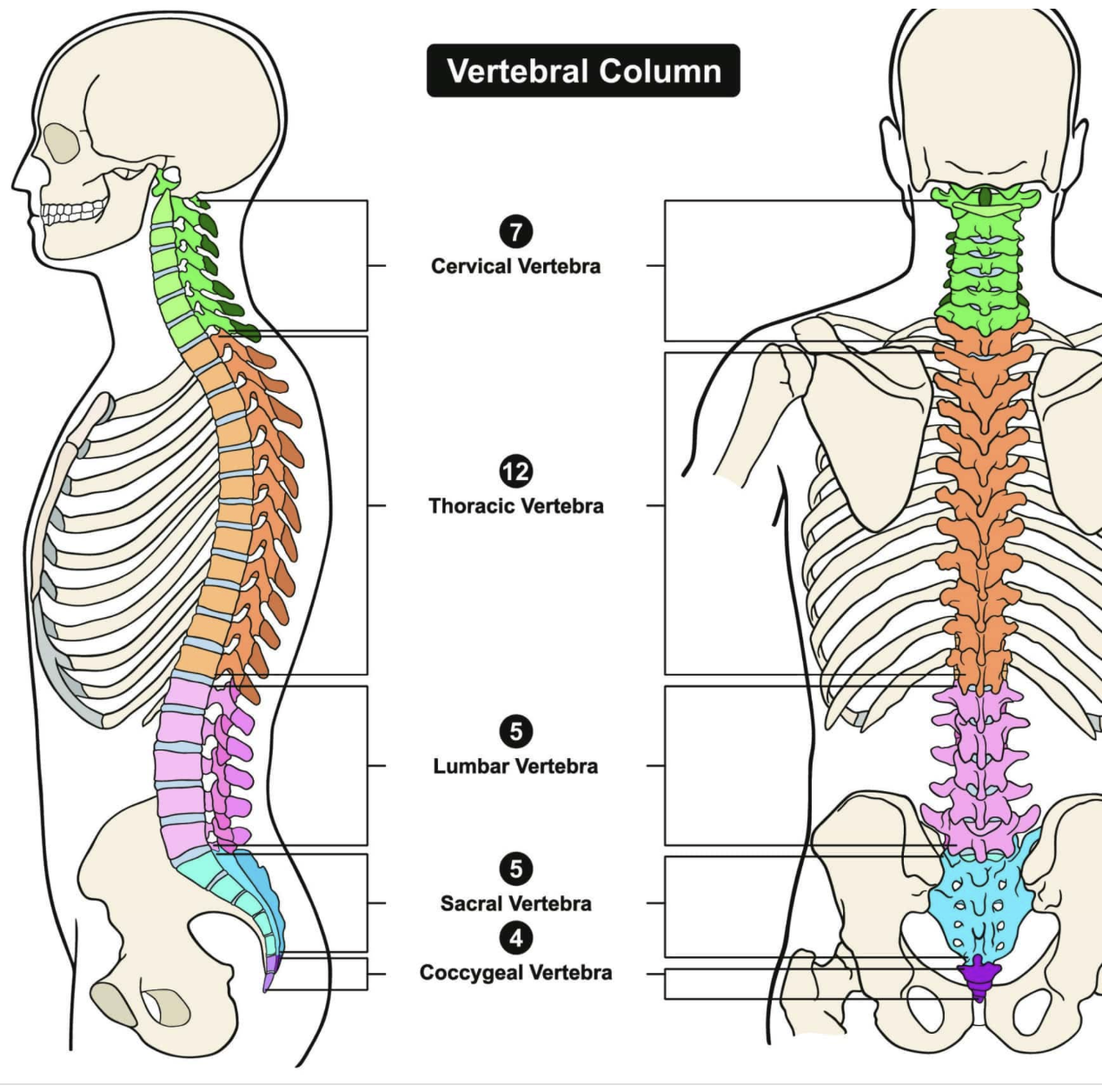
^^What are the five major regions of the vertebral column?^^
* 7 cervical
* 12 thoracic
* 5 lumbar
* sacrum - 5 fused bones
* coccyx- inferior to the sacrum
* 12 thoracic
* 5 lumbar
* sacrum - 5 fused bones
* coccyx- inferior to the sacrum
59
New cards
Intervertebral disc facts
* Cushion pads between vertebrae
60
New cards
What is the jelly sphere that absorbs stresses/forces in the discs called?
What is the function of nucleus pulposus?
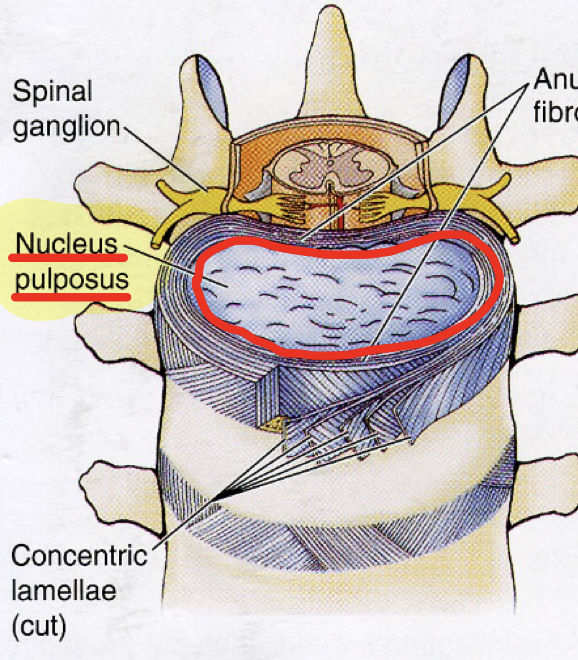
61
New cards
What are the outer rings of ligaments that surround the nucleus pulposus and allow flexion and rotation in the discs?
What is the function of the annulus fibrosis?
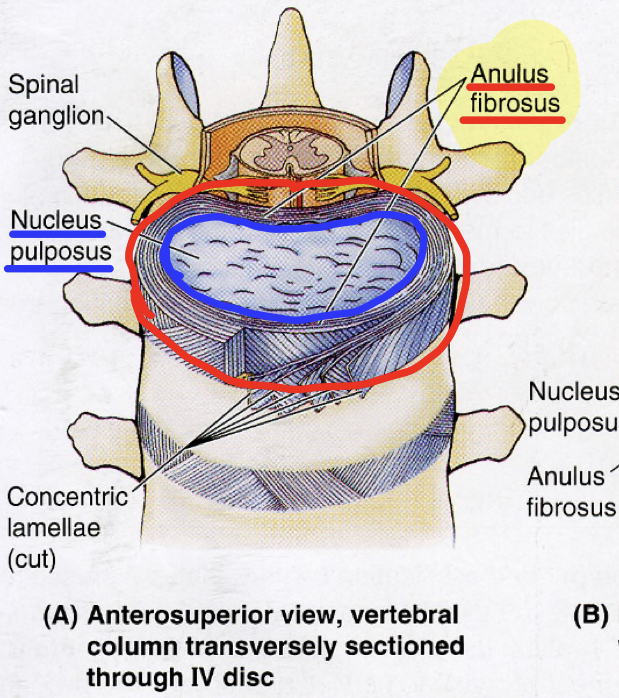
62
New cards
Parts of the intervertebral discs!
* ^^Body:^^ thick part that will have the annulus fibrosis and nucleus pulposus
* ^^Vertebral arch:^^ posterior arch of vertebral foramen
* ^^Vertebral foramen:^^ opening for spinal chord
* ^^Spinous process:^^ posterior bone projection
* ^^transverse process:^^ outer projections
* ^^superior/inferior articulation process/facets:^^ joints that connect other vertebrae together
* ^^Vertebral arch:^^ posterior arch of vertebral foramen
* ^^Vertebral foramen:^^ opening for spinal chord
* ^^Spinous process:^^ posterior bone projection
* ^^transverse process:^^ outer projections
* ^^superior/inferior articulation process/facets:^^ joints that connect other vertebrae together
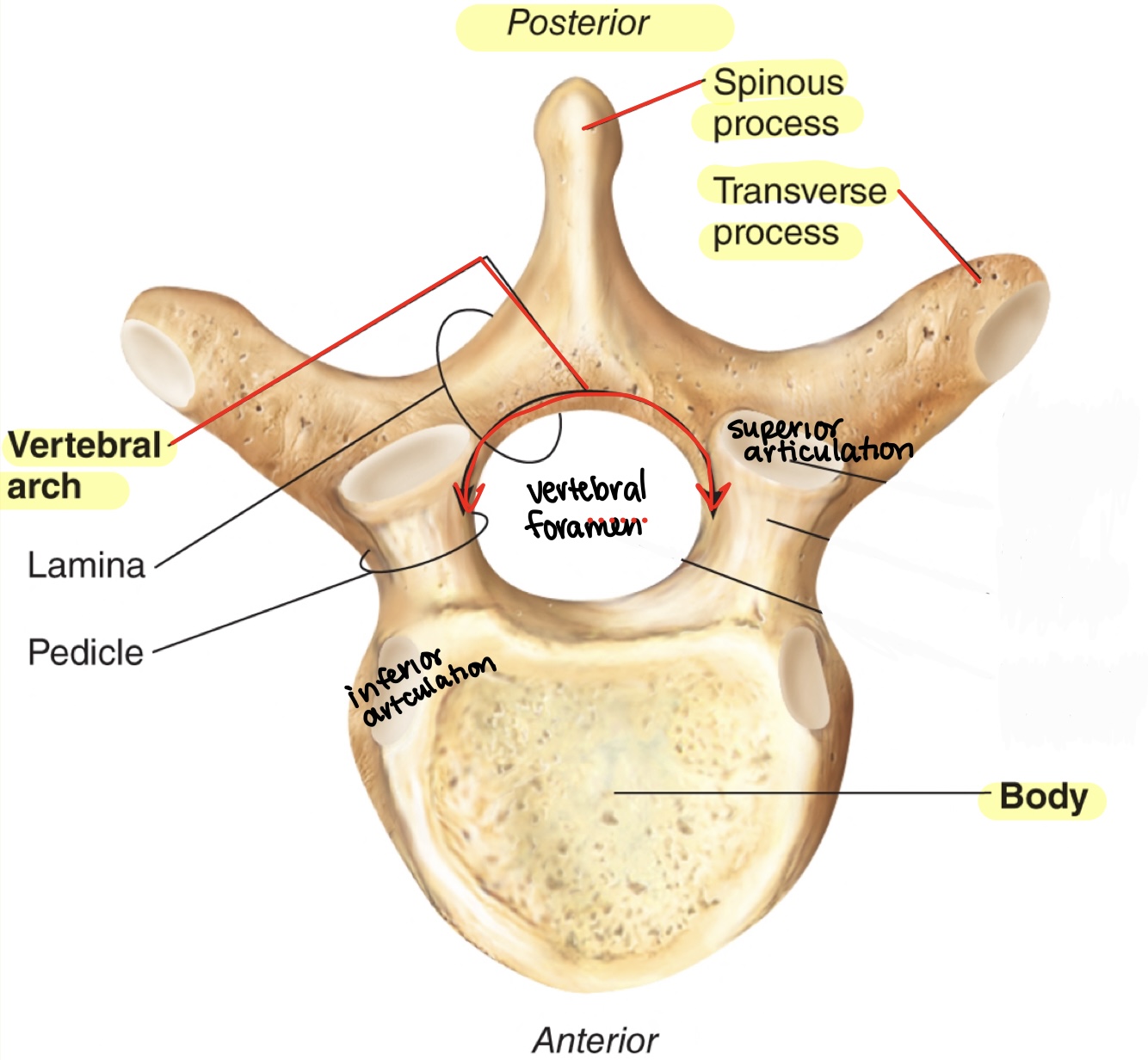
63
New cards
vertebral ROM
* extension and flexion
* lateral flexion
* rotation
* lateral flexion
* rotation
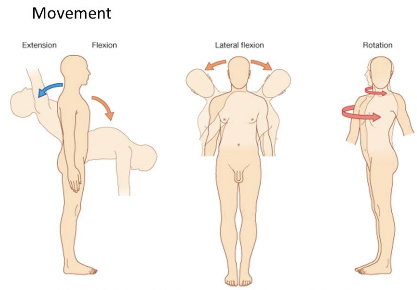
64
New cards
cervical vertebrae characteristics
* __smallest and lightest__
* C3-C7 typical structure
* spinous process short and bifid EXCEPT C7 which allows for up and down ROM
* C3-C7 typical structure
* spinous process short and bifid EXCEPT C7 which allows for up and down ROM
65
New cards
What is the first cervical vertebrae?
What type of vertebrae is the atlas?
66
New cards
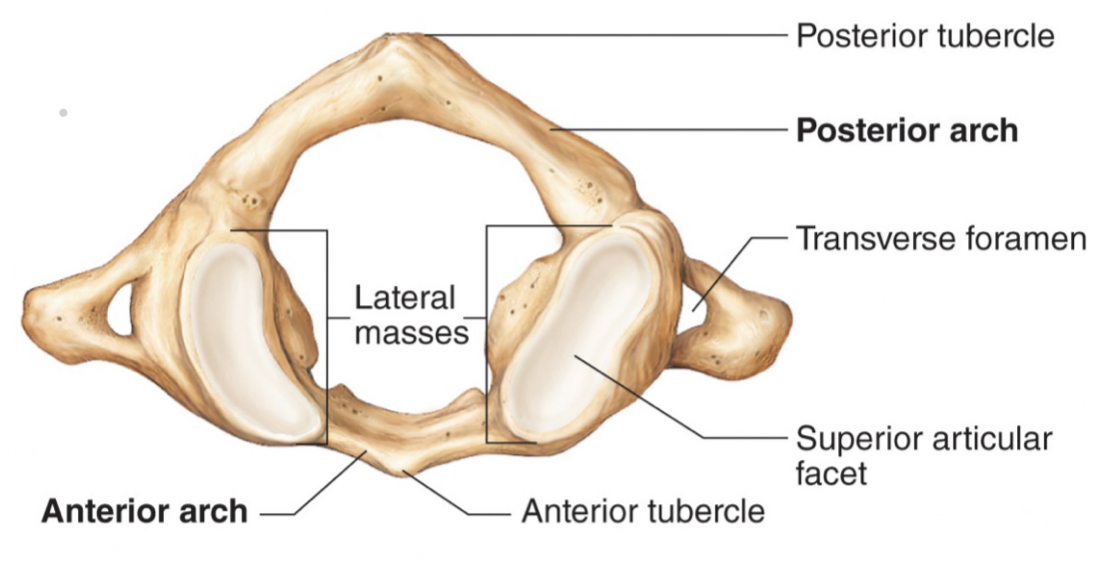
atlas characteristics
* supports the skull
* NO body and spinous process
* flexion and extension, nodding “yes”
* NO body and spinous process
* flexion and extension, nodding “yes”
67
New cards
what is the second cervical vertebrae?
What type of vertebrae is the axis?
68
New cards
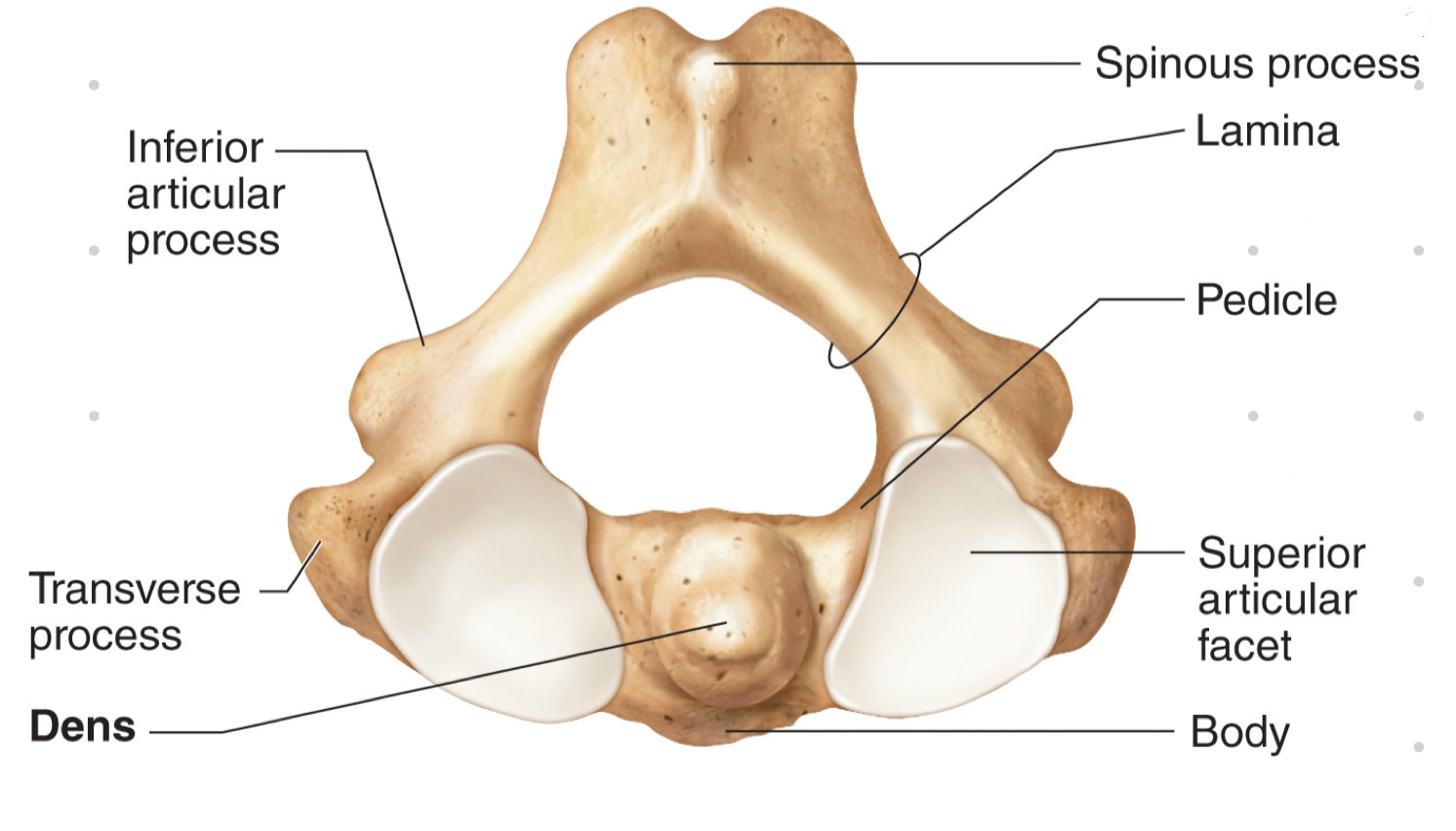
axis characteristics
* body and spinous process
* dens projects superiorly (where atlas and axis fuse)
* pivot, side-to-side ROM, shaking head “no”
* dens projects superiorly (where atlas and axis fuse)
* pivot, side-to-side ROM, shaking head “no”
69
New cards
muscles of the neck
__flexion: sternocleidomastoid__
extension: trapezius, splenus
lateral flexion: splenius cervisis/capitus
extension: trapezius, splenus
lateral flexion: splenius cervisis/capitus
70
New cards
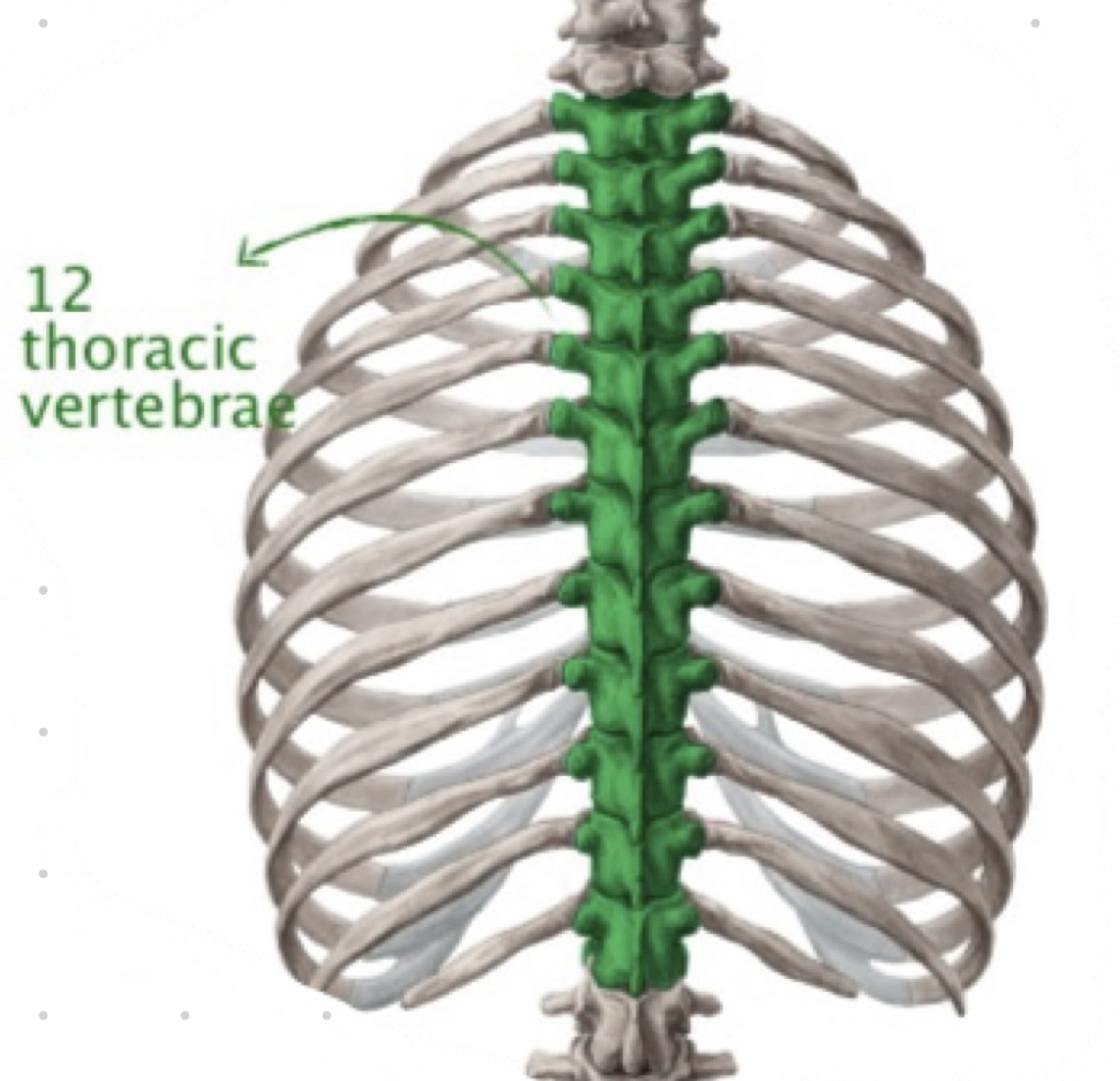
thoracic vertebrae characteristics
* 12, heart-shaped bodies
* T1-T12 have demifacets for articulation with ribs
* __spinous process long and point inferiorly, help stop hyperextension__
* rotation with limited flexion and extension
* T1-T12 have demifacets for articulation with ribs
* __spinous process long and point inferiorly, help stop hyperextension__
* rotation with limited flexion and extension
71
New cards
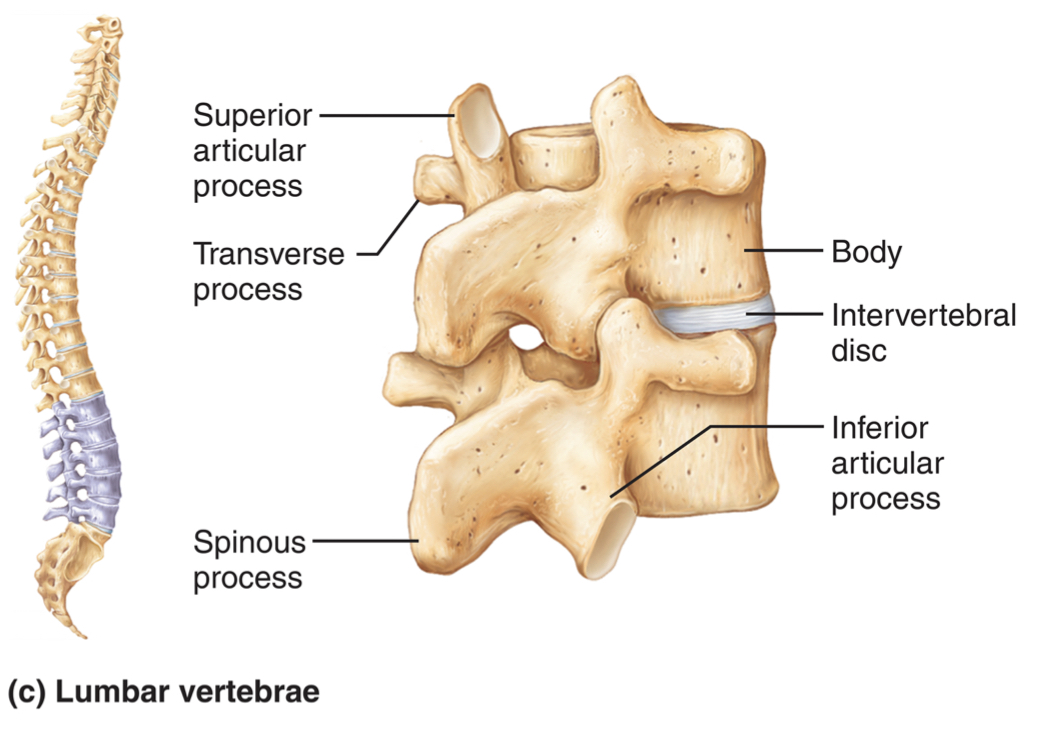
lumbar vertebrae characteristics
* bodies are thick and robust __because they deal w/ most stress__
* spinous p. short and flat, __point POSTERIORLY to allow flexion__
* transverse p. thin and tapered
* flexion and extension, not a lot of rotation
* spinous p. short and flat, __point POSTERIORLY to allow flexion__
* transverse p. thin and tapered
* flexion and extension, not a lot of rotation
72
New cards
sacrum characteristics
* posterior side of pelvis
* 5 fused vertebrae
* 5 fused vertebrae
73
New cards
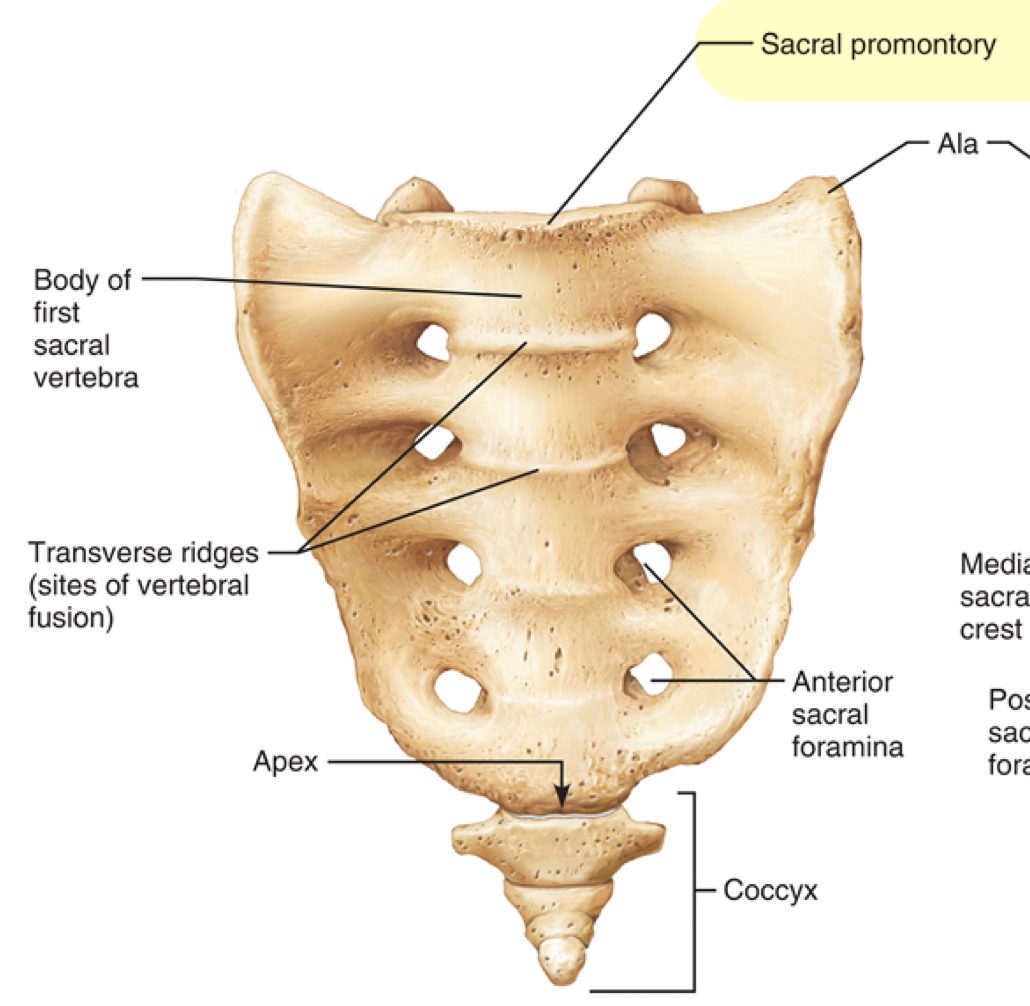
What is the sacral promontory?
Where does the first sacral vertebrae bulge into the pelvic cavity?
74
New cards
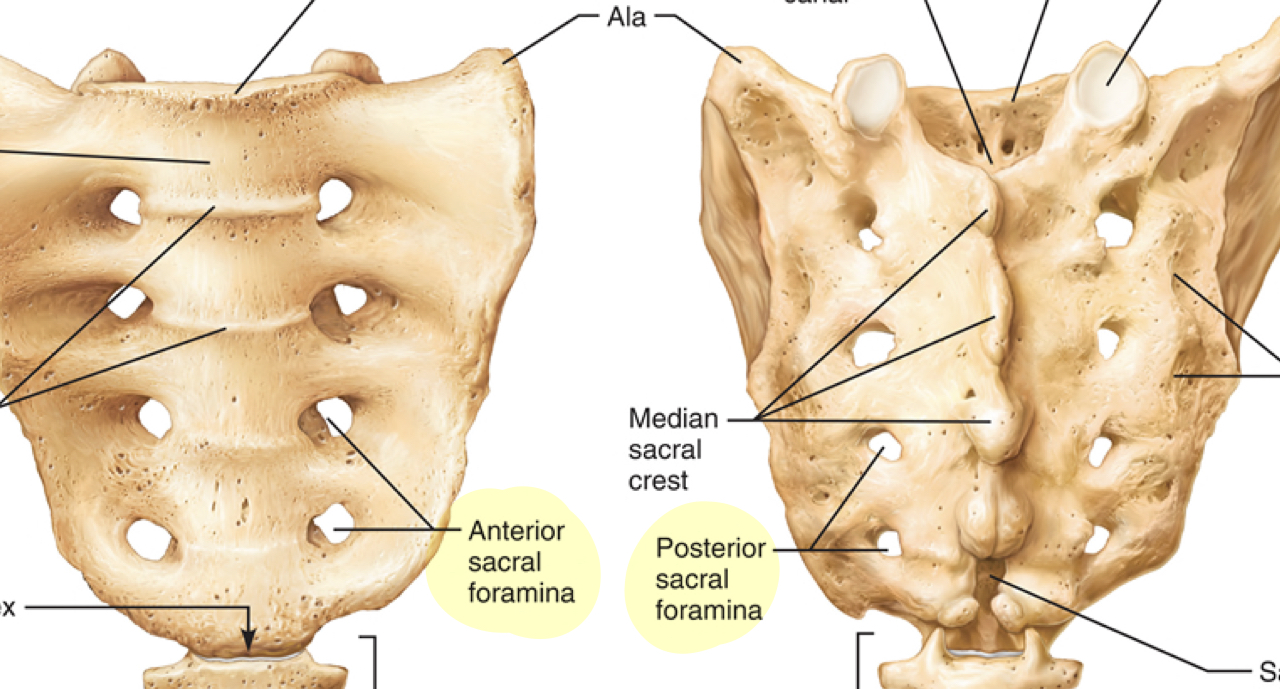
What is the anterior/posterior sacral foramina?
What is the passage for ventral rami(branch) of sacral nerves?
75
New cards
What is the framework of the chest components called?
What is the thoracic cage?
76
New cards
What makes up the Thoracic Cage?
* thoracic vertebrae POSTERIORLY
* ribs LATERALLY
* sternum and costal cartilage ANTERIORLY
* ribs LATERALLY
* sternum and costal cartilage ANTERIORLY
77
New cards
^^What are the functions of the thoracic cage?^^
What protects the thoracic organs, supports the shoulder girdle and upper limbs, and provides attachment sites for back muscles?
78
New cards
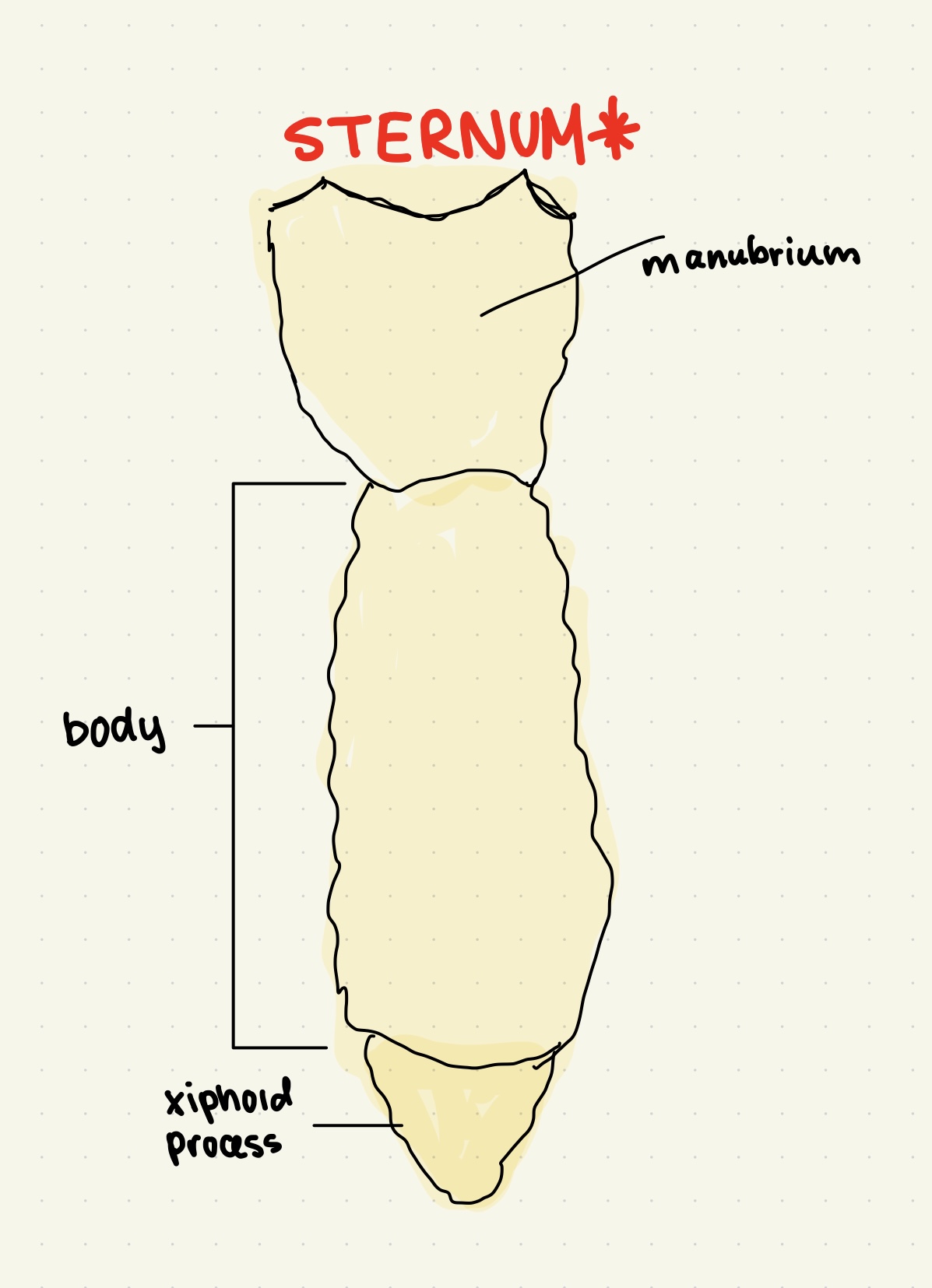
__**What are the three sections of the sternum?**__
What do the __manubrium, body, and xiphoid process__ make up?
79
New cards
manubrium facts
superior part of sternum, clavicular notches on sides articulate w/ medial end of claviclebod
80
New cards
sternum body facts
bulk of sternum, side notches are articulations for costal cartilage (2-7)
81
New cards
xiphoid process facts
inferior end of sternum, ossifies around age 40
82
New cards
__**ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS FOR STERNUM*****__
* __JUGULAR NOTCH:__ indentation at superior manubrium
* __STERNAL ANGLE:__ horizontal ridge where manubrium joins body
* __XIPHISTERAL JOINT:__ where body and xiphoid process meet
* __STERNAL ANGLE:__ horizontal ridge where manubrium joins body
* __XIPHISTERAL JOINT:__ where body and xiphoid process meet
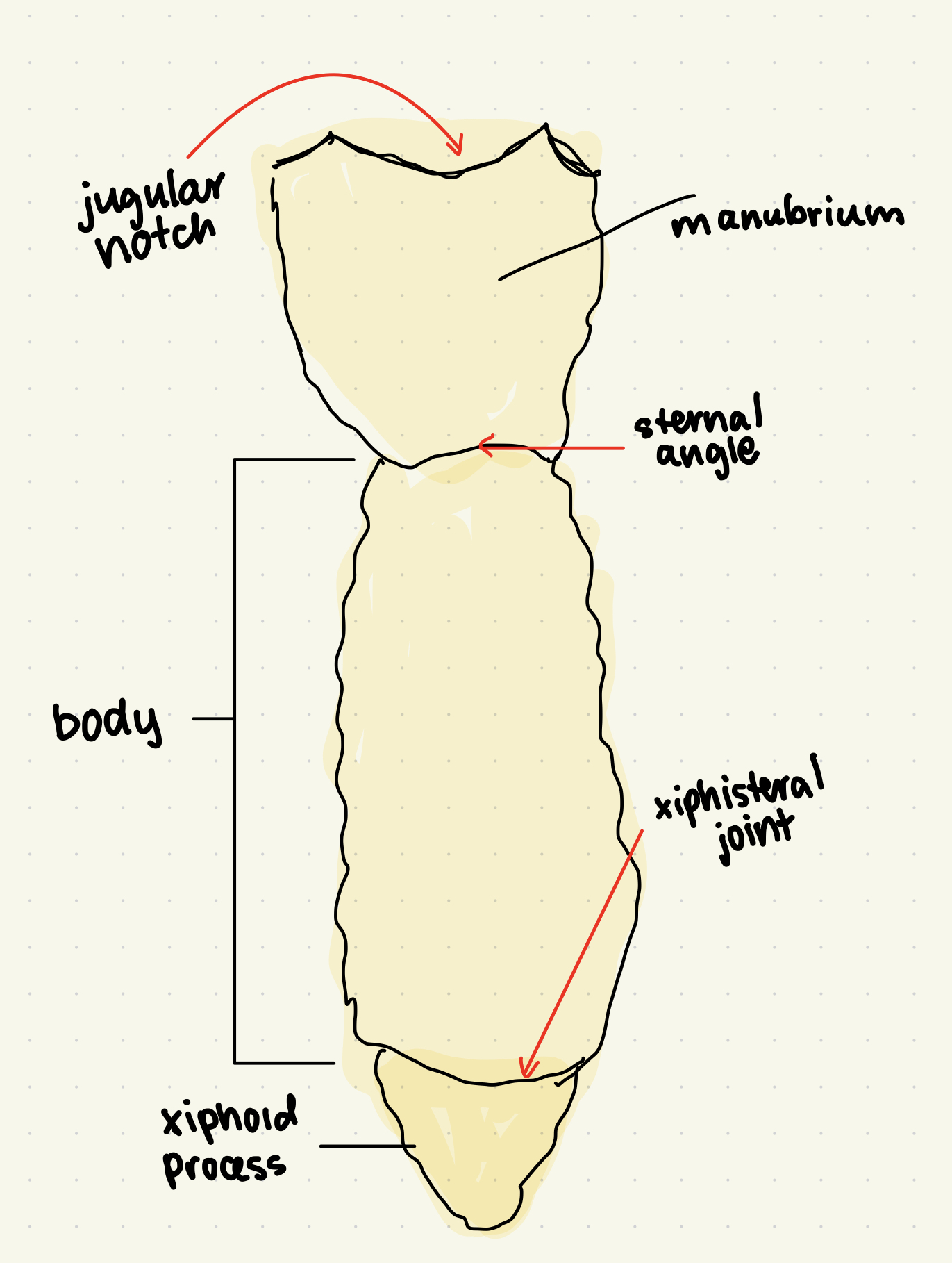
83
New cards
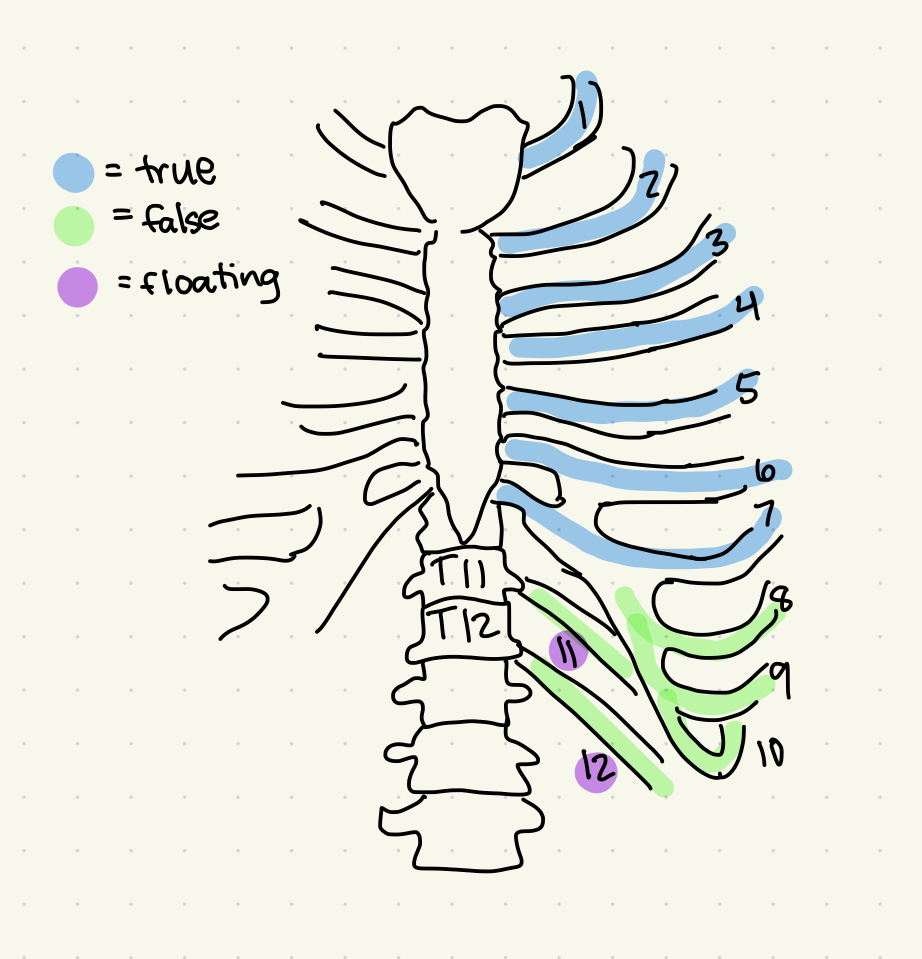
rib facts
* all ribs attaches to the vertebral column
* 12 pairs of ribs
* 12 pairs of ribs
84
New cards
Which ribs, directly connected to the sternum, are known as “true ribs?”
What are the 7 superior ribs called?
85
New cards
Which ribs, indirectly connected to the sternum, are known as “false ribs?”
What are the 5 inferior ribs called?
86
New cards
What are ribs 11 and 12 known as?
Which ribs are called “floating ribs?”
87
New cards
drawing of ribs
88
New cards
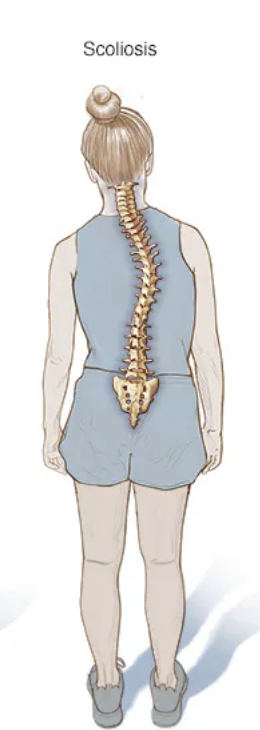
__**what is abnormal lateral curvature of the spine called?**__
What is __**scoliosis**__**?**
89
New cards
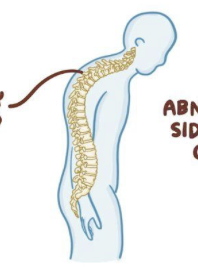
What is __kyphosis__?
__**What is exaggerated thoracic curvature called?**__
90
New cards
In who does kyphosis typically happen to?
What axial skeleton disorder happens to older people?
91
New cards
Why would people who have kyphosis look like a “hunchback?”
How does thoracic vertebrae having long, inferior pointing spinous p. make people with hypnosis look?
92
New cards
__**What is the most important muscle of respiration?**__
What process does the __diaphragm__ play an important part in?
93
New cards
__**diaphragm facts**__
* __most important for respiration__
* __separates thoracic and abdominal cavities__
* __FLATTENS as is contracts__
* __ARCHED in rest__
* innervated by phrenic nerve
* __separates thoracic and abdominal cavities__
* __FLATTENS as is contracts__
* __ARCHED in rest__
* innervated by phrenic nerve
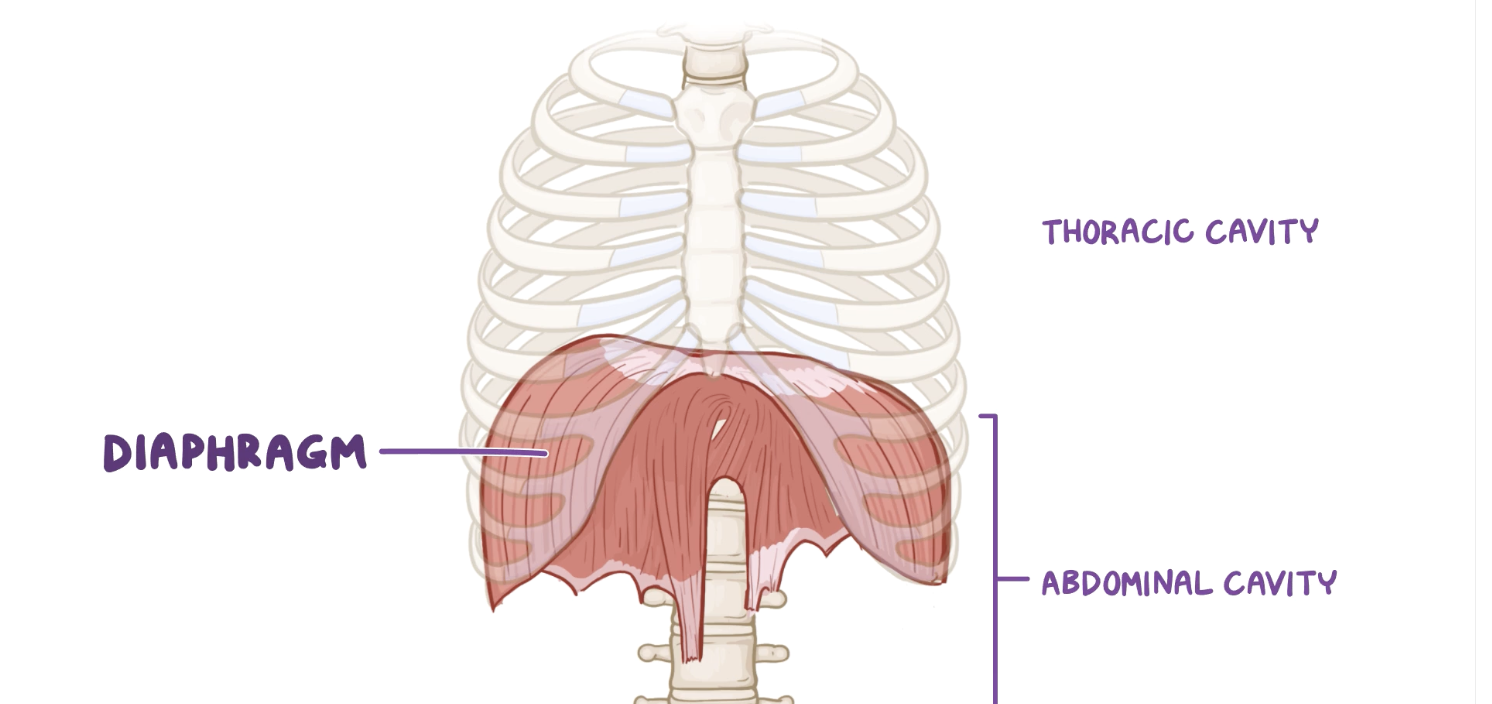
94
New cards
What are the external and internal intercostal muscles involved in?
What other muscles are involved in breathing?
95
New cards
external intercostal = inspiration, rib cage up and out
internal intercostal = aid expiration during heavy breathing, rib cage in and down
96
New cards
^^What are the muscles of the abdominal wall?^^
* rectus abdominus: “six pack”
* external and internal obliques: sides
* transverse abdominis: deep to obliques
* serratus anterior: superior to obliques
* linea alba: which line of CT that runs down abdomen
* external and internal obliques: sides
* transverse abdominis: deep to obliques
* serratus anterior: superior to obliques
* linea alba: which line of CT that runs down abdomen
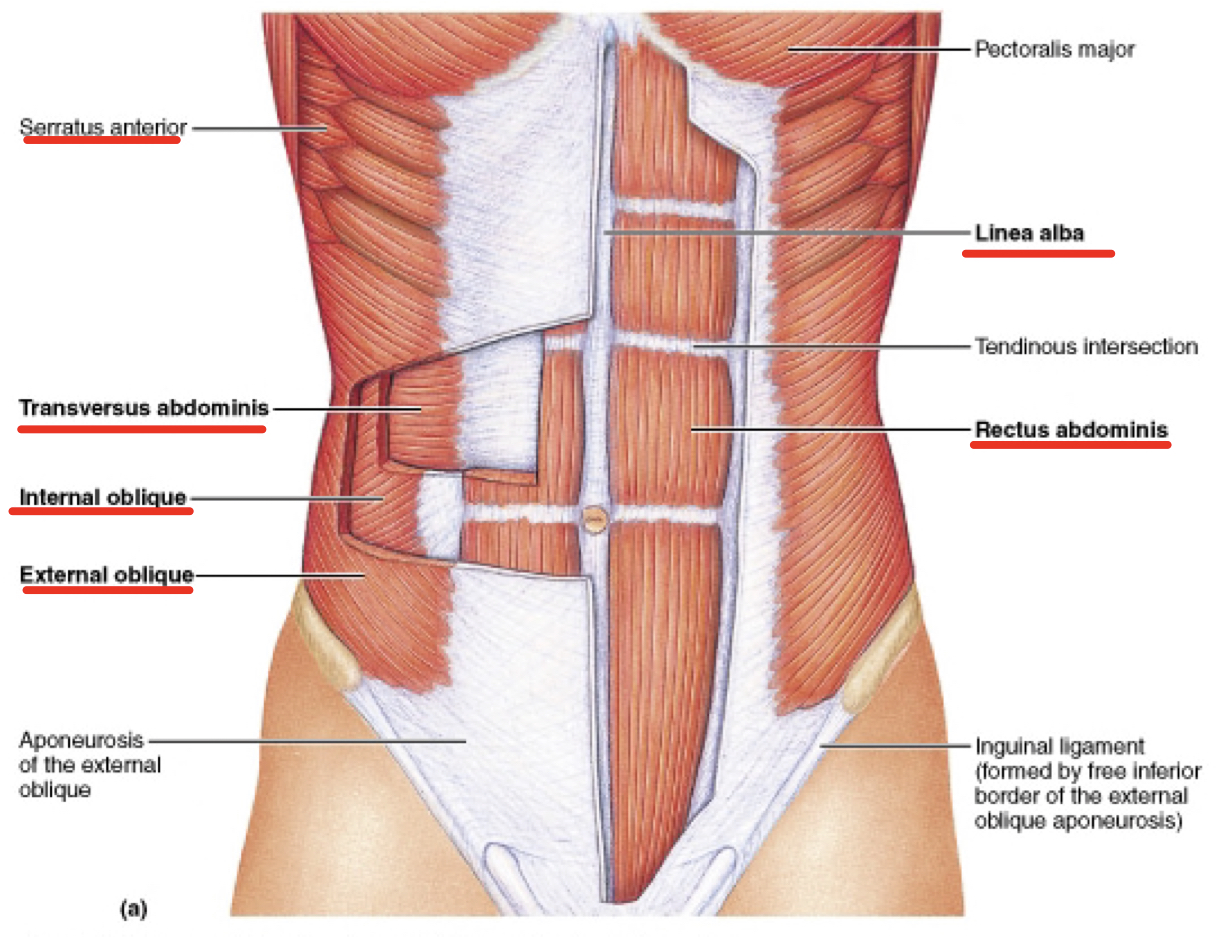
97
New cards
__**Why are the abdominal wall muscles so important?**__
What muscles __support and protect abdominal organs__? (also flex vertebral column)
98
New cards
When do you use the abdominal muscles?
literally anything. laughing, peeing, birth, etc.
99
New cards
What muscles do trunk extension, maintain normal curvature, and for column from skull to sacrum?
What is the function of deep back muscles?
100
New cards
What is the ^^erector spine group^^?
What are the largest and most important deep back muscles called?